Female Pathology
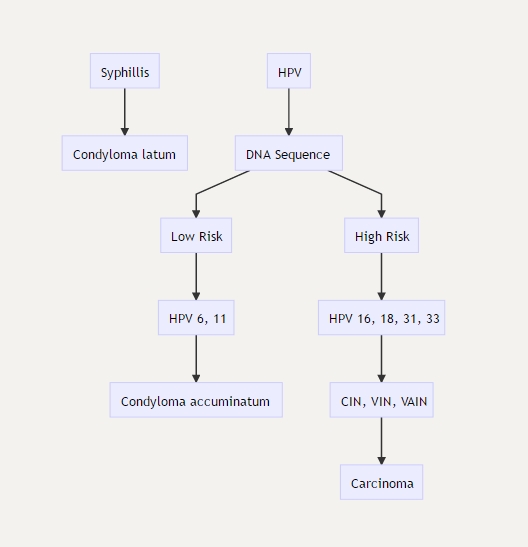
HPV and Squamous Cell Carcinoma
HPV
Location
Neoplasia
Vulvar
VIN, vulvular intraepithelial neoplasia
Vagina
VAIN, vaginal intraepithelial neoplasia
Cervix
CIN, cervical intraepithelial neoplasia
Vaccine
Gardasil (HPV 6, 11, 16, 18): vaccine against HPV, is now FDA approved for both males and females.
Cervarix (HPV 16, 18): protect against CIN and carcinoma
anti HPV 6 and 11: protect against condylomas
Fence circles 6, 11, 16, 18 only 
Pap Smear
_Pap Smear: gold standard screening test used for the detection of squamous dysplasia and cancer. It can also be used as a tool to evaluate hormone status.
_Screening begins at age 21 and is initially performed every 3 years.
_In order to be considered an adequate sample, it must contain sampling from the squamocolumnar junction (transformation zone) cells. This would include both metaplastic squamous cells and mucus-secreting columnar cells.
_Abnormal Pap smear findings include dysplasia or carcinoma in situ (CIS), both of which are characterized by the following findings on histology:
Koilocytic atypia
Nuclear enlargement ("raisinoid" appearance)
Nuclear hyperchromasia
Coarse chromatin granules
Perinuclear halo
 Pap smears. A‚ Normal. Large‚ flat cells with small nuclei. B‚ Dysplasia. Large‚ dark nuclei indicate damaged DNA; cytoplasmic halo indicates human papillomavirus (HPV) effect. C‚ Malignant. Compact cells with huge‚ irregular‚ dark nuclei indicate malignancy.
Pap smears. A‚ Normal. Large‚ flat cells with small nuclei. B‚ Dysplasia. Large‚ dark nuclei indicate damaged DNA; cytoplasmic halo indicates human papillomavirus (HPV) effect. C‚ Malignant. Compact cells with huge‚ irregular‚ dark nuclei indicate malignancy.
 Normal (left) and abnormal pap smear. Normal: small nucleus to cytoplasm ratio, pink color.
Normal (left) and abnormal pap smear. Normal: small nucleus to cytoplasm ratio, pink color.
Abnormal pap smear is followed with colposcopy and biopsy. Colposcopy: 
_Pap smear has limited efficacy in screening for adenocarcinoma (does not have stages)
Vulvar SCC
_Relatively rare, malignant carcinoma arising from the squamous epithelium of the vulva.
_The lesions commonly present as leukoplakia 
_Biopsy may be required to distinguish vulvar carcinoma from other causes of leukoplakia (lichen problems).
_The etiology may be HPV-related (associated with “high-risk” types 16 and 18) or non-HPV related.
_HPV 16 and 18 makes E6 and E7 that increases destruction of p53 and Rb. Loss of these tumor suppressor proteins increase risk for VAIN, CIN , VIN
_HPV related vulvar carcinoma (VIN, Vulvar Intraepithelial Neoplasia) risk factors related to HPV exposure, multiple partners, early intercourse. Women of reproductive age, 40-50s (get around 25-30, takes 15 years to develop)
Non-HPV vulvar carcinoma
_Often arise from long-standing lichen sclerosis, which are generally seen in elderly women (average age is >70 years old).
Vaginal SCC
_Carcinoma arising from the squamous epithelium lining the vaginal mucosa.
They most commonly develop from the extension of a squamous cell carcinoma of the cervix.
In general, primary squamous cell carcinomas of the vagina are rare
There is a high association with "high-risk" HPV 16 and 18 serotypes
Precursor lesion is vaginal intraepithelial neoplasia (VAIN)
_The route of lymph node metastasis differs based on the location of the primary tumor:
Upper ⅓ of vagina drains to iliac nodes
Lower ⅔ vagina drains to inguinal nodes
The distinct routes of lymphatic drainage correspond to the embryologic origin of different parts of the the vagina; recall that the upper ⅓ of the vagina is derived from the paramesonephric duct, while the lower ⅔ of the vagina is derived from the urogenital sinus.
CIN and Cervical Carcinoma
CIN
_Pathogenesis:
Strongly associated with "high-risk" HPV 16, 18, 31, & 33
HPV infects immature basal cells of the squamous epithelium and immature metaplastic squamous cells at the squamocolumnar junction. Infection usually eradicated by immune system in acute inflammation. Persistent infection leads to risk for CIN and then carcinoma
_Koilocytes (seen in all HPV related diseases) are seen beginning at the basal layer and extending outward. These are cells with a clear halo surrounding hyperchromatic, atypical nuclei. Increased mitotic activity.
_Classification of CIN:
CIN 1: dysplasia involving lower 1/3 of the epithelium
CIN 2: dysplasia involving lower 2/3 of the epithelium
CIN 3: dysplasia involving slightly less than the entire thickness of the epithelium
CIS (Carcinoma in situ): dysplasia involving the entire thickness of the epithelium.
