03 Blood
Anticoagulants
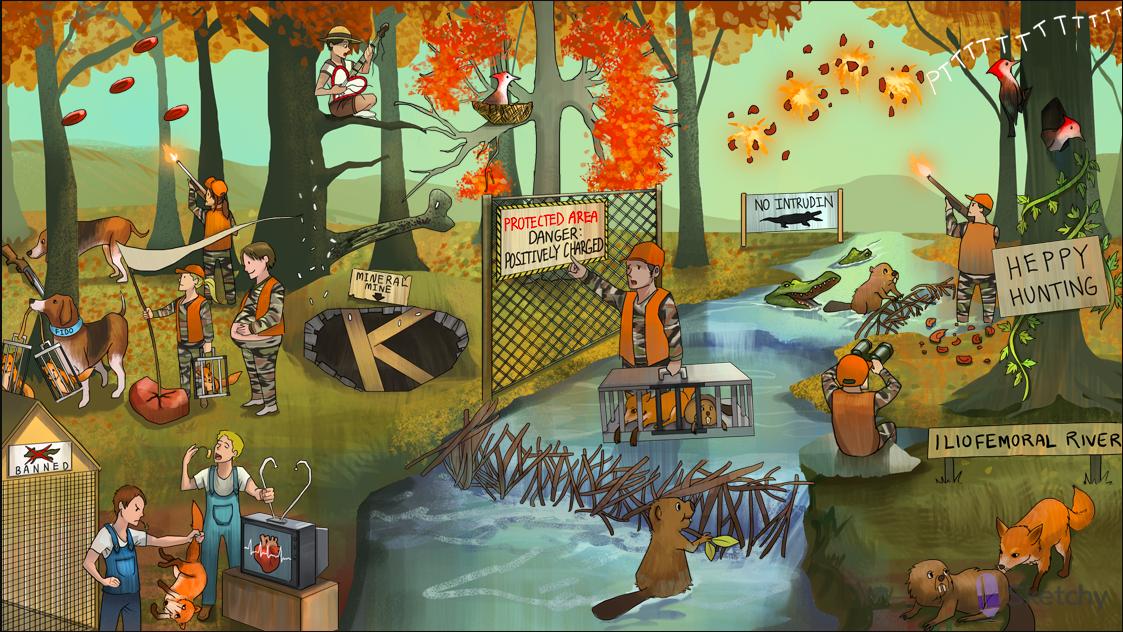
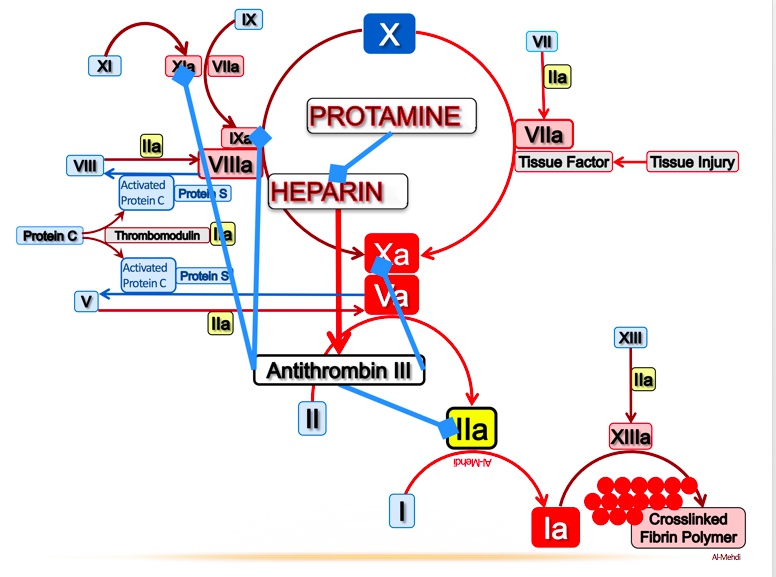
Heparin

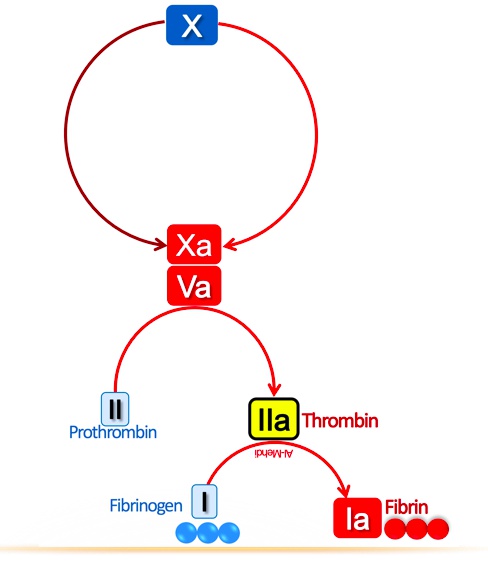
Beaver dam: fibrin clot
Throm-beaver: thrombin
Throm-beaver preparing stick: thrombin transforms fibrinogen into fibrin
Throm-beaver’s II shaped teeth: factor II aka thrombin
FoX: factor X
FoX waking up throm-beaver: factor Xa converts prothrombin into thrombin

Heppy hunting: heparin
Heppy hunter father: unfractionated heparin
Trap with III shaped bars: unfractionated heparin binds antithrombin III
Trapped throm-beaver and foX: the unfractionated heparin-antithrombin III complex irreversibly inactivates thrombin and factor Xa

Ivy: administer IV heparin in the setting of an acute DVT, PE, or MI
Heparin only prevents further clot formation, does not break down clot
Hunting at the iliofemoral river: heparin can be used for deep vein thrombosis (DVT) prophylaxis (iliac, femoral, popliteal)
Beaver dam on the iliofemoral river: heparin can be used for acute treatment of deep vein thrombosis (DVT)
Lung shaped tree: pulmonary arterial tree
Bird’s nest on ischemic, leafless branch: heparin can be used for prophylaxis and acute treatment of pulmonary embolism (PE)
Broken heart strings: heparin is used in the setting of an acute MI

Birdwatching father: monitor PTT to assess unfractionated heparin level
Activated partial thromboplastin time (PTT)
Woodpecker inside treetrunk: PTT measures the function of the intrinsic pathway of the coagulation cascade

Hitting four clay plates: antibodies against heparin bound to platelet factor 4 cause heparin induced thrombocytopenia (HIT)
Broken plates: heparin can cause thrombocytopenia, but increased thrombosis via platelet activation
Throm-beaver dam around broken plates: HIT results in paradoxical thrombosis in the setting of thrombocytopenia
Depleted mineral mine: heparin can cause hypoaldosteronism (a mineralocorticoid)
Big K: heparin induced hypoaldosteronism (Type 4 RTA) causes hyperkalemia
Porous termite damage: heparin can cause osteoporosis

Protected area deterring the hunter: protamine sulfate reverses the anticoagulant effect of unfractionated heparin (less effective for LMWH and fondaparinux)
Protamine sulfate is a positively charged molecule that binds to unfractionated heparin (negatively charged)

Heppy hunter daughter inside: low molecular weight heparin (LMWH) (-parin suffix), not as well reversed by protamine sulfate
Trap with III: LMWH binds antithrombin III
FoX in small trap: the LMWH-antithrombin complex inhibits factor Xa with less of an effect on thrombin


Long tapering flag: LMWH has a prolonged half-life, less frequent dosing, thus can be given at home. Also safer, not PTT
Heppy pregnant hunter: heparin is safe in pregnancy
Intact clay plates: LMWH is less likely to cause HIT
Decay flag breaking a kidney shaped rock: renal insufficiency prolongs the half-life of LMWH (unfractionated eliminated by liver)

