14 Parathyroid
Vitamin D
_..


Endogenous vitamin D is produced by photoconversion of 7-dehydrocholesterol to vitamin D3 in sun-exposed skin in the stratum basale (most important source)..
_..
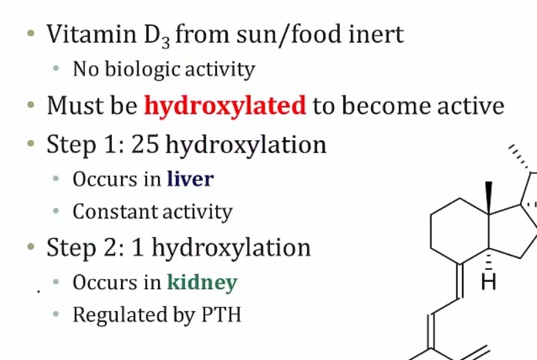

25-OH storage form
_..

constant production
long half life
_..
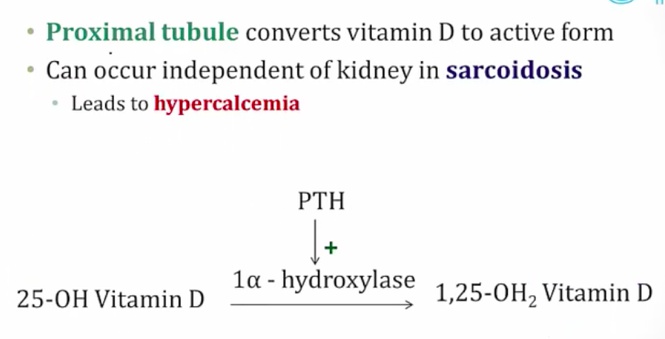
_..

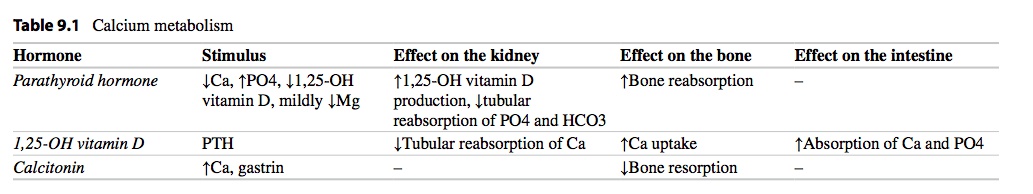
Mostly increase Ca and bone mineralization (add Ca to bone). At very high levels can cause bone resorption.
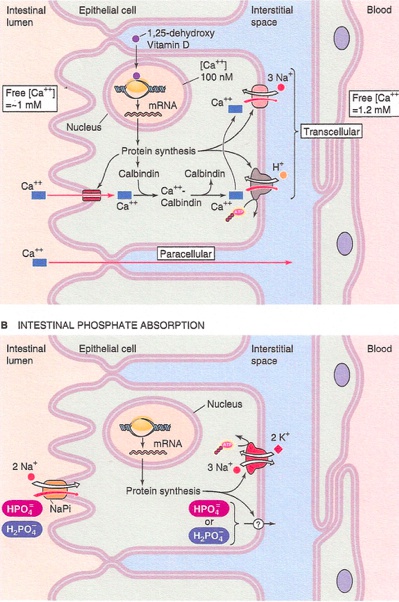
_The effects of vitamin D in the intestines include increasing the absorption of Ca 2+ via induction of vitamin-D dependent Ca2+-binding protein (calbindin-D-28K), and increasing the absorption of phosphate by upregulating Na-Pi symporter..
Deficiency
_..

Osteomalacia
_..

