01 Thyroid
Parathyroid Embryology
Pharyngeal pouch 3
_Forms the inferior parathyroid glands (dorsal wing) and thymus (ventral wing)., 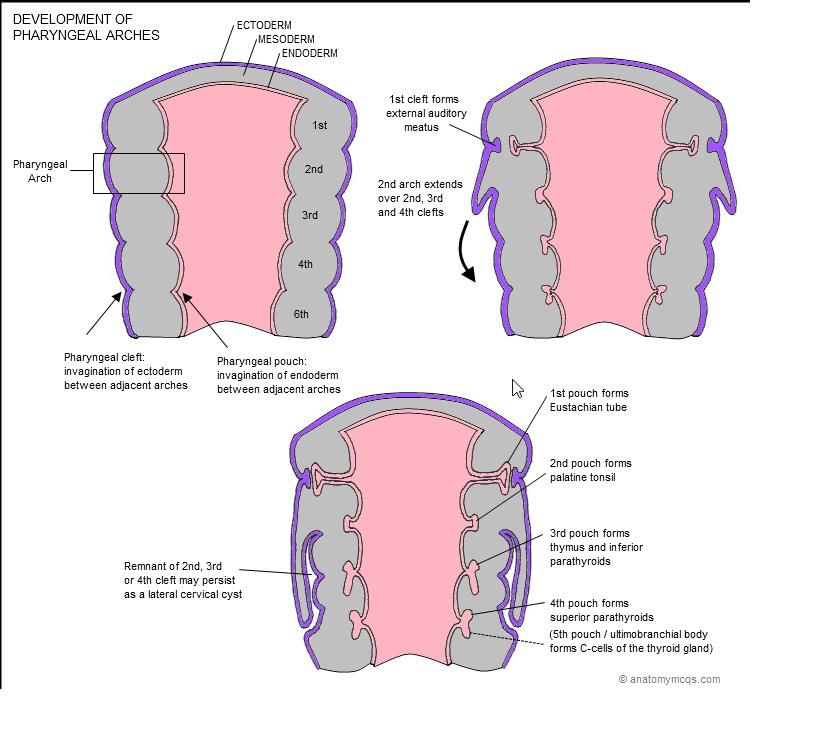
Pharyngeal pouch 4
_Forms the superior parathyroid glands (dorsal wing) and ultimobranchial body (ventral)., 
_Note that the parathyroid glands formed by pharyngeal pouch 3 migrate below the parathyroid glands of pharyngeal pouch 4..
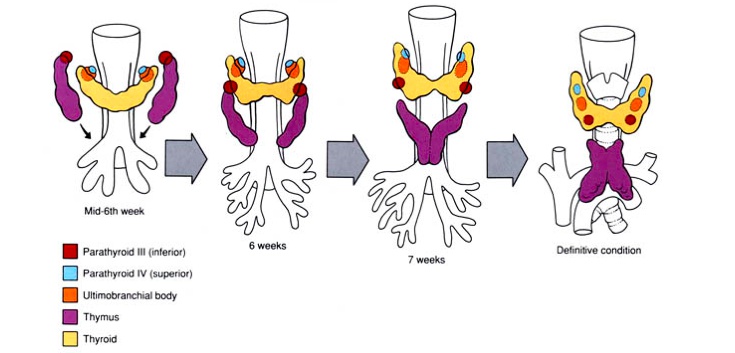
_Neural crest cells subsequently migrate into the ultimobranchial body to form parafollicular C-cells of the thyroid gland..
Postbranchial body
_Aka ultimobranchial body.,
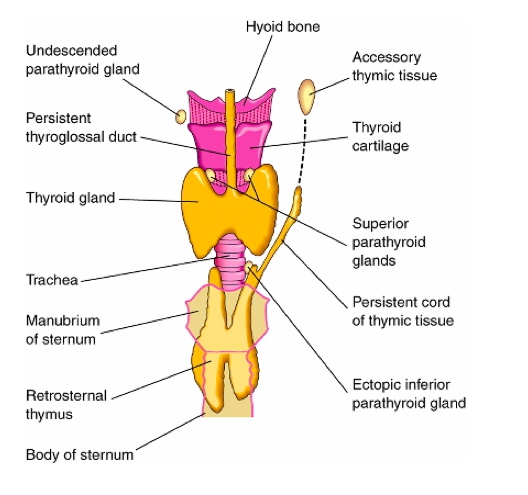
Ectopic thymic and parathyroid tissues
_ can be found in the lateral regions of the neck along its path of migration.,
Thyroid Formation
_On day 24, the primitive pharynx of the embryological foregut derives the thyroid diverticulum which in turn forms the thyroid gland.