Fido with a pair of foXes: fondaparinux
Fido with two cages: fondaparinux binds antithrombin III with higher specificity than LMWH
FoX in small trap: the fondaparinux-antithrombin complex inhibits factor Xa with less of an effect on thrombin
Fido can't pick up gun: fondaparinux has the lowest risk of HIT
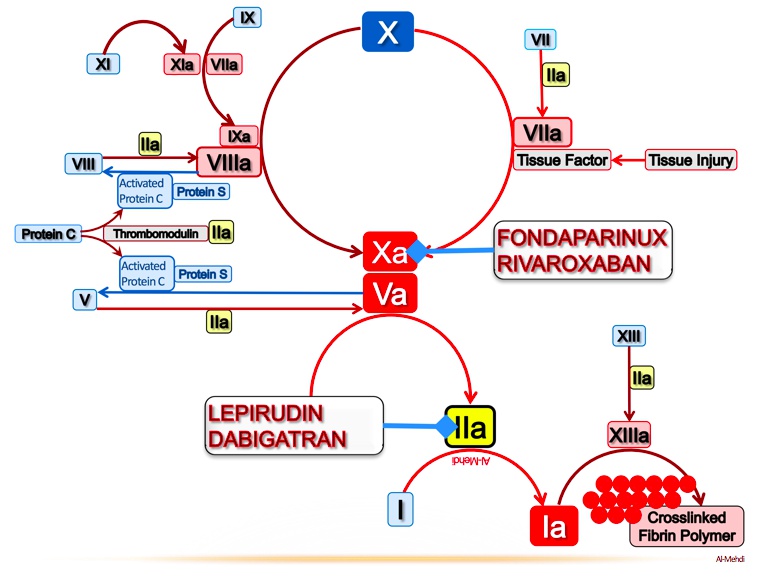

No intRUDIN: bivaliRUDIN is a direct thrombin inhibitor
Big GATOR: arGATROban and dabiGATRAN are direct thrombin inhibitors
Intrudin’ gator directly eating the throm-beaver: use direct thrombin inhibitors (argatroban, dabigatran, bivalirudin) in HIT


Banned foXes: direct factor Xa inhibitors rivaroXaBAN and apiXaBAN
Directly grabbing foX: factor Xa inhibitors bind directly
Open mouth: factor Xa inhibitors are oral medications
Irregularly irregular TV signal: direct Xa inhibitors are used for long term anticoagulation in atrial fibrillation

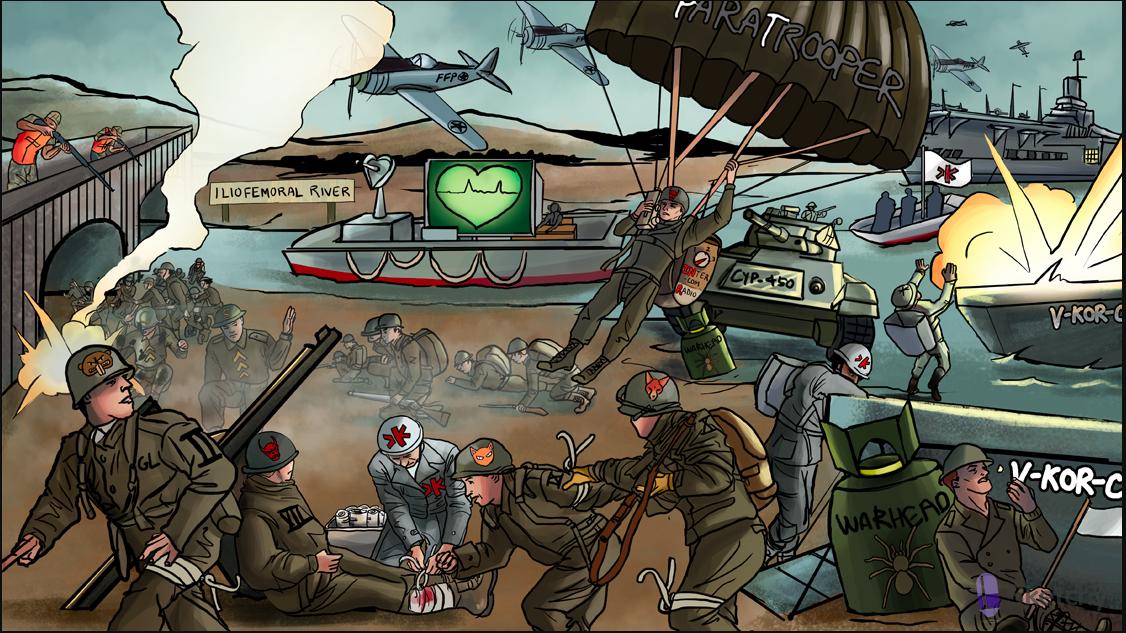
Warfarin

Vit K medic stops bleeding: vitamin K is a cofactor for the enzymatic activation of clotting factors
Vit K medic applies gamma-shaped bandage: vitamin K promotes gamma carboxylation of coagulation factors II, VII, IX, X
GL: gamma carboxylation occurs at the glutamic acid residue on factors II, VII, IX, X
Throm-beaver with II shaped teeth: factor II (thrombin)
Seven deadly sins devil: factor VII
Nine lives cat: factor IX
FoX: factor X
Corporal: vitamin K promotes gamma carboxylation of proteins C
Sergeant: vitamin K promotes gamma carboxylation of proteins S
Corporal and Sergeant hold their troops back: proteins C and S are anticoagulant factors
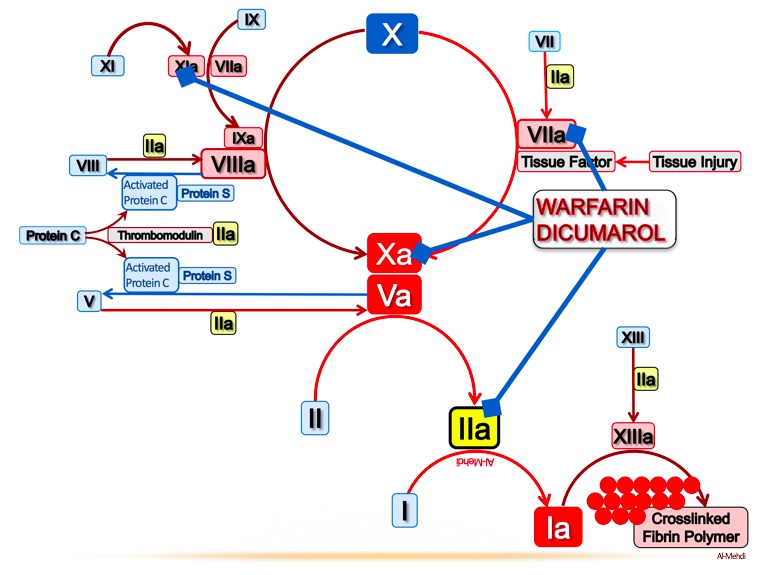
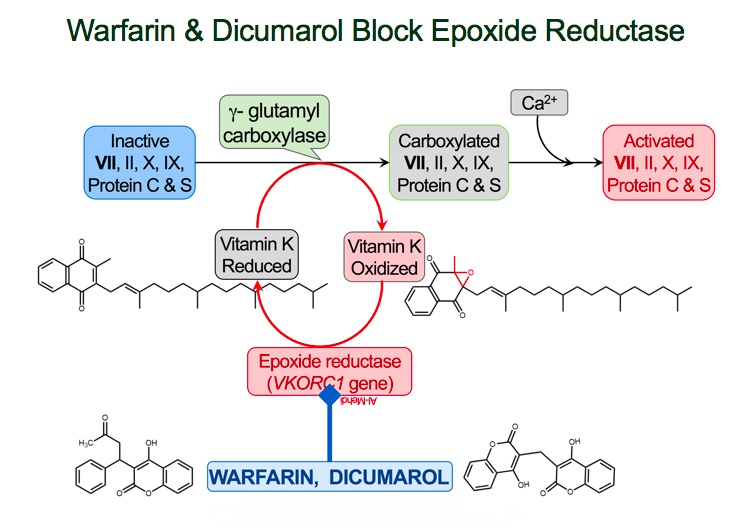