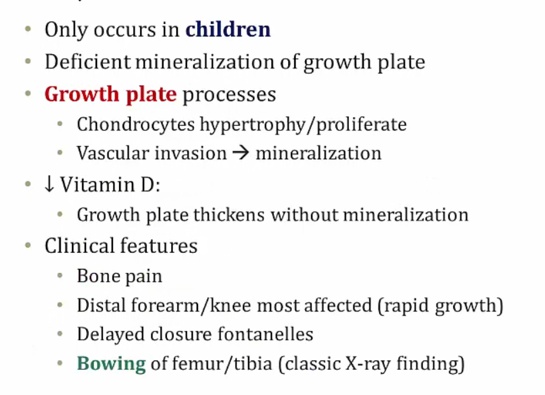
Rickets
.,
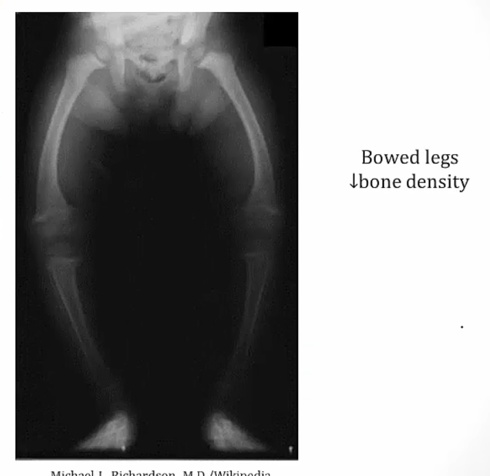
_..

Excess
_..

loss of appetite and stupor (unconsciousness)
Osteoporosis drugs
Bisphosphonates
_The first-line treatment for osteoporosis. They induce apoptosis and inhibit differentiation and activity in osteoclasts (block osteoclast binding and the formation of the osteoclastic ruffled border). Bisphosphonates also appear to bind to the hydroxyapatite of the bone, stabilizing it against recognition by the osteoclasts.,
_Examples include the “-dronate” drugs:
Medronate
Clodronate
Alendronate.,
_Uses:
Osteoporosis
Hypercalcemia
Bone malignancy
Paget disease of the bone.,
_SE include:
Esophagitis (patients are advised to take with water and remain upright for 30 minutes)
Dysphagia
Gastric ulcers
Osteonecrosis of the jaw.,
SERMS
_selective estrogen receptor modulators.,
_Have tissue specific effects. In some tissues they behave as estrogen agonists whereas in other tissues they behave as estrogen antagonists.,
_Include tamoxifen and raloxifene.,
Raloxifene
_Inhibits bone resorption by acting as an estrogen agonist in the bone. It can be successfully combined with bisphosphonates to prevent osteoporosis in postmenopausal women.,
_Iinhibits bone resorption in postmenopausal women by inhibiting osteoclasts. However because of the increased risk of endometrial hyperplasia and cancer, is NOT considered a first-line SERM for the treatment of osteoporosis.,
_Some common side effects include:
Edema
Hot flashes
Arthralgias
Note that both cause decreased bone density in premenopausal women, so they should NOT be used to treat or prevent osteoporosis in this population.
Serious adverse effects include:
Venous thromboembolism
Fatal stroke in patients with cardiovascular disease
Endometrial cancer.,
Teriparatide
_Has been shown to increase bone density and bone mass.
In postmenopausal women, decreases osteoporosis-related fractures.
Should not be used in patients with previous bone radiation or other predispositions to osteosarcoma.,
Denosumab
_A human monoclonal anti-RANKL antibody used for the treatment of:
Osteoporosis
Treatment-induced bone loss
Bone metastases
Multiple myeloma
Giant cell tumor of bone.,
_ Adverse effects include:
Joint and muscle pain in the arms or legs
Increased risk of infection
Hypocalcemia
Osteonecrosis of the jaw
Atypical hip fractures (from too little bone turn over).,
Calcium
_Plasma Ca2+ exists in three forms:
Free ionized (45%)
Bound to albumin (40%)
Bound to anions (15%)..
Free, ionized Ca2+ is biologically active.
Ionized calcium binds to negatively charged sites on protein molecules, competing with hydrogen ions for the same binding sites on albumin and other calcium-binding proteins.
This binding is pH dependent and alters the level of ionized calcium in the blood. An increase in pH, alkalosis, promotes increased protein binding (less H+ competing), which decreases free calcium levels. Acidosis, on the other hand, decreases protein binding, resulting in increased free calcium levels..
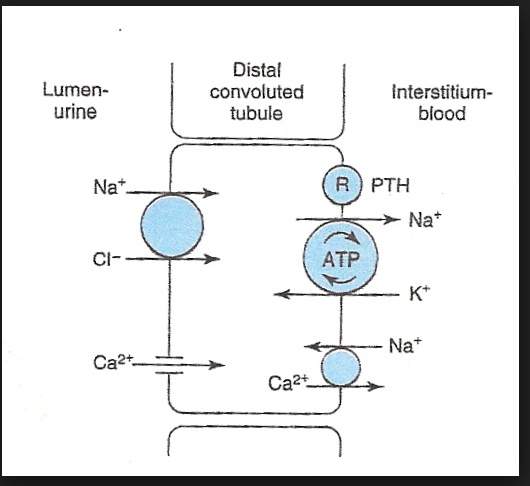
_Diuretics can alter calcium levels. Loop diuretics decrease calcium reabsorption in the thick ascending limb of the nephron, while thiazides increase its reabsorption in the distal convoluted tubule. To remember this difference, use the mnemonic "The loop loses calcium"..
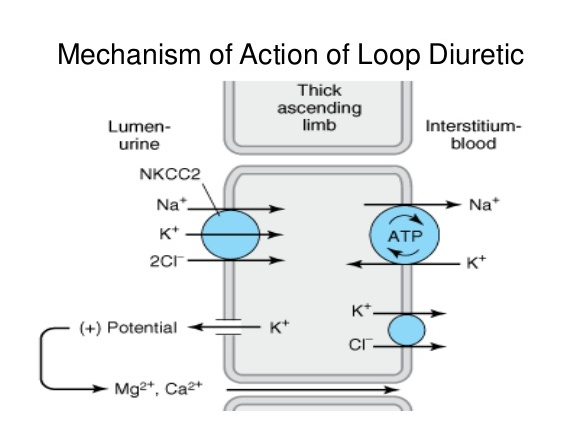
_Active reabsorption by the Na+/K+/2Cl- cotransporter leads to a backleak of K+. The positive lumen potential created by this backleak will induce paracellular reabsorption of Mg2+ and Ca2+. Blocking the Na+/K+/2Cl- cotransporter with a loop diuretic will decrease calcium reabsorption into the blood..