Foregut, between copula and Tuberculum impar.. 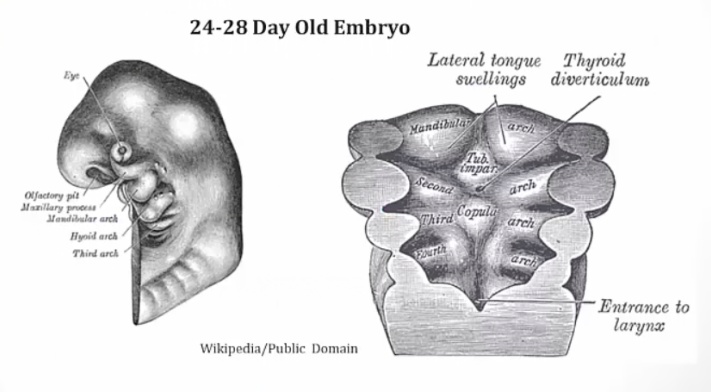
_The thyroid diverticulum migrates caudally down the midline, ventral to the hyoid bone and laryngeal cartilages, to its adult anatomic position..
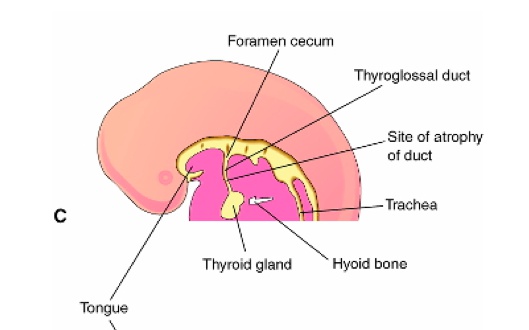
Thyroglossal duct
_The thyroid remains connected to the tongue via this duct during thyroid development and migration, which later obliterates.
Typically regresses, but may form the adult pyramidal lobe of the thyroid.
Foramen cecum indicates the former site of the duct., 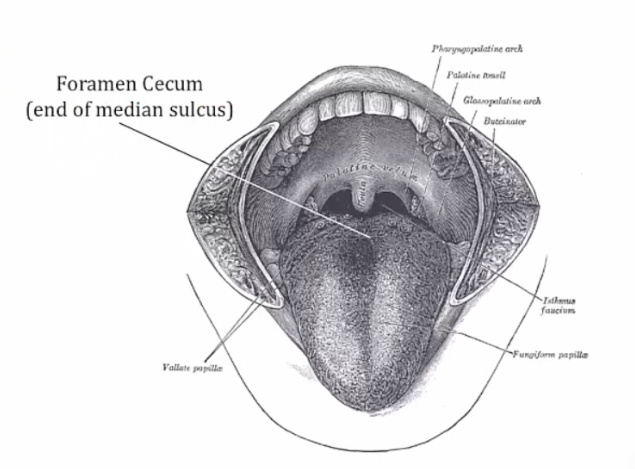
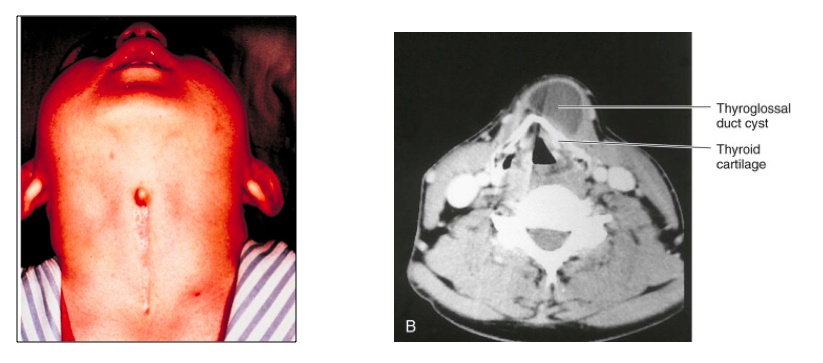
A thyroglossal duct cyst/sinus occurs when part of the thyroglossal duct fails to obliterate correctly, subsequently forming a cyst or sinus.
