21 Antiarrhythmics
Overview
_..

restrict use to dangerous arrythmias

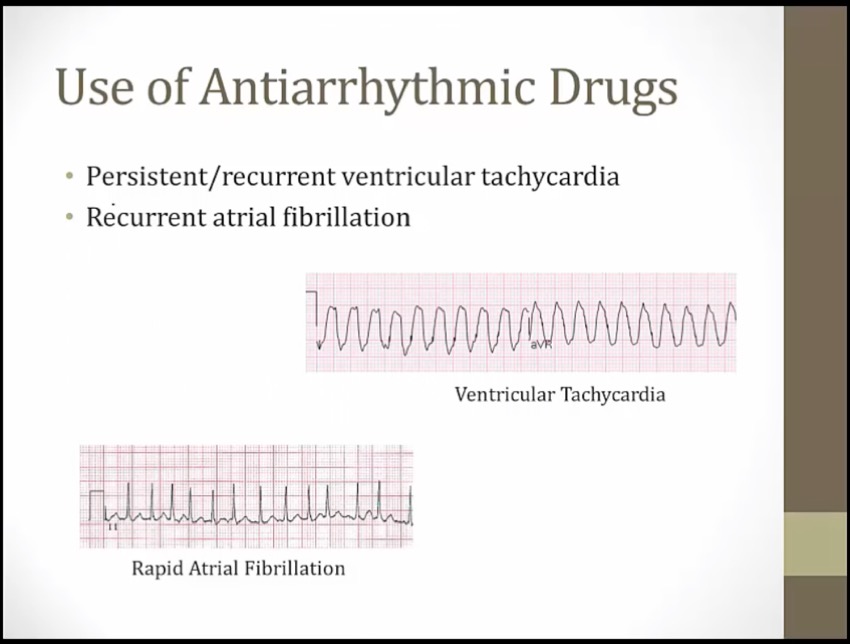
life threatening VTACH
Mechanisms
_..
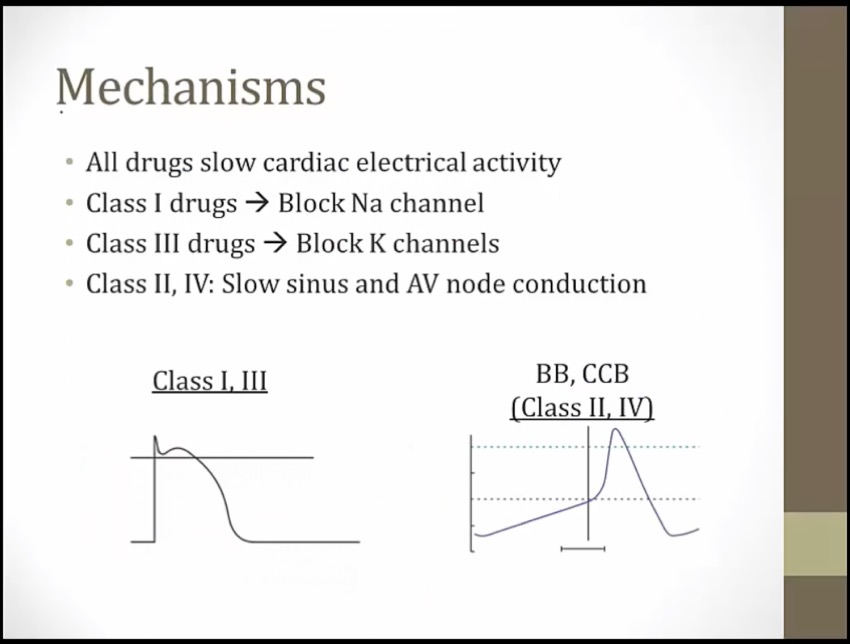
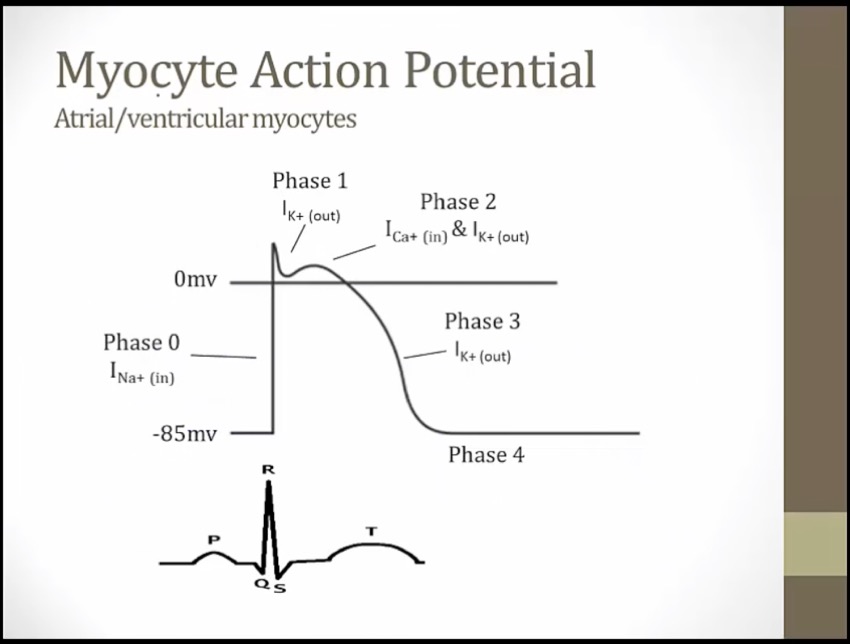
phase = single myocyte, EKG = hundreds of myocytes
phase 0: depolarization of 1 myocyte; QRS depolarization of hundreds of myocytes
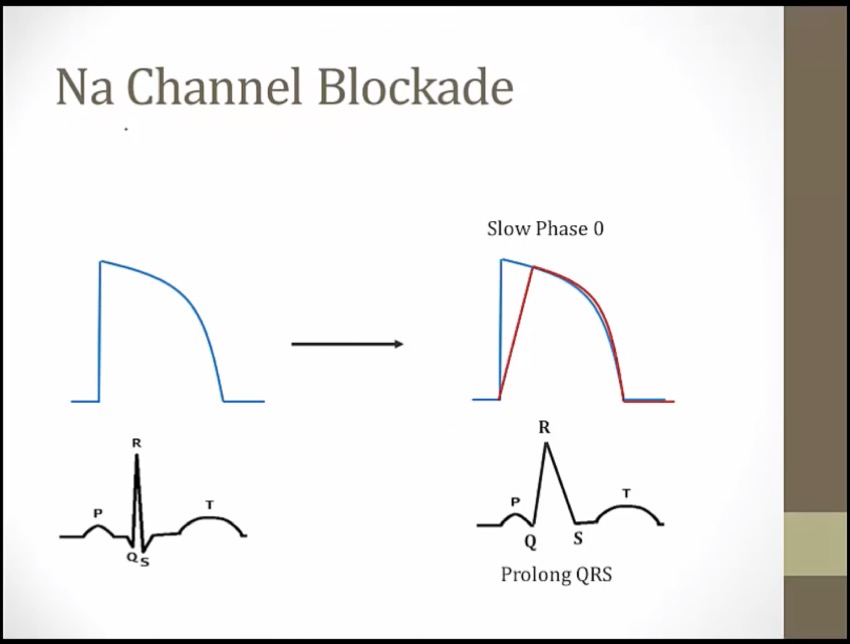
if Na channel blocked, phase 0 delayed, QRS will be widened
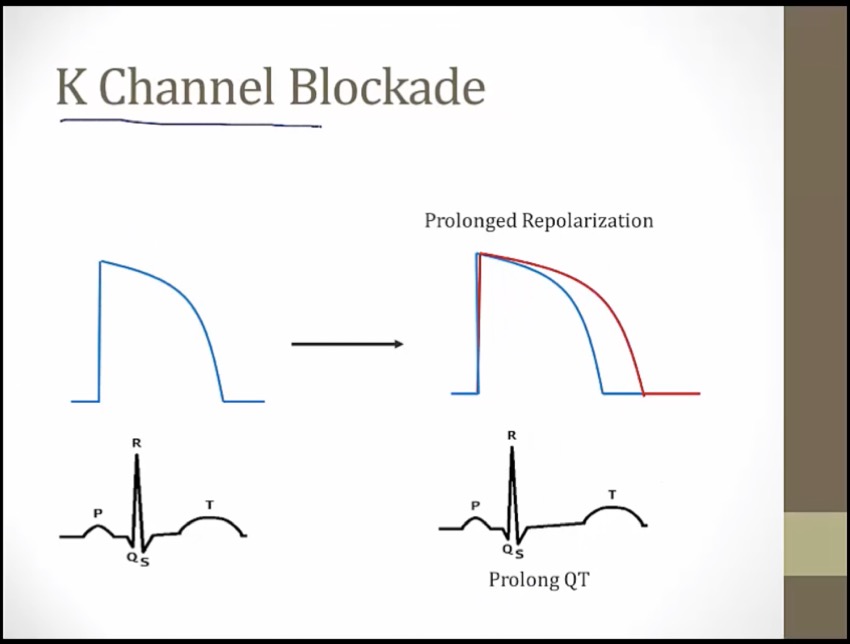
phase 0-3, depolarization and repolarization = QT
drugs block K channel length phase 1-3, QT
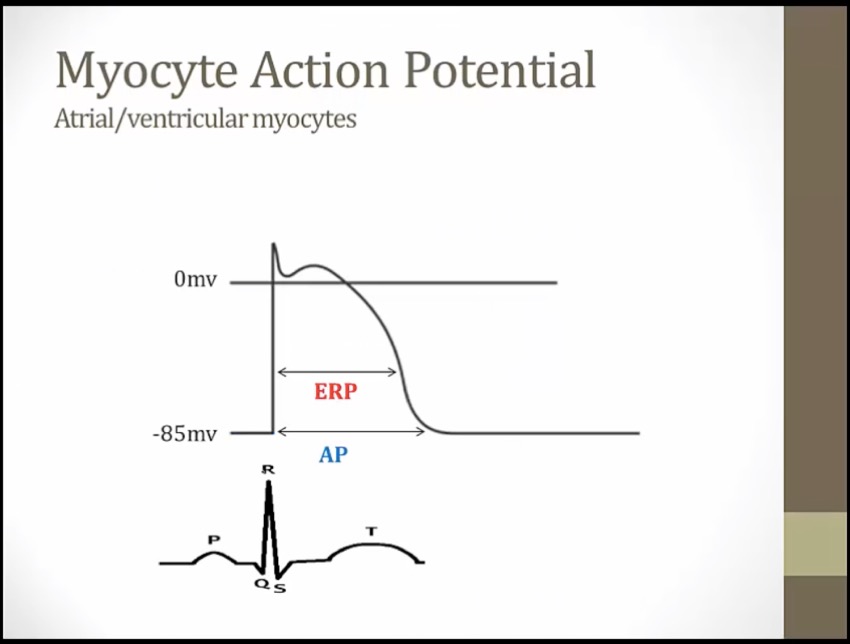
AP duration: time for AP to begin and end
ERP: effective refractory, cannot go another AP
cell does not have to down to -85 to depolarize again, midway through phase 3
Class I
_..

