13 Electrolytes
Overview
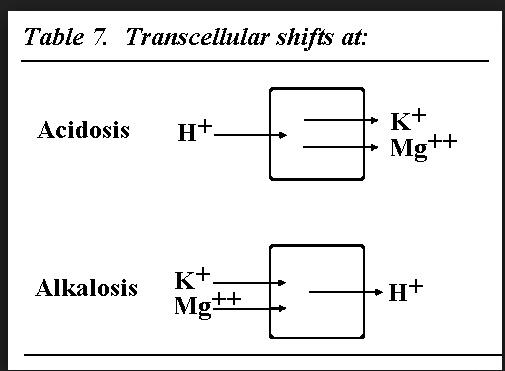
hyperkalemia: wide QRS, peaked T, weakness
hypokalemia: flat T, U wave, weakness
hypercalcemia: stones, bones, groans, psychiatric overtones
hypocalcemia: tetany, seizures
hypermag: decreased DTR, paralysis, bradycardia, hypotension
hypomag: tetany, arrhythmia, confusion
Hyperkalemia
_..

_..



hyperkalemia: Na channels inactivated, slowing depolarization
Reversal potential of K is shifted positive. Driving force for K to leave the cell via Leak K channels is decreased so there is less "leak" K current and the RMP is depolarized compared to normal. The more positive RMP means more Na channels will randomly open and more of them will become inactivated. This means fewer Na channels are available to respond by opening when full depolarization occurs.
_..

insulin deficient, beta blockers, digoxin: Na/K pump
insulin and catecholamines stimulates pump (insulin deficient and bb increase K)
hyperosmolarity: uncontrolled hyperglycemia

Banana peels: beta-2 activation can cause hypokalemia (due to increased insulin activity)
rhabdomyolysis: lysis of cells, hyperkalemia
hyperosmolar state: draw water out of cell, take K with it, create high K gradient in cell that leaves

Hypokalemia
_..


_..


Hypercalcemia
_..

promotes water loss and nausea: dehydrated
_..

mets to bones increase turnover
Hypocalcemia
_..

_..

Hyperphosphatemia
_..

metastatic calcification: end stage renal pts with high phosphate
_..

phosphate laxatives: bowel prep for GI exam
Hypophosphatemia
_..

_..

ammonia binds phosphate
tumor: inhibit transporter in PCT, don't resorb phosphate
Hypermagnesemia
_..

_..

important cause
Hypomagnesemia
_..

drags K and Ca with it
_..

Last updated