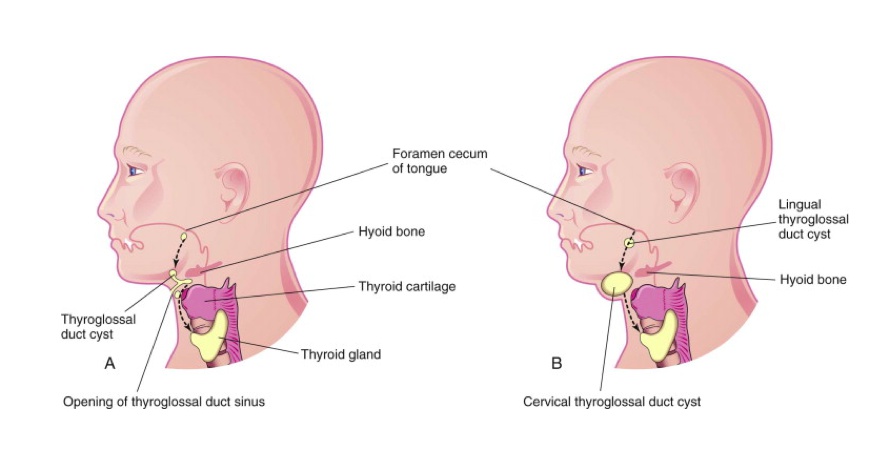
_Is commonly located ventral to the hyoid bone and laryngeal cartilage.,
_Symptoms:
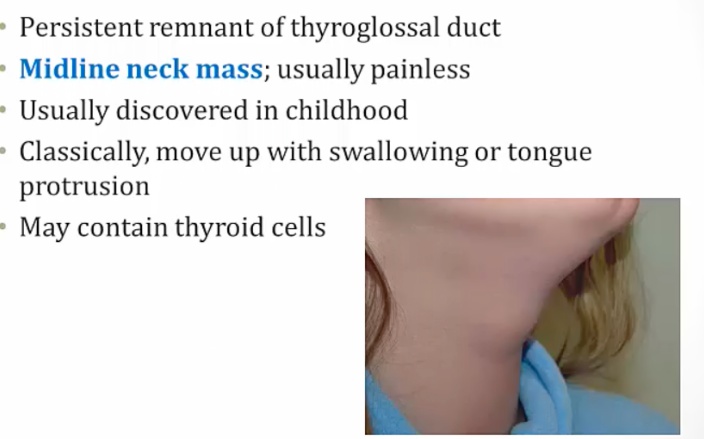
In front of hyoid bone (right):
Moves because still connection with mouth/tongue..
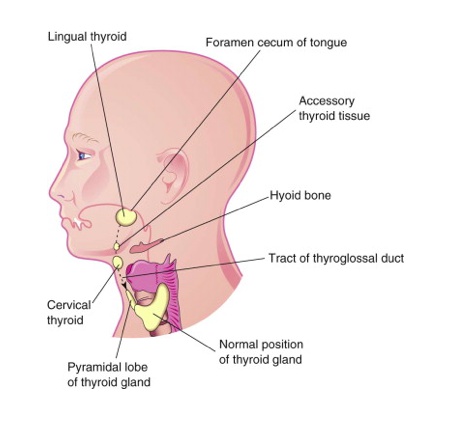
Ectopic thyroid tissues:
Puberty/pregnancy: more demand for thyroid hormone, leads to stimulation and growth of thyroid tissue
Hypothyroidism stimulates more production of ectopic tissue.,

_A lingual cyst occurs when a thyroglossal duct cyst is located at the base of the tongue..
Thyroid and parathyroid anatomy
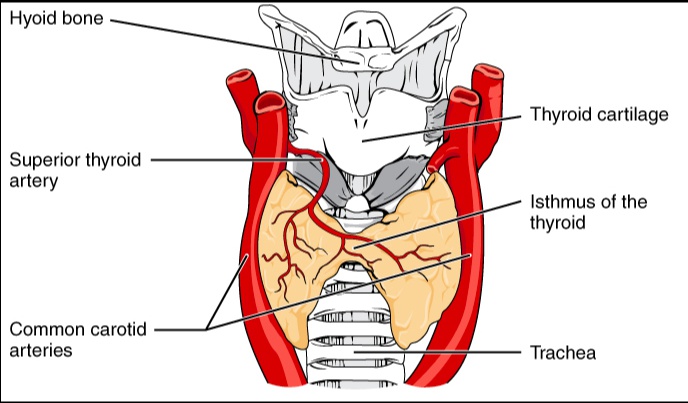
_The thyroid gland consists of 2 lobes located anterolaterally, which span the area between the oblique line of the thyroid cartilage and the 5th tracheal ring..