_Thiazide diuretics block the apical Na+/Cl- symporter, and as a result intracellular sodium is reduced. This ramps up the activity of the basolateral Ca2+/Na+ exchanger (to increase Na+ pumped into the tubular cell), which will increase calcium reabsorption into the blood..

Cinacalcet
_Increases the sensitivity of the Ca2+-sensing receptor (CaSR) in the parathyroid gland to circulating Ca2+. This decreases the secretion of parathyroid hormone.,
_Is indicated in the treatment of:
Hypercalcemia due to primary hyperparathyroidism (e.g. parathyroid carcinoma)
Secondary hyperparathyroidism in chronic kidney disease patients
.,Cinacalcet may cause hypocalcemia.
PTH

Soluble in water.,
Effects
_..

_..

_..

1, 25 OH2 Vit D is active form
Overall effect: decreased phosphate in serum
_..
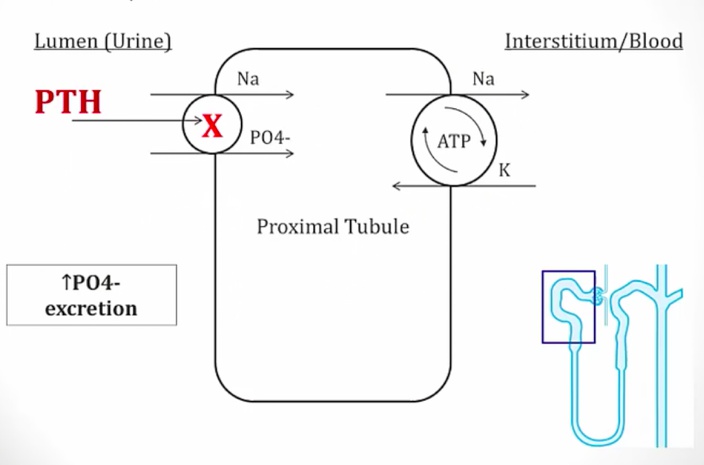
Decreased phosphate in serum
Increased phosphate secretion
_..
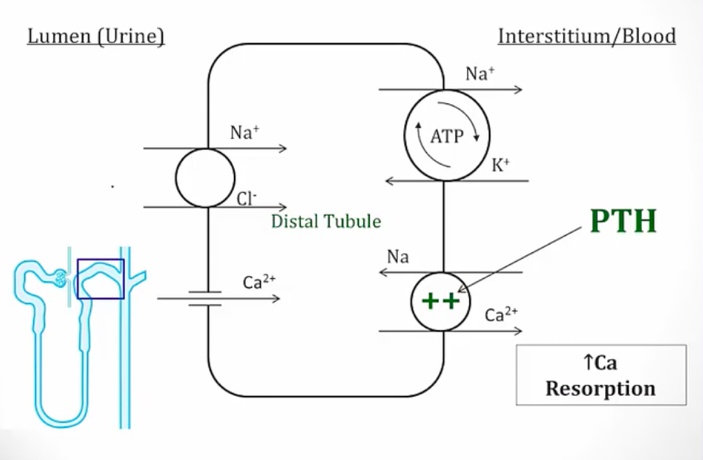
_..