Na blocked, depolarization longer, longer AP and ERP
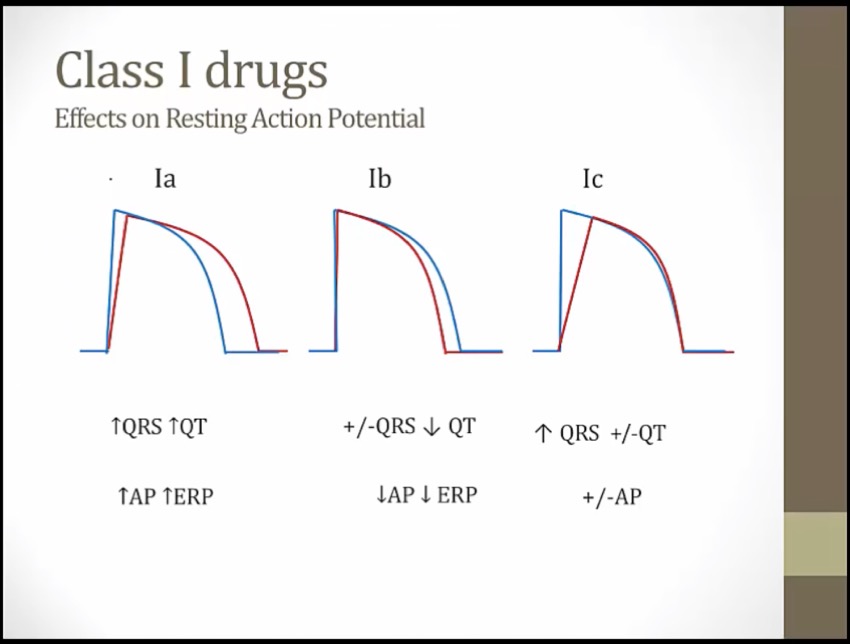
1a: Na blockade stretch QRS. K blockade stretch QT
1b: shrink AP duration and shrink of QT
Ic: pure Na channel blockade. Not significant QT changes or AP (start and stop at same time)

Soloist: class I antiarrhythmics
Soloist holding peanut butter jar: class I antiarrhythmics block sodium channels (phase 0)
Soloist tipping mic stand: class I antiarrhythmics decrease the slope of the phase 0 upstroke (slows conduction of the cardiac AP)
Illuminated atria, ventricles, and His-Purkinje system: class I antiarrhythmics affect the Na+ dependent cardiac action potential (no action at the SA and AV nodes, upstroke by Ca channels)
Wide QRS shaped crack: class I antiarrhythmics widen the QRS complex on the ECG (decreased AP conduction velocity) (faster cells bind more and slow down more) (QRS widen as HR increases)
1A
_..
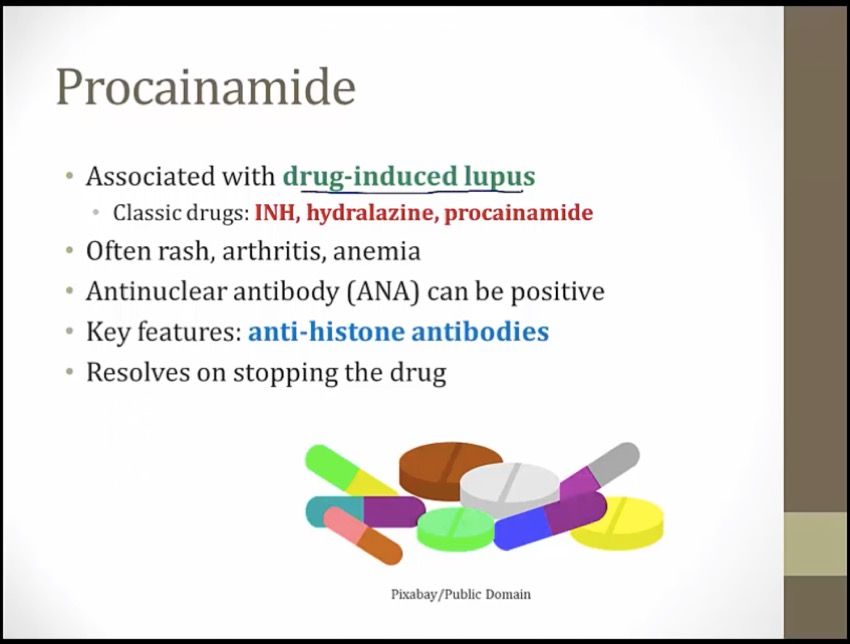
symptoms similar to traidtional lupus with ANA positive
unique with antihistone antibodies

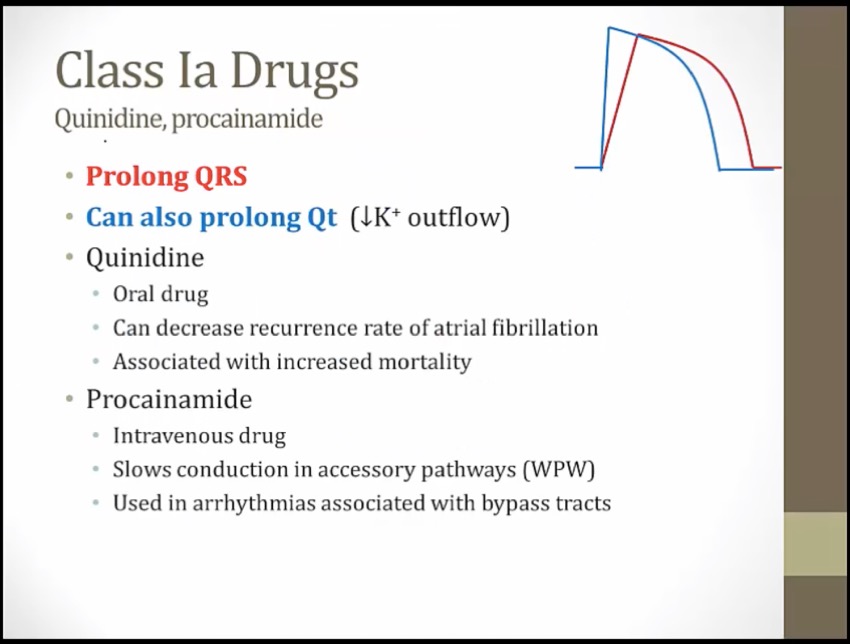
Class IA antiarrhythmics: quinidine, procainamide, disopyramide
Dining prom queen: quinidine (class IA antiarrhythmic)
Prom king: procainamide (class IA antiarrhythmic)
"Disappears!": disopyramide (class IA antiarrhythmic)
Lightly held peanut butter jar: class IA antiarrhythmics have an intermediate binding affinity for the Na+ channel (intermediate use-dependence, moderate slowing of the phase 0 upstroke)
Pushing away the curtain: class IA antiarrhythmics also block K+ channels, prolonging phase 2 and 3 of the cardiac action potential -> prolonged refractory period
Illuminated top and bottom of heart: class IA antiarrhythmics treat supraventricular and ventricular arrhythmias
White wolf pack: class IA antiarrhythmics treat Wolff-Parkinson-White (WPW) syndrome (a type of SVT) (extra pathway stopped)
Tin cans: quinidine toxicity can cause cinchonism (a syndrome of tinnitus, headache,dizziness)
Broken plates: quinidine can cause thrombocytopenia
Prom king's lupus wolf: procainamide can cause a lupus-like syndrome
Darts deflating failing heart balloon: disopyramide can exacerbate heart failure (negative inotropy)
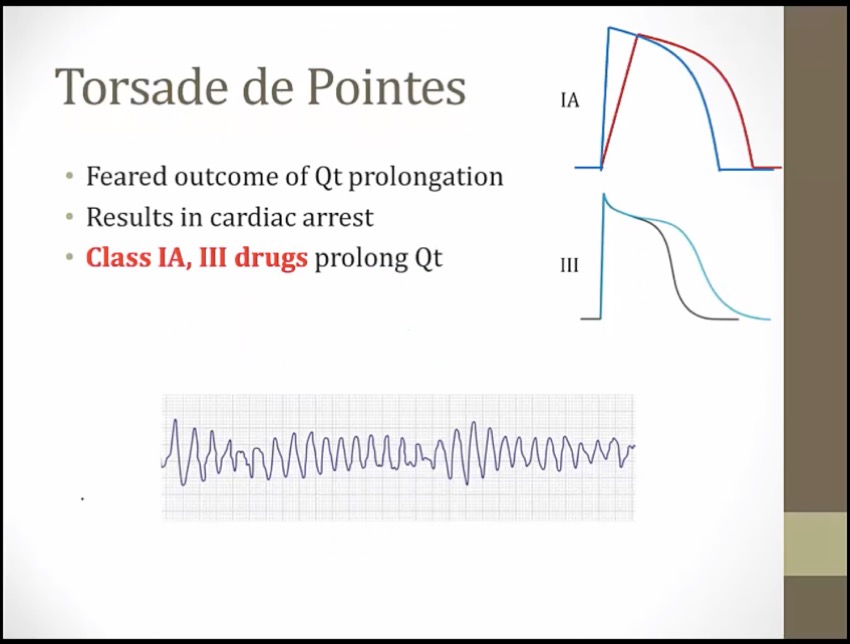
Twisted torsades streamer: class IA antiarrhythmics can cause Q-T interval prolongation (precipitates torsades) (K channel prolongation)
1B
_..

most effects at fast HR
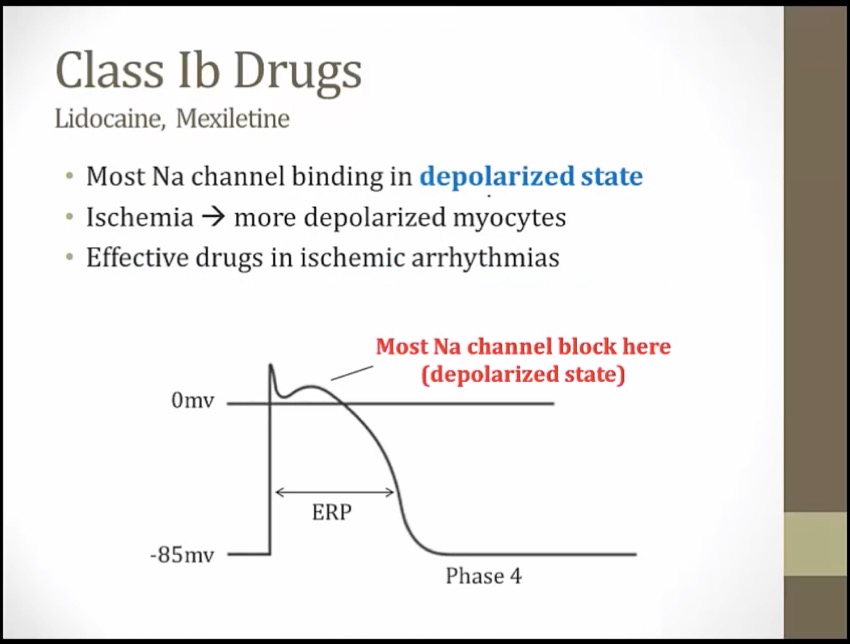
ischemia: myocytes can't maintain negative membrane potential, depolarized

