13 Sickle Cell
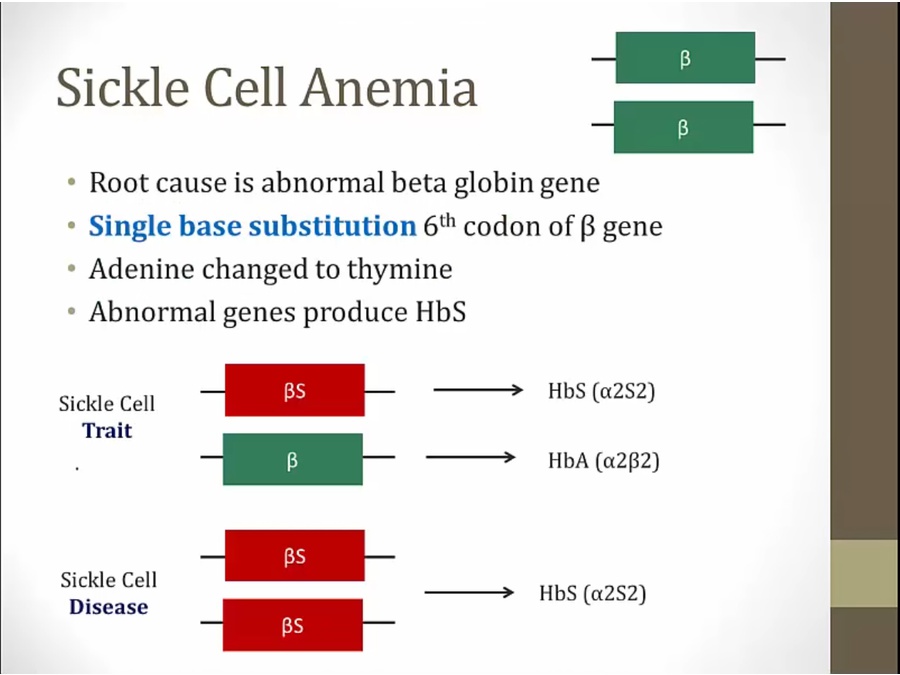
2 genes, 1 from each parent
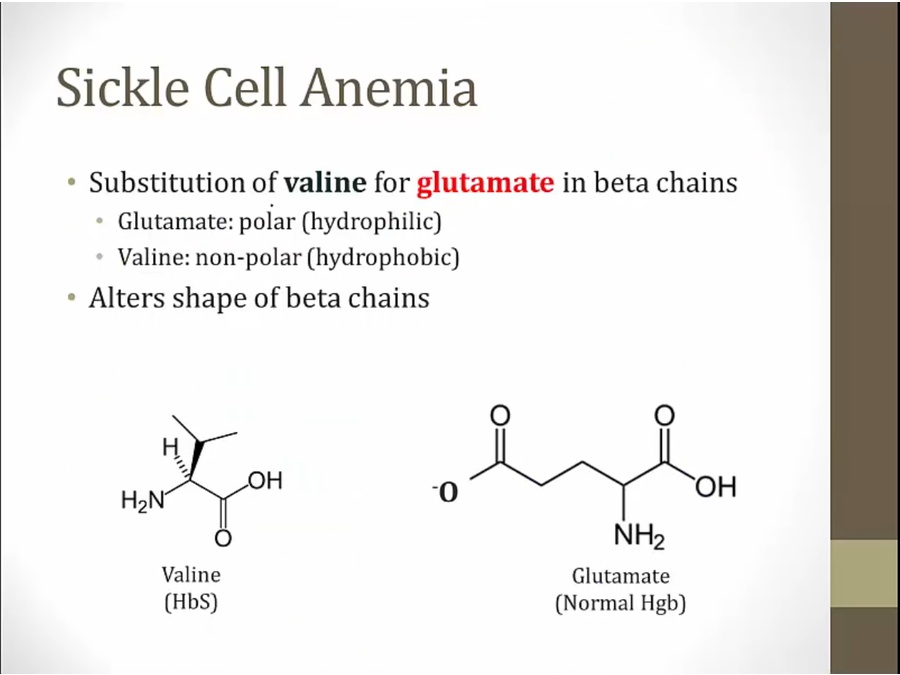
A to T leads to aa substition
dehydration/acidosis: acute exacerbation
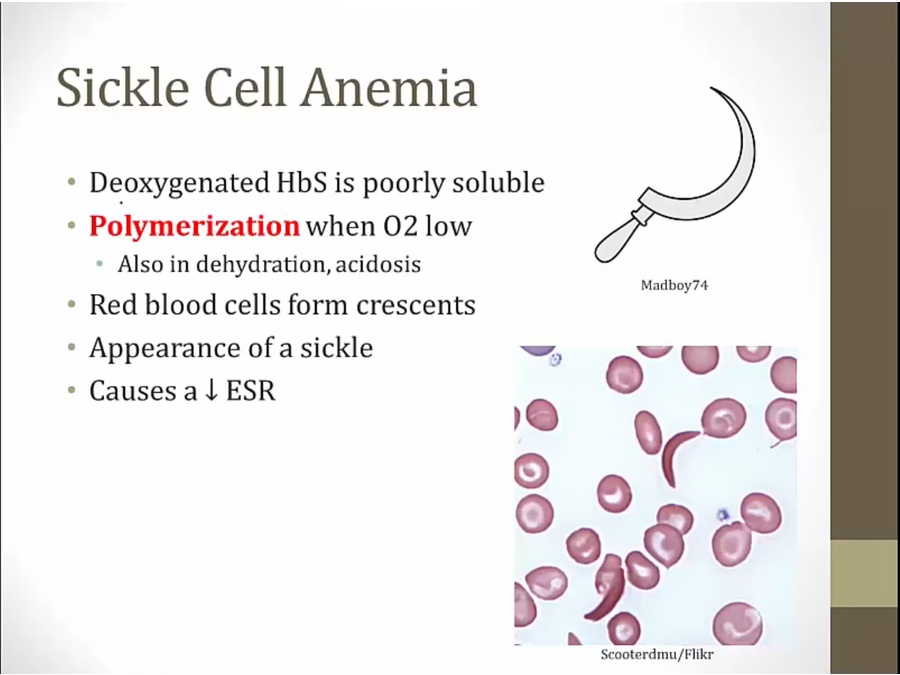
polymerize and make RBC form crescents
decrease ESR instead of up