_Parathyroid analog used to treat osteoporosis.,
_..

_..
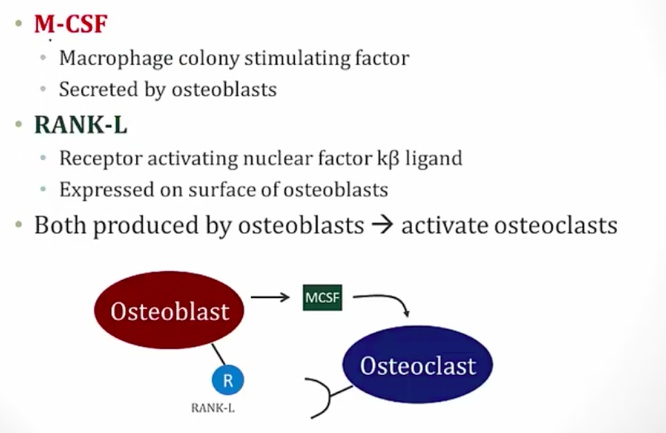
OPG is secreted by osteoblast. It's a soluble RANk that inactivates RANK-L
_..

pregnancy: increased estrogen and bone density
stress: increased glucocorticoids and decreased bone density
_..
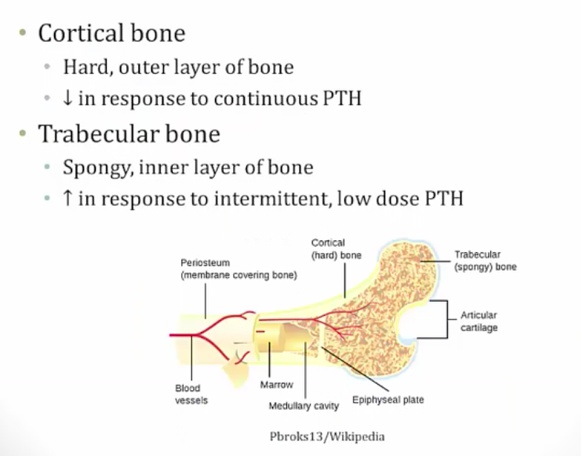
_..