unbinds when myocytes exit depolarized states
less effect at slow heart rates: drug quickly unbinds with heart beat, little left at next heart beat
more effective at faster HR: less time for drug to unbind
ischemic VTACH: ischemic tissues at depolarized state, fast HR
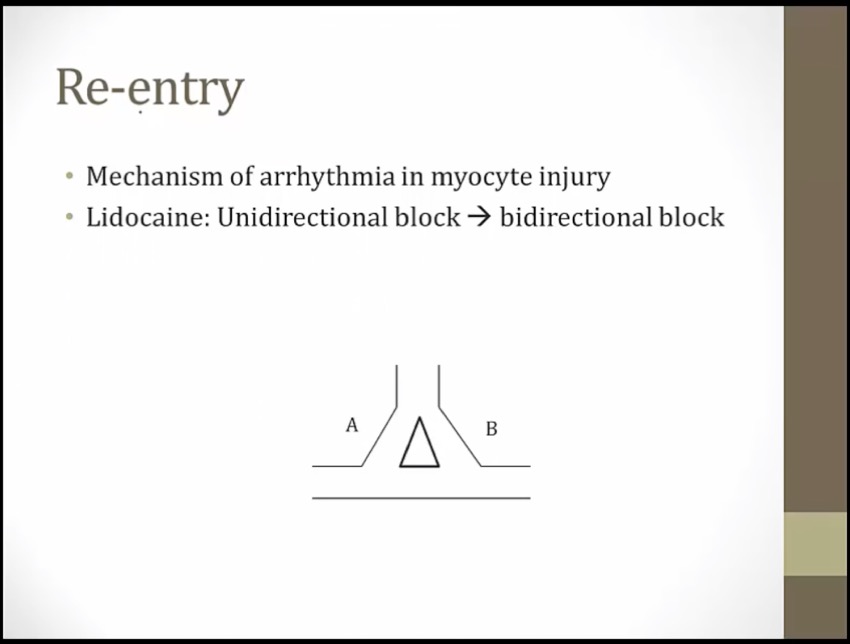
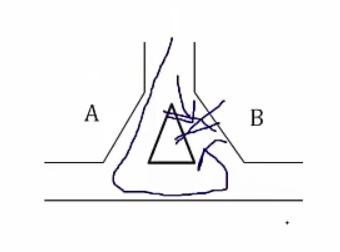
convert unidirectional block on one side to bidirectional block so that electrical current can't go in either direction

mexiletine: oral, can't be used locally
CNS effect from Na blockade in CNS
block too much Na: heart stop conducting normally

Class IB antiarrhythmics: lidocaine, mexiletine, phenytoin
"LIED": lidocaine (class IB antiarrhythmic)
Friendly Towing: phenytoin (an anti-epileptic) shows some class IB antiarrhythmic properties
Mexican flag: mexiletine (class IB antiarrhythmic)
Dropped peanut butter jar: class IB antiarrhythmics have an low binding affinity for the Na+ channel (low use-dependence, modest slowing of the phase 0 upstroke)
Pulling in the curtain: class IB antiarrhythmics shorten phase 2 and 3 of the cardiac action potential -> shortened refractory period
Illuminated, cracked bottom of heart: class IB antiarrhythmics treat ventricular arrhythmias (especially in ischemic tissue) (rapid binding and unbinding selects for tissues with Na in open/inactive states. Ventricles/HIS has longer AP compared to atrium)
"DEAD": class IB antiarrhythmics treat ischemia induced ventricular arrhythmias (dead tissues have reduced AP with delayed Na channel transition from inactivated to resting)
Brain trucker hat: class IB antiarrhythmics cause neurological side effects (e.g.paresthesias, tremor, convulsions)
1C
_..

can go into cardiac arrest if QRS too long: limited use

more mortality with pts with cardiomyopathies

Class IC antiarrhythmics: propafenone, flecainide
Flakes: flecainide (class IC antiarrhythmic)
purple phone: propafenone (class IC antiarrhythmic)
Tightly held peanut butter jar: class IC antiarrhythmics have an strong binding affinity for the Na+ channel (strong use-dependence, drastic slowing of the phase 0 upstroke)
Untouched potassium curtain: class IC antiarrhythmics do not affect the cardiac action potential duration
Illuminated top and bottom of heart: class IC antiarrhythmics treat supraventricular and ventricular arrhythmias
Irregularly irregular signal: class IC antiarrhythmics treat atrial fibrillation (and flutter)
Converting the signal: class IC antiarrhythmics can restore and maintain normal sinus rhythm in atrial fibrillation and flutter
"Healthy hearts only!": class IC antiarrhythmics are contraindicated in patients with history of structural or ischemic heart disease (proarrhythmic effects) (can cause delayed in conduction speed out of proportion to prolongation of refractory period)
Use Dependence
_..
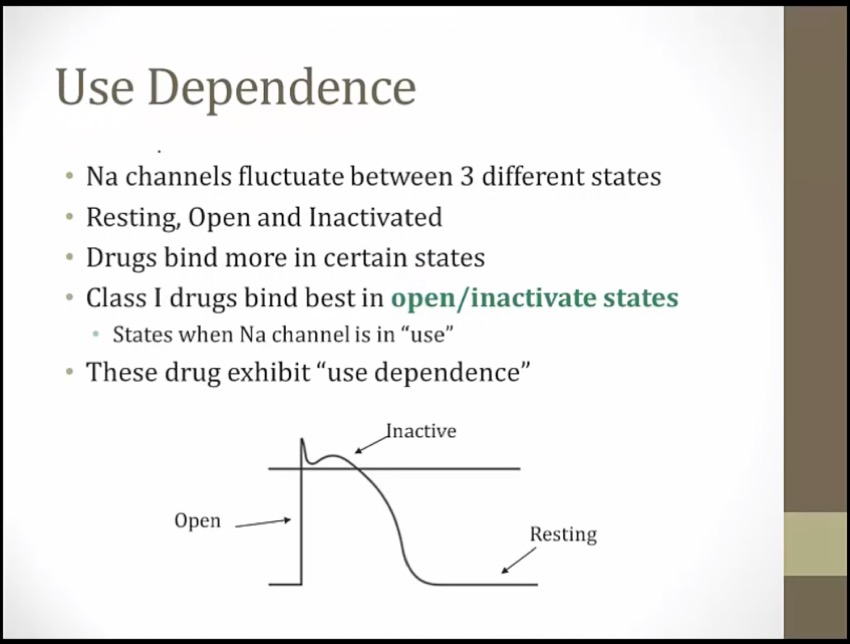
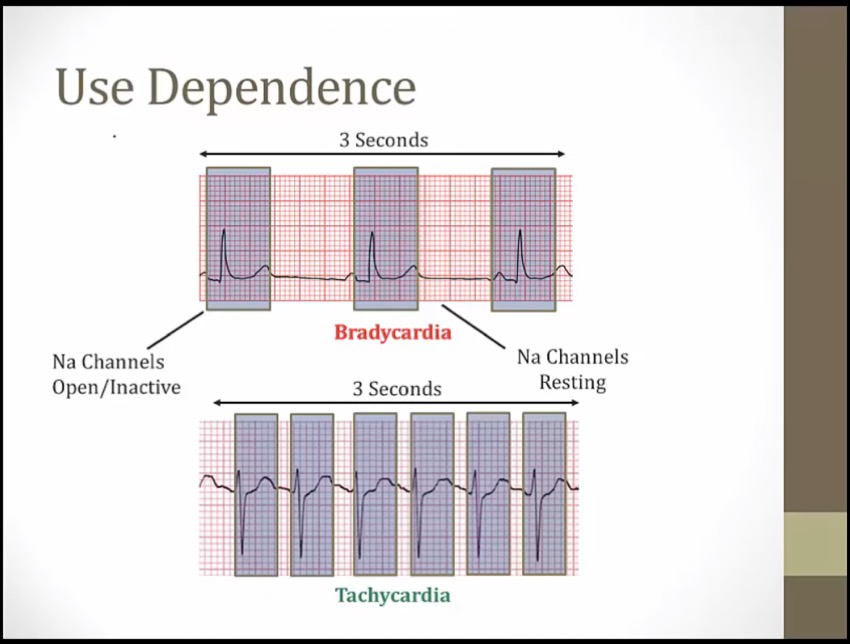
more effects at faster HR
tachycardia: Na spend most of time in activated state
stress test: get HR very high to see if QRS prolongs

Heart watch tipping mic stand: "use dependance"- class I antiarrhythmics have a greater effect on rapidly depolarizing tissues (increased heart rate causes slower phase 0 upstroke) (great for tachycardias and minimally affect normal cells)
Class IC antiarrhythmics: propafenone, flecainide
Flakes: flecainide (class IC antiarrhythmic)
purple phone: propafenone (class IC antiarrhythmic)
Tightly held peanut butter jar: class IC antiarrhythmics have an strong binding affinity for the Na+ channel (strong use-dependence, drastic slowing of the phase 0 upstroke)
Class III
_..

phase 0 not affected: QRS same
Amiodarone
_..
safest in terms of torsades

lipid soluble: accumulates everywhere, but not much problem with heart conduction
long half life


