Pretest GI
Functional Constipation
functional constipation: poor anal sphincter tone, stool in rectum, dilated/stool anal canal on xray
Hirschsprung: poor anal sphincter tone, no stool in rectum
Peptic Ulcer
The presence of nocturnal abdominal pain (may have emesis with pain) and GI bleeding (occult) in a patient with a positive family history.,
Eosinophil Esophagitis
path: allergic response
pt
male > females
hx of atopy/food allergy
symptoms: like GERD, not relieved with PPI
diagnosis
blood: IgE and eosinophilia
endoscopy: mucosal furrowing, strictures (dysphagia, pain)
biopsy: eosinophils
treatment: avoid food allergens, steroids.,
case: An 8-year-old boy presents to your office for a second opinion. He has a 2-year history of intermittent vomiting, dysphagia, and epigastric pain. His father reports he occasionally gets food “stuck” in his throat. He has been on a proton pump inhibitor for 18 months without symptom relief. His past history is significant only for eczema and a peanut allergy. Endoscopy was performed 6 months ago; no erosive lesions were noted and a biopsy was not performed. You arrange for a repeat endoscopy with biopsy. Microscopy on the biopsy sample reveals many eosinophils.
Malrotation, Volvulus
volvulus
Meconeum Ileus
meconeum ileum
Echogenic bowel on prenatal ultrasound can be an early hint.
UC
Labs: ASCA is positive in about 55% of those with Crohn disease, but are uncommon in ulcerative colitis; conversely, p-ANCA is positive in about 70% of patients with ulcerative colitis, but in less than 20% of patients with Crohn disease.
complication: The most serious complication of ulcerative colitis is toxic megacolon, a medical and surgical emergency in which patients develop fever, tachycardia, dehydration, leukocytosis, and electrolyte abnormalities associated with a markedly dilated colon. This complication comes with a high risk of intestinal perforation.
Patients with ulcerative colitis have a markedly elevated risk of colonic carcinoma; after 10 years of disease, the annual cumulative risk is 0.5% to 1% a year. Strictures are more common in Crohn disease and are unusual in ulcerative colitis.
Gerd
Growing well and developing properly and has no other medical problems such as reflux-induced apnea or bradycardia or aspiration pneumonia, pharmacologic treatment is not necessary, as most infants will outgrow this common problem of esophageal reflux.
Surgical correction is reserved for infants with poor weight gain or reflux-associated apnea and bradycardia who have failed pharmacologic therapy.
Direct hyperbilirubinemia
Cystic fibrosis and α1-antitrypsin deficiency should be considered in the diagnostic evaluation of any child with obstructive jaundice.
Other diseases to be excluded are galactosemia, tyrosinemia, and urinary tract or other infections (including toxoplasmosis, cytomegalovirus, rubella, syphilis, and herpesvirus).
Ultrasound examination to rule out choledochal cyst may be included with a technetium 99mTc hepatic iminodiacetic acid (HIDA) scan to assess the patency of the biliary tree.
Liver biopsy can assist in the diagnosis by providing a histologic diagnosis (eg, hepatitis, biliary atresia), tissue for enzyme activity (ie, inborn error of metabolism), or tissue for microscopic determination of storage diseases.
ABO and Rh incompatibility occasionally cause direct hyperbilirubinemia if there were brisk hemolysis at birth, which would then lead to inspissated bile syndrome.
Foreign Body in Esophagus
The foreign body usually passes uneventfully into the stomach. However, button batteries that lodge in the esophagus must be removed urgently via endoscopy as they carry a high risk of esophageal perforation in as little as 1 hour.
Do not use balloon catheter. Use endoscopy. However, this does not allow direct visualization of the mucosa to determine the extent of the injury and also carries the risk of aspiration; it should be performed only by experienced personnel.
Hypernatremia
pt
emesis, diarrhea, decreased urine output
symptoms
decreased weight
lethargy, hard to wake up: sign of hypotonic dehydration
normal bp and hr: The extracellular fluid and circulating blood volumes tend to be preserved with hypernatremic dehydration at the expense of the intracellular volume. Therefore, hypotension may not be observed.
skin doughy
treatment
nl saline
DO NOT use 1/4 nl saline: Use of 1/4 normal saline (38.5 mEq sodium/L) or D10 water (100 g glucose/L) in this dehydrated child would not expand the intravascular space and its hyponatremic nature might lead to cerebral edema.
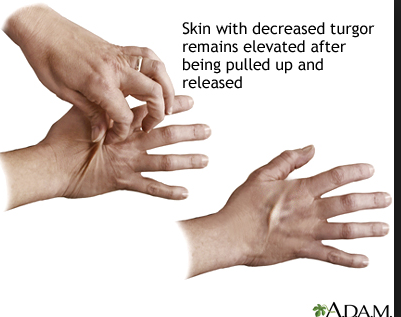
Glucose in hypernatremia
Hyperglycemia may be seen in hypernatremic dehydration because of decreased insulin secretion and cell sensitivity to insulin.
Central Pontine Myelinolysis
This most often occurs when someone is being treated for low blood sodium hyponatremia and the sodium is replaced too fast. Sometimes, it occurs when a high level of sodium in the body (hypernatremia) is corrected too quickly.
