04 Cardiac Cycle
Pressure Volume Curve
PV Curve
_..

_..
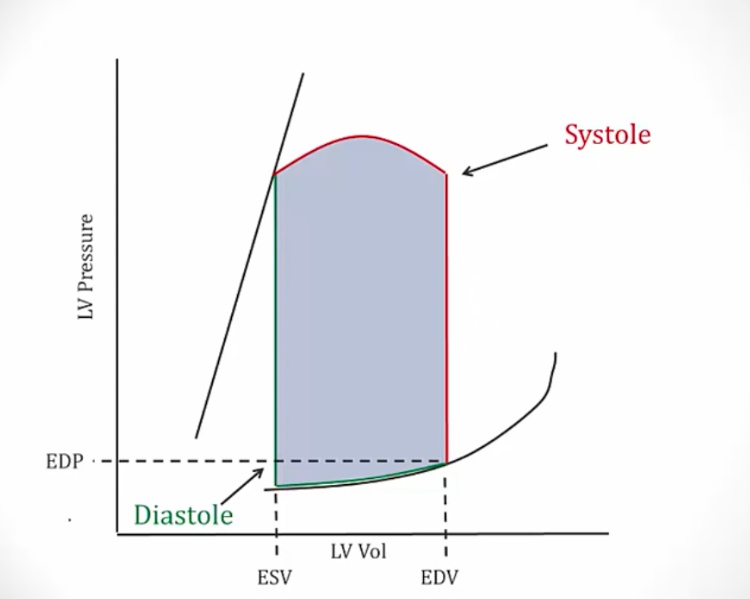
Isovolumetric contraction
_Point 3 to 5
.,At point 3, the cycle is at end diastole with the mitral valve closed; LV has been filled by the EDV. The ventricles begin contraction when the mitral valve closes and before the aortic valve opens (point 5), the period of highest O2 consumption

Systolic ejection
_Point 5 to 7.

.,At point 5, pressure in ventricle rises high enough to push open aortic valve and the total stroke volume is ejected into the aorta. The ventricle volume decreases, but the ventricular pressure continues to increase until near the very end of this phase. At point 7 , the pressure drop causes the aortic valve to close. The width of the pressure-volume loop is measured graphically to represent the stroke volume. The volume remaining in the LV at point 7 is end systolic volume.
Isovolumetric Relaxation
_Point 7 to 1.

.,After point 7, the ventricle begins to relax. Since all the valves are closed again, the ventricular volume is constant (isovolumetric) in this phase
Ventricular Filling
_Point 1 to 3.

.,At point 1, the mitral valve opens and the filling of the ventricles begins. Initially, a rapid filling period begins which is followed by a reduced filling
Valves
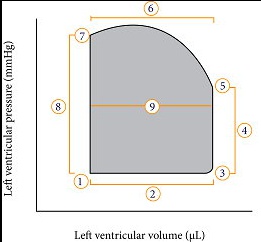
[](Valves on PV Curve <img src='d839YQG.jpg' alt='' /)..
3: mitral valve closes
5: aortic valve opens
7: aortic valve closes
1: mitral valve opens

Preload Increases
_Leads to an increase in ventricular end-diastolic volume and results from increased venous return. This, in turn, results in an increase in stroke volume and ejection fraction based on the Frank-Starling relationship. Since increased preload causes increased stroke volume, this results in an increased width of the pressure-volume loop..

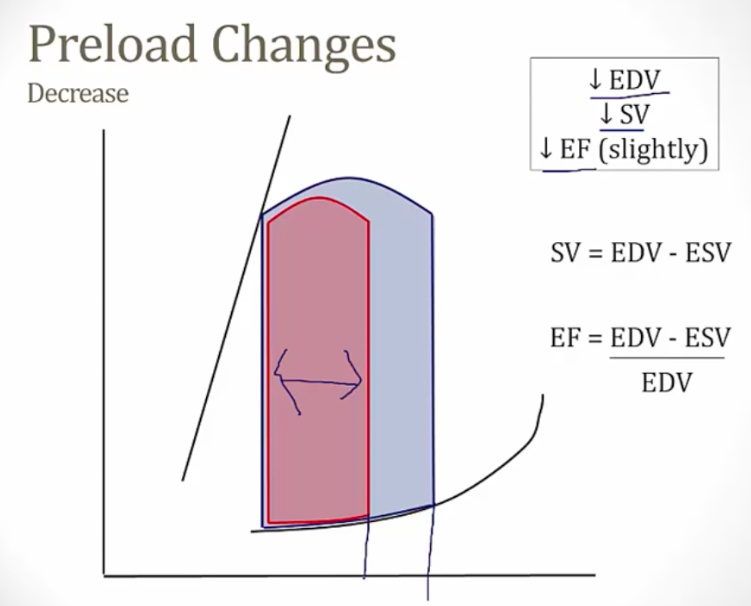
Preload Decreases
_ Decreased width..
Afterload Increases
Requires the ventricle to pump against a higher pressure = higher pressure overall
At end of systole, same pressure leaves more volume in the ventricles = increased ESV = decreasing stroke volume..