High grade dysplasia (carcinoma in situ) in the uterine cervix. The abnormal epithelium is extending into a mucus gland to the left of centre. This disease can progress to invasive cancer (squamous cell carcinoma) of the cervix:  CIN III
CIN III  Development of dysplasia and carcinoma of the cervix. Repeated human papillomavirus (HPV) infections convert normal epithelium (left) into increasingly severe dysplasia until malignant epithelium breaks through the basement membrane to become invasive cancer‚ capable of metastasis by invasion of blood vessels and lymphatics.
Development of dysplasia and carcinoma of the cervix. Repeated human papillomavirus (HPV) infections convert normal epithelium (left) into increasingly severe dysplasia until malignant epithelium breaks through the basement membrane to become invasive cancer‚ capable of metastasis by invasion of blood vessels and lymphatics. 
_CIN I to III can regress. CIS cannot regress and will proceed to invasive squamous cell carcinoma once it breaks through basement membrane.
_Carcinoma in situ is characterized by atypical changes extending through the entire thickness of the epithelium.
As it has not yet invaded the basement membrane, it is considered a precancerous lesion.
Invasive cervical carcinoma
_Two subtypes of cervical carcinoma are SCC (80%) and adenocarcinoma (columnar cells). Both types are related to HPV.
_(Cervical carcinoma risk factors)Risk factors for cervical carcinoma are:
Multiple sexual partners (#1 risk factor)
Immunodeficiency (AIDS defining illness): Immune systems fail to destroy HPV
Early sexual intercourse
Birth control pills
Smoking
_ Cervical carcinoma is AIDS defining illness
_Cervical cancer is now the least common gynecologic cancer due to the success of the Pap smear screening tests. It typically presents with foul smelling discharge and irregular bleeding, which is often postcoital.
_Advanced tumors invade locally through anterior uterine wall into the bladder, blocking the ureters. Hydronephrosis with postrenal failure is a common cause of death in advanced cervical carcinoma.
Cervical squamous cell carcinoma 

_Pap smear is the screening test of choice because it can discover cervical dysplasia before it progresses to invasive carcinoma. Dysplastic cells demonstrate koilocytosis (cellular changes in which cells appear to have halo nuclei on cytologic examination).
Vulva Pathology
Anatomy
skin and mucosa of female genitalia external to hymen
lined by squamous epithelium
Bartholin Cysts
_ Cystic dilation of Bartholin glands, happens in women of reproductive age due to infection and STI 
_Bartholin gland produce mucus-like fluid via ducts into lower vestibule.
_Bartholin cysts typically arise due to inflammation and obstruction of the gland
_Bartholin cysts commonly present with a unilateral, painful cystic lesion at the lower vestibule adjacent to the vaginal canal.


Lichen Sclerosis
_Lichen Sclerosis is a benign lesion characterized by a thinning of the epidermis and fibrosis (sclerosis) of the underlying dermis.
_The lesions of lichen sclerosis commonly present as a white patch (leukoplakia) with “parchment-like” vulvar skin (like paper). 
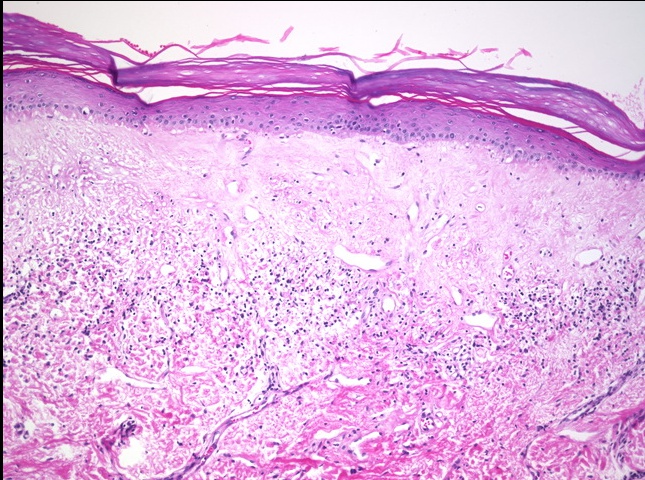
_Lichen Sclerosis is most commonly seen in postmenopausal women, and there is believed to be a possible autoimmune and atrophy etiology.
_Lichen Sclerosis is associated with a slightly increased risk of squamous cell carcinoma.
Lichen Simplex Chronicus
_Lichen Simplex Chronicus is a benign lesion characterized by hyperplasia of the vulvar squamous epithelium.

_The lesions of lichen simplex chronicus commonly present as leukoplakia with thick, leathery vulvar skin. 
_The development of lichen simplex chronicus is associated with chronic irritation and scratching of the vulva.
_Lichen Simplex Chronicus does not carry an increased risk of squamous cell carcinoma.
Lichen sclerosis
Lichen simplex chronicus
skin thinning
skin thickening
autoimmune, atrophy
chronic irritation
risk of scc
no risk
Condyloma
_Condyloma is a sexually transmitted lesion that can be caused by either HPV 6, 11 (condyloma accuminatum) or secondary syphilis (condyloma latum). These lesions can be differentiated by the following:
Condyloma accuminatum: warty growth on the external genitals (vulva, vaginal canal, cervix) or at the anus, consisting of fibrous overgrowths covered by thickened epithelium showing koilocytosis.
Condyloma latum: Less common. eruption of flat-topped papules, found at the anus and wherever contiguous folds of skin produce heat and moisture.
 condyloma accuminatum:
condyloma accuminatum:  _Condylomas rarely progress to carcinoma, and this is because HPV types 6 and 11 are considered “low-risk.”
_Condylomas rarely progress to carcinoma, and this is because HPV types 6 and 11 are considered “low-risk.”