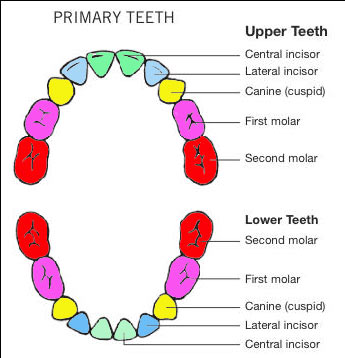
Teething
In general, mandibular teeth erupt before maxillary teeth; teeth tend to erupt in girls before they do in boys.
mandibular central incisors at 5 to 7 months
maxillary central incisors at 6 to 8 months
Lateral incisors (mandibular then maxillary) erupt next at 7 to 11 months
first molars (10-16 months)
the cuspids (16-20 months)
second molars (20-30 months)
Abd pain
Recurrent abdominal pain is a common complaint occurring in at least 10% of schoolage children. In children older than 2 years, less than 10% of cases have an identifiable organic cause.
Any signs or symptoms of organic causes, such as growth failure, should be pursued. If nothing in the history or physical examination is found, as is likely in the case described, reassurance of the children and family members is indicated.
Tooth Decay
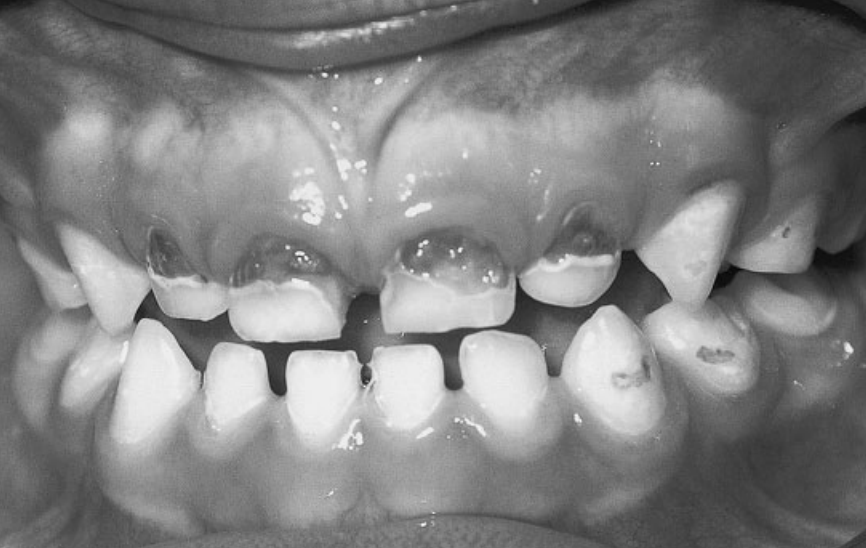
The pattern of dental disease found with the use of bottles that contain high concentrations of sugars, which promotes dental disease, includes extensive maxillary decay (especially frontal) and posterior maxillary and mandibular decay, but essentially normal mandibular frontal teeth.
Teeth transport
time: rate of success, decreasing from 90% in the first 30 minutes to 5% after 2 hours
The teeth can be rinsed in cold water, but not brushed (to avoid damaging the root and periodontal ligament).
Milk or saline are good transport media if the child is uncooperative or for some other reason the teeth cannot be reinserted at the scene.
Teeth may also be transported in the mouth of the older, cooperative patient or the parent.
The immediate application of acrylic splints is needed to keep the teeth in place, so immediate dental attention is required.
trauma: The need for full tetanus immunization should be evaluated
A completely avulsed primary tooth is generally not replaced, to avoid damage to the underlying permanent tooth
congenital hernia
surgery
Drain Cleaner
Endoscopic examination of the esophagus and stomach is a diagnostic method of determining the extent of the mucosal injury.
Avoid vomiting: it would expose the mucosal surfaces to the caustic agent a second time.
The child can be given small amounts of milk or water, but large amounts, which might cause vomiting, are unwise
Neutralization of the caustic can result in an exothermic reaction and produce a thermal burn
Charcoal does not absorb the alkaline agent in drain cleaner
Activated Charcoal
Good for certain toxins (phenobarbital, TCA, theophylline)
moa: Activated charcoal exerts its effect by adsorbing particles of toxin on its surface.
Compounds not adsorbed include alcohols, acids, ferrous sulfate, strong bases (such as drain cleaners and oven cleaners), cyanide, lithium, and potassium.
Cow's Milk
Cow’s milk contains an insufficient quantity of iron to sustain normal RBC production. Therefore, children whose primary caloric source is cow’s milk are likely to develop iron-deficiency anemia, characterized by microcytosis and hypochromia on the peripheral smear.
Gag and Chokes
An infant who gags and chokes while feeding may have an uncoordinated suck-swallow reflex, or may have significant gastroesophageal reflux. More rarely there may be an H-type tracheoesophageal fistula. A modified barium swallow with fluoroscopy allows direct visualization of the swallow reflex. In some situations during the modified barium swallow, the patient may be given different consistencies of food to document if thickened feeds.
Black Stools
The patient’s story is concerning for peptic ulcer disease. An upper GI series may show findings suggestive of the diagnosis, but endoscopy is the preferred diagnostic method, as it allows biopsy for microscopy and culture, and direct visualization.
Gerd
The child may have gastroesophageal reflux, causing Sandifer syndrome, a condition in which infants will arch and become tonic to protect their airway from the refluxing gastric contents. While an upper GI series can sometime diagnose gastroesophageal reflux, esophageal pH probe is currently the preferred diagnostic test.
Last updated