Low Mg leads to increased GI/renal absorption

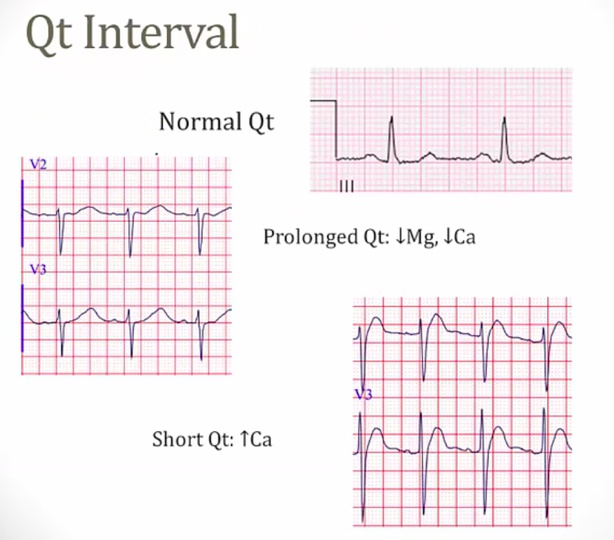
_..
PTHrp
_.,

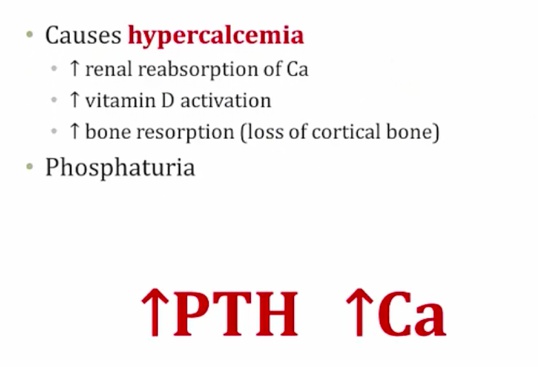
Hyperparathyroidism
_.,

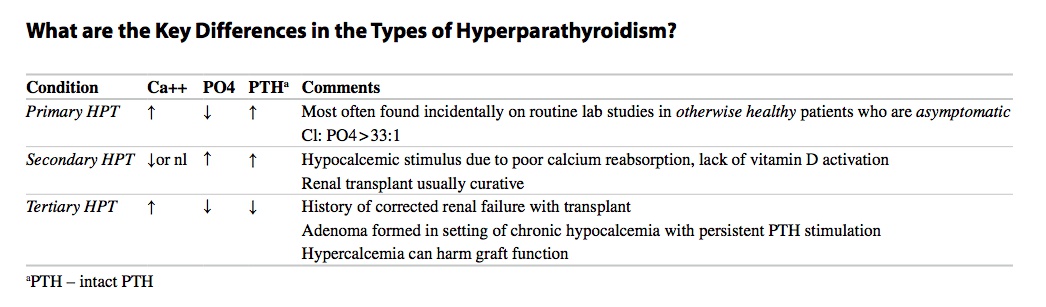
Primary Hyperparathyroidism
_Cause:

.,
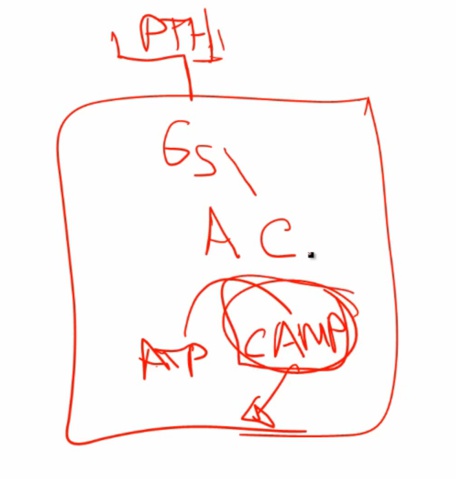
Increased cAMP
Increased Alk Phos: alkaline environment needed to lay down Ca in bone. Increased osteoblast > increased laying down bone and produce alk phos (sign of osteoblast activity)

.,
_Symptoms:

malignancy: symptoms happens earlier

metastatic calcification of renal tubules

classic: pancreatitis
nephrocalcinosis:
.,
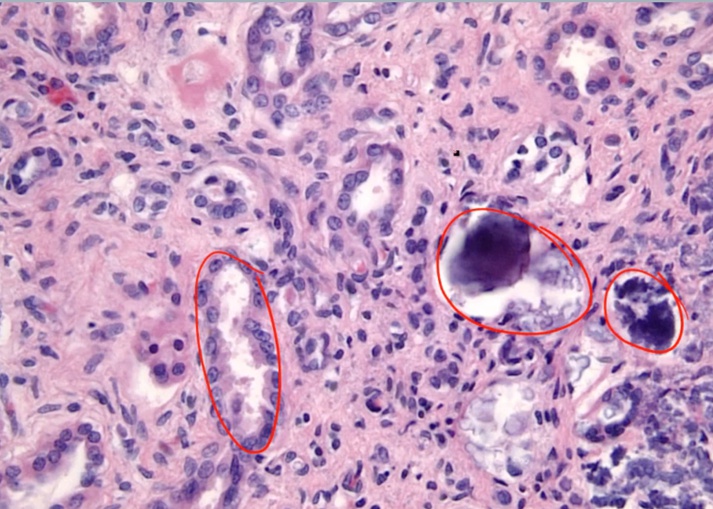
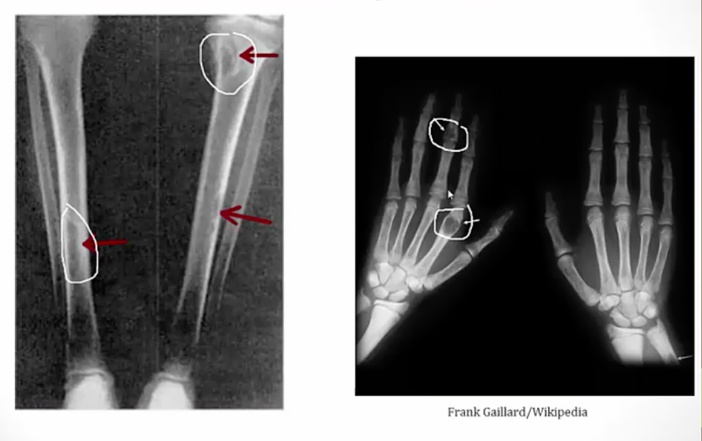
Osteitis Fibrosa Cystica