V-KOR supply boat: vitamin K epoxide reductase (VKOR) converts vitamin K epoxide (inactive) into vitamin K (active)



Warhead destroying V-KOR supply boat: warfarin inhibits vitamin K epoxide reductase (VKOR)
Incapacitated Vit K medic: inhibition of VKOR prevents activation of Vit K
Wounded VII soldier: factor VII is the first clotting factor to be reduced when starting warfarin
Delayed warhead detonation: warfarin’s onset of action is 8-12 hours, not immediate
Long tapering flag: long half-life
Open mouth: oral administration



ParaTrooper: monitor warfarin activity with prothrombin time (PT)
Extrinsically parachuting in: PT is a measure of the function of the extrinsic coagulation pathway
Parachuting VII soldier: factor VII is the main component of the extrinsic coagulation pathway
INtercom Radio: the international normalized ratio (INR) is also used to measure warfarin activity
Goal INR 2-3 for prevention and treatment of thrombosis

Irregularly irregular signal: warfarin is used for long term anticoagulation in atrial fibrillation. Abnormal heart can increase thrombus formation
Warship protecting the iliofemoral river: warfarin can be used for DVT prophylaxis

Teratogenic tarantula: warfarin can cause hemorrhage and abnormal bone formation in utero
CYP-450 chrome tank crushing warhead: warfarin is a substrate of cytochrome P-450 (drugs increase CYP activation increase warfarin metabolism)
Soldiers charging past the injured corporal: the anticoagulant protein C is reduced early in warfarin therapy, resulting in a hypercoagulable state in early days
Black soot on corporal: warfarin induced skin necrosis due to early hypercoagulable state
Heparin hunters patrolling the bridge: coadministration of heparin when starting warfarin therapy prevents the early hypercoagulable state (heparin bridge)

Distant Vit K medic reinforcements: warfarin anticoagulation can be reversed with vitamin K (delayed effect)
FFP Fighter Pilot: fresh frozen plasma (FFP) provides coagulation factors for immediate reversal of warfarin anticoagulation
Antiplatelet
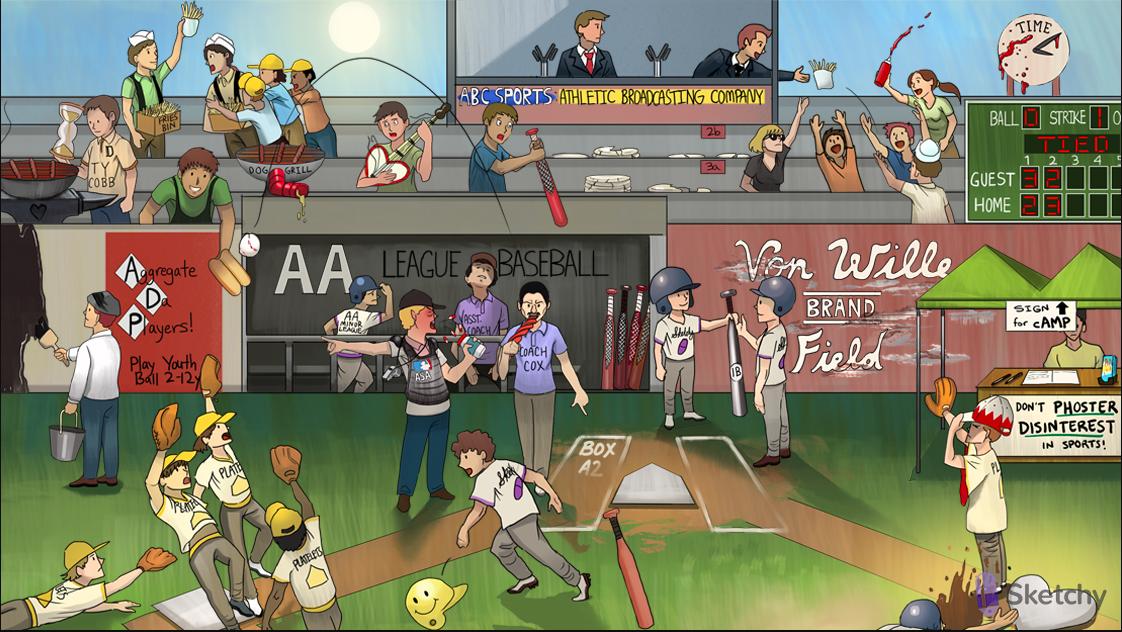

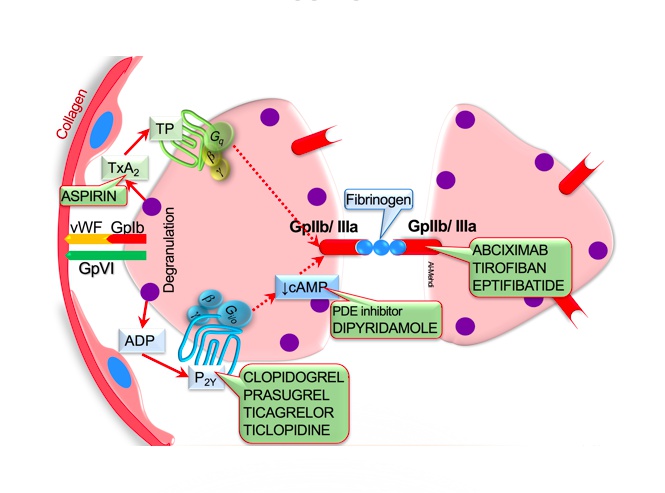
Adhesion to endothelium:
Peeling Von Wille brand Field: damaged vascular epithelium exposes collagen and von Willebrand factor
Holding 1b bat: binding of von Willebrand factor to GP1b receptors activates platelets
Secretion:
Home plate: activated platelet degranulation
Aggregated players: platelet degranulation releases ADP, 5-HT, and TXA2, stimulating platelet aggregation
Aggregate Da Players! Play Youth ball 2-12y: adenosine diphosphate (ADP) binds to the P2-Y12 receptor on platelets causing aggregation
Thrown happy face helmet: platelet degranulation releases serotonin (5-HT), causing platelet aggregation and vasoconstriction
Batter’s box: thromboxane A2 (TXA2) is synthesized by COX-1, causes platelets to change shape, release granules
Aggregation:
Fries: fibrinogen
Crowd of spectators from seats 2b-3a: platelet surface receptor GP IIb/IIIa binds fibrinogen to promote platelet aggregation
Seats 2b-3a: platelet surface receptor GP IIb/IIIa (binds fibrinogen)

