09 Starling
Starling Curve
_..

preload can be either pressure or volume
the more you load the ventricle with fluid, the more it'll pump
allows heart to pump with higher venous return, otherwise blood would pool in venous system
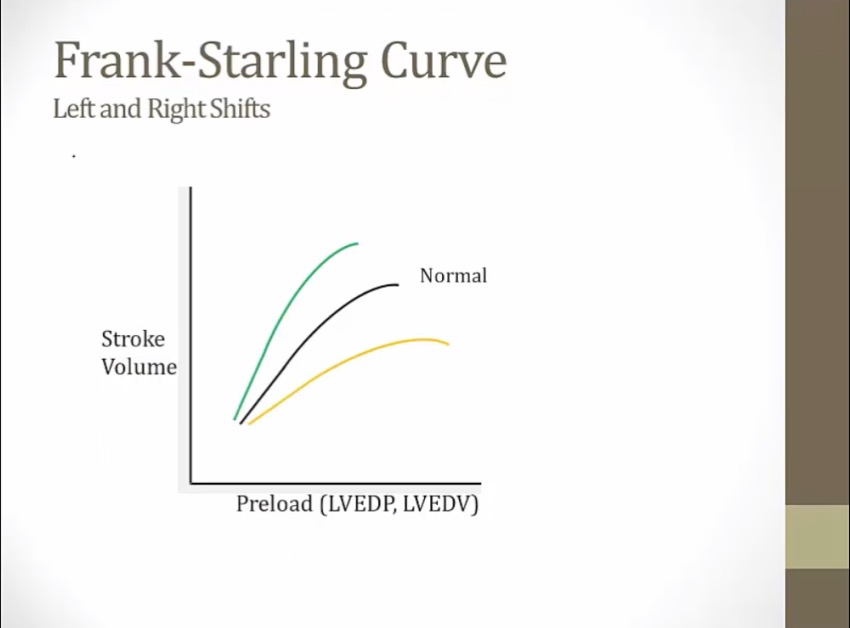
shifting to left: at same preload, more stroke volume


TPR = SVR = peripheral resistance
Venous Return
_..

venous return = CO: blood returned to heart = blood pumped out of heart
X axis could be either venous return or CO
as CO increases, RAP falls

RAP equal to venous pressure from SVC/IVC
Increased CO: pulls more blood out of RV/RA, lowers RA pressure

how actually drawn

MSFP defined by volume in venous system and tone of veins in body
MSFP = pressure when CO is 0
_..

green: right shift


increased TPR: same CO leads to lower venous pressure and lower RAP
Combined Curves
_..

HF
_..
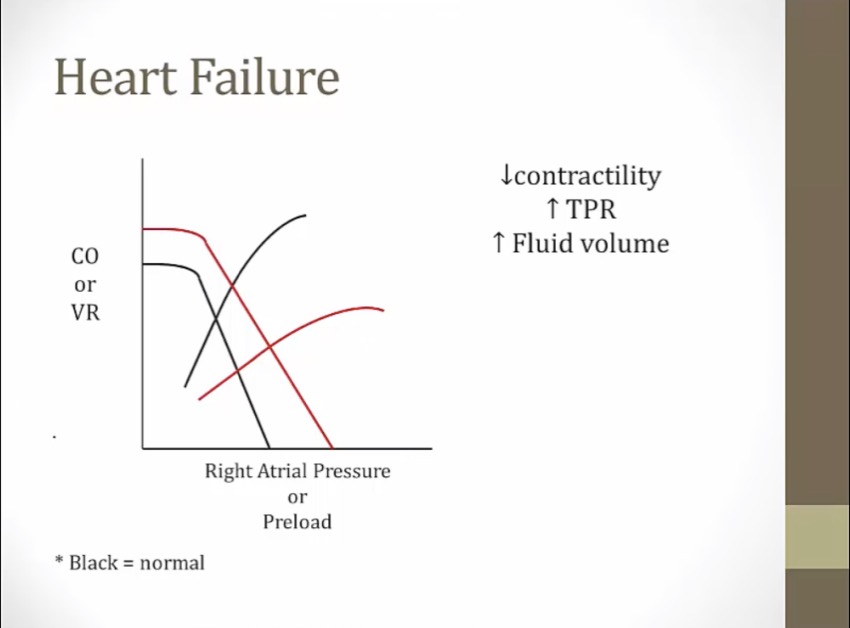
lower contractility: shift to right of starling curve
fluid retention: increased fluid volume, shift venous return curve right
increased TPR: changes slope of venous return curve


lower CO and higher RAP
Hemorrhage
_..

blood loss: shift venous return left
TPR up: slope left
contractility: starling curve up

lower CO, lower RAP
Exercise
_..

venous contraction from sympathetic activation
venous contraction: move to right
decreased TPR: slope right
higher CO in exercise
Fistula
_..

same as exercise
high output heart failure

nl: arteriole connectes arteries and veins. Arteries have high resistance
AV: bypass from A to V with low resistance
result: TPR down
Vasopressors
_..

_..


Last updated