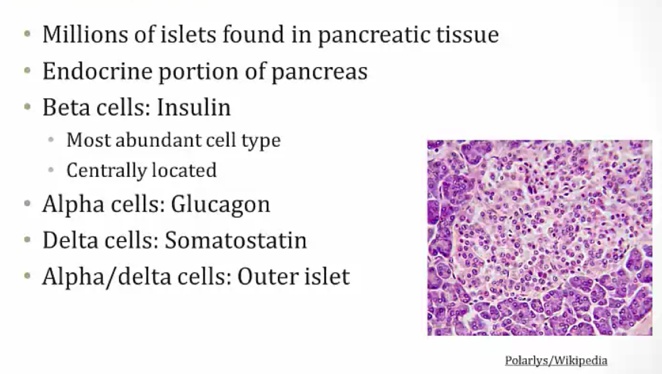
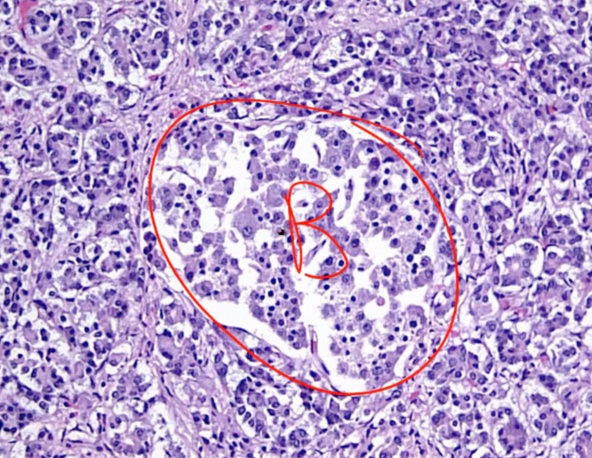
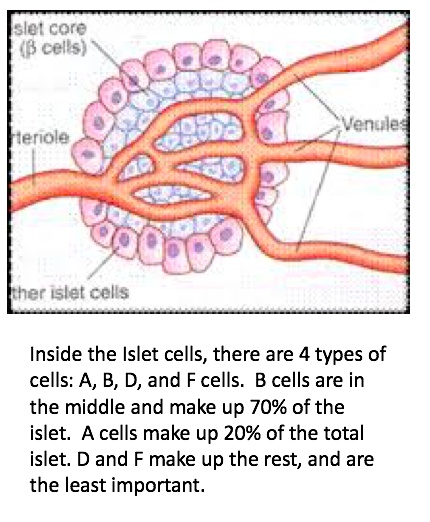
10 Endocrine Pancreas
Islets of Langerhan
_..
more in the tail than head of pancreas
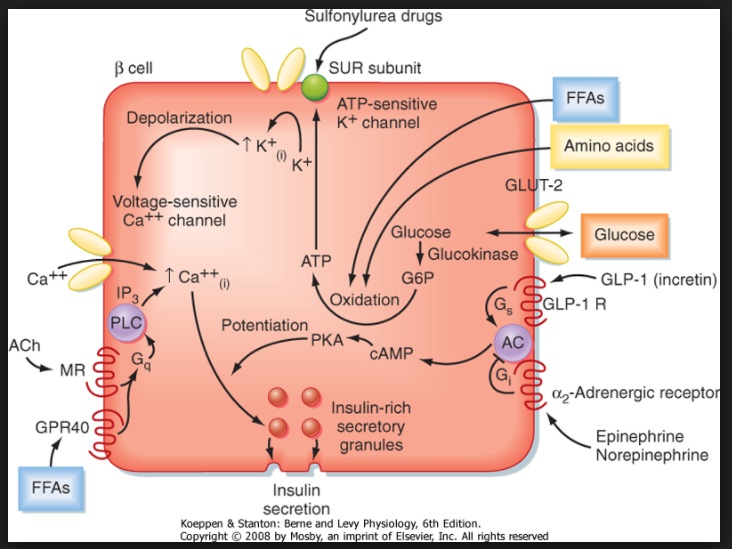
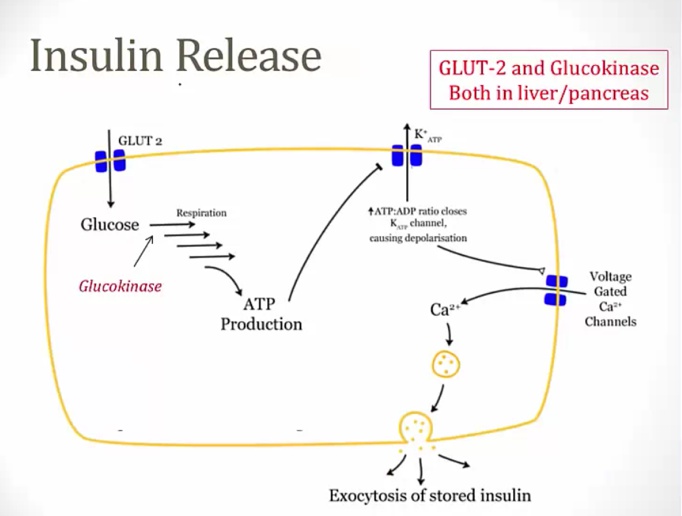
Glucokinase
_Enzyme stimulated by insulin. Insulin promotes transcription.,
_.,