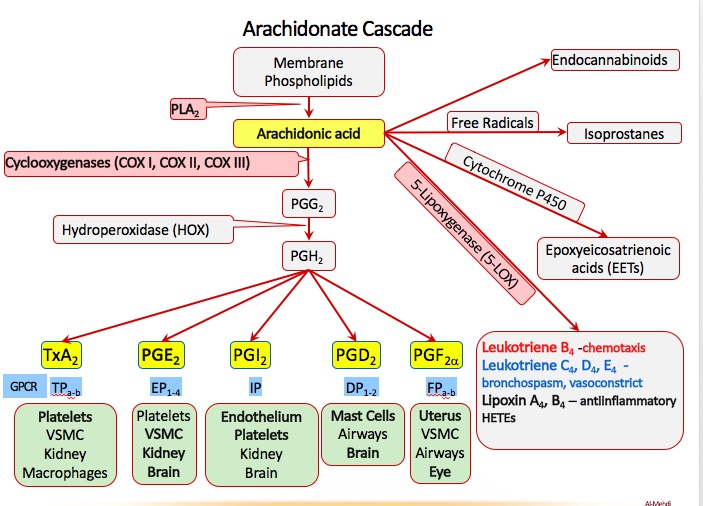
Head Coach Cox: cyclooxygenase 1 (COX-1) synthesizes prostanoids (e.g. prostaglandins, TXA2) within platelets. Always on
Sleeping assistant coach: COX-2 expression induced by inflammation
AA minor league dugout: COX-1 synthesizes TXA2 from the precursor molecule arachidonic acid (AA)
Coach Cox twisting hat: TXA2 (synthesized by COX-1) causes vasoconstriction

ASA umpire: aspirin (ASA)
Acetyl-whistle: aspirin irreversibly acetylates COX-1 and COX2. Whistle and done
ASA umpire ejecting the coaches: aspirin irreversibly inhibits COX-1 and COX-2
ASA umpire chewing tablets: give chewable aspirin in setting of acute MI
Swollen ASA umpire: aspirin “pseudo-allergy” due to excess leukotriene synthesis (use clopidogrel instead)
Ketchup time: antiplatelet therapy increases bleeding time (measure of platelet function)


Hot dog grill: thienopyridines with -“grel” suffix (e.g. clopidogrel, ticagrelor, prasugrel) are ADP receptor inhibitors
Grill man catching the baseball: thienopyridines (e.g. clopidogrel) irreversibly bind to the P2Y12 ADP receptor preventing platelet aggregation


Greasy grill pipe: antiplatelet agents (e.g. aspirin, ADP receptor inhibitors) reduce cardiovascular events in patients with peripheral artery disease
Angina anvil: antiplatelet agents (e.g. aspirin, ADP receptor inhibitors) reduce cardiovascular events in patients with coronary artery disease
Broken heart strings: use antiplatelet therapy (e.g. aspirin, ADP receptor inhibitors) in the setting of MI and other acute coronary syndromes
Black paint stroke: antiplatelet therapy (i.e. aspirin and ADP receptor inhibitors) prevents ischemic stroke in patients with atherosclerosis and known cerebrovascular disease
Corked bat: dual antiplatelet therapy (i.e. aspirin and ADP receptor inhibitors) prevents coronary stent thrombosis

Ty Cobb: ticlopidine (an ADP receptor inhibitor)
Falling granules: ticlopidine can cause granulocytopenia
Ketchup time: antiplatelet therapy increases bleeding time (measure of platelet function)

ABC sportscaster grabbing fries: abciximab blocks the GP IIb/IIIa receptor preventing platelet aggregation
Antibody-shaped microphones: abciximab is a monoclonal IgG antibody
Tied game: eptifibatide and tirofiban block the GP IIb/IIIa receptor to prevent platelet aggregation
Broken plates: GP IIb/IIIa inhibitors can cause thrombocytopenia
Ketchup time: antiplatelet therapy increases bleeding time (measure of platelet function)


Don’t phoster disinterest: phosphodiesterase inhibitors (e.g. dipyridamole, cilostazol)
Phosphodiesterase inhibitors increase cAMP, impairing platelet function
Two pyramids: dipyridamole (an antiplatelet phosphodiesterase inhibitor)
Lost the ball: cilostazol (an antiplatelet phosphodiesterase inhibitor)
Dilated red sleeves: cilostazol causes arterial vasodilation
Dirt clods hitting leg: cilostazol treats symptoms of claudication due to peripheral artery disease
Dilated red crown: cilostazol causes coronary artery vasodilation
Stolen heart base: cilostazol can cause coronary steal, divert blood away from stenotic areas

Thrombolytics
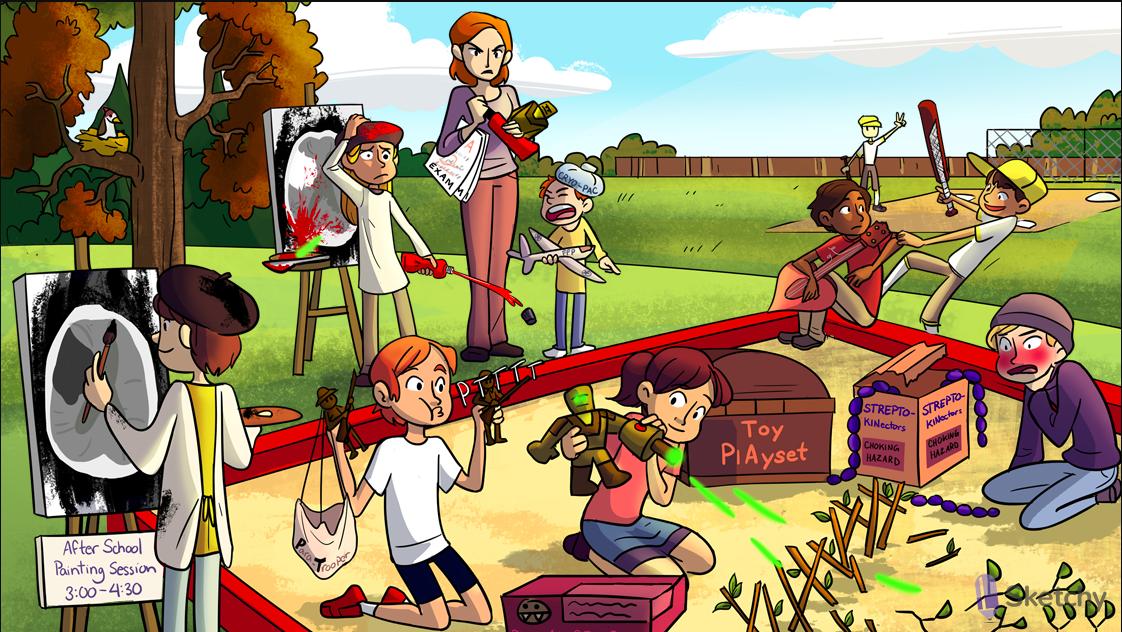

Mesh of sticks: fibrin clot
toy playset: -teplase suffix of recombinant forms of tPA (e.g. alteplase, reteplase, tenecteplase)
Strepto-kinectors: streptokinase (a fibrinolytic)
Purple sphere chain: streptokinase is synthesized by streptococci
Plasma general: plasminogen
Plasma general activation: plasminogen is converted to plasmin by TPA and streptokinase
Plasma beams destroying wall: plasmin degrades fibrin clots

End pathway affected, thus:
Fibrinolytics prolong PT
Fibrinolytics prolong PTT
D-shaped twigs: D-dimer is a fibrin degradation product formed from clot lysis: excessive clot formation is followed by clot breakdown.