isthmus
_Thin band of tissues between 2 lobes., 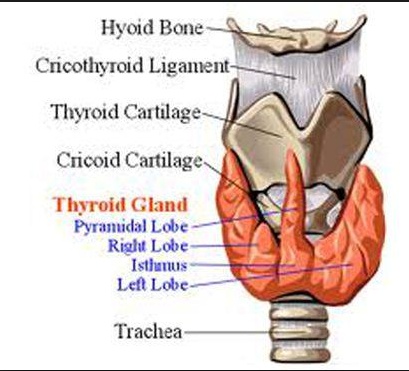
Pyramidal lobe
_Lobe above isthumas. Remnant of thyroglossal duct., 
Blood supply
_The thyroid receives arterial supply from the superior (via external carotid) and inferior thyroid (via thyrocervical trunk of subclavian) arteries.. 
Vein drainage
_Three separate veins provide drainage of the thyroid gland:
Superior thyroid vein — Drains to internal jugular vein
Middle thyroid vein — Drains to internal jugular vein
Inferior thyroid vein — Drains to the brachiocephalic vein..

_The functional anatomy of the thyroid gland consists of:
Follicles
Colloid
Parafollicular cells..


Thyroid follicles are formed by single layer of epithelial cells known as follicular cells which synthesize, store and secrete thyroid hormone.
Colloid
_Found within the lumen of each thyroid follicle. In this compartment, thyroid hormone is stored as a component of thyroglobulin.,
Parafollicular cells
_Synthesize and secrete the hormone calcitonin.,
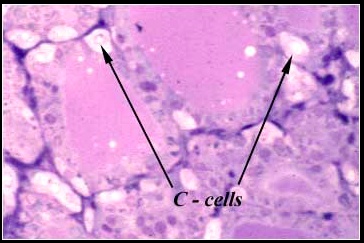
Follicular vs parafollicular
_The follicular cells of the thyroid gland are derived from endoderm. Parafollicular C cells are derived from neural crest cells..
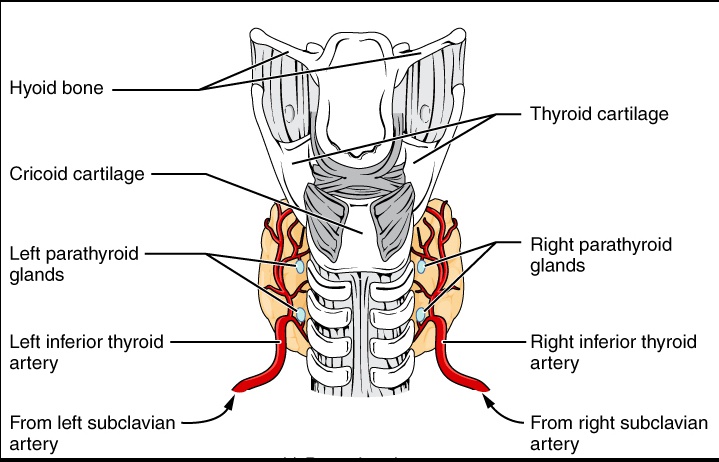
Parathyroid
_These are 4 small circular glands found on the posterior surface of the thyroid gland. Clinical Correlate: Thyroid surgery is a common cause of removal or damage to the parathyroid glands.. 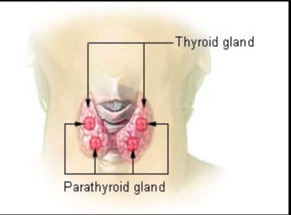
Thyroid physiology
Thyroid hormones
_Contain element Iodine, found in table salt..
_In order to be incorporated into thyroid hormones, iodine needs to be
 ..
..
_There are three types of thyroid hormone:
Thyroxine (T4)
Triiodothyronine (T3)
Reverse triiodothyronine (rT3)..
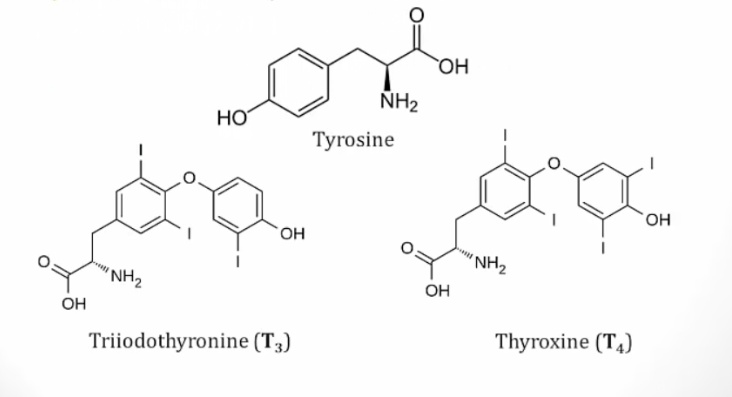
T4 vs. T3
T4 makes up the majority of thyroid hormone produced. It has a longer half life than T3.