.,
Cystica means bone change
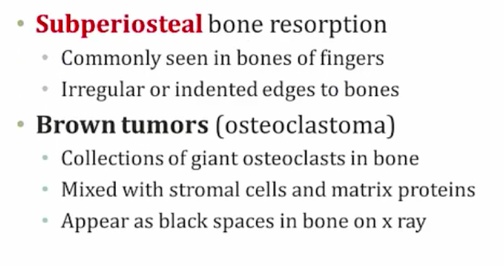
Periosteum: membrane surrounding the bone
.,
_Histology shows fibrosis and bone spicules
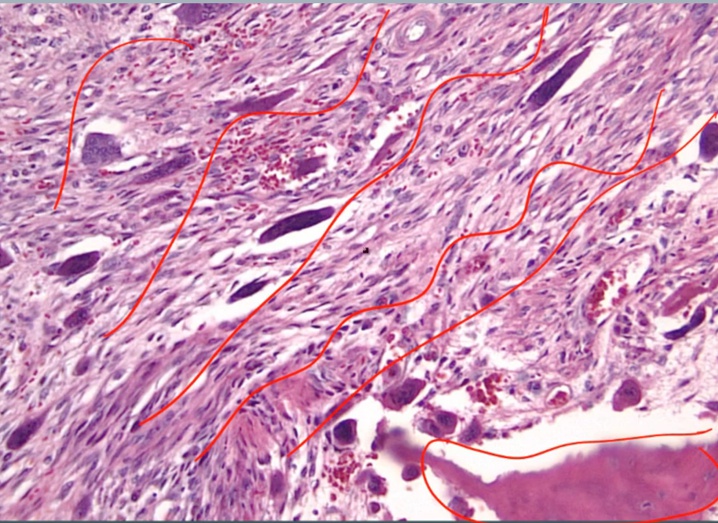
.,
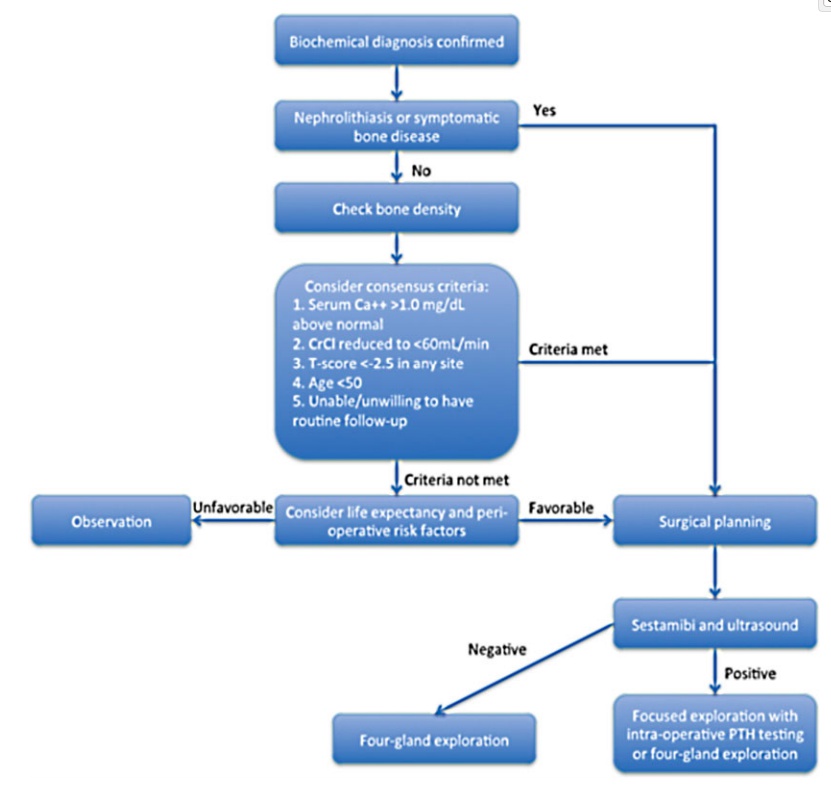
Primary hyperparathyroidism treatment