Black paint stroke: IV fibrinolytics may be used in the setting of an ischemic stroke
Administer IV fibrinolytics within 3-4.5 hours of ischemic stroke symptoms
Bird’s nest on ischemic branch: IV fibrinolytics can be used for acute treatment of severe DVT and PE
Broken heart strings: fibrinolytics may be used in the acute management of MI
Corked bat: percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) is the preferred reperfusion option in acute STEMI
Calling for 2: perform PCI ideally within 2 hours in setting of acute STEMI

Red paint stroke: hemorrhagic stroke is a side effect of fibrinolytic therapy
Traumatic plasma beam: recent head trauma is a contraindication for fibrinolytic therapy
Red palette knife: recent intracranial surgery is a contraindication for fibrinolytic therapy
High pressure paint tube: severe hypertension is a contraindication for fibrinolytic therapy
White area on CT indicates cerebral hemorrhage - a contraindication for fibrinolytic therapy
Choking hazard: streptokinase can cause allergic reaction and even anaphylaxis
increased risk for maternal hemorrhage, avoid in pregnancy

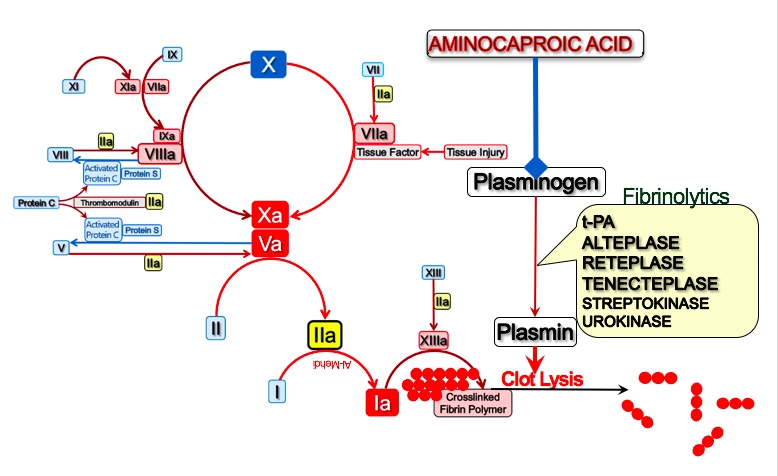
Cap on paint tube: aminocaproic acid can be used to reverse fibrinolysis
Plasma general competitively tucked under arm: aminocaproic acid competitively inhibits plasminogen activation
Exams: tranexamic acid can be used to reverse TPA
Fighter pilot: FFP can be used to reverse coagulopathy
Cryo ice pack: cryoprecipitate can be used to reverse coagulopathy

Dyslipidemia
Statins
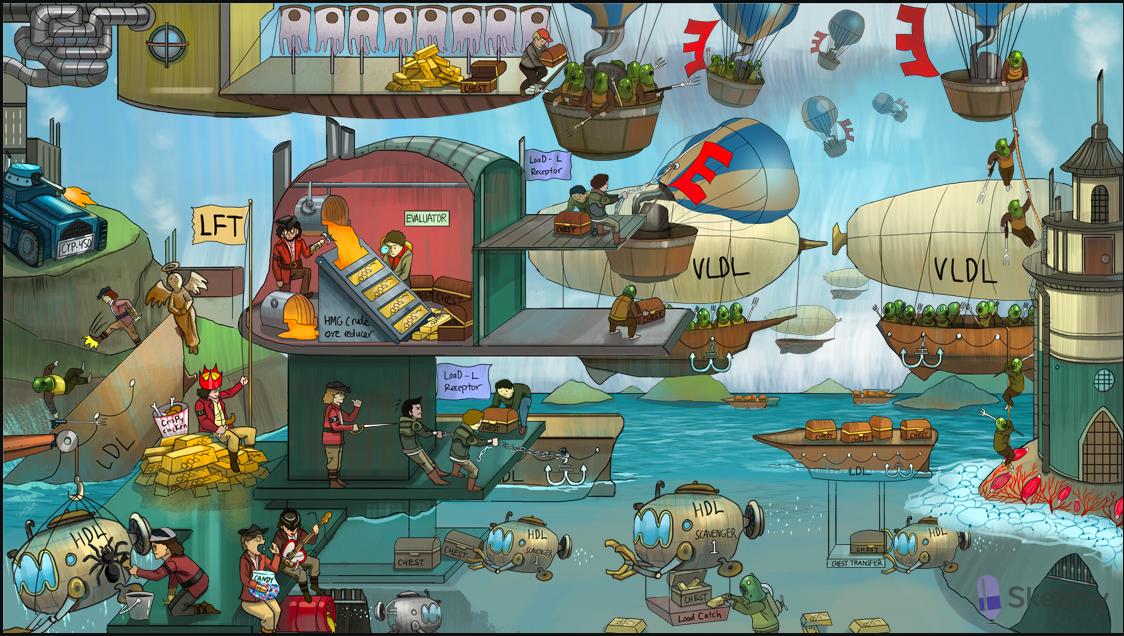

Intestinal airbase: lumen of the small intestine (site of free fatty acid and cholesterol absorption)
Gold bars: cholesterol
Chest: cholesteryl ester
Cholesterol esters are packaged into the interior of chylomicrons (intestinal cell)
Tridents: triglycerides
Trident passengers: triglycerides make up most of the chylomicron
E-shaped flag: chylomicrons contain surface apolipoproteins A, B, C and E
Chylomicrons deliver triglycerides from the intestines to peripheral tissues
Lipo-Port Lighthouse: lipoprotein lipase (LPL)
Trident passengers disembarking at Lipo-Port Lighthouse: triglycerides in chylomicrons are hydrolyzed by LPL, releasing free fatty acids
Muscle shells: free fatty acids can be used for energy by heart and skeletal muscle
Adipocyte sea foam: free fatty acids can be converted back into triglycerides and stored in adipose tissue
Hot air balloon: chylomicron
Chylomicron remnants return to the liver
Liver station: import and export of lipoprotein transporters
LoaD L receptor: LDL receptor
Pulling in E-shaped flag: LDL receptor binds to ApoE and transports chylomicron remnant into liver via endocytosis
Cholesterol from chylomicron remnants used by the liver

HMG crude ore reducer: HMG CoA reductase synthesizes cholesterol in the liver
Evaluator: first intermediate in cholesterol synthesis is mevalonic acid

Very-low-density airship: very low density lipoprotein (VLDL)
Trident passengers: triglycerides make up most (60%) of the VLDL
Cholesterol esters are packaged into the interior of VLDLs (hepatocyte)
B-shaped anchor: apolipoprotein B100 is found on “bad cholesterol” (LDL and VLDL)
B-shaped anchor: apolipoprotein B100 is found on “bad cholesterol” (LDL and VLDL)
VLDLs deliver triglycerides from the liver to peripheral tissues
Trident passengers disembarking at Lipo-Port Lighthouse: triglycerides in VLDLs are hydrolyzed by LPL, releasing free fatty acids
Low-density ship: low density lipoprotein (LDL formed as VLDLs lose triglycerides via LPL and hepatic lipase)
Chest cargo: LDLs contain a core of cholesterol esters
LDLs deliver cholesterol to peripheral tissues expressing LDL receptors
Pulling in B-shaped anchor: LDL receptor binds ApoB and transports LDL particle into liver via endocytosis