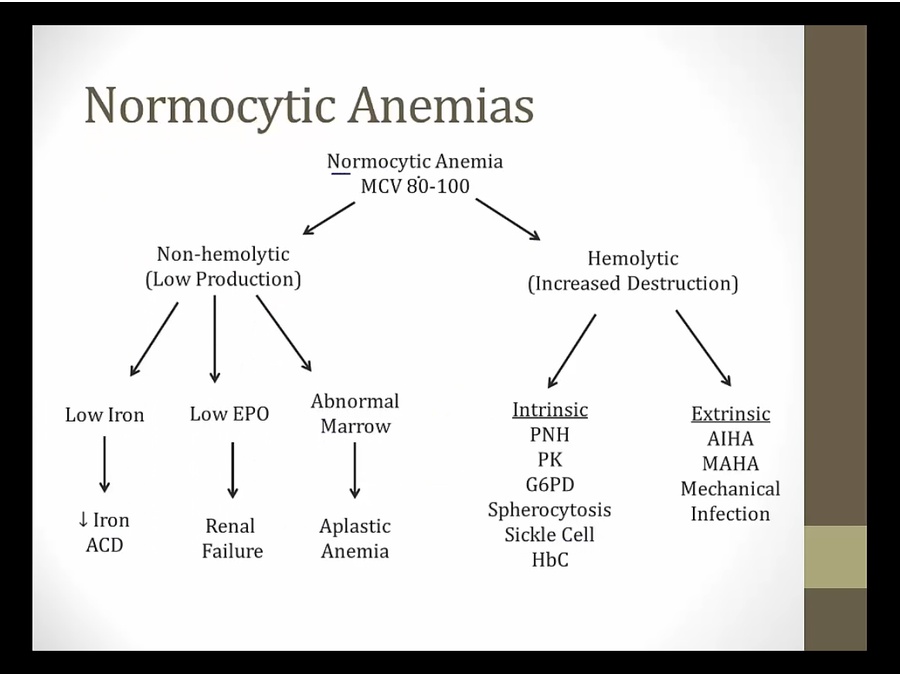
Symptoms

hemolytic anemia similar to beta thalassemia major
vaso occlusion: more dangerous and unique symptoms
Hemolysis
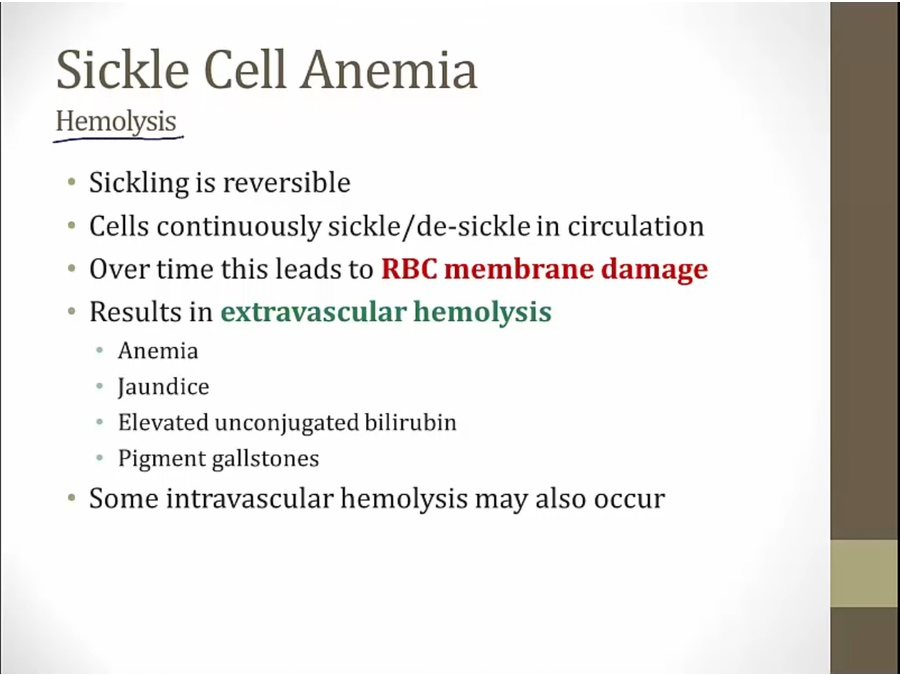
sometimes simply rupture in vasculature

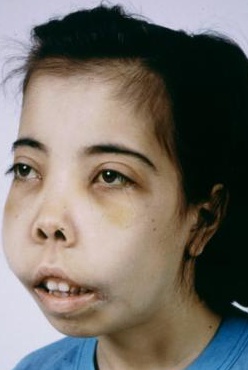