_..

Glut-2 Transporter
_.,

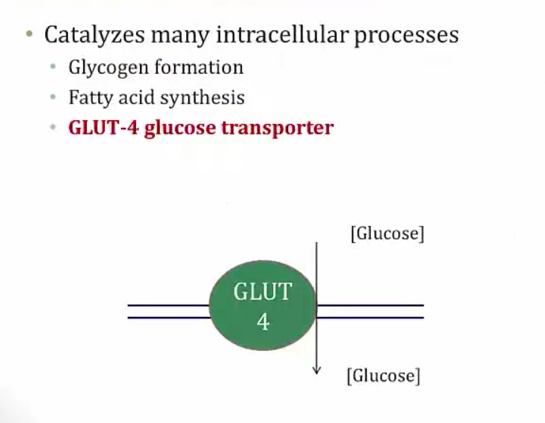
Glut-4 Transporter
_..
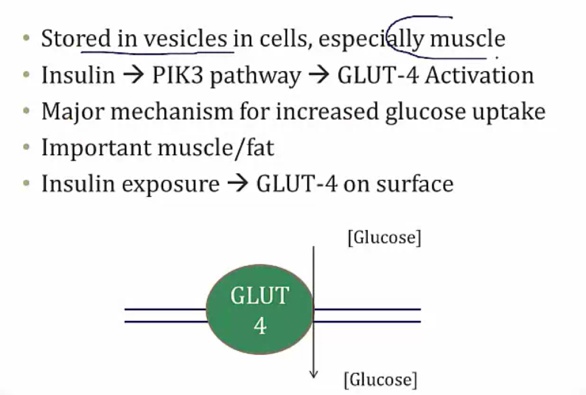
Insulin dependent organs
_..

Insulin independent organs
_..

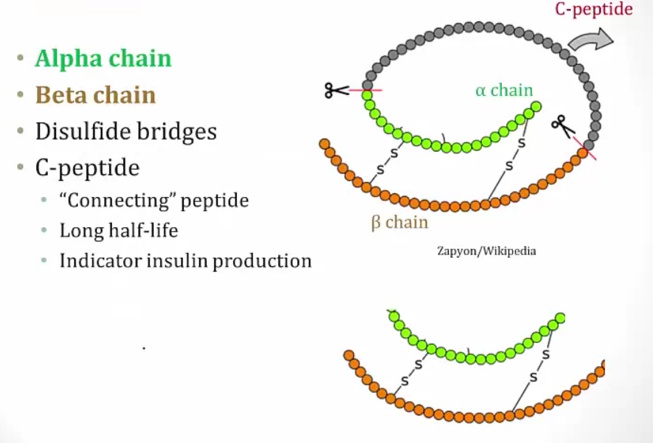
Insulin
Structures
made of amino acids..