whirl with whiskers coming out
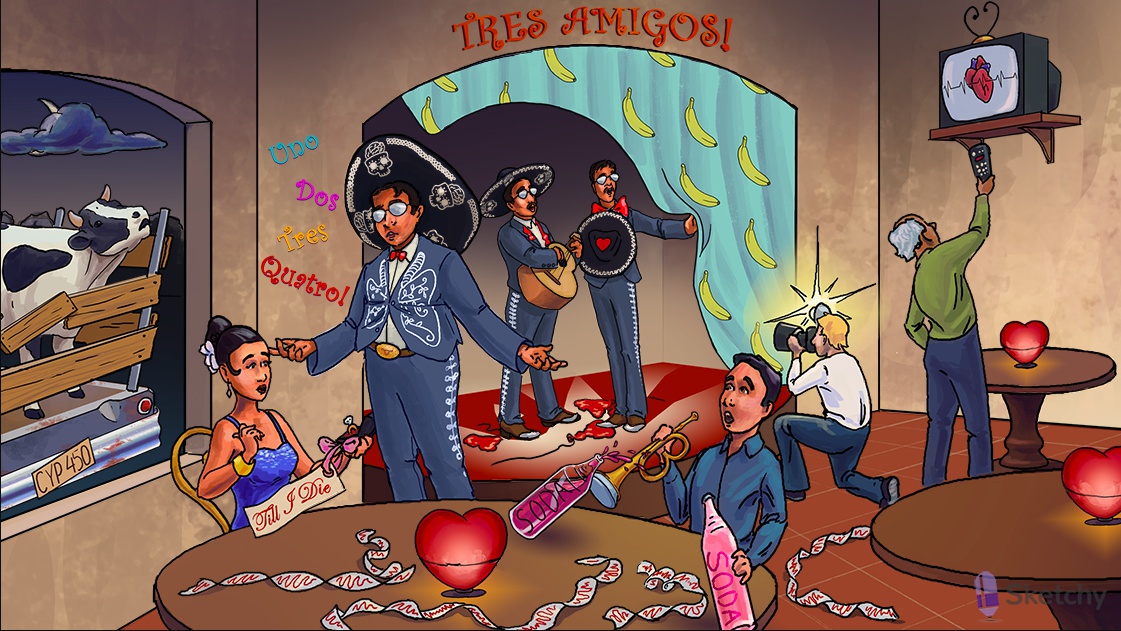



Amigo: amiodarone (class III antiarrhythmic)
Amiodarone shares properties of class I, II, III, and IV antiarrhythmics
Heart illuminated on top and bottom: class III antiarrhythmics treat both supraventricular arrhythmias and ventricular arrhythmias
Irregularly irregular signal: class III antiarrhythmics treat atrial fibrillation (and flutter)
Converting the signal: class III antiarrhythmics can restore and maintain normal sinus rhythm in atrial fibrillation and flutter
Skull brains: amiodarone has many neurologic side effects (e.g.tremor, ataxia, peripheral neuropathy, sleep disturbances)
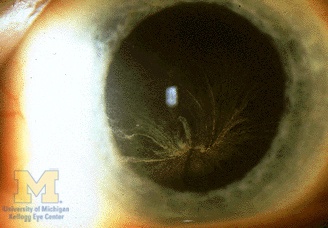
Gray sunglasses: amiodarone can cause gray corneal microdeposits
Big and small bowties: amiodarone can cause hyper or hypothyroidism
Fibrotic lung embroidery: amiodarone can cause pulmonary fibrosis
Tight button: amiodarone induced lung fibrosis causes restrictive lung disease
Hat shielding heart: amiodarone can cause heart block (Class II activity)
Trampled failing heart balloon: amiodarone can induce heart failure
Liver spot: amiodarone can cause hypersensitivity hepatitis
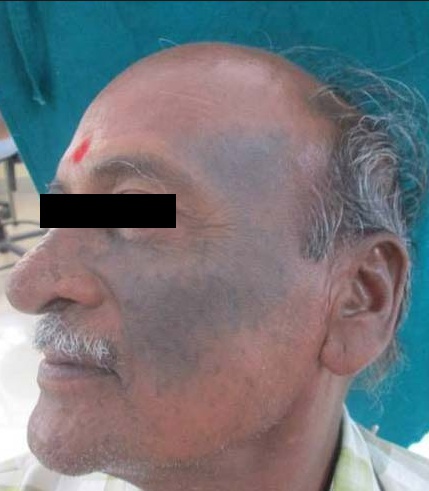
Gray-blue outfits: amiodarone can cause gay-blue skin discoloration
Flash photo: amiodarone can cause photodermatitis
Broken chrome bumper: amiodarone inhibits the cytochrome P450 system
Sotalol and Dofetilide
_..
cardiomyopathy: e.g. AFIB with decreased EF
Reverse Use Dependence

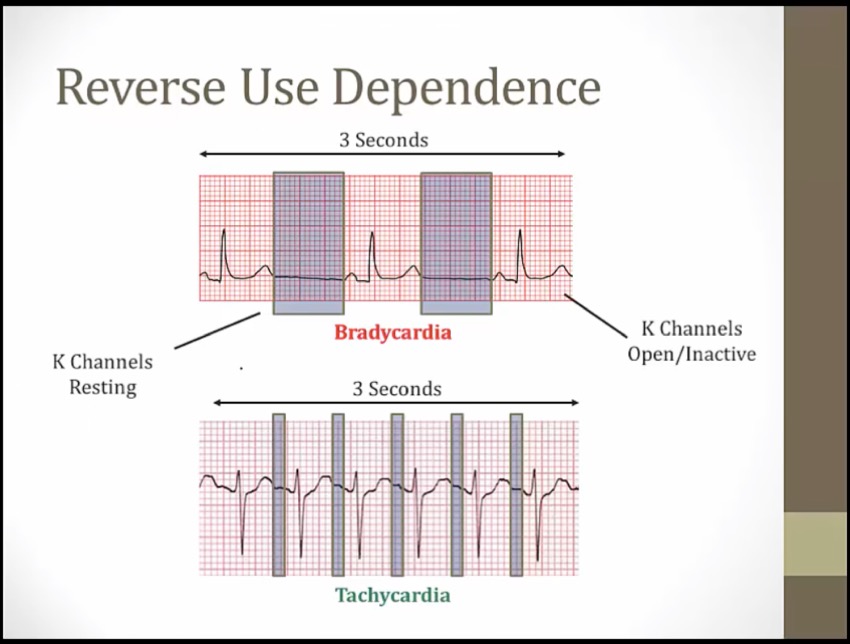


"till I die": -tilide suffix shared by dofetilide and ibutilide (class III antiarrhythmics)
Soda: sotalol (class III antiarrhythmic)
Muted bugle: sotalol is also a beta blocker (-lol suffix)
Heart illuminated on top and bottom: class III antiarrhythmics treat both supraventricular arrhythmias and ventricular arrhythmias
Irregularly irregular signal: class III antiarrhythmics treat atrial fibrillation (and flutter)
Converting the signal: class III antiarrhythmics can restore and maintain normal sinus rhythm in atrial fibrillation and flutter
Twisted streamer: sotalol, dofetilide, and ibutilide can induce torsades (although all type III antiarrhythmics can widen the QT interval)
Ibutilide
_..

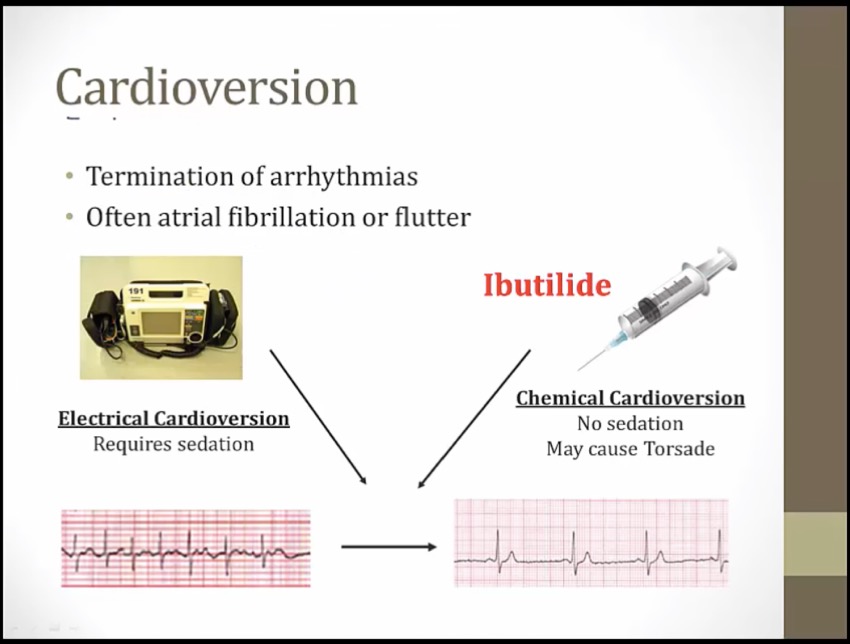
sedation: uncomfortable to pts
convert arrythmia to sinus rhythm
Ibutilide: no sedation, no shock
monitored for several hours