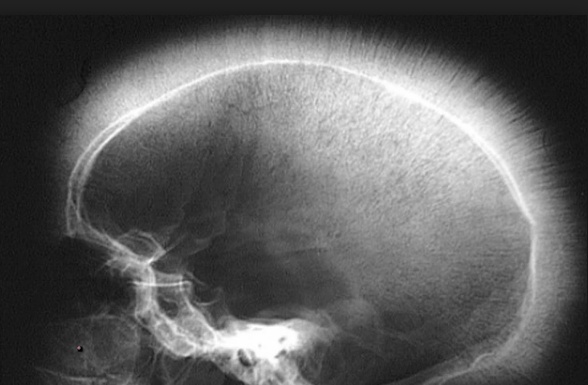

Vasoocclusion

heart, brain
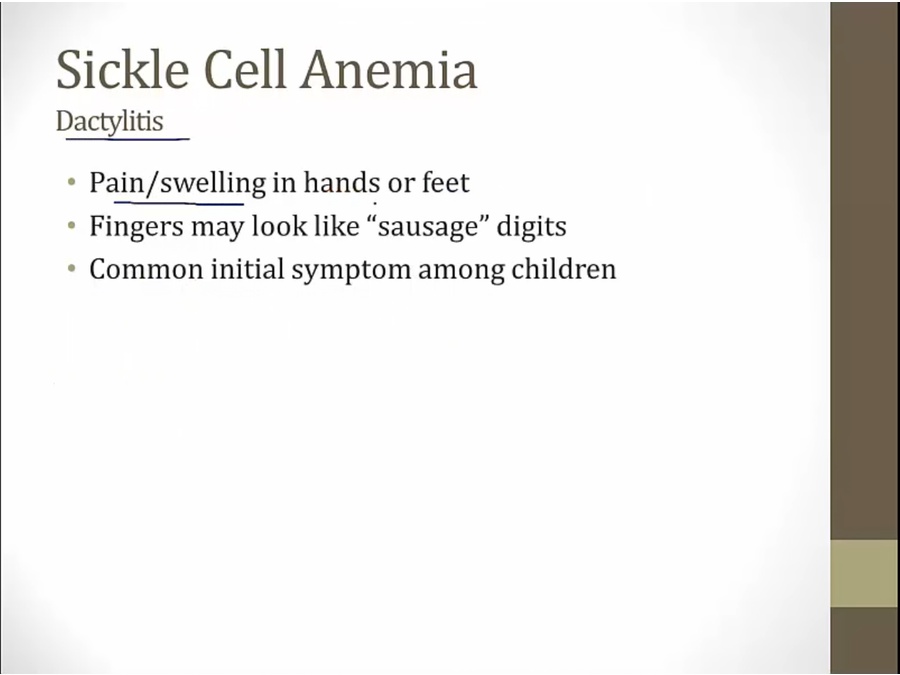
first thing that happen
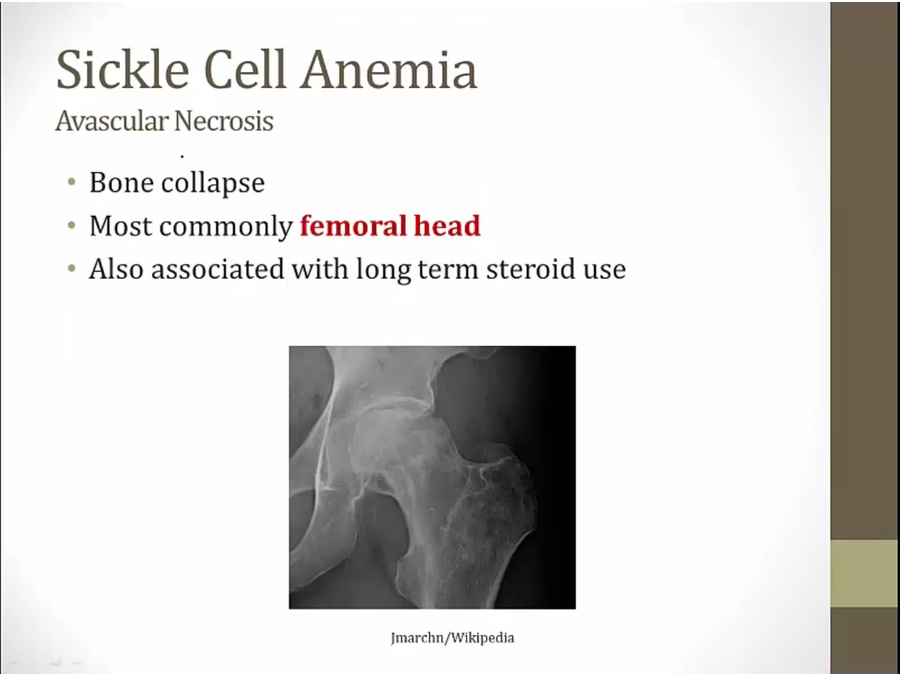
jagged femoral head

dehydration lead to sickling
can become dependent on narcotics
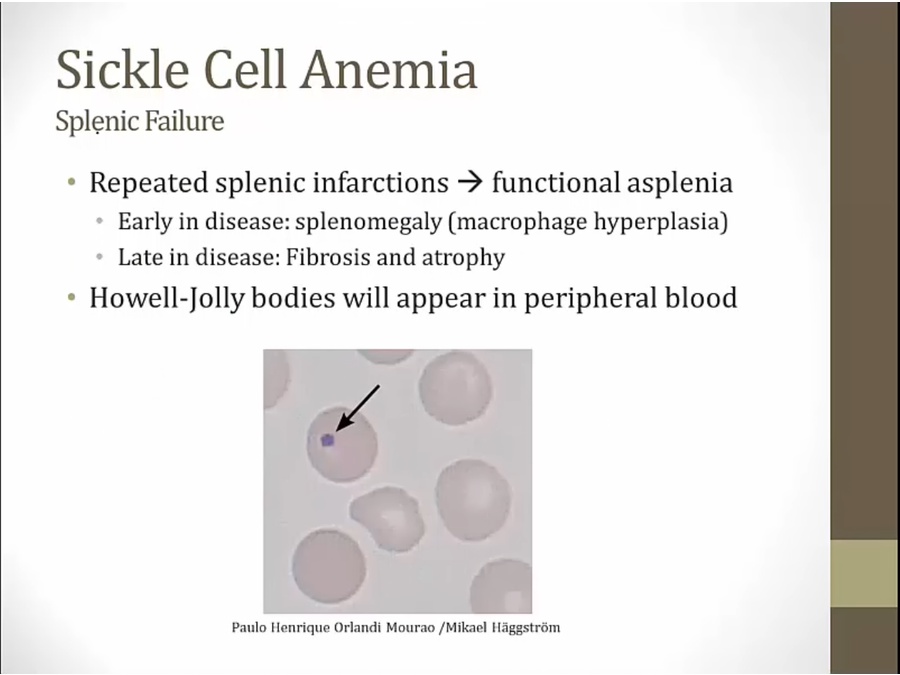