_Histologically, condylomas associated with HPV are characterized by koilocytes with “raisin-like” nuclei surrounded by a halo.
Low mag: warts like 
 High mag: koilocytes, raisin like nucleus
High mag: koilocytes, raisin like nucleus 
Extramammary Paget Disease
_Extramammary Paget Disease is characterized by malignant epithelial cells with pale cytoplasm and eccentric, hyperchromatic nuclei (Paget cells) in the epidermis of the vulva.
Extramammary disease, malignant paget cells infiltrating dermis. Epithelial near top. Looks like melanoma. 
_The lesions of extramammary paget disease commonly present as erythematous, pruritic, ulcerated vulvar skin. 
_Extramammary Paget disease represents carcinoma in situ (CIS), however, unlike paget disease of the nipple (breast involvement), there is usually no underlying carcinoma.
_It is very important to distinguish extramammary paget disease from melanoma, which is a lesion that rarely occurs on the vulva. The following histologic staining is used to make the differentiation:
Paget cells: PAS positive, keratin positive, S100 negative (Pas: mucous secretion from epithelial cells)
Melanoma: PAS negative, keratin negative, S100 positive
Vagina Pathology
Anatomy
_- stratified, non-keratinized squamous epithelium
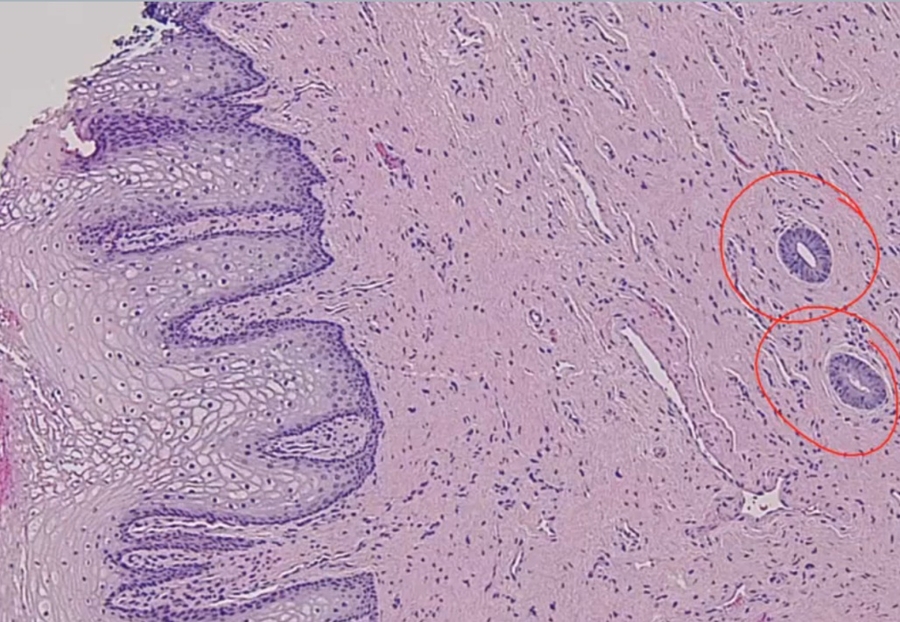
Adenosis
 _ Focal persistence of columnar epithelium in the upper vagina.
_ Focal persistence of columnar epithelium in the upper vagina.
During development, squamous epithelium from lower 1/3 (urogenital sinus) of the vagina grows upward to replace columnar epithelium lining of upper 2/3 of vagina (mullerian ducts) 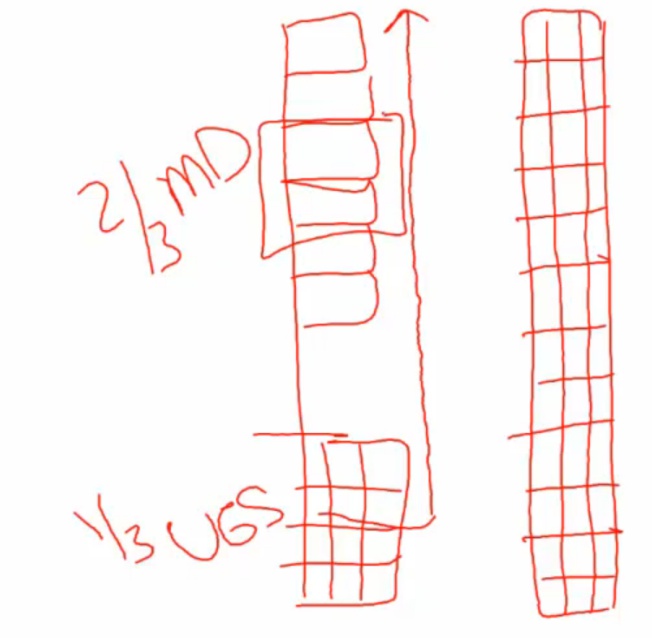
_In utero exposure to diethylstilbestrol (DES) is a major risk factor for adenosis of the vagina.
Adenosis of vagina: 
Clear Cell Adenocarcinoma
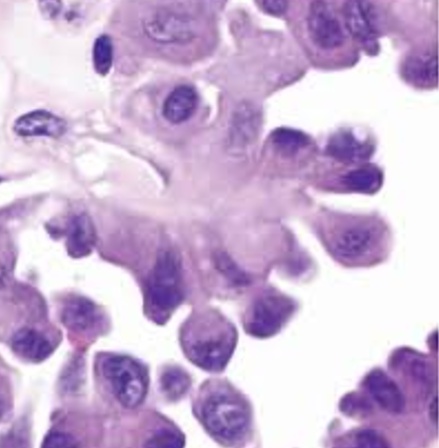
_Clear Cell Adenocarcinoma of the vagina is a rare, malignant tumor of glands with clear cytoplasm that is a complication associated with diethylstilbestrol-associated vaginal adenosis. It is commonly associated with exposure to DES in utero (Estrogen crosses placenta, distrupting development of squamous epithelium)
_When viewed microscopically, the tissue demonstrates cells with hyperchromatic nuclei (also known as "Hobnail" nuclei) protruding into the gland lumen.