"till I die": -tilide suffix shared by dofetilide and ibutilide (class III antiarrhythmics)
Heart illuminated on top and bottom: class III antiarrhythmics treat both supraventricular arrhythmias and ventricular arrhythmias
Irregularly irregular signal: class III antiarrhythmics treat atrial fibrillation (and flutter)
Converting the signal: class III antiarrhythmics can restore and maintain normal sinus rhythm in atrial fibrillation and flutter
Class II
_..
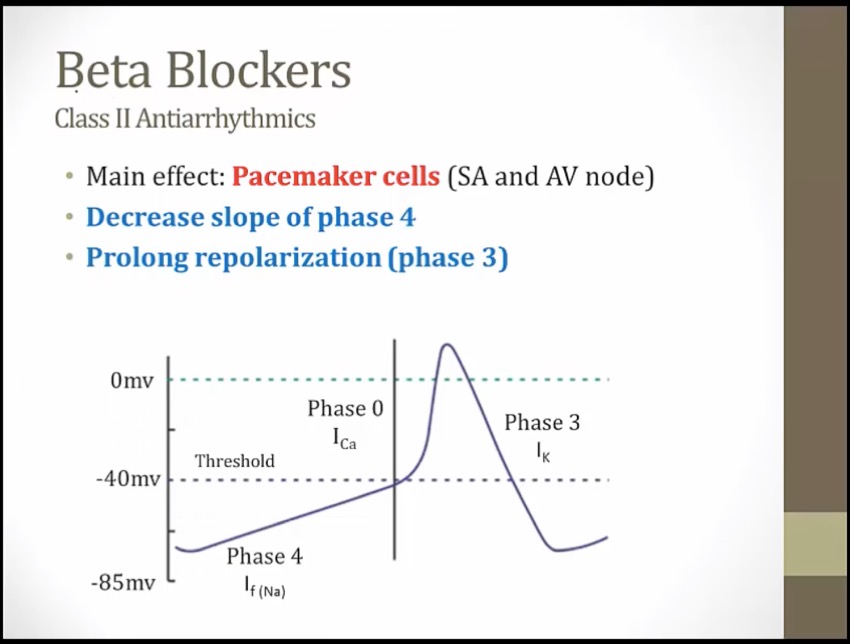
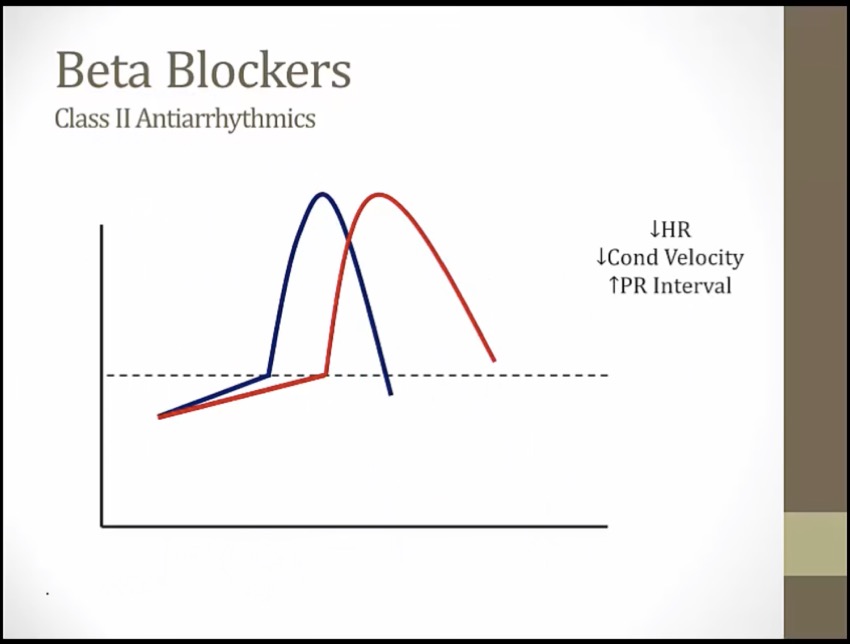
Class IV
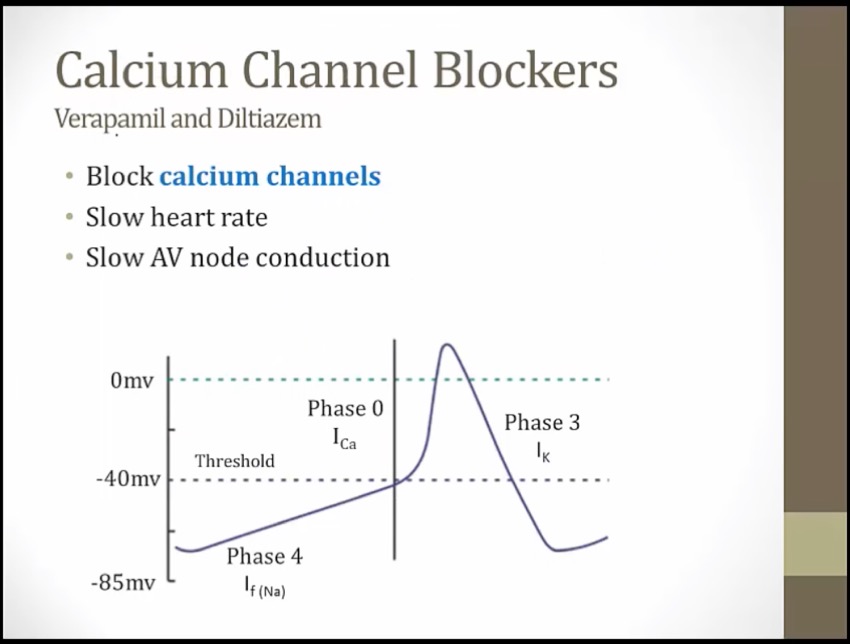
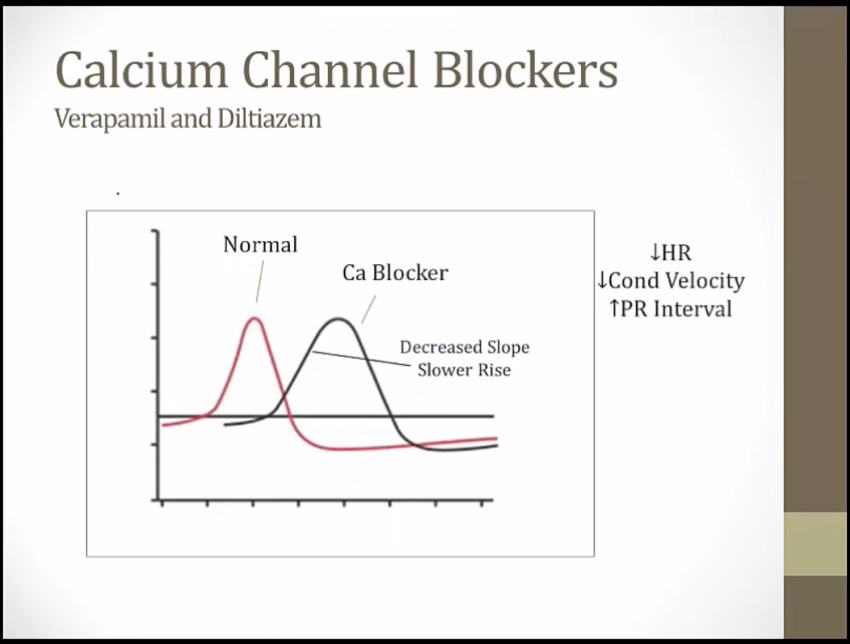
slower phase 0, drags out entire process of depolarization/repolarization
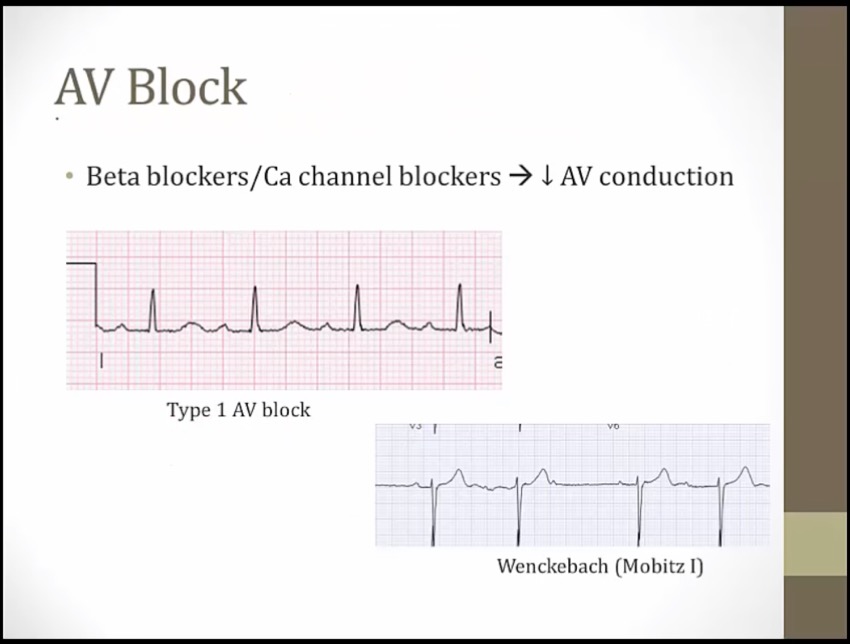
_..
slow conduction through AV node
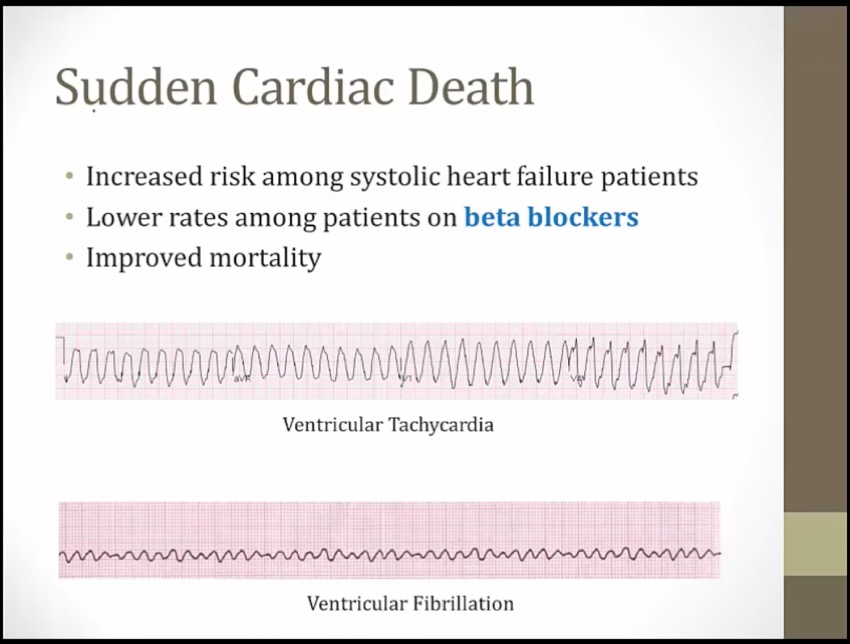
pts with systolic HF is at risk for sudden cardiac death, commonly develop VTACH/VFIB
probably result of effect on ventricular myocytes instead of SA/AV node
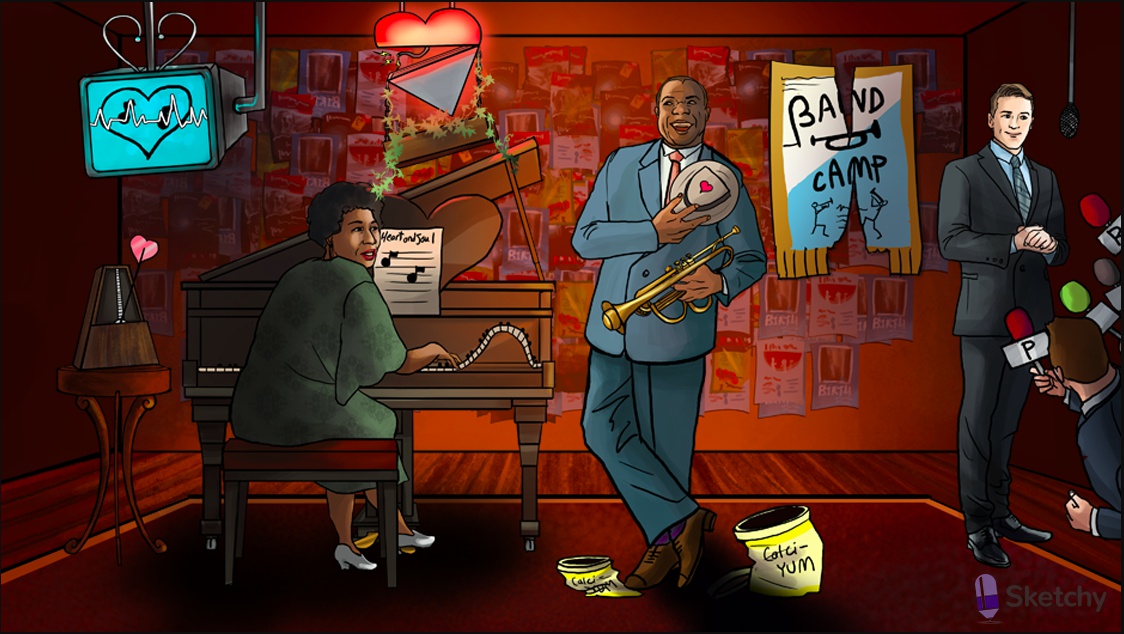