T3 is less abundant but more potent than T4.
Reverse T3 (rT3) is found in the blood and has no biologic activity..
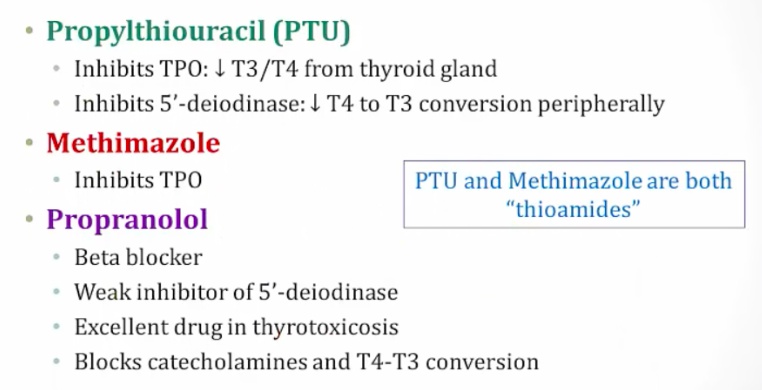
5-deiodinase
_Deiodinate T4 to T3 in peripheral tissues., 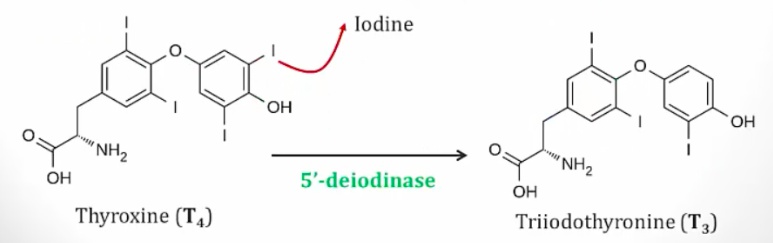
[_](5'-deiodinase inhibited by)Inhibited by
propylthiouracil
propanolol
amiodarone.,
 propanolol: for thyrotoxin. Catecholamine can result in hyperthyroidism
propanolol: for thyrotoxin. Catecholamine can result in hyperthyroidism
Also amiodarone: 
Thyroglobulin
large, tyrosine-rich glycoprotein
Synthesizes T3/T4
resides in the colloid.
Made by follicular cells.,

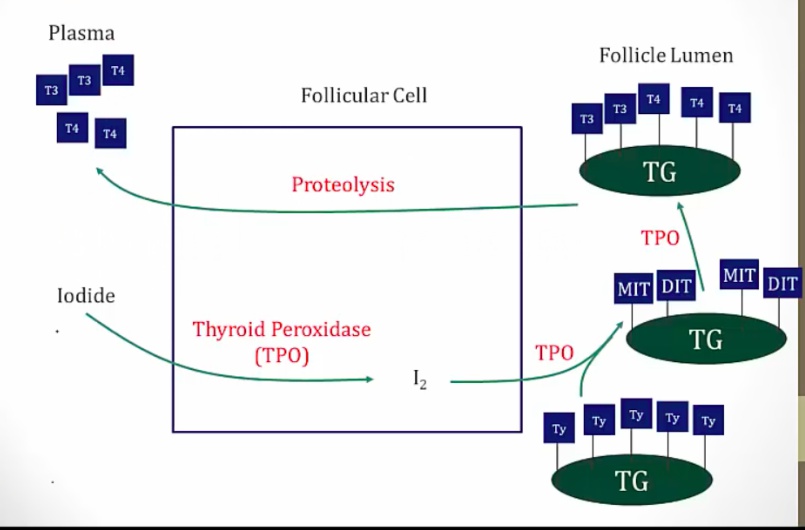
Thyroid Hormone Synthesis
_Overview steps of thyroid hormone synthesis:
Iodide transport into follicular cells
Iodide oxidized to I2
Tyrosine added to I2, becoming DIT/MIT
DIT/MIT coupling
Proteolysis releases thyroid hormones..