Clear cell adnocarcinoma:  Hobnail nuclei:
Hobnail nuclei: 
Sarcoma Botryoides
_ A malignant mesenchymal proliferation of immature skeletal muscle. This is a rare variant of rhabdomyosarcoma.
_ Aka Embryonal Rhabdomyosarcoma
_ Most commonly seen in girls and boys younger than age 4.
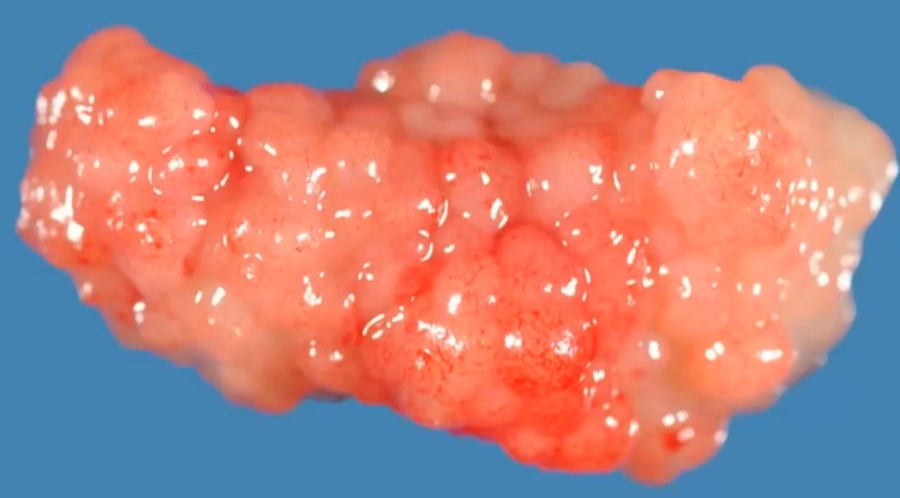
_Grossly, it presents as multiple polypoid masses resembling a "bunch of grapes" projecting out of the vagina, and will often be seen protruding from the vulva; clear/yellow in color. In young boys it will be seen protruding from the penis.
Embryonal rhabdomyosarcoma (sarcoma botryoides) of vagina. The grape-like tumor protrudes through the introitus: 
_Microscopic observation of Sarcoma Botryoides reveals striated, spindle shaped tumor cells known as rhabdomyoblasts (immature muscle cells). Has cytoplasmic cross-striations like skeletal muscle cells 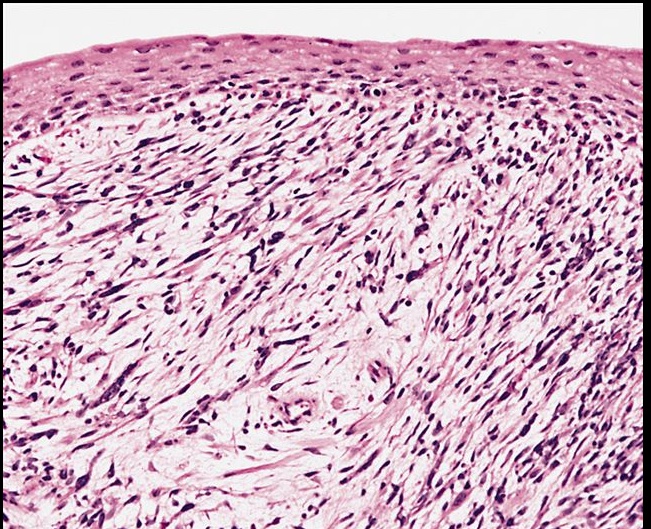
_ Stains positive for desmin (intermediate filaments in muscle cells) and myogenin (transcription factor only found in immature muscle cells).
Cervix Pathology
Anatomy
_Neck of uterus
Divided into endocervix and exocervix
Exocervix: nonkeratinized squamous epithelium
Endocervix: columnar cells
Junction: transformation zone
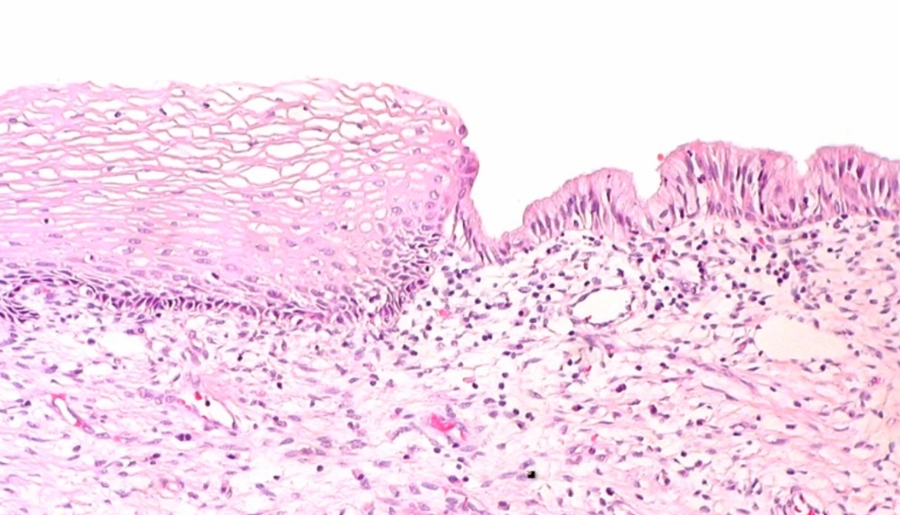
Most cervical pathology stems from the effects of sexually transmitted infections.