Contractility Increases
_The ventricle is able to develop greater tension than usual during systole, causing an increase in stroke volume..

Decreased Contractility
 ..
..
Compliance Changes
_Stiffer ventricle: higher pressure at lower volume. This results in a decrease in end-systolic volume..

When Value High
SV
EDV
ESV
Preload
up
up
same
Compliance
up
up
same
Contractility
up
same
down
Afterload
down
same
up
Jugular Venous Tracing
_Measures pressure in the:
Jugular vein
Right atrium, left atrium
Pulmonary vein..

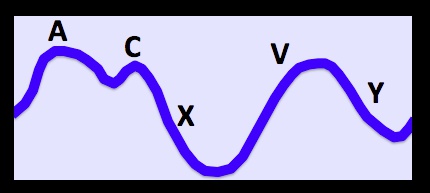
c: tricuspid valve/mitral valve close. S1 sound
v: atrium relax, blood to RV..
A Wave
_Increase in right atrial pressure during atrial contraction (i.e atrial systole).,

a wave = Atrial contraction
Absent a wave
_Characteristic of atrial fibrillation due to a lack of coordinated atrial contraction.,

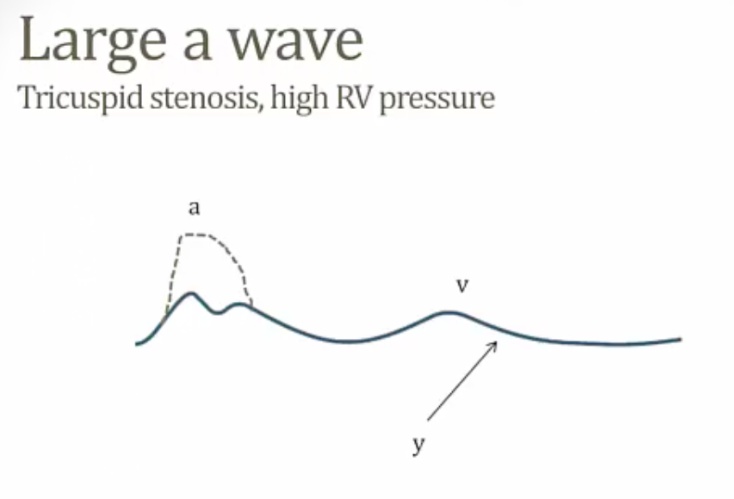
Large/giant a wave
_Indicate the right atrium is contracting against increased resistance to right ventricular filling. May be seen with:
Tricuspid stenosis
Right ventricular hypertrophy
Pulmonic stenosis
Pulmonary hypertension
Right atrial myxoma
RHF.,
Cannon a wave
_Are caused by the right atrium contracting against a closed tricuspid valve, which most commonly occurs during junctional arrhythmias
Vent Tach
3rd degree (complete) heart block
PAC/PVC.,

V wave
_Increase in right atrial pressure during late ventricular systole due to right atrial filling against a closed tricuspid valve. Usually corresponds with (or occurs just after) the T wave on EKG.,

v wave = Venous filling
Large, giant V wave
_aka CV fusion.,
_Can occur due to tricuspid or mitral regurgitation.,

C wave
_Increase in right atrial pressure during right ventricular isovolumic systole (contraction); due to bulging of the tricuspid valve into the right atrium.,

c wave = triCuspid valve
X Descent
_Is the decrease in jugular venous pressure due to movement of blood from the venous system to the right atrium. It is caused by atrial relaxation and the downward displacement of the closed tricuspid valve during right ventricular systole.,