have spleen but not working

can die from infection
salmonella encapsulated, staph not
The spleen may demonstrate brownish discoloration (hemosiderosis) due to extensive ingestion of sickled RBCs by splenic macrophages (extravascular hemolysis).

fish bone: Osteomyelitis
sickle: In Sickle Cell disease

sickle: Increased risk of infection in sickle cell or asplenic patients
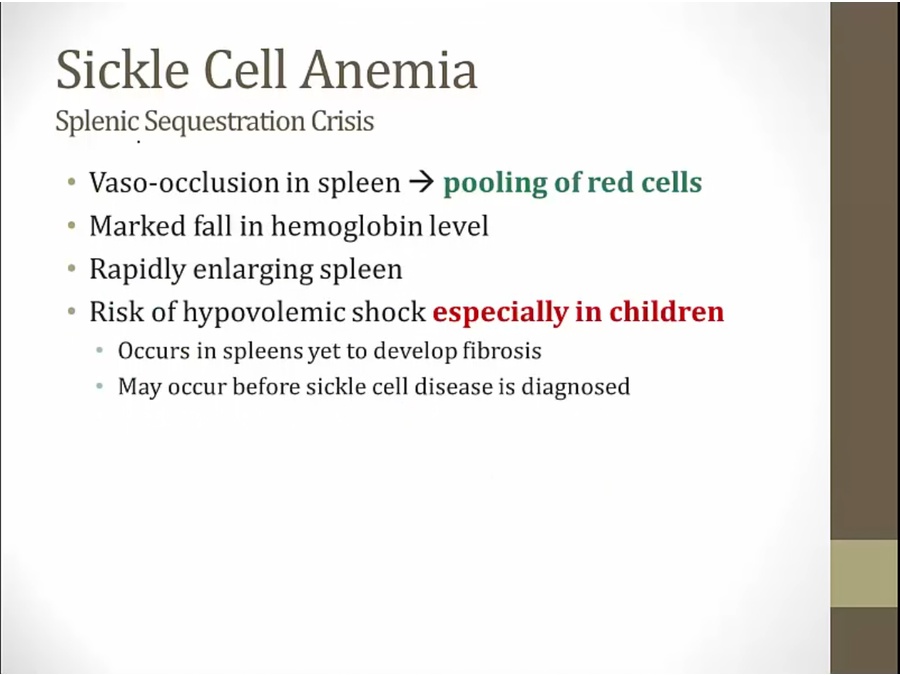
pooling of RBC in spleen from obstruction
children: spleen not yet fibrosis
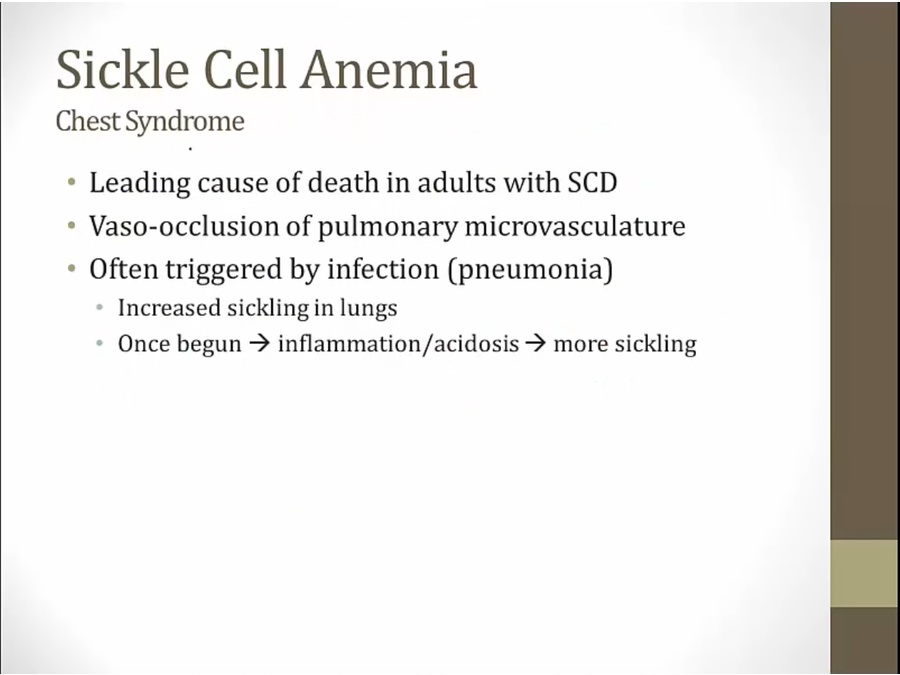
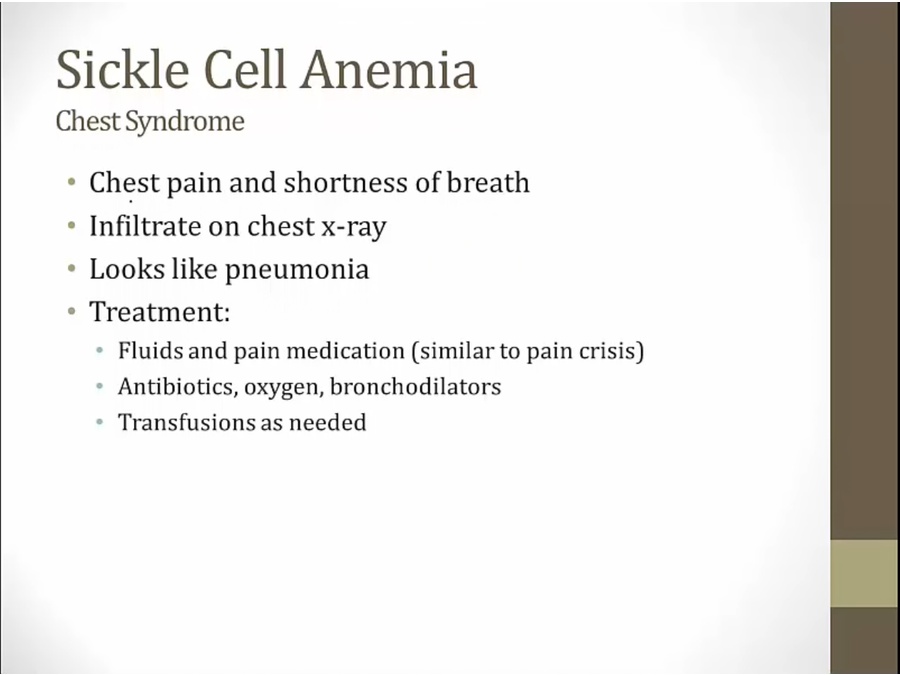