High-density submarine: high density lipoprotein (HDL)
Deep sea diver collecting gold bars: HDL extracts cholesterol from peripheral tissues
Load Catch: lecithin:cholesterol acyltransferase (LCAT) converts free cholesterol into cholesterol esters for transport by HDL
Loaded submarine: mature HDL particle contains LCAT-generated cholesterol esters
Nascent HDL is secreted by the liver and intestine
Chest Transfer platform: HDL transfers cholesterol esters to LDLs and VLDLs to be transported back to the liver
Scavenger-1 dock: HDL delivers cholesterol esters directly to the liver via scavenger 1 receptor

Steampunk pirate: statins (e.g. simvastatin, atorvastatin, rosuvastatin) (most effect at liver, high first past effects)
knocking over HMG crude ore reducer: statins inhibit HMG CoA reductase
Statin-punk threatening workers to pull in LDL ship: statins cause increased LDL receptor expression on hepatocytes, clearing LDLs from circulation
Statins act through competitive inhibition of HMG-CoA reductase, preventing conversion of HMG-CoA to mevalonic acid (the rate-limiting step in cholesterol biosynthesis). Decreased liver cholesterol synthesis leads to increased hepatic clearance of LDL from the circulation by LDL receptors. After mediating endocytosis of LDL particles, the LDL receptors are returned to the cell surface for reuse (receptor recycling); LDL is digested and used for metabolic purposes. This increase in LDL receptor recycling allows intrahepatic cholesterol levels to remain at normal levels while blood levels are kept low.

Sinking LDL ship: statins are most effective drugs for lowering LDLs (30-60%)
Statin-punk kicking off trident passenger: statins can lower triglycerides (mild effect)
Raised HDL submarine: statins can increase HDL (mild effect)
Gold bar plunder: hypercholesterolemia (LDL) treated with lifestyle modification and statins (first-line agent)
Guardian angel: statins improve survival (MOST EFFECTIVE lipid-lowering drug for preventing future cardiovascular events)
Yellow-filled coronary crown: statins are the only lipid-lowering drug consistently proven to reduce risk of atherosclerotic heart disease
Broken heart strings: statin therapy initiated in setting of MI and other acute coronary syndromes (ACS)
Candy jar: statins reduce risk of cardiovascular events and mortality in high-risk diabetics
Clogged pipe: statins reduce risk of cardiovascular events and mortality in patients with peripheral artery disease
Black paint stroke: statins reduce risk of future vascular events in patients with history of TIA or stroke

Tarantula: statins may be teratogenic
Bite out of crispy chicken: statins can cause myopathy weeks to months after starting therapy (muscle weakness/soreness)
Crispy chiKen bucket: statins can cause elevations in serum CK (myopathy)
Raised LFT flag: mild elevations in liver function tests (LTFs) are common (reversible with discontinuation of statin)
chrome tank: all statins except for pravastatin are metabolized by cytochrome p450 (CYP-450) in the liver
Cholestyramine
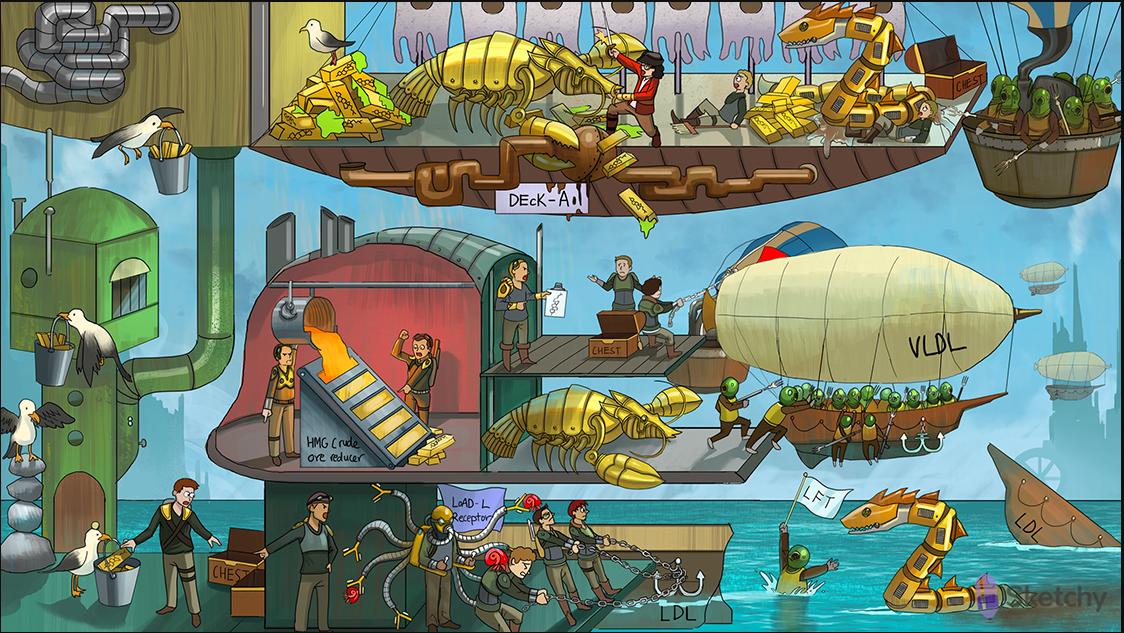

Liver station worker loading sea“gall”s: the liver metabolizes cholesterol into bile acids (conjugated to become water soluble)
Sea”gall”s exiting liver station: bile acids (derived from cholesterol) are secreted from the liver into the biliary tract
Sea“gall” droppings: bile acids (derived from cholesterol) are released into the intestinal lumen
Sea”gall” droppings swept back to liver station: normally 95% of bile acids in the ileum are recycled back to the liver through enterohepatic circulation

Cho“lobster”amine: bile acid binding resins (e.g. cholestyramine, colestipol, colesevelam)
Disabled sea”gall” droppings sweeper: bile acid resins prevent recycling of bile acids to the liver
Activating HMG crude ore reducer: resins interrupt bile acid recycling, causing HMG CoA reductase to synthesize more cholesterol
Activating LoaD-L receptor: resins interrupt bile acid recycling, causing upregulation of LDL receptors and uptake of circulating LDL

Cho“lobster”amine scaring airship away: bile acid resins (e.g. cholestyramine, colestipol, colesevelam) cause hypertriglyceridemia (increased VLDLs)
Sea“gall” stones: bile acid resins (e.g. cholestyramine, colestipol, colesevelam) can cause cholesterol gallstones
Cho“lobster”amine clamping pipe: bile acid resins can cause constipation and bloating
DEcK-A: bile acid resins impair absorption of fat-soluble vitamins A, D, E and K
Cho“lobster”amine clashing with statin-punk: bile acid resins decrease statin absorption (must be given 4hrs apart)
synergistic response: statin and cholestyramine

Z-shaped eel: ezetimibe
Z-shaped eel blocking gold delivery at intestinal airbase: ezetimibe blocks intestinal absorption of cholesterol]
Hot air balloon: chylomicron
Empty chest delivery: ezetimibe restricts liver’s access to exogenous cholesterol
Activating HMG crude ore reducer: ezetimibe blocks intestinal cholesterol absorption, causing HMG CoA reductase to synthesize more cholesterol
Sunken LDL ship: ezetimibe blocks intestinal cholesterol absorption, causing upregulation of LDL receptors and uptake of circulating LDL

Oily water: ezetimibe may cause diarrhea/steatorrhea
Raised LFT flag: ezetimibe may cause increased liver function tests (LFTs)