Cervicitis
_is condition that involves inflammation of the cervix that typically occurs in the transformation zone. Most commonly (>50%) caused by ascending infections from Chlamydia or Gonorrhea
Other common causes cervicitis include:
Trichomonas vaginalis: foul smelling, frothy, yellow/green discharge
Candida albicans: white, chunky, cottage cheese discharge
Gardnerella vaginalis (Bacterial vaginosis): foul smelling, fishy, grey discharge
HSV-2
HPV
_Acute cervicitis
Presents with vaginal discharge, bleeding, pain, dyspareunia (pain with intercourse)
If untreated it can progress to chronic cervicitis, which carries an increased risk for infertility
_Follicular cervicitis
Subtype of cervicitis caused by Chlamydia trachomatis
Histologically, it is characterized by lymphoid germinal centers and vacuoles containing reticulate bodies.
_Common cause of neonatal conjunctivitis and pneumonia
Uterine Pathology
Anatomy
Endometrium: mucosal lining of uterine cavity
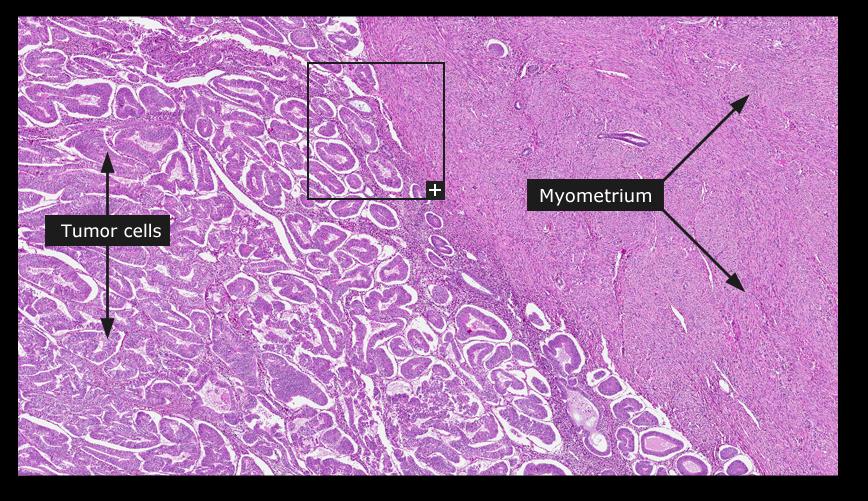
Myometrium: smooth muscle underneath
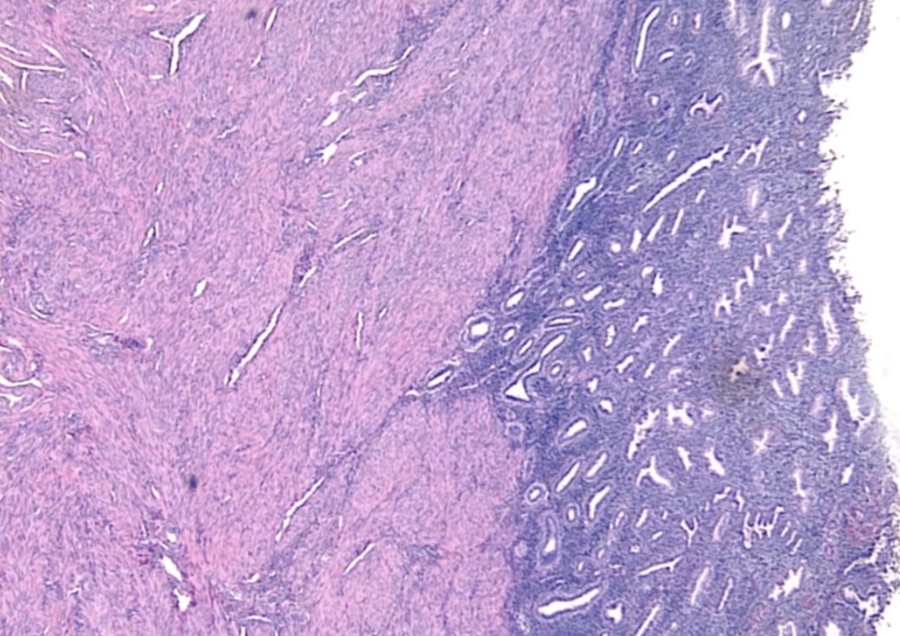
Left: endometrium. Right: myometrum
Endometerium is hormone sensitive. Estrogen: growth. Progesterone: preparation. Menstruation: shedding
Endometritis
_Endometritis is infection of the endometrium. It is the most common genital tract infection following delivery or abortion, especially in preterm deliveries. It is most often caused by bacterial infection of the endometrium.
_Acute (early-onset) Endometritis is caused by a bacterial infection (e.g., GBS (Group B Strep), Bacteroides, Peptostreptococcus, Ureaplasma) of the endometrium. Usually due to retained products of conception (after delivery or miscarriage) that act as a nidus for infection.
_Presents as fever, abnormal uterine bleeding, and pelvic pain.
_Biopsy of the endometrium will reveal neutrophils within the endometrial glands.
 Acute endometritis
Acute endometritis
_Chronic (late-onset) Endometritis is caused by chronic inflammation of the endometrium. Causes include retained products of conception, chronic pelvic inflammatory disease (e.g., Chlamydia), IUD (e.g., Actinomyces israelii), and TB.
_Biopsy of the endometrium will reveal lymphocytes and plasma cells seen within endometrial stroma. Also, granulomas will be seen in the case of TB infection. Plasma cells are necessary for the diagnosis of chronic endometritis given that lymphocytes are normally found in the endometrium.  Chronic endometritis
Chronic endometritis
_Presents as abnormal uterine bleeding, pain, and infertility.