treated with antibiotics because looks just like pneumonia. Don't know if microbe present or not

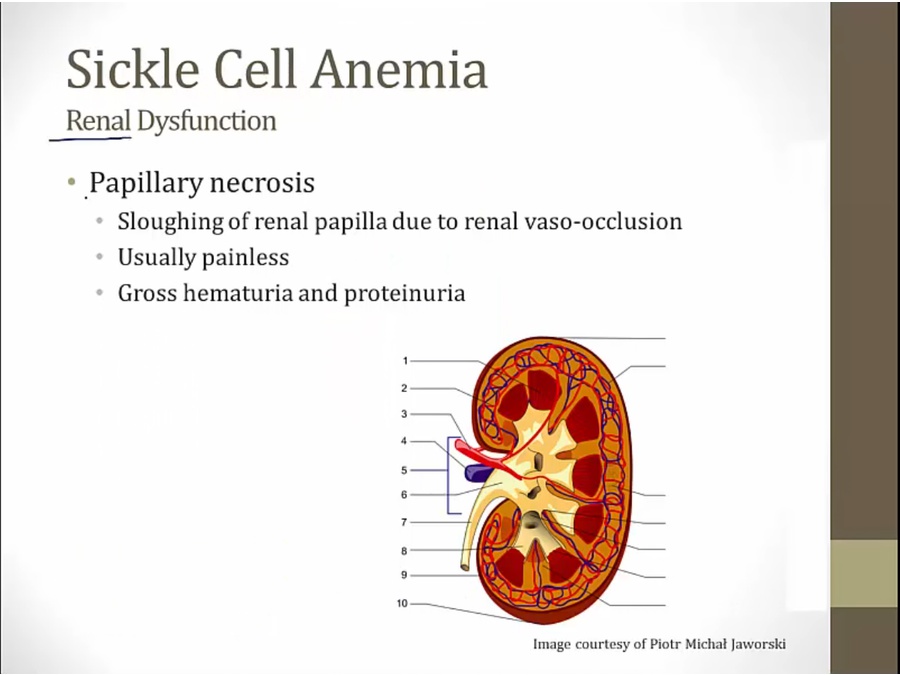
papillary necrosis
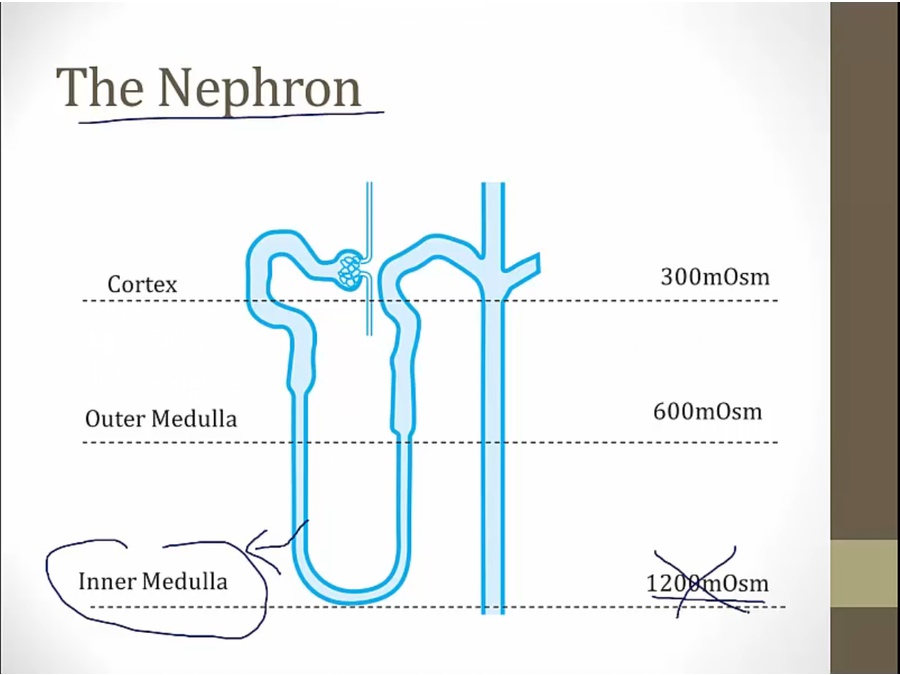
high concentration in medulla abolished
Treatment

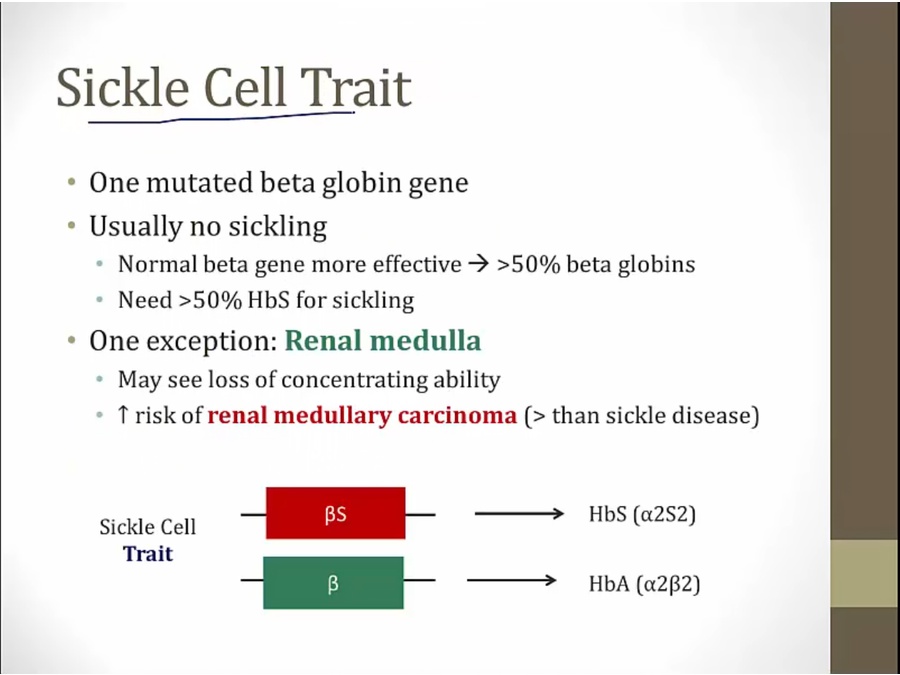
Trait
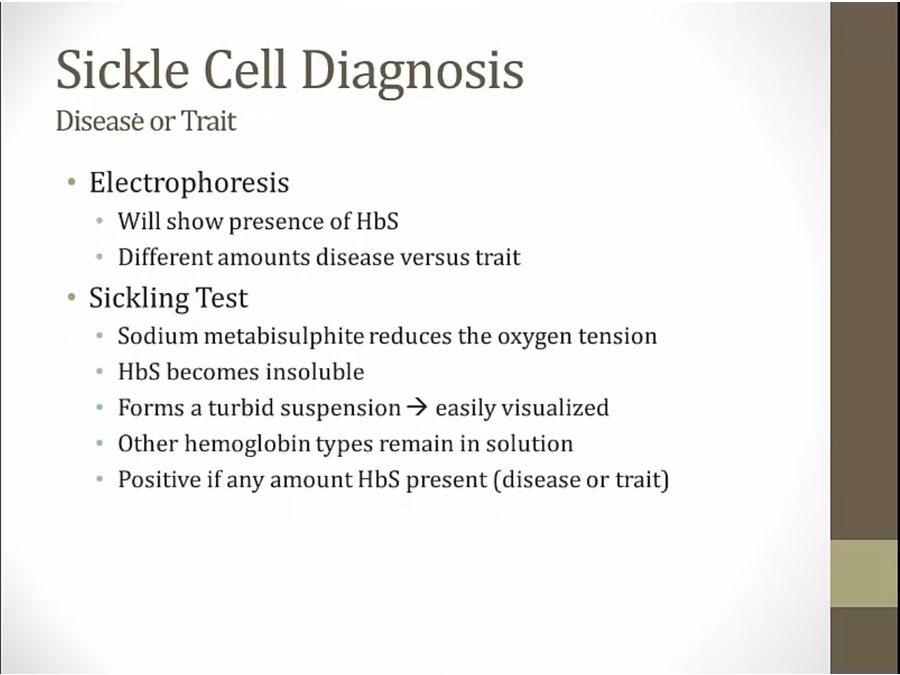