X descent = atrial relaXation
Absent x descent
_Occurs in tricuspid regurgitation. Backflow of blood into the right atrium during systole prevents relaxation of right atrial pressure. (may see a positive wave).,
Prominent x descent
_Occurs in:
Constrictive pericarditis (also has a prominent “y” descent)
Cardiac tamponade (absent “y” descent).,

Prominent x descent due to high JVP
Y Descent
_Decrease in right atrial pressure following the peak of the “v” wave; due to tricuspid valve opening and right atrium emptYing.,

Absent y
_Cardiac tamponade (The right atrium is unable to relax following the "v" wave due to the presence of fluid around the heart).,
In cardiac tamponade, right ventricular filling is impaired throughout diastole, and therefore the y-descent (which represents the fall in right atrial pressure immediately after tricuspid valve opening as blood rushes into the right ventricle) is blunted (less steeply downsloping).
In Tamponade, active pressure is being exerted on the heart throughout the cardiac cycle. The pericardial pressure exceeds the diastolic pressure, leading to decreased filling pressure gradient. This results in a blunted or absent Y descent.
Slow y
_Tricuspid stenosis is a common cause on JVP.,
Rapid y
_Occurs in:
Constrictive pericarditis
Severe right heart failure
Tricuspid regurgitation (The large CV wave sets the stage for a large “y” descent.).,
In pericardial constriction, the earliest phase of diastolic right ventricular filling is not impaired and the y-descent is not blunted -- in fact, because it is descending from a higher-than-normal right atrial pressure, the y-descent may be accentuated, commonly called a "rapid y-descent".
In Constrictive Pericarditis, the pericardium is rigid and can't move inwards or outwards properly. During the cardiac cycle, the ventricle is constricted after its systole but pericardium has not moved with it. Therefore there is lots of room in between and there is minimal pressure at the start of diastole. This leads to rapid ventricular filling as no resistance is offered to the expanding ventricle. This results in a prominent Y descent.
Tricuspid valve opens
_From v wave to c wave.,

Tricuspid valve closes
_From c to v wave.,

Happens during S1
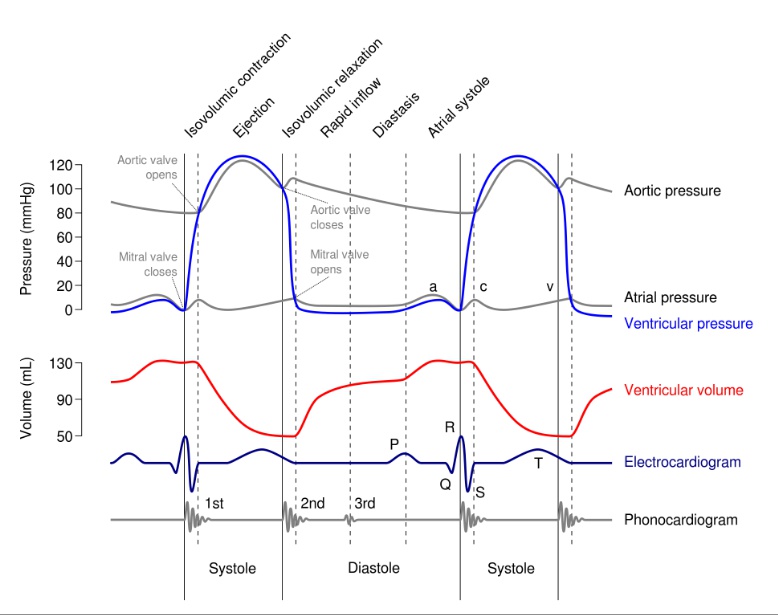
Cardiac Cycle
_The process of cardiac filling and ejection, and is often visualized with electrocardiography or jugular venous pressure readings..
_Cardiac cycle overview process:
Atrium contract, pump blood into ventricle
Mitral valve and tricuspid closes
Isovolumetric ventricular contraction
Aortic and pulmonic valve opens
Blood flows from ventricle to aorta and pulmonary artery
Aortic valve closes
isovolumetric relaxation
Mitral valve opens, back to #1..
Atrial Systole
_The activation of the atria, pumping atrial blood into the ventricles. Also known as atrial kick. Happens before mitral valve closes..