Insulin and autonomics
_amino acids, glucose, GLP-1, Ach stimulate release..
_E, NE, somatostatin, Growth hormone, glucocorticoids..
_Autonomic control plays a minor role in insulin control, except during sympathetic activation..
Islets are richly innervated by both adrenergic and cholinergic nerves.
In general, any condition that activates the sympathetic branch of the autonomic nervous system (such as hypoxia, hypoglycemia, exercise, hypothermia, surgery, or severe burns) suppresses the secretion of insulin by stimulation of α2 (Gi) adrenergic receptors.

A2 adrenergic
_Stimulation of α2 adrenergic receptors (Gi) inhibits insulin secretion..
a2 adrenergic receptor antagonists increase basal concentrations of insulin in plasma
B2
_B2(Gs) adrenergic receptor agonists increase insulin release..
However, liver gluconeogenesis is also increased and is the dominant effect. The end result is hyperglycemia.
β2 adrenergic receptor antagonists decrease insulin in plasma. However, there is an overall decreased glucose level in plasma, as b2 receptors on hepatocytes are also blocked from gluconeogenesis.

Vagal
_β2 (Gs) adrenergic receptor agonists and vagal nerve stimulation enhance release..

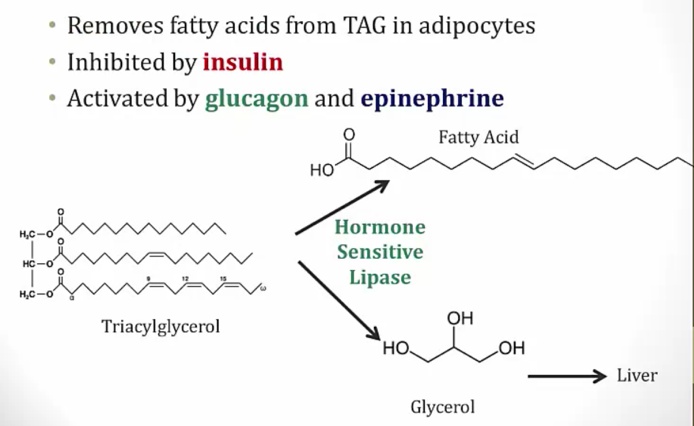
Liver, adipocytes, and autonomics
_The effects on blood glucose levels are also determined by glycogenolysis in hepatocytes and gluconeogenesis in hepatocytes assisted by lipolysis in adipocytes..
Glycogenolysis and gluconeogenesis in hepatocytes is stimulated by beta-2 agonism via activation of glycogen phosphorylase kinase by epinephrine and glucagon (Gs).
Lipolysis is stimulated by activation of hormone-sensitive lipase (HSL) in adipocyte cytoplasm by epinephrine via the beta-3 agonism (Gs) and glucagon (Gs).
_..