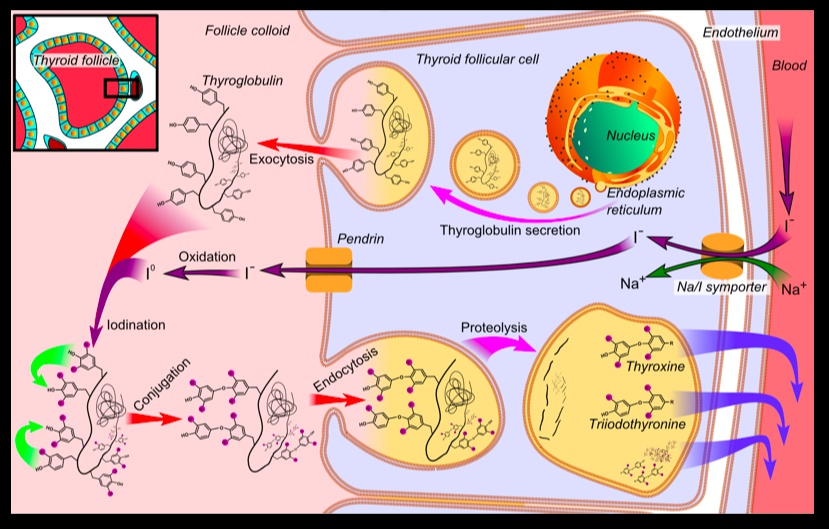
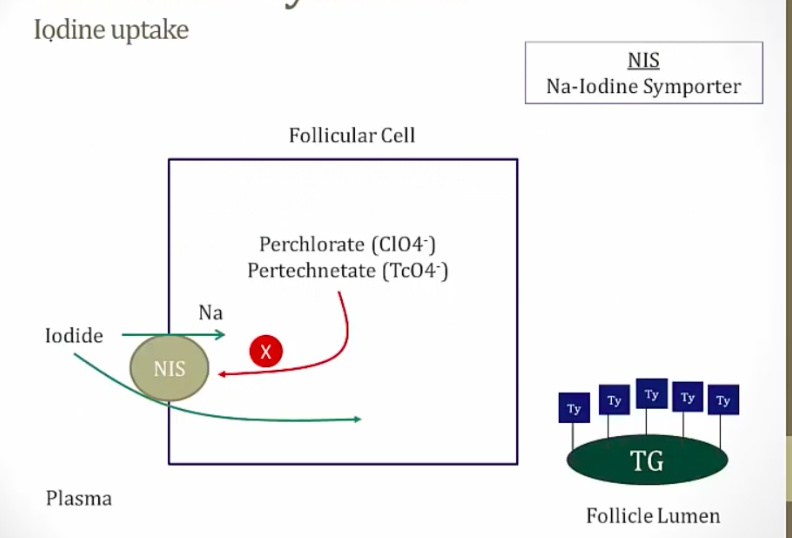
_Iodide (I-) is transported into the follicular cell via the Na-I cotransporter and then into the lumen of the follicle.. 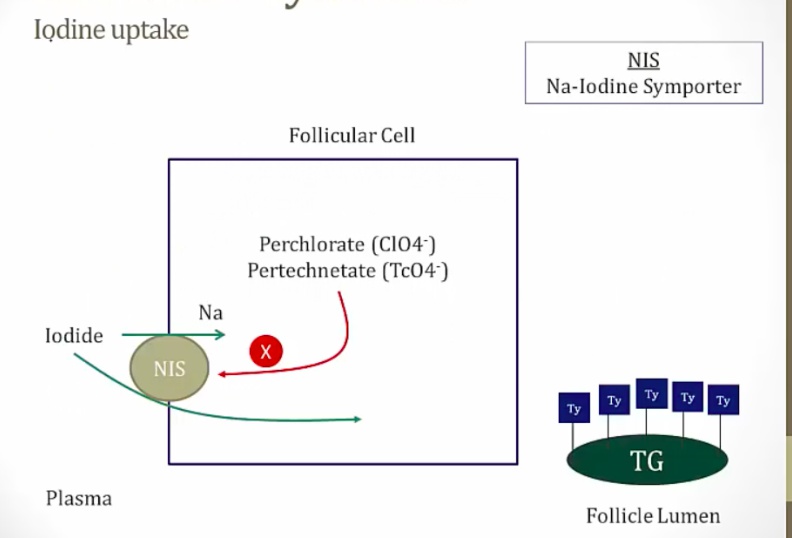
Thyroid peroxidase
Found on the luminal surface of the follicular cell, oxidizes I- to I2 (iodine).
Conjugates I2 to tyrosine residues on thyroglobulin to form monoiodotyrosine (MIT) and diiodotyrosine (DIT) residues. This reaction is called organification.
