03 Failure To Pass Meconium
Overview
Newborn constipation has to causes:
Failure to pass meconium: nothing comes out in first 24 - 48 hrs
Biliary emesis: anything obstructing
Imperforate anus
Meconium Ileus
Hirschsprung: can present in either first 48 hrs or yr 2
Constipation in general: decrease in frequency, increase in difficulty/hardness in year 2
voluntary holding
medication SE
diet
anatomy
neurologic problems (rare)
Imperforate anus
Path: part of VACTRL
symptoms: no hole, maybe stool if fistula present
diagnosis: xray (cross table)
treatment
Mild: anus where it supposed to be but not connected. Surgery now
Severe: anus pouch far from skin. Wait for baby to get bigger with more colon. Colostomy now and fix later
Watch out for VACTERL
cross table X-ray:

VACTERL
Prepare for intubation vs surgery. See if heart and tracheal look good
Vertebral: US sacrum
Anal: X-Ray
Cardiac: Echocardiogram
TracheoEsophageal: Catheter with X-ray from nostril to stomach. Coiled up
Renal: VCUG
Limb: X ray wrist
Colostomy
a surgical operation in which a piece of the colon is diverted to an artificial opening in the abdominal wall so as to bypass a damaged part of the colon.,
Meconium Ileus
path: CF
Demographics: infant failure to pass meconium with prenal screen positive or no prenatal care
diagnosis: x-ray show transition point and gas filled plug. Echogenic bowel on prenatal ultrasound can be an early hint.
treatment:
water-enema to diagnose and dissolve plug
CF: sweet chloride test to confirm, ADEK supplement, pancreatic enzyme, pulmonary toilet to prevent respiratory infections

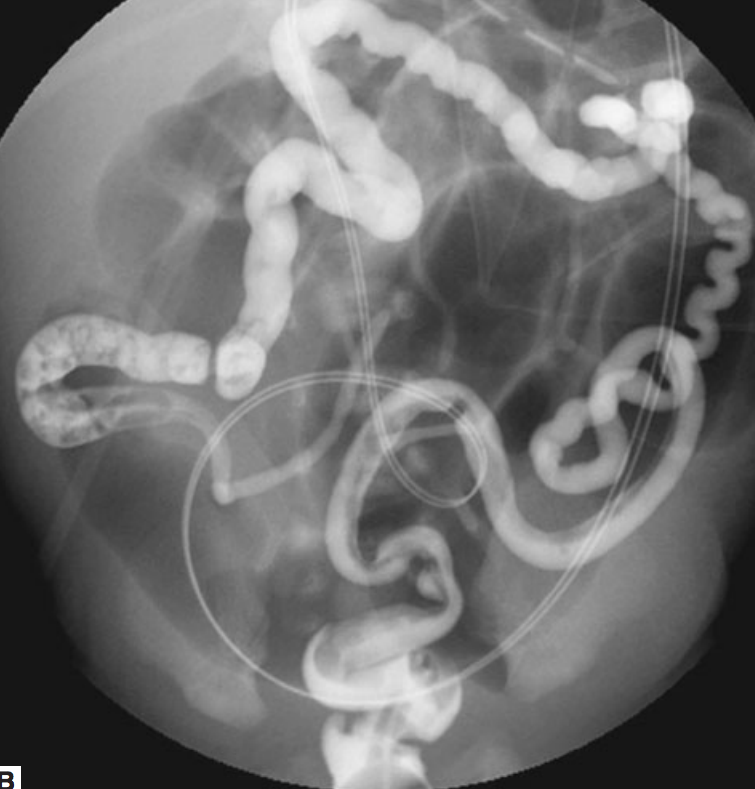
Hirschsprung
path: failure of migration of Auerbach and Meissner plexus inhibitory neurons that allow relaxation. Fails to innervate distal colon
demographics:
90%: failure to pass meconium: palpable colon, distended, explosive diarrhea on digital rectal exam
10%: chronic diarrhea with overflow incontinence. Enough good colon push liquid part of stool around obstruction = watery diarrhea
diagnosis
Step 1: xray. Bad colon normal. Good colon dilated
90%: contrast enema to see transition point
10%: anal rectal manometry: increased tone
best test: biopsy show no plexus
treatment: surgical resect bad colon
Voluntary holding
path: fear of pain, defecation, embarrassment. Water absorbed as stool sits = hard stool = constipation
demographics: cognitive impaired higher risk
begin toilet training and going to school for first time
voluntary holding at first turn involuntary
overflow incontinence: water
encopresis: stooling in bed. Liquidy stool comes out
diagnosis: clinical. Bowel habits
treatment
bowel regiments. Stool softeners, motility agents, behavior modification
disimpaction: under anesthesia unlike adults
Last updated