post-op: takes time for remaining glands to start working.,
Secondary
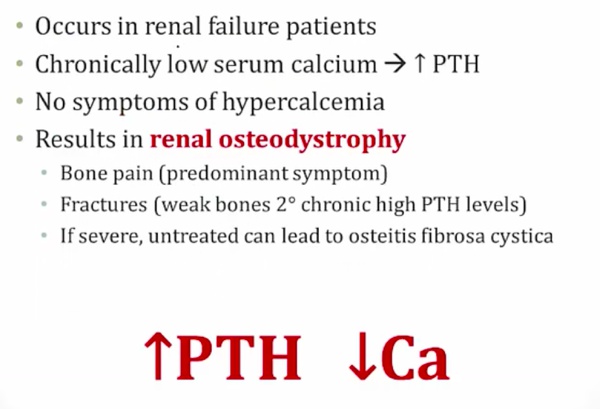
bone pain from PTH
high alk phos
.,
Tertiary

.,
parathyroid independent of Ca
_..
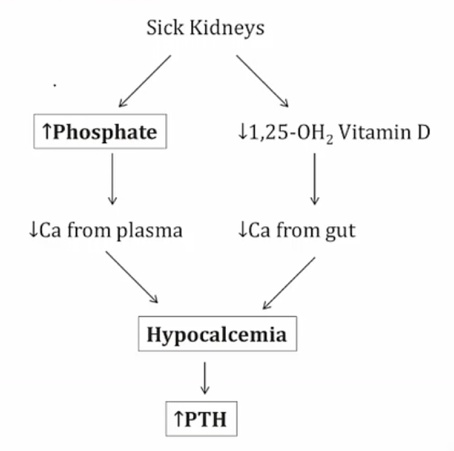
Can't excrete phosphate > more binding with Ca
Can't activate Vit D > Less Ca reabsorption
Familial hypocalciuria hypercalcemia


.,
Hypoparathyroidism
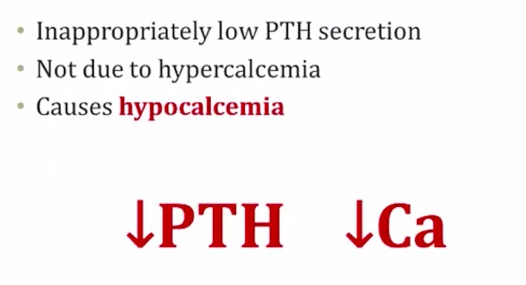
.,

.,

Autoimmune
Congenital: DiGeorge
Radiation
.,
post-op: days/weeks later
APS-1

.,
Digeorge
_..

thymic aplasia

.,
Pseudohypoparathyroidism
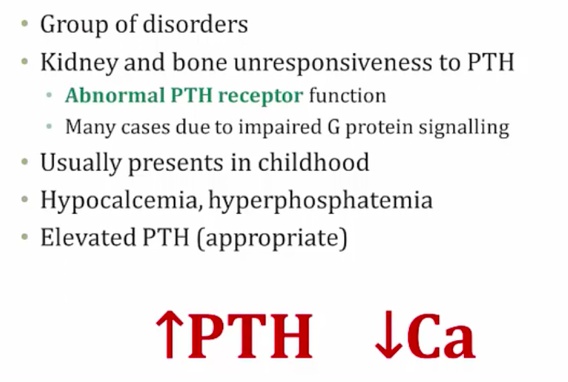
Gs receptors

.,
Named pseudo because has signs and symptoms of hypoparathyroidism but not because of low hypoparathyroidism.
Albright's Hereditary Osteodystrophy, AHO
[_](Albright's Hereditary Osteodystrophy, AHO, inheritance, labs, symptoms)

.,
Increased PTH, decreased Ca: Ca lost somewhere
_..