Endometriosis
_Endometriosis is the ectopic implantation and proliferation of endometrial glands and stromal tissue outside of the uterine endometrial lining.
Regurgitation Theory: menstrual flow backs up through the fallopian tubes, with subsequent implantation of endometrial tissue in the peritoneum. (Retrograde flow commonly occurs in normal women)
Vascular/Lymphatic Dissemination: endometrial cells enter vascular/lymphatic system, which allows deposition in distant sites.
Metaplastic Theory: endometrial tissue arises from endometrial differentiation of coelomic epithelium.
_The most common clinical presentation of endometriosis is a woman in her 20s or 30s that presents with infertility and the three D's:
Dysmenorrhea (painful menses)
Dyspareunia (painful sexual intercourse)
Dyschezia (painful defecation)
Cyclic bleeding and symptoms correspond to hormonal status, and because these lesions are hormonally responsive the symptoms may worsen leading up to menstruation.
Ovaries (most common location, increased cancer risks): may produce a "chocolate cyst"
Uterine ligaments: may produce pelvic pain
Rectouterine pouch of Douglas: may produce dyschezia
Bowel serosa: may produce abdominal pain and adhesions
Bladder wall: may produce pain with urination
Fallopian tube mucosa: scarring increases risk for ectopic tubal pregnancy
_Chocolate Cysts (also known as an endometrioma) manifest when endometriosis is occurring in the ovaries, and with monthly hemorrhage it leads to the creation of a blood-containing cyst.
Chocolate cysts vary with the menstrual cycle because they contain estrogen responsive endometrial tissue.
_The menstrual-type bleeding of the ectopic endometrium most commonly occurs in the ovary, and this forms blood-filled "chocolate cysts" and reddish-bluish-brown "powder-burn" serosal nodules.  Chocolate cysts of ovary. Caused by endometrium growing and shedding inside ovary.
Chocolate cysts of ovary. Caused by endometrium growing and shedding inside ovary. 

 Powder burn serosal nodules
Powder burn serosal nodules
_The first-line treatment for women with mild/moderate pain caused by endometriosis is NSAIDs plus combined(estrogen and progestin) oral contraceptives (OCPs). An alternative to combined OCPs is progestin-only hormonal therapy (e.g. medroxyprogesterone).
_Danazol is a synthetic androgen that acts to inhibit FSH and LH production by the anterior pituitary (negative feedback). It is FDA-approved to treat women with endometriosis-related pain; however, it is rarely used due to its adverse effects (hirsutism, acne, hepatotoxicity, etc.)
_Women with severe/refractory symptoms due to endometriosis can be treated with GnRH agonists such as leuprolide.
Women with endometriosis that fail medical therapy are candidates for laparoscopic excision of the endometriosis lesions.
Adenomyosis
_Adenomyosis refers to the presence of endometrial glands and/or stroma within the uterine myometrium.
Adenomyosis will commonly present with menorrhagia, dysmenorrhea. Patients with adenomyosis will have a symmetrically enlarged “boggy” uterus found on bimanual exam. The diagnosis of adenomyosis is made with biopsy, and the definitive treatment is with hysterectomy.
A boggy uterus is a finding upon physical examination where the uterus is more flaccid than would be expected.
Endometrial hyperplasia
_Endometrial hyperplasia is the abnormal proliferation of endometrial glands relative to stroma; usually caused by excess unopposed estrogen stimulation (obesity, PCOS, estrogen replacement) 

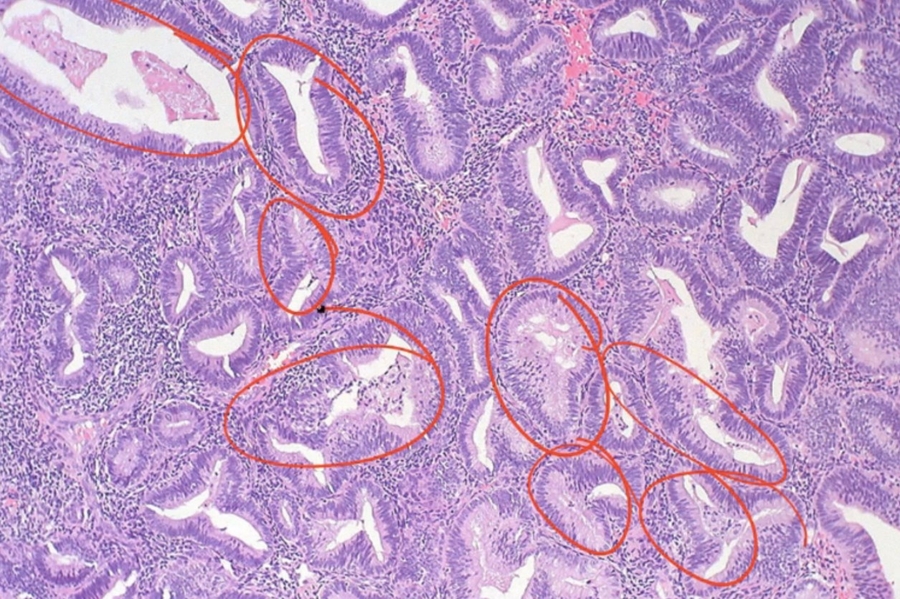
_The risk factors for endometrial hyperplasia are related to increased exposure of unopposed estrogen:
Early menarche; late menopause
Nulliparity
Anovulatory cycles
PCOS (polycystic ovarian syndrome)
Obesity (increased conversion of androgens into estrone and estradiol by aromatase within adipocytes)
Estrogen-secreting tumors (e.g., granulosa cell tumors)
Tamoxifen (partial agonist of estrogen receptors in endometrial tissue)
Use of unopposed estrogen without progesterone in hormone replacement therapy
_Endometrial hyperplasia usually presents as postmenopausal vaginal bleeding.