Steam-ctopus man: evolocamab is a PCSK9 inhibitor
Pesky “9” crabs inhibiting Load L receptor workers: PCSK9 normally causes degradation of LDL receptors
Octopus antibody-shaped claws: many PCSK9 inhibitors (evolocumab) are antibodies
Steam-octopus man removing pesky crabs: evolucamab binds PCKS9 and prevents degradation of LDL receptors, increasing uptake of circulating LDL
Fibrates
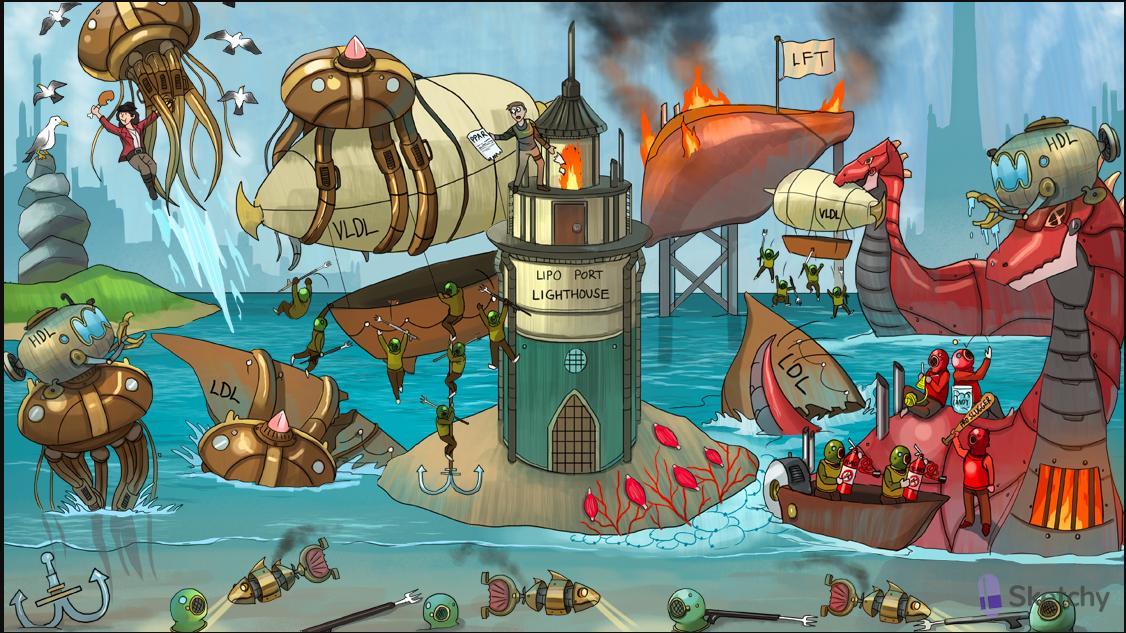

Lipo-Port Lighthouse: lipoprotein lipase (LPL)
Trident passengers disembarking at Lipo-Port Lighthouse: triglycerides in VLDLs are hydrolyzed by LPL, releasing free fatty acids
Muscle shells: free fatty acids can be used for energy by heart and skeletal muscle
Adipocyte sea foam: free fatty acids can be converted back into triglycerides and stored in adipose tissue
Gem-fibrozil jellyfish: fibrates (e.g. gemfibrozil and fenofibrate)
newsPPAR: PPAR-alpha
Lighthouse keeper lighting newsPPAR signal: fibrates activate PPAR-alpha to upregulate LPL

Trident passengers escape airship: fibrates decrease serum triglycerides (increase hydrolysis of VLDL and chylomicron triglycerides via LPL)
Gem-fibrozil jellyfish takes down airship: fibrates decrease serum VLDL 35-50% (stimulate LPL and reduce hepatic VLDL secretion)
Gem-fibrozil jellyfish sinks ship: fibrates decrease serum LDL (mild effect) by reducing hepatic VLDL production
Elevated high-density submarine: fibrates increase serum HDL (mild effect)

Elevated statin-punk eating crispy chicken: fibrates combined with statins increases risk of myopathy
Sea“gall” stones: fibrates can cause cholesterol gallstones
Niacin

Loch Niacin monster: niacin (aka vitamin B3), normally incorporated in NAD
Elevated high-density submarine: niacin is MOST EFFECTIVE drug for increasing serum HDL (30%)
Trident passengers escape airship: niacin decreases serum triglycerides (reduces hepatic VLDL secretion)
Loch Niacin monster takes down airship: niacin decreases serum VLDL (reduced hepatic secretion)
Loch Niacin monster sinks ship: niacin decreases serum LDL (mild effect) by lowering VLDL

Red fiery furnace: niacin can cause cutaneous flushing and warmth
Pro-slugger bat: prostaglandins (cause flushing)
Fire extinguisher: NSAIDs (including aspirin) can be used to prevent flushing from niacin
Elevated candy: niacin can cause hyperglycemia
Yellow knitting needles: niacin can cause hyperuricemia (precipitate gout)
Raised LFT flag: niacin can cause elevated liver function tests (LFTs) leading to severe hepatotoxicity (requires monitoring)
Fish Oil

Omega fish leaking oil with omega tails: fish oils (omega-3 fatty acids)
Sunken tridents: fish oil can lower serum triglycerides (by decreasing VLDL and apoB production)
Anti-inflammatory
NSAIDS

PLA2y ball: phospholipase A2 (PLA2) hydrolyzes arachidonic acid from the cell membrane

AA league: arachidonic acid (precursor molecule to prostanoids and leukotrienes
Head coach Cox: cyclooxygenase-1 (COX-1) is constitutively expressed
Assistant coach: cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) expression is induced by inflammation
Assistant coach in endothelial dugout: COX-2 is expressed in vascular endothelial and smooth muscle cells
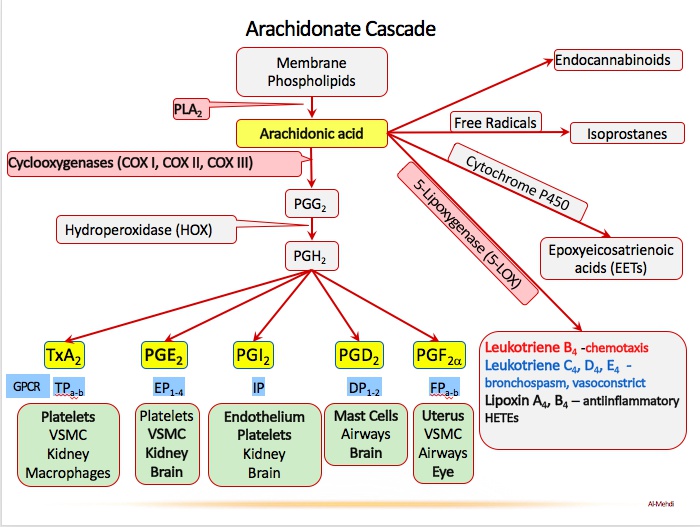

Batter’s box: thromboxane A2 (TXA2) is synthesized by COX-1
Twisted red hat: TXA2 (synthesized by COX-1) causes vasoconstriction
Pro-slugger bat: prostaglandins
Pro-slugger protecting catcher with gastrointestinal pads: COX-1 synthesizes gastric
cytoprotective prostaglandin (gastric mucous secretion)


Pro-cycler pitching machine: prostacyclin (PGI2) is synthesized by COX-2
Pro-cycler’s dilated red barrel: PGI2 causes vasodilation
Pro-cycler dispersing the plates: PGI2 inhibits platelet aggregation
Pro-sluggers at the afferent tunnel: COX-1 and COX-2 synthesize prostaglandins that dilate the afferent arteriole
Pro-slugger activating the sprinkler: COX-2 synthesizes prostaglandins that increase
vascular permeability
Pro-slugger in pain: COX-2 synthesizes prostaglandins that increase pain sensitivity
Pro-slugger with flaming head: COX-2 synthesizes prostaglandins that induce fever