JVP shows a wave:

S1
_The sound of the atrioventricular (tricuspid and mitral) valves closing; it occurs at the beginning of isovolumetric ventricular contraction and beginning of QRS.,

EKG: S1 is QRS

JVP shows c wave. c wave = triCuspid valve closing and bulging into RA


Isovolumetric Ventricular Contraction
_The ventricles contract after mitral valve closes and before the aortic and pulmonic valves open.,

JVP: c wave from triCuspid valve bulging into RA

PV curve goes from 3 to 5

_Isovolumetric contraction..
Rapid Ventricular Ejection
_The period of ventricular contraction after the aortic and pulmonic valves have opened (pushed open by pressure) and before middle point of ejection cycle, when the ventricles are ejecting blood into the pulmonic and systemic circulations.,

Reduced Ventricular Ejection
Follows rapid ventricular ejection and results from decreased ventricular volume. This follows the length-tension relationship described by the Frank-Starling equation, where contraction strength is directly related to the load; therefore, a decreased volume would translate into a decreased load, which means less contraction strength and reduced ventricular ejection.
X descent = atrial relaXation
V wave = Venous filling

PV curve goes from 5 to 7

S2
_Is the sound of the aortic and pulmonic valves closing.,

V wave = Venous filling


_Normally, the aortic valve closes before the pulmonic valve. "Splitting” of the second heart sound can occur during inspiration when negative intrathoracic pressure increases venous return, ultimately delaying closure of the pulmonic valve..

Isovolumetric Ventricular Relaxation
_The period between the aortic valve closing and the mitral valve opening.,

V wave = Venous filling. Right after T wave on EKG

PV curve goes from 7 to 1

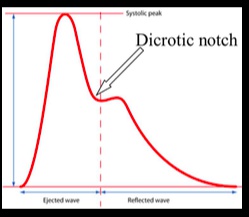
Dicrotic Wave
_The trough is where the aortic valve closed, and the following "bump" in pressure results from aortic pressure recoil against a closed aortic valve..
Rapid Ventricular Filling
_Happens when the atrial pressure becomes slightly greater than the ventricular pressure. It starts when the mitral and tricuspid valves open.,

y = atrium emptYing

PV curve goes from 1 to 3

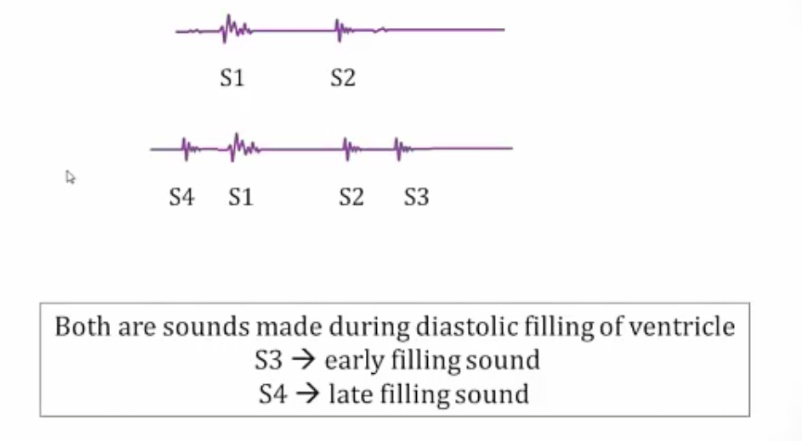
S3
_Results from blood sloshing against the ventricular walls during the middle third of diastole.,

_Physiologic S3, aka suckers:
Demographics: young patients <30, pregnant women
Vigorous LV relaxation lowers pressure rapidly, resulting in rapid LV filling
Normal LA pressure..
_Pathologic S3, aka pushers:
High LA pressure, leading to rapid early filling of LV
Usually association with high LVEDP (dilated ventricle)..
_Louder when patient lies on left side and with exhalation due to heart closer to chest wall.,

_Sounds like Ken-tu-cky.,
S4
_Is a low frequency diastolic sound that occurs during the late diastolic filling phase (the atrial kick). It results from an atrial kick filling a ventricle with decreased compliance, often seen in left ventricular hypertrophy. (Blood hitting stiff wall).,

_Usually caused by stiff left ventricle from:
Long standing HTN
Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy
Diastolic HF.,

_Cannot occur in Afib because there is no atrial kick.,
_It is sometimes heard in the elderly due to a stiff ventricle.,
_Sounds like Ten-nes-see.,
Last updated