MIT: 1 iodine
DIT: 2 iodine
Couples MIT and DIT.,

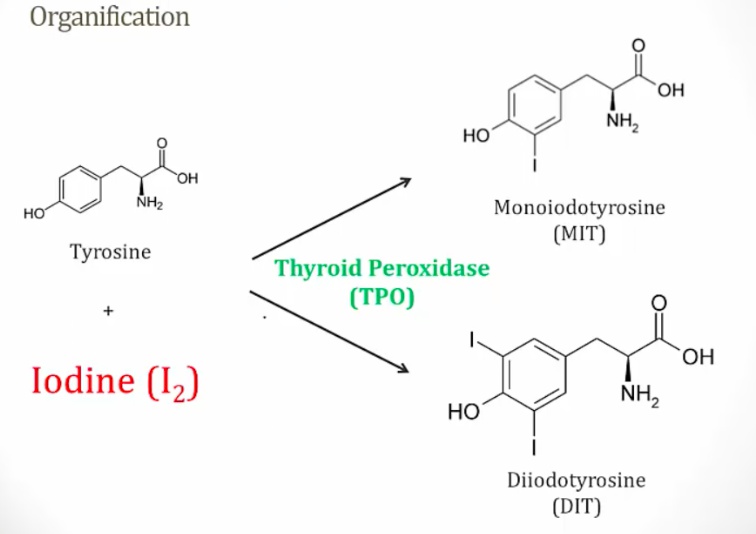
[_](What's T4 and T3 coupled from)
DIT + DIT = T4
MIT + DIT = T3..

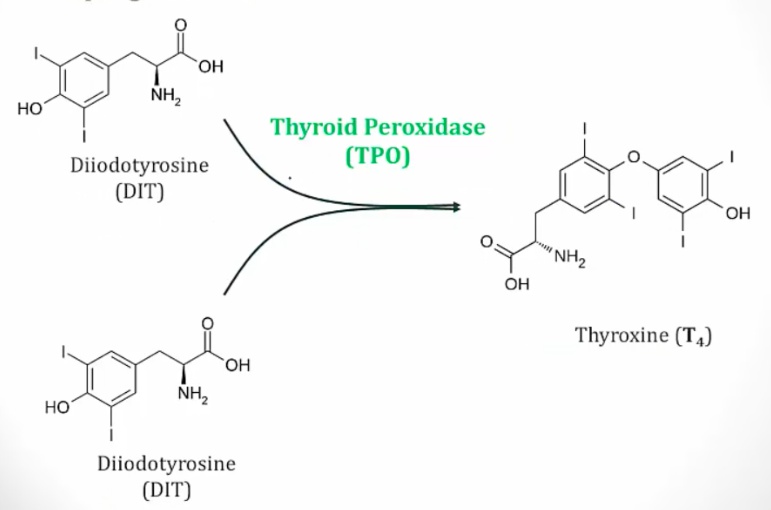
_Iodinated thyroglobulin is stored in colloid within the follicular lumen. Upon stimulation by TSH, follicular cells endocytose thyroglobulin and lysosomal enzymes digest thyroglobulin, secreting T3 and T4 into the circulation.. 
_Residual MIT and DIT are deiodinated by thyroid deiodinase. The I2 that is generated is recycled to synthesize more thyroid hormone..
_The Na-I transporter is competitively inhibited by anions including:
Thiocyanate [SCN]−
Perchlorate
Pertechnetate.,
These anions inhibit the uptake of I- into follicular cells, thereby interfering with the synthesis of thyroid hormone.
Thyroid peroxidase
_Inhibited by propylthiouracil and methimazole.,
Wolff-Chaikoff effect.
_High levels of iodine inhibit thyroid hormone synthesis by blocking the organification step. Less synthesis of MIT/DIT.,
Amiodarone

 Competes with T4
Check TSH level in patients before start amiodarone..
Competes with T4
Check TSH level in patients before start amiodarone..
Radioactive Iodine
 ..
..
Thyroxine-Binding Globulin, aka TBG
_Three proteins are involved in the transport of T3 and T4 in the blood:
Thyroxine-binding globulin (TBG) has the highest affinity for T3 and T4, and binds the majority of T3 and T4 in peripheral blood. However, it has the lowest plasma concentration of the three proteins.
Albumin carries T3 and T4, and has the highest plasma concentration.
Transthyretin (aka pre-albumin) transports T4 only..
_Only free T3 or T4 is active, whereas TBG-bound T3 or T4 is inactive. However,

TBG acts as pool of T4 to be released..