Anti-inflammatory fire extinguisher: non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs)
Head coach and assistant coach doused by fire extinguisher: NSAIDs reversibly inhibit both COX-1 and COX-2

BLAC sox: diclofenac and ketorolac (NSAIDs)
INDIGO sox: indomethacin (NSAID)
SOX CAM: meloxicam and piroxicam (NSAIDs)
ApPROXimately 110 mph: naproxen (NSAID)
ASA umpire: aspirin
Celebrating catcher drenching the assistant coach: celecoxib is a selective COX-2 inhibitor
acetaminophen

Ketchup on clock: inhibition of COX-1 by NSAIDs can prolong bleeding time
kidney:
Constricted proximal end of hose: NSAIDs cause afferent arteriole vasoconstriction, decreasing GFR
Bursting from high pressure: NSAIDs can increase blood pressure due to COX inhibition in the kidney, decreasing sodium excretion
Baseball-filled kidney containers: NSAIDs can cause acute interstitial nephritis
Sloughing off cleat spikes: NSAIDs can cause renal papillary necrosis (sloughing of renal papillae)
Elevated “lift-ium” balloons: NSAIDs can increase serum lithium concentrations
Depleted mineral mine: NSAIDs can cause hypoaldosteronism (decreased mineralocorticoids)
Big K: NSAID induced hypoaldosteronism can cause hyperkalemia. Type 4 RTA
GI:
Ketchup on the gastrointestinal pads: inhibition of COX-1 by NSAIDs can cause GI bleeding
Burned hole in the gastrointestinal pads: inhibition of COX-1 by NSAIDs can cause gastric inflammation, erosions, and ulceration
Bone:
Plastic Bone-shaped balloon: NSAIDs (indomethacin most commonly) can cause aplastic anemia

ASA umpire: aspirin
ASA umpire ejecting the coaches: aspirin irreversibly inhibits COX-1 and COX-2
Acetylation whistle: aspirin acetylates COX-1 and COX-2 resulting in irreversible inhibition

Child in Kawasaki’s ATV: aspirin is useful in Kawasaki disease (the most common vasculitis syndrome of childhood)

Rays: Aspirin use in children can lead to development of Reye’s syndrome (rapidly
progressive encephalopathy with hepatic dysfunction
Tissue box: Reye’s syndrome occurs when a child is given aspirin in the setting of a viral illnes
Brain hat: Reye’s syndrome encephalopathy (e.g. confusion, seizure, coma)
Fat liver spot: Reye’s syndrome hepatic dysfunction (e.g. hepatic steatosis, hepatomegaly)

Mudpile: aspirin toxicity can cause an anion gap metabolic acidosis (S in MUDPILES)
Blowing “OH-” bubbles: aspirin causes a respiratory alkalosis, stimulate respiratory center directly
Tin cans: aspirin can cause tinnitus

Charcoal lines: activated charcoal can be used to absorb aspirin in setting of acute toxicity
Bases loaded hose: alkalinization of the serum and urine with a basic solution (e.g. sodium bicarbonate) increases the renal excretion of aspirin (aspirin is acid)

Fire extinguisher behind cracked kidney-shaped glass: minimize NSAID use in patients at risk for acute kidney injury
Exiting pregnant lady: avoid NSAIDs in 3rd trimester due to risk of premature closure of ductus arteriosus (highest risk with indomethacin and ibuprofen)

Celebrating catcher drenching the assistant coach: celecoxib is a selective COX-2 inhibitor
Clean gastrointestinal pads: celecoxib has a reduced ulcer and bleeding risk by avoiding COX-1 inihibtion. Does not inhibit platelet aggregation

Rotten sulfur eggs: celecoxib is a sulfa drug, allergy
Thrombus ice cubes: celecoxib may increase the risk of ischemic cardiovascular disease. Reduced synthesis of prostacyclin for platelet inhibition

Icy medicine spray on assistant coach: acetaminophen inhibits COX-2, acting as an antipyretic and analgesic (not anti-inflammatory)
Goat scared by the icy-medicine: toxic levels of acetaminophen deplete glutathione in the liver (inactivates the toxic metabolite: NAPQI)
Liver spot: acetaminophen causes hepatotoxicity (via the toxic metabolite: NAPQI)

N-flower seeds: n-acetylcysteine
Goat attracted by N-flower seeds: n-acetylcysteine restores hepatic glutathione stores to treat acetaminophen hepatotoxicity
Charcoal lines: activated charcoal can be used to absorb acetaminophen in setting of acute toxicity
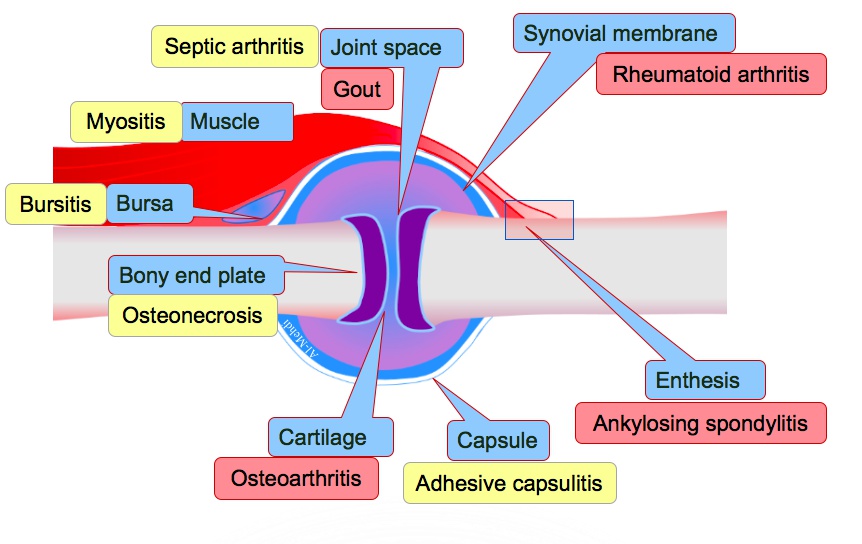
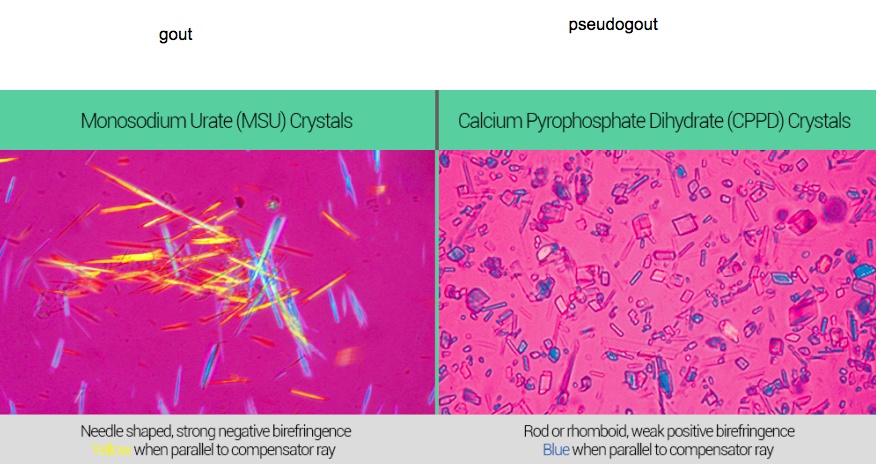
Gout