_Classified histologically based on architectural growth pattern (simple or complex) and the presence or absence of cellular atypia. The most important predictor for progression to carcinoma is the presence of nuclear atypia.
Endometrial hyperplasia is a precursor to endometrial carcinoma, thus patients with endometrial hyperplasia are at increased risk of developing endometrial carcinoma.
Endometrial carcinoma
_Endometrial carcinoma is a malignant proliferation of endometrial glands (adenocarcinoma). 
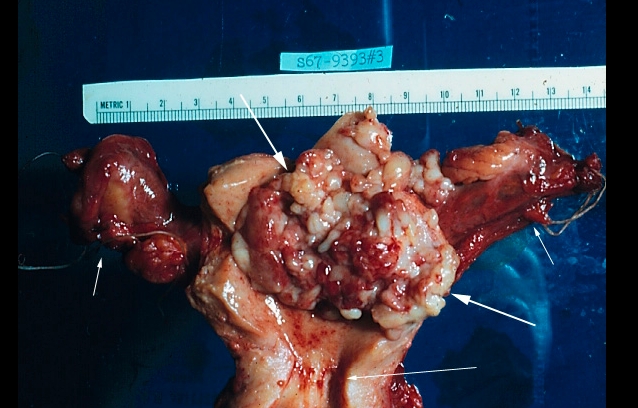
_Most common invasive carcinoma of the female genital tract.
_Endometrial carcinoma most commonly presents in patients between ages 60 and 70, and classically presents with post-menopausal vaginal bleeding.
_There are two distinct pathways that lead to the development of endometrial carcinoma:
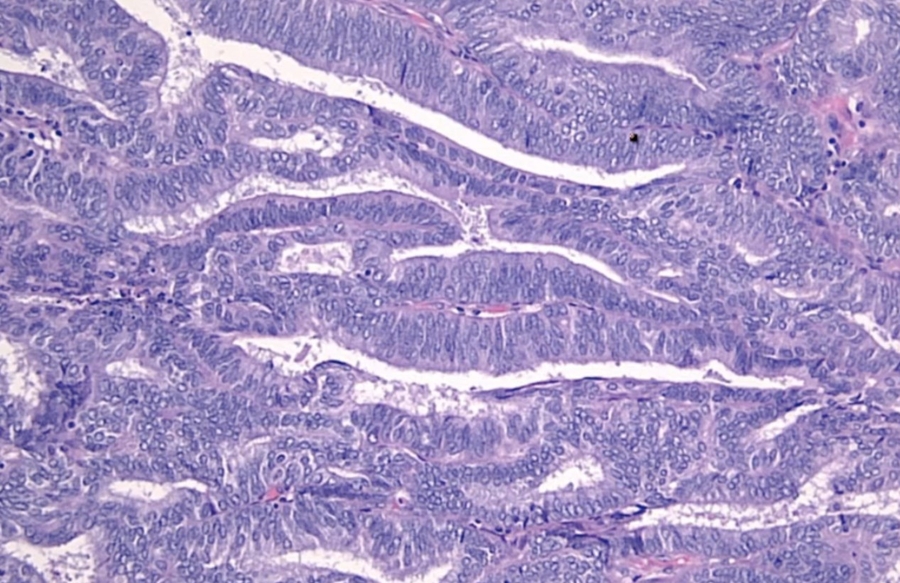
Endometrial hyperplasia pathway (75% of cases): patient with unopposed estrogen develops endometrial hyperplasia, which eventually advances to carcinoma. Average age is 60 years. Histology is endometrioid (normal endometrium-like). It is commonly driven by a PTEN mutation.
Sporadic pathway (25% of cases): carcinoma arises in an atrophic endometrium. There is no evident precursor lesion. Average age is 70 years. Histology is usually serous and is characterized by papillary structures with psammoma body formation. It is commonly driven by a p53 mutation, and the tumor exhibits aggressive behavior. (Necrosis > calcification > psamomma body)
Endometrioid. Looks like endometrium but disorganized with minimum stroma
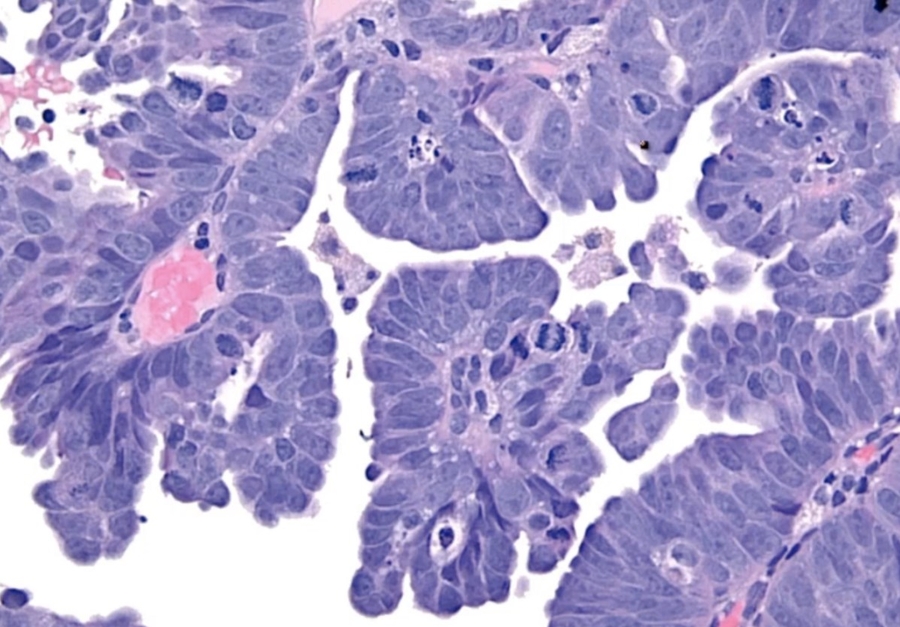
Sporadic pathway. Serous.