Ddx
Hypercalcemia
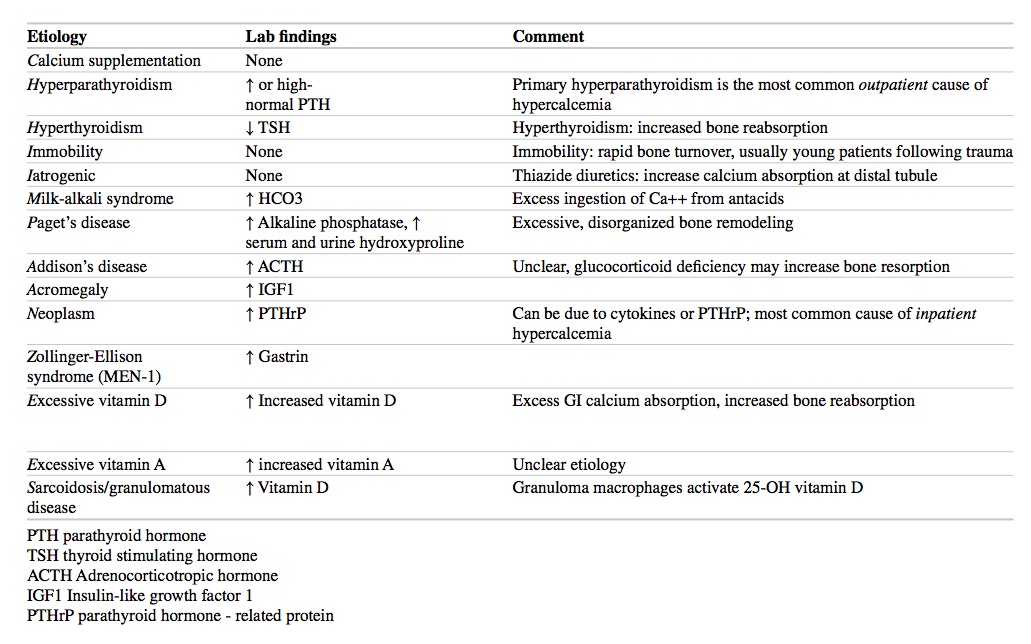
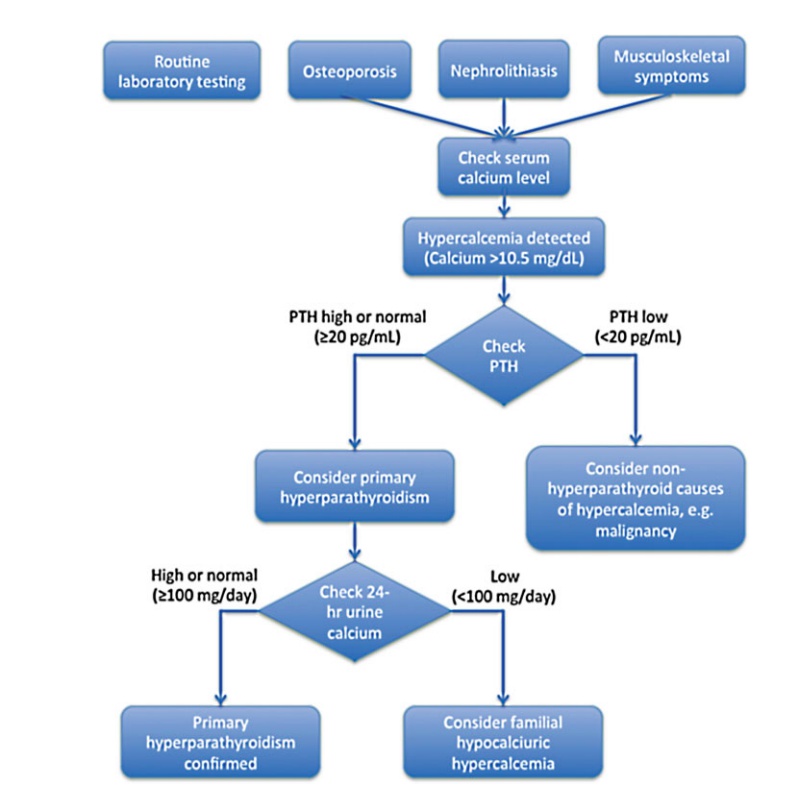
Hyperparathyroidism workup:
Last updated