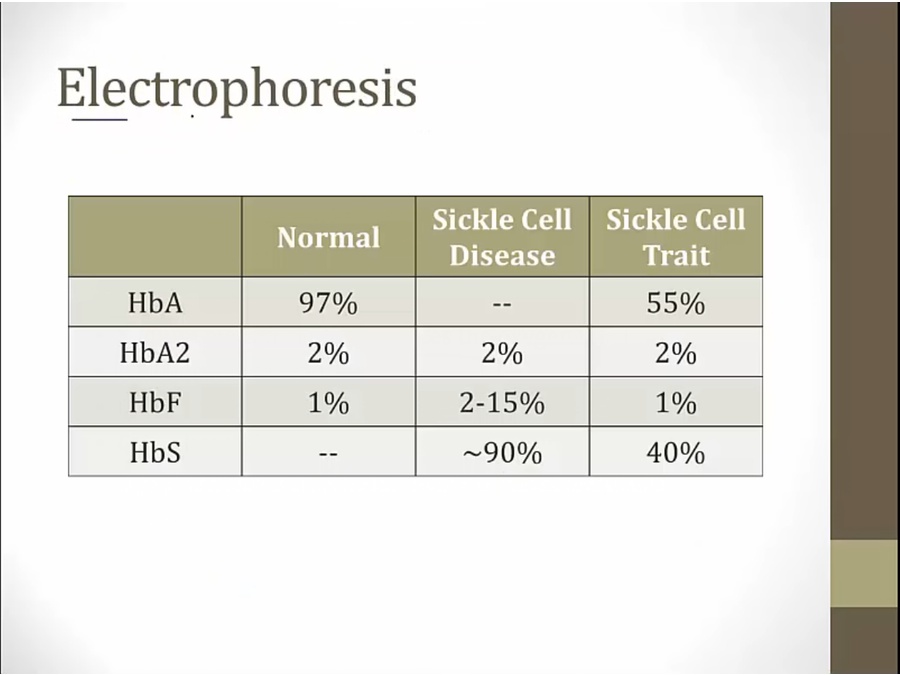
Diagnosis
Malaria

most severe form
just as likely to be infected, less likely to die
Thalassemia
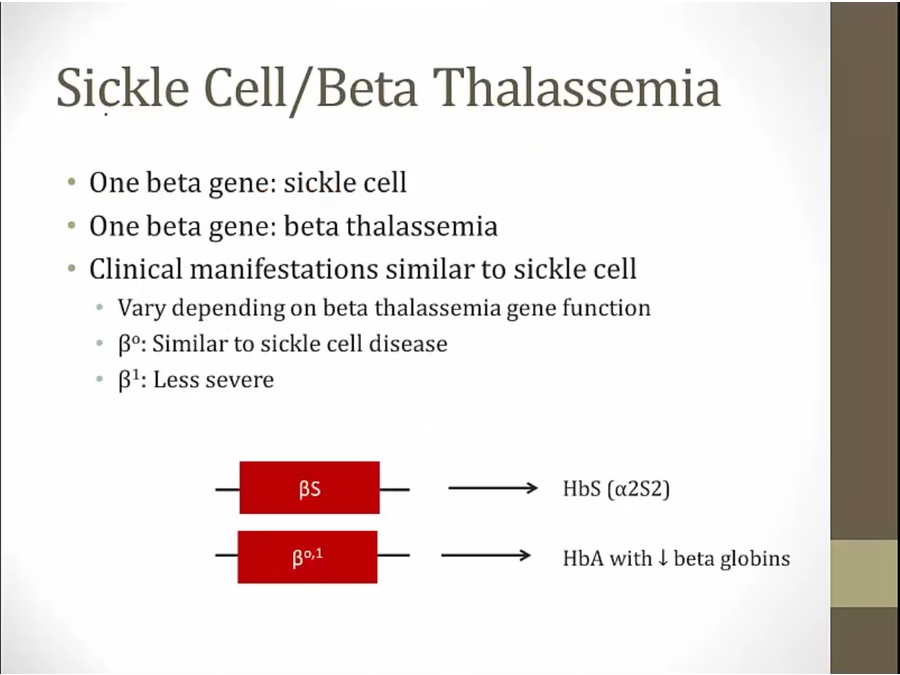
less beta production depending on how severe infection is
HbC
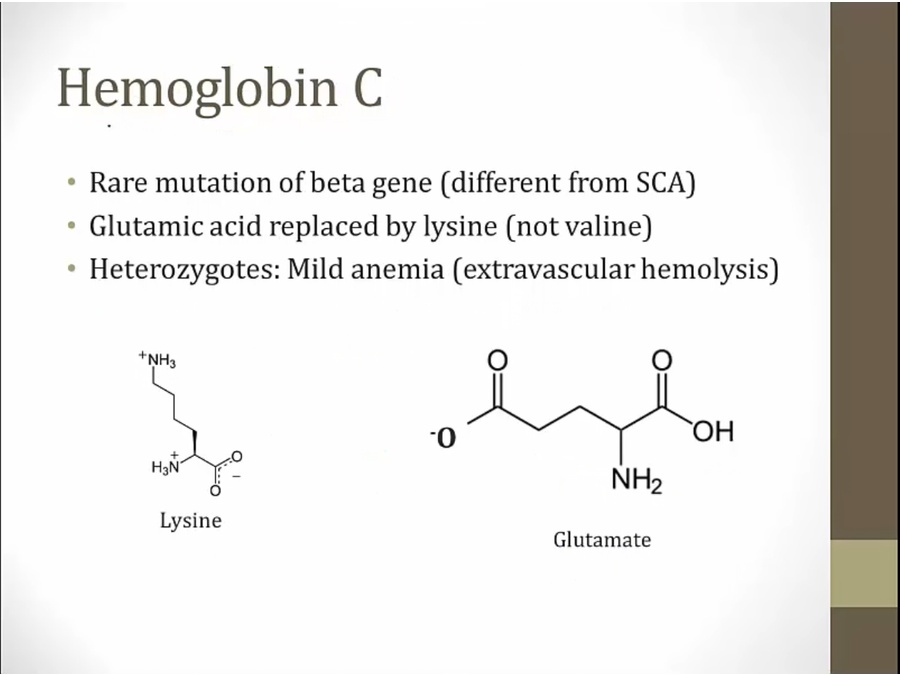