_The risk factors for endometrial carcinoma include:
Prolonged unopposed estrogen exposure (refer to endometrial hyperplasia section for examples)
Diabetes
Hypertension
Hereditary Nonpolyposis Colorectal Cancer (HNPCC)
_The prognosis of endometrial carcinoma correlates with degree of myometrial invasion (the deeper it invades, the worse the prognosis). Think of its progression as an uncontrolled proliferative (follicular) phase of menstrual cycle: Normal endometrium transforms into simple hyperplasia, which transforms into complex hyperplasia, then atypical hyperplasia, and finally results in endometrial adenocarcinoma.
Simple hyperplasia: OCPs (oral contraceptive pills)
Atypical hyperplasia: hysterectomy
Invasive carcinoma: some combo of surgery/chemo/radiation
Leiomyoma
_ (Fibroid) is a benign proliferation of myometrial smooth muscle cells
_It often presents with multiple discrete tumors that are well-demarcated (i.e., encapsulated) by a pseudocapsule. No necrosis or hemorrhage Uterine cavity in middle: 
_Whorled patterns of smooth muscles on microscopic exam
_Most common benign tumors in women.
_The peak occurrence is seen in African American women between 20 and 40 years of age. (Premenopausal women because responsive to estrogen)
_Abnormal uterine bleeding (e.g., menorrhagia, postcoital spotting), which is by far the most common symptom → chronic iron deficiency anemia (dizziness, weakness, fatigue) if the bleeding is severe. Due to impringe on pelvic structures. No pain
Secondary dysmenorrhea, especially if menorrhagia is present
Compression of surrounding structures, depending on the number and location of the fibroids. For example:
Constipation if the bowel is compressed
Hydronephrosis if one or both of the ureters are compressedVenous stasis if the inferior vena cava is compressed
Infertility, however the overwhelming majority of women with fibroids can conceive without difficulty
_Fibroids are hormonally responsive to estrogen (and to progesterone), and as a result they may:
Increase in size during pregnancy or when exposed to high levels of exogenous or endogenous estrogen
Stop growing or even decrease in size during/following menopause
Leiomyomas do not progress to a leiomyosarcoma.
There is recent evidence that leiomyomas may also produce EPO (which can potentially cause erythrocytosis).
_Treatment:
Hysterectomy
Myotomy for women who wish to preserve fertility
Leiomyosarcoma
_Leiomyosarcoma is a malignant proliferation of smooth muscle arising from the myometrium that typically arises de novo (they do NOT arise from a leiomyoma).
_Leiomyosarcomas have an increased incidence in African Americans. Often in postmenopausal women.
_Leiomyosarcomas are a highly aggressive tumor with a tendency to recur. They commonly present as a bleeding mass fungating from the myometrium into the lumen of the uterus, sometimes even protruding through the cervix.
_Grossly, leiomyosarcomas appear as bulky irregularly shaped tumors with areas of necrosis and hemorrhage. Histological features include necrosis, mitotic activity, and cellular atypia. (single lesion)
Asherman Syndrome
_Repeated dilation and curettage (D&C) procedures that remove the stratum basalis, the stem cell layer of the endometrium that generates functionalis layer for growth and shedding. This renders the endometrium unable to regenerate, resulting in endometrial fibrosis and scarring. Asherman syndrome is an etiology of secondary amenorrhea.
Anovolatory Cycle
_Anovulatory cycle is a condition characterized by a lack of ovulation. It results in an estrogen-driven proliferative phase without a subsequent progesterone-driven secretory phase. Proliferative glands eventually break down and shed resulting in uterine bleeding. It represents a common cause of dysfunctional uterine bleeding, especially during menarche and prior to menopause.
Endometrial polyp
Hyperplastic protrusion of the endometrium.
It will commonly present as abnormal uterine bleeding.
Can arise as a side effect of tamoxifen, which has anti-estrogenic effects on the breast but weak pro-estrogenic effects on the endometrium.
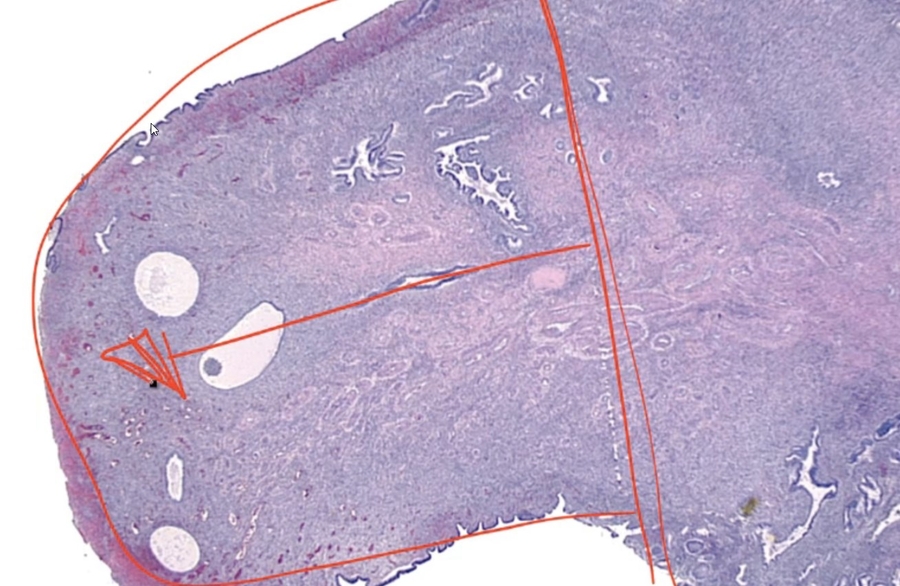
Growth of polyp causes bleeding
Last updated