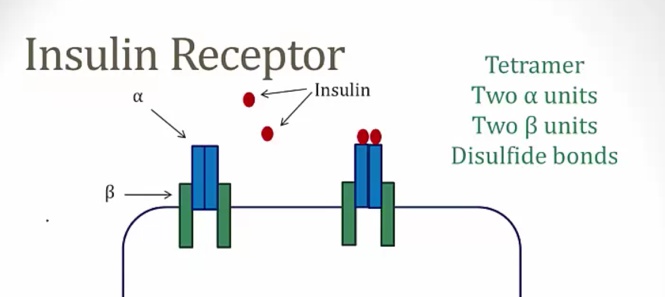
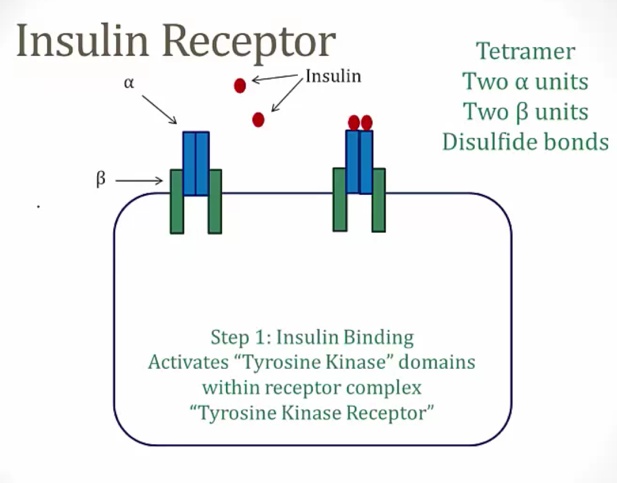
Insulin Receptor
_..
_..
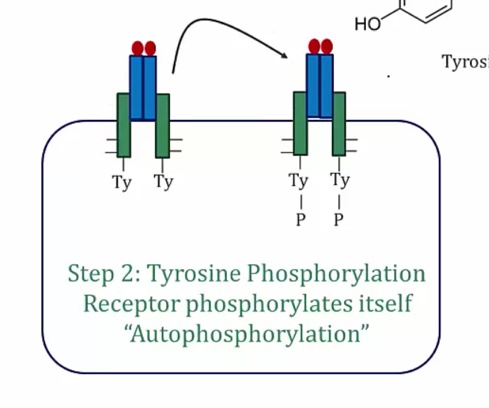
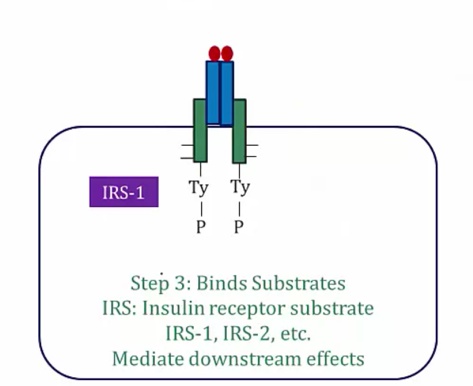
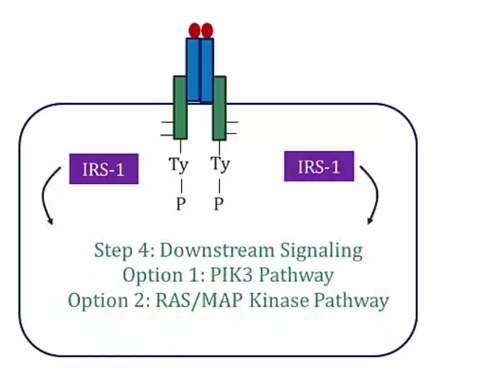
PIK3 pathway
PIP2 phosphorylated to make PIP3..

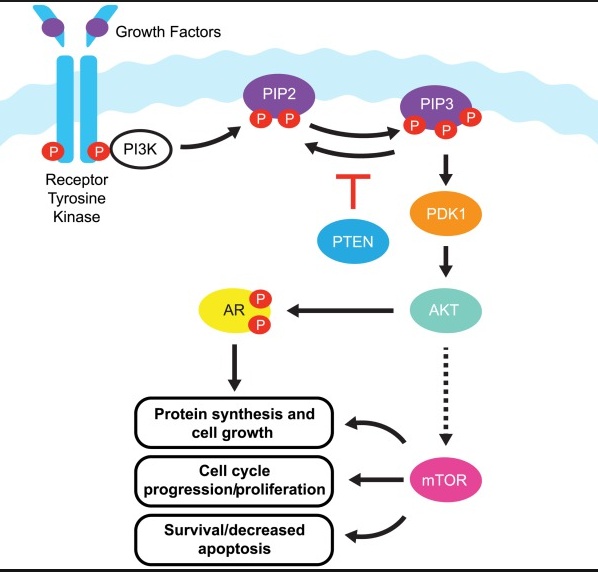
_..
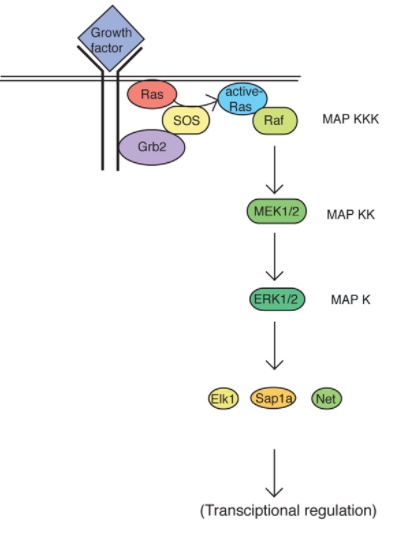
RAS/MAPK pathway
_..

Insulin effects
_..
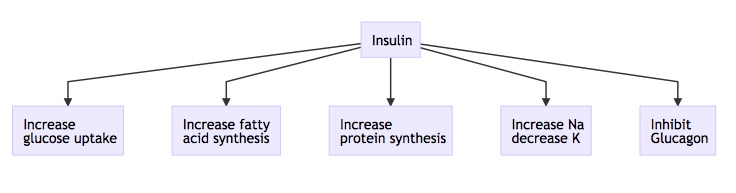
also tells bones and keratinocytes to grow (tall children)
_..

_..
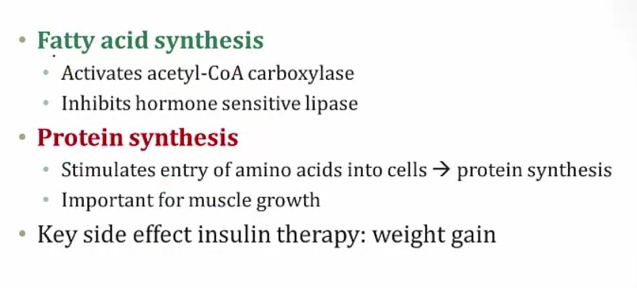
_..
_..

Glucagon
_..

_..
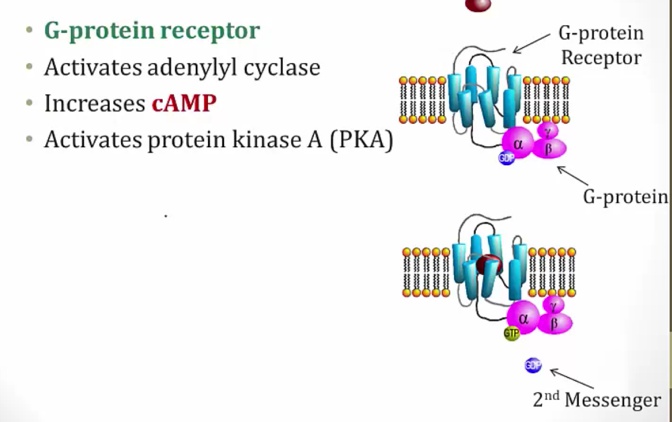

Glucagon Effects
_..
Muscle triggers by Ca and exercise, not glucagon
Gluconeogenesis mostly in liver
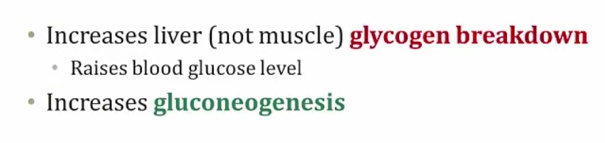
Insulin: aa uptake in muscle

_Glucagon increases urea production because amino acids are used for gluconeogenesis (stimulated by glucagon), and the resulting amino groups are incorporated into urea..
_Uses:
Hypoglycemia..
IV dextrose is best. If not, then IM