lysine more polar than valine: not as severe of a problem
lysing more positive than glutamate, less travel than HbS and Hb normal on electrophoresis
very rare to be homozygous
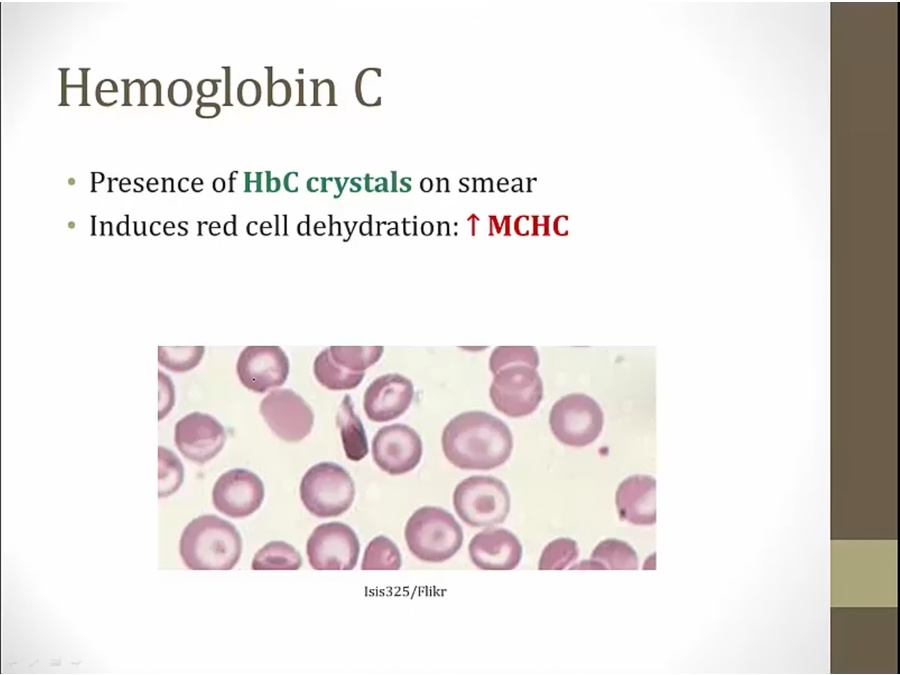
Hb SC

heterozygous: usually mild anemia without sickling
except HbS plus HbC
Last updated