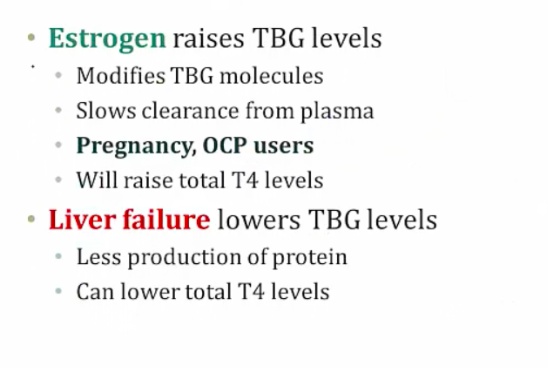
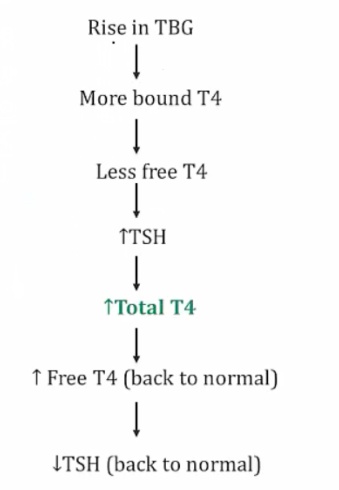
_Conditions where TBG is increased (e.g. pregnancy) or decreased (e.g. liver failure) can affect total T3 or T4 levels. Increased estrogen during pregnancy causes increased TBG, which results in increased total T3 and T4 levels. However, the free T3 and free T4 levels are actually normal (therefore, pregnancy is not a hyperthyroid state)..
Thyroid Hormone Receptors
_ these are..

Thyroid Hormone functions
_ It mediates:
Metabolism and growth
Glucose, lipid metabolism
Cardiac function
Bone growth
CNS and ANS activity
Temperature regulation.,
Thyroid Hormones Metabolic Effect
_Increases basal metabolic rate and oxygen consumption via multiple mechanisms, including:
Increasing glycogenolysis and gluconeogenesis
Increasing lipolysis
increases LDL receptor in liver > decrease serum LDL
increase cholesterol secretion in bile
decrease cholesterol/TG concentration
increases basal metabolic rate (amount of energy used if slept all day)
Increasing and upregulating Na/K ATPase activity (more ATP needed, higher RR/temp)..
hyperthyroid patient: hyperglycemia, weight loss, tachycardia, tachypnea
hypothyroid patient: high cholesterol..
Thyroid Hormones and Bone
_Affects growth and maturation by promoting bone growth/turnover, and acting synergistically with growth hormone and insulin-like growth factor-1 (IGF-1).,
Thyroid Hormones and CNS
_Is important in perinatal maturation of the central nervous system (CNS).,
A hypothyroid neonate is at an increased risk for mental retardation.
Thyroid Hormones and Cardiac Effect
_Affects the autonomic nervous system (ANS) by increasing sympathetic activity (β-adrenergic tone)., For example, thyroid hormone leads to the up-regulation of β1-adrenergic receptors in the heart.
Hyperthyroid patient: tachycardia
_Affects temperature regulation by increasing thermogenesis by increase more Na/K ATP pump.,
[_](4 B's of thyroid function)To recall major thyroid hormone functions, remember the 4 B's:
BMR (increase)
Bone growth
Brain maturation
Beta-adrenergic..
Pregnancy and thyroid hormones
_  ..
..
TRH
_Thyrotropin releasing hormone (TRH) from the hypothalamus stimulates the secretion of thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH) by the anterior pituitary..
_TSH from anterior pituitary stimulates increased synthesis and secretion of thyroid hormones, by binding follicular cell receptors and increasing intracellular levels of cAMP (adenylate cyclase-cAMP mechanism).. 
_T3 and T4 down-regulate TRH receptors in the anterior pituitary leading to an inhibition of TSH secretion. This is an example of negative feedback..  T3/T4 levels sensed by hypothalamus
T3/T4 levels sensed by hypothalamus
Thyroid-stimulating immunoglobulins, TSI
_Auto-antibodies (IgG) against TSH receptors. Binding to TSH receptors on follicular cells stimulates T3/T4 release., Patients with Graves disease exhibit high concentrations of TSI.
_  ..
..
Calcitonin
_Produced by the parafollicular cells (C cells), serves to lower blood calcium levels. It does this by several mechanisms including:
Increasing osteoblastic activity in bone
Decreasing osteoclastic activity in bone
Inhibiting intestinal absorption
Inhibiting renal tubular reabsorption (promoting excretion in urine)
Minor role in human calcium handling, but used in pharmacologic therapy for hypercalcemia.,
_The stimulus for calcitonin secretion is increased serum calcium concentration..
_Calcitonin opposes the actions of parathyroid hormone and is not important in normal Ca2+ homeostasis..
Last updated