Beta blocker overdose
Activates glucagon receptor not beta receptor. Same downstream effect


high protein: insulin high to make protein in muscle. Glucagon high to make glucose from aa and prevent lipid synthesis
result: less fat after protein meal..
Pancreatic tumors
_Are of neuroendocrine origin..
_Histology shows rosettes:..
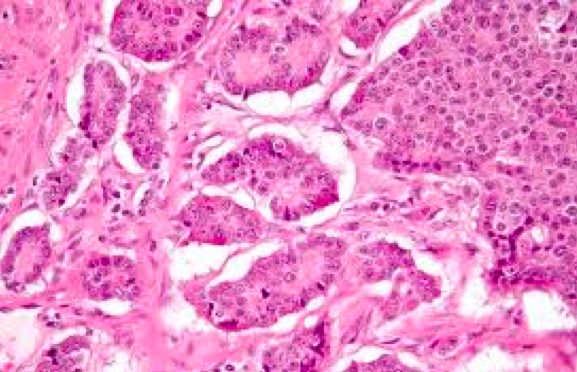
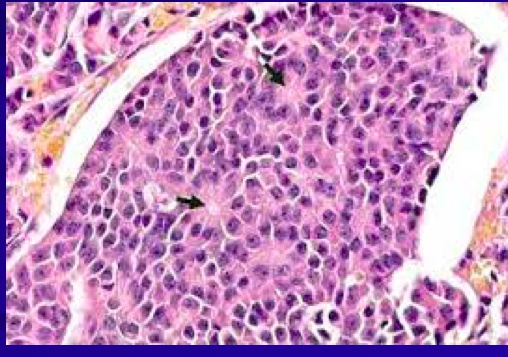
Insulinoma
_..


Whipple's triad: fasting hypoglycemia, neuroglycopenic problem, problem relieved by glucose
.,
_..
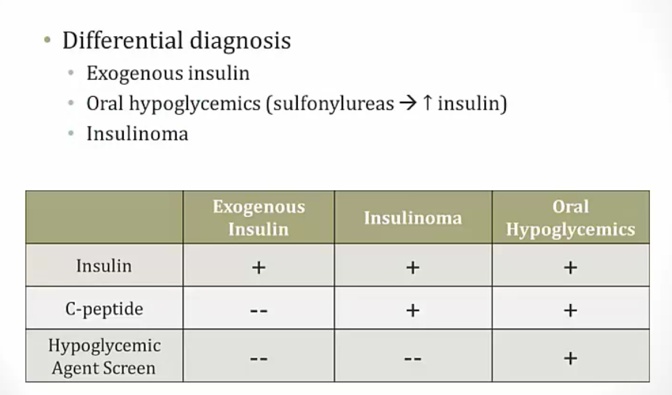
elevated c-peptide/pro-insulin: prove from pancreas
exogenous insulin: people may use for gains

_..
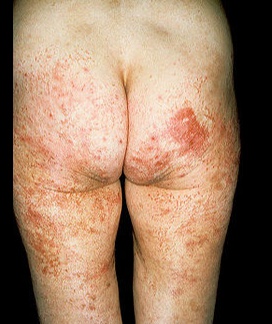
Glucagonoma
_..

_.,
Looks like diabetes



Glucagonomas are glucagon-secreting neuroendocrine tumors of alpha cells in the pancreas.
Other symptoms:
Deep vein thrombosis
Depression
Diarrhea
Anemia of chronic Disease (normocytic, normochromic anemia)
_..

Somatostatinoma

.,
VIPoma
Pancreatic neuroendocrine (islet cell) tumors that secrete vasoactive intestinal polypeptide (VIP). The increased pancreatic secretions and increased GI relaxation result in severe diarrhea, which can in turn cause hypokalemia and achlorhydria.

VIPoma is also termed “WDHA syndrome” for
Watery
Diarrhea
Hypokalemia
Achlorhydria..
Gastrinoma
_Aka zollinger ellison syndrome.,
_Excess production of HCl will cause recalcitrant gastric ulcers, duodenal ulcers, and chronic watery diarrhea., Other symptoms of ZES include epigastric pain, steatorrhea, and vomiting. Gastrin activates stomach parietal cells (which secrete HCl) and enterochromaffin-like cells (which secrete histamine).
Secretin Stimulation test
_Used to diagnosis gastrinoma. Indicates that gastrin levels remain elevated after the administration of secretin (normally inhibits gastrin release).,
Last updated