Disconnected bottom: beta blockers decrease atrioventricular conduction (AV block)
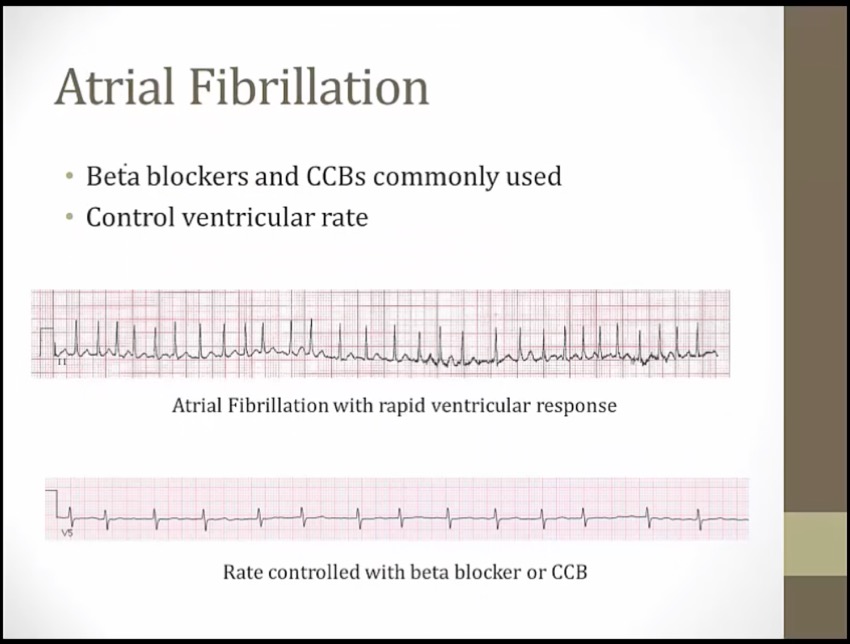
Lit up top: beta blockers treat supraventricular arrhythmias (e.g. atrial fibrillation with RVR)
Ivy: IV beta blockers (e.g. esmolol) can be used for acute supraventricular arrhythmias
Irregularly irregular static: beta blockers are useful in atrial fibrillation and flutter
Metronome: beta blockers prevent rapid ventricular response in atrial fibrillation and flutter ("rate control") (increase AV node refractory period, slow ventricular response rate)
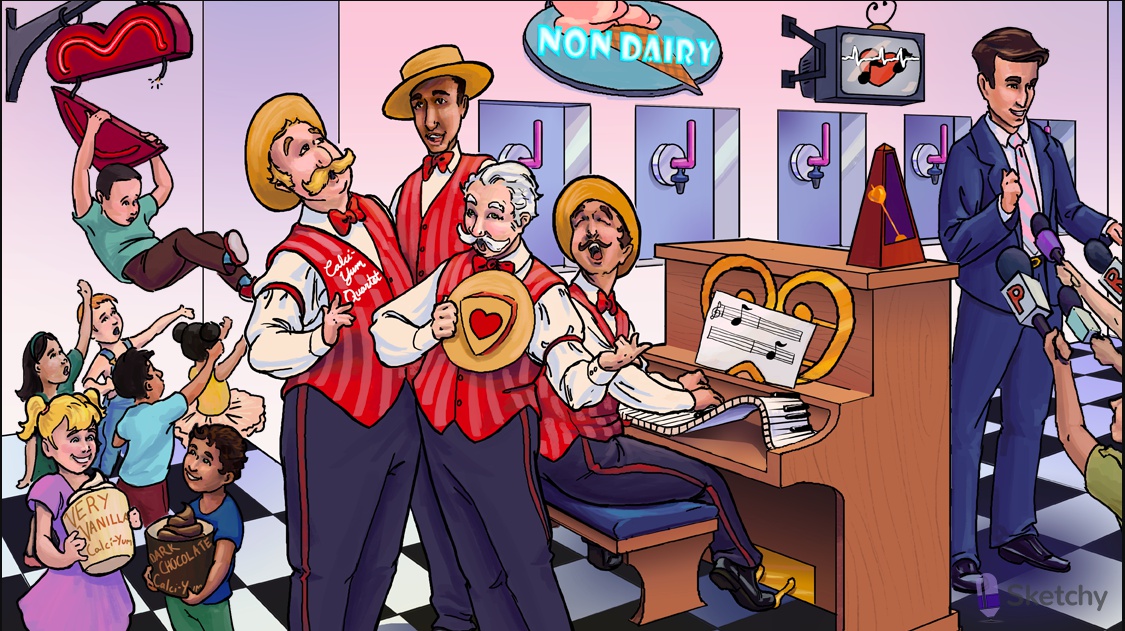

Illuminated top: non-dihydropyridine CCBs treat supraventricular arrhythmias (e.g. atrial fibrillation with RVR)
Irregularly irregular signal: non-dihydropyridine CCBs are useful in atrial fibrillation (and flutter)
Metronome: non-dihydropyridines prevent rapid ventricular response in atrial fibrillation and flutter ("rate control")
Others
Adenosine
_..
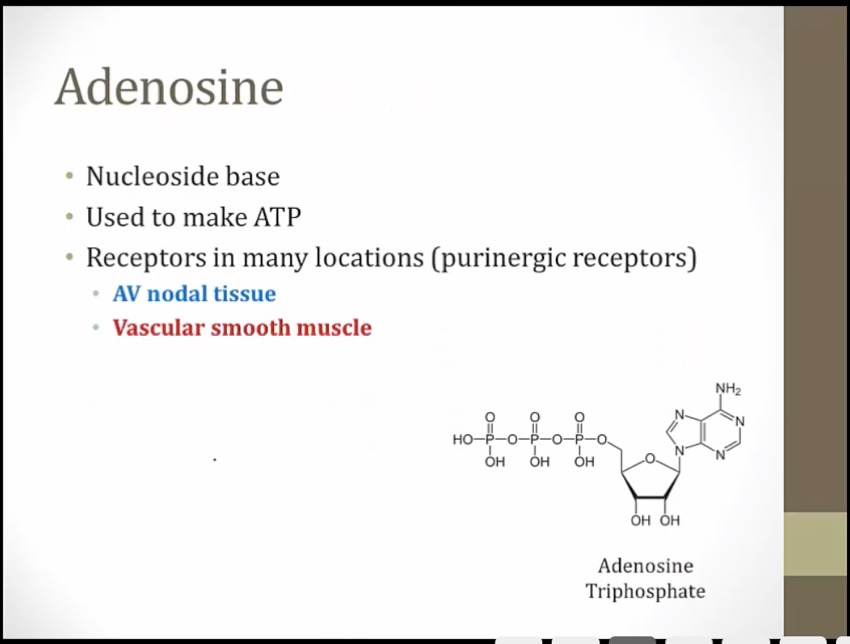

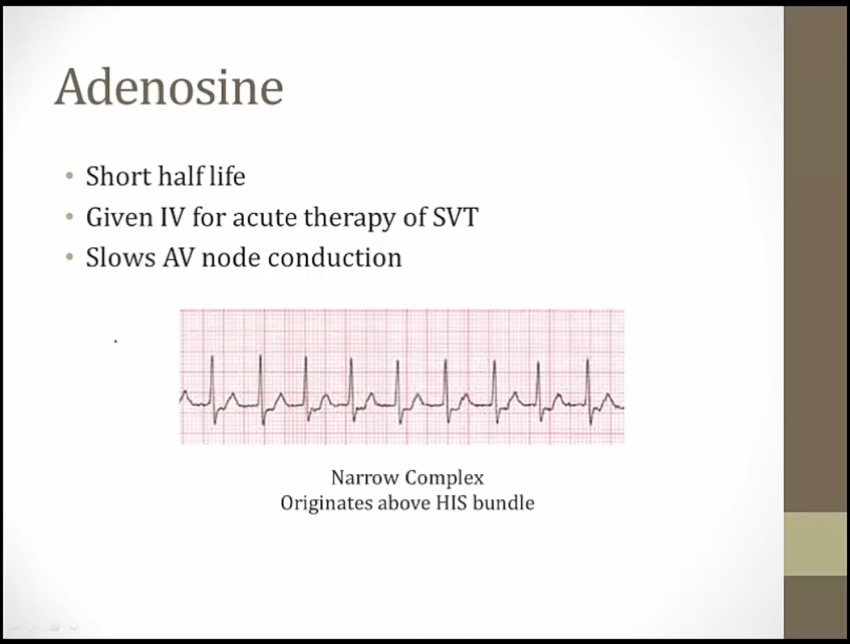
SVT: fast and narrow QRS
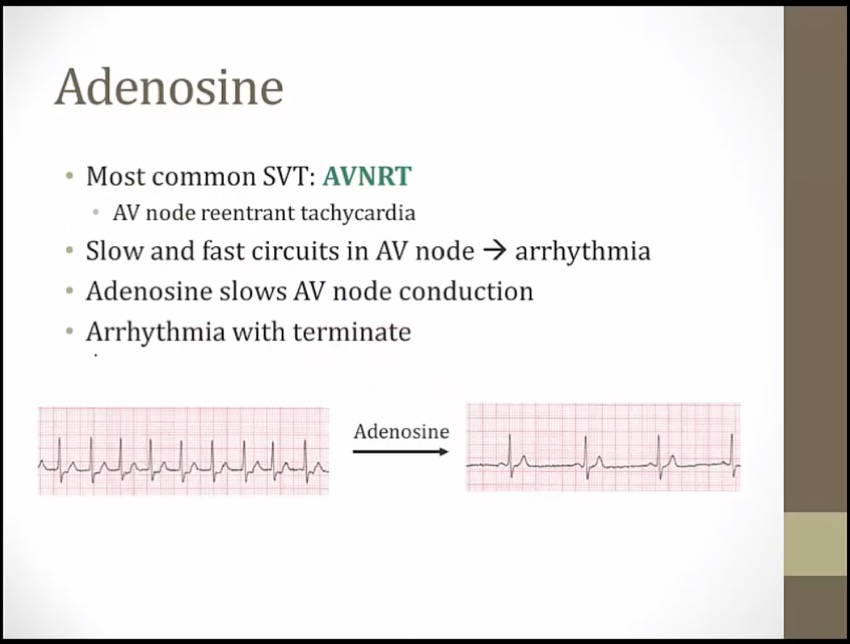
if SVT caused by AVNRT, then arrythmia will terminate
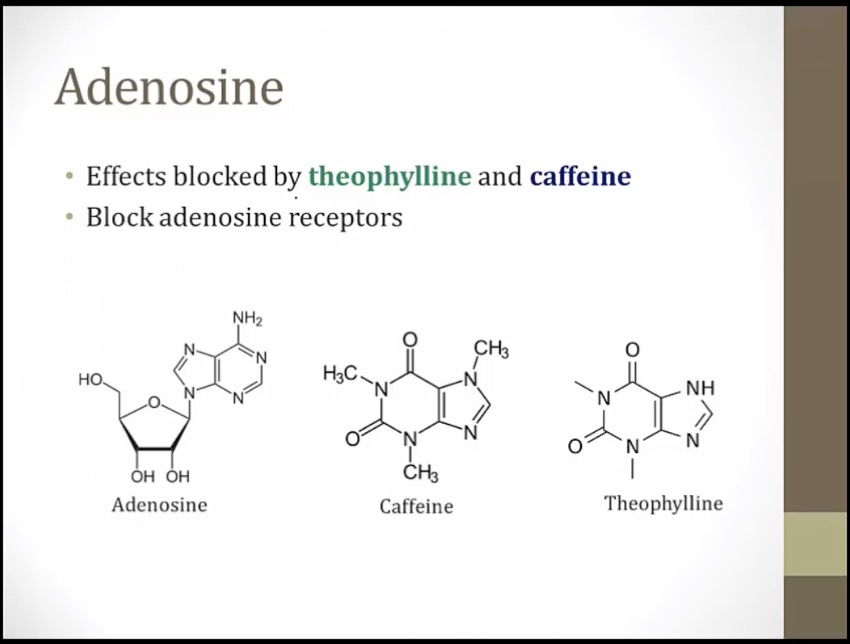
similar structure as adenosine

receptors on vascular smooth muscle
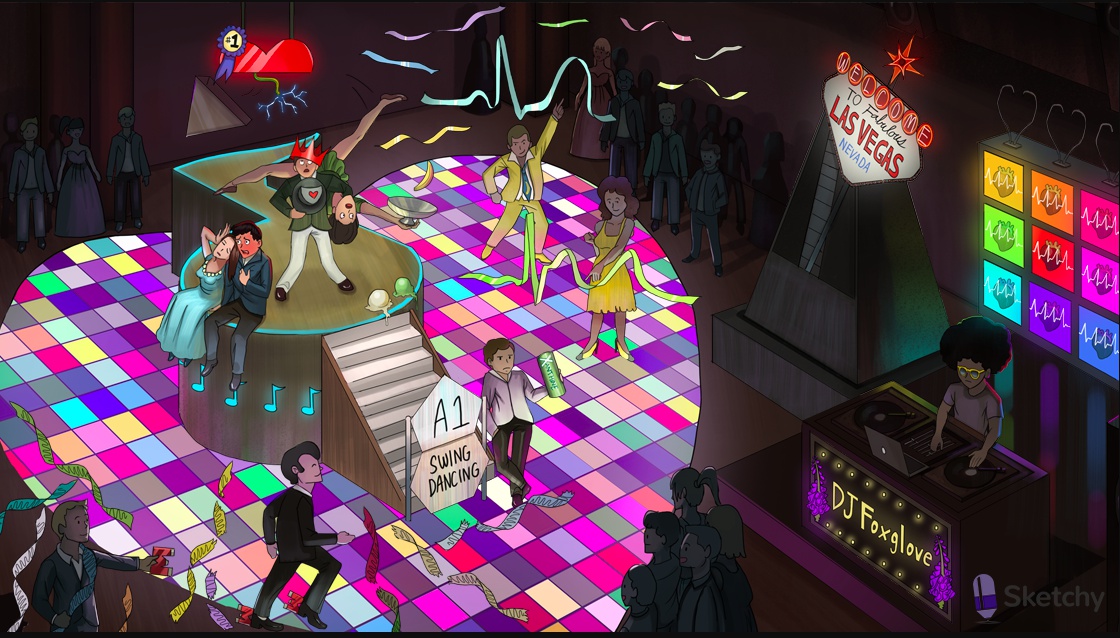

Swing dancing: adenosine (a purine nucleoside with antiarrhythmic properties)
Purine shaped gate: adenosine is a purine nucleotide
A1 Swing: adenosine activates inhibitory A1 receptors on the myocardium and at the SA and AV nodes
Falling calci-yum ice cream: activation of A1 receptors suppresses inward Ca2+ current (hyperpolarization, suppressed Ca2+ dependent AP
Banana flying out of cup: activation of A1 receptors increases outward K+ current (hyperpolarization, suppressed Ca2+ dependent AP)
Note shaped dance floor: adenosine inhibits the AV nodes (decreased AV conduction, prolonged AV refractory period)
Disconnected bottom of heart: adenosine decreases atrioventricular conduction
Dilated coronary crown: adenosine causes coronary dilation (mediated by A2 receptors)
Illuminated #1 top of heart: adenosine is a first line agent for acute treatment of supraventricular arrhythmias (e.g. PSVT)
Hat blocking heart: adenosine causes transient high grade heart block (direct AV node inhibition) (very quick half life, 10 seconds)
Flushed dancer: adenosine can cause cutaneous flushing
Dancer clutching chest: adenosine can cause shortness of breath, chest pain, and an impending sense of doom
Fainting dancer: adenosine can cause headache and hypotension
Energy drink blocking A1 gate: the actions of adenosine are inhibited by caffeine and theophylline (methylxanthines)
Mg
_..
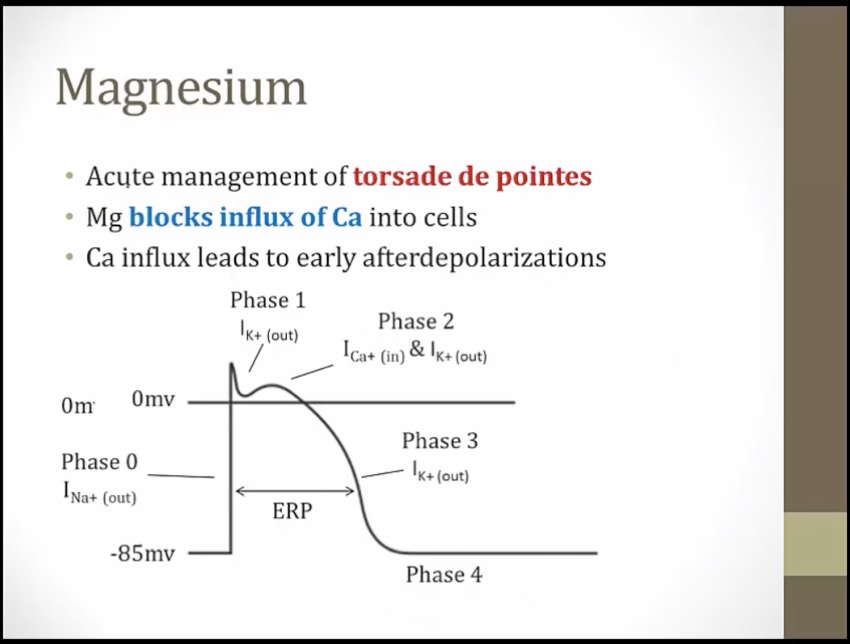
Ca influx causes early after depolarizations, occur during phase 3 where cell depolarizes again and again

Magnets: magnesium is useful for the treatment of certain arrhythmias (e.g. torsades)
Torn twisted torsades streamers: magnesium treats torsades de pointes
Atropine
_..
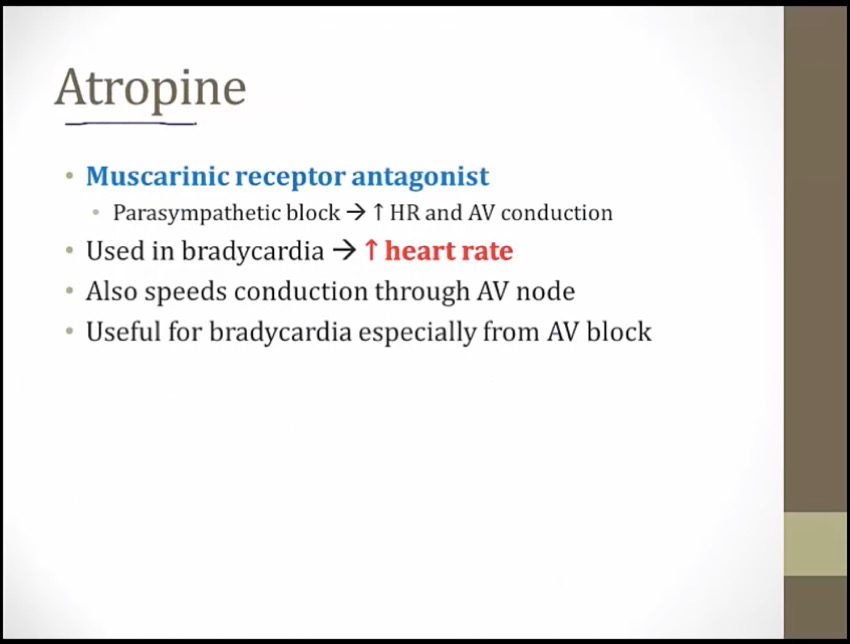
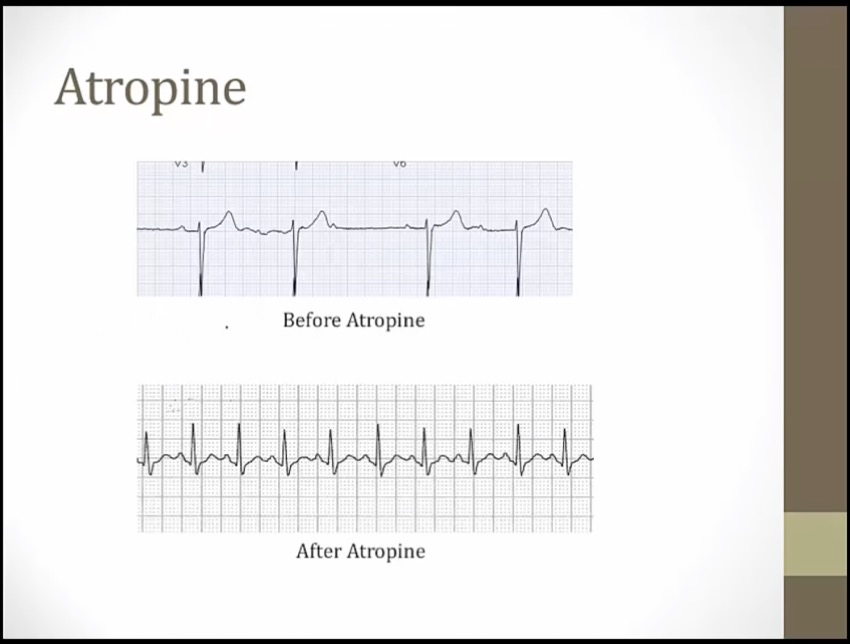
top: Wenckeback
bottom: all P waves conducted


Alice: atropine (antimuscarinic)
Heart with jewel nodes: antimuscarinics block parasympathetic activation of M2 receptors on the SA and AV nodes (increased heart rate, increased AV conduction). Parasympa slows HR/AV conduction. Inhibition results in opposite
Elevated heart watch: antimuscarinics (e.g. atropine) increase heart rate (useful in the treatment of bradycardia)
Heart shield: heart block (atrioventricular block)
Falling heart shields: antimuscarinics (e.g. atropine) increase AV conduction (useful in the treatment of heart block)
Digoxin
_..
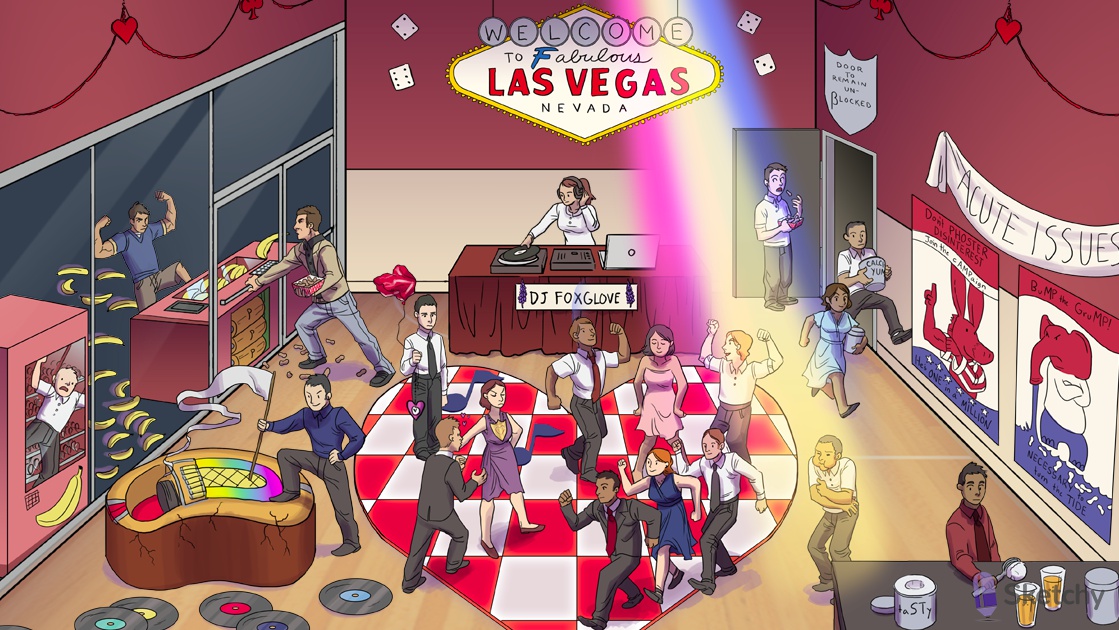


DJ Foxglove: digoxin - derived from the foxglove plant. Only one approved for chronic HF
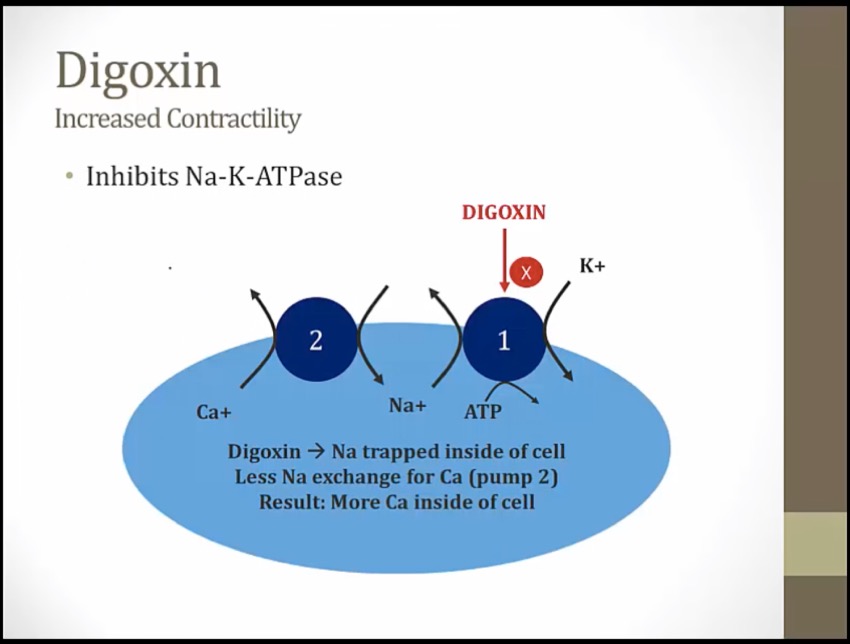
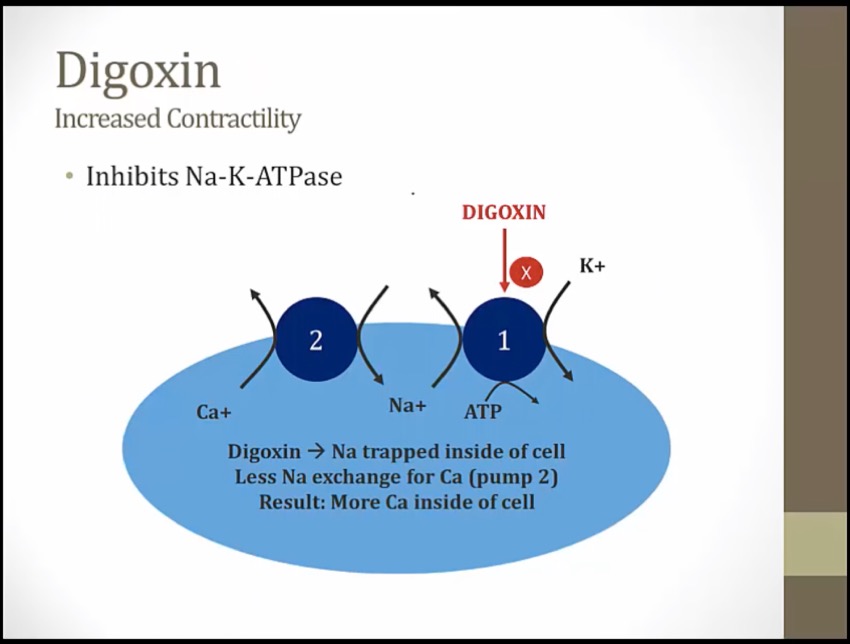
Knocked over banana vending machine: inhibition of Na+/K+ ATPase
Three P batteries: ATPase
Obstructed salty sodium peanuts: increased intracellular sodium as a result of Na+/K+ ATPase inhibition
Salty peanuts sneaking in the calci-yum icecream: increased intracellular sodium promotes calcium influx at the Na+/Ca2+ exchanger
Flexed arm: increased cardiac contractility due to increased sarcoplasmic calcium stores

DJ foxglove: digoxin has antiarrhythmic properties
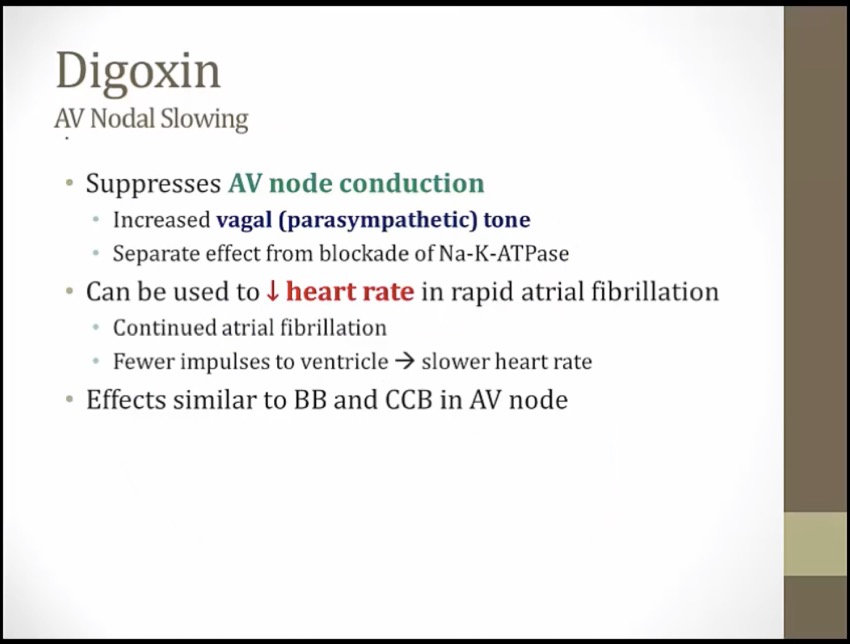
Vegas: digoxin exerts direct parasympathomimetic effects via direct stimulation of the vagus nerve -> (more at) AV nodal inhibition
Irregularly irregular signal: digoxin is useful in atrial fibrillation (and flutter) (1st goal is rate not rhythm)
Metronome: digoxin prevents rapid ventricular response in atrial fibrillation and flutter ("rate control")
_..

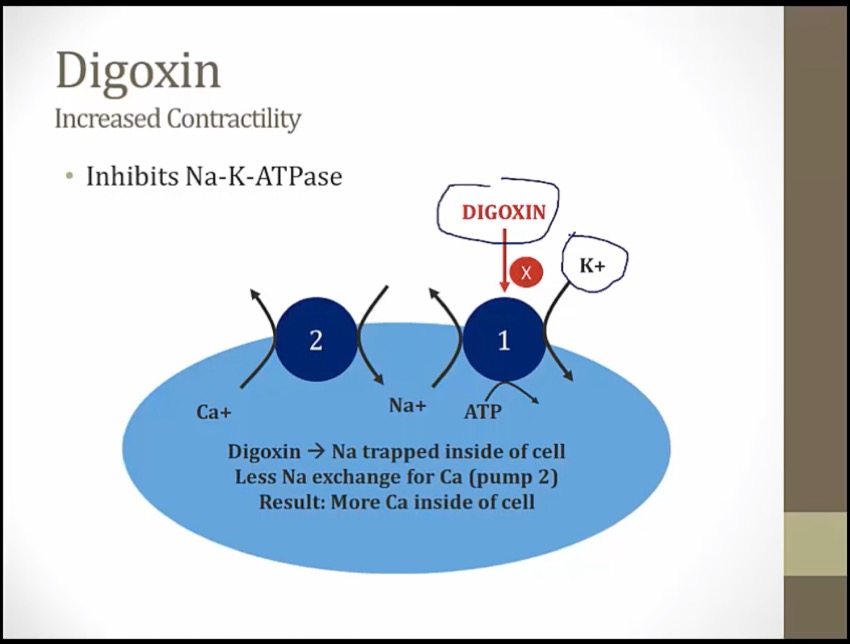
compete for binding, with hypokalemia, more digoxin activity

Na/K pump everywhere
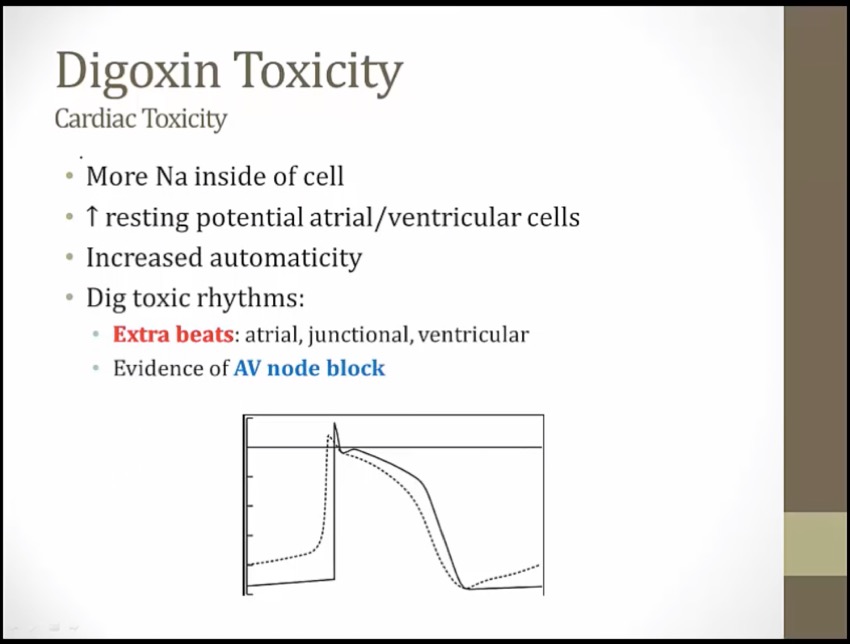
more Na: spontaneous depolarization
phase 4 not flat, goes up
hyperkalemia seen in digoxin toxicity


Pile of bananas: side effect of hyperkalemia
Various dances on the heart shaped dancefloor: digoxin may induce various arrhythmias
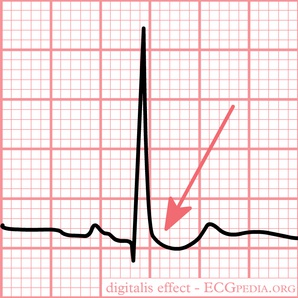
TaSTy scoop: chronic digoxin use may cause "scooped" concave ST segments on ECG
Dangling heart watch: side effect of bradycardia
SA music note: side effect of bradycardia due to parasympathetic activity at SA node
Heart shield: side effect heart block
AV music note: side effect of heart block due to parasympathetic activity at AV node
Gi side effects include nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain
Yellow spotlight: side effect of xanthopsia (objects appear yellow)
Remain unblocked: digoxin is contraindicated in heart block, CI with BB
Kid stuffed inside banana depleted vending machine: hypokalemia exacerbates digitalis toxicity, more binding with less K competing
Long tapering decay flag on cracked kidney: renal insufficiency increases the serum half life of digoxin, increasing susceptibility to toxicity
Records in kidney jukebox: many antiarrhythmics inhibit renal clearance of digoxin, increasing susceptibility to toxicity
Fabulous: digoxin immune Fab reverses digoxin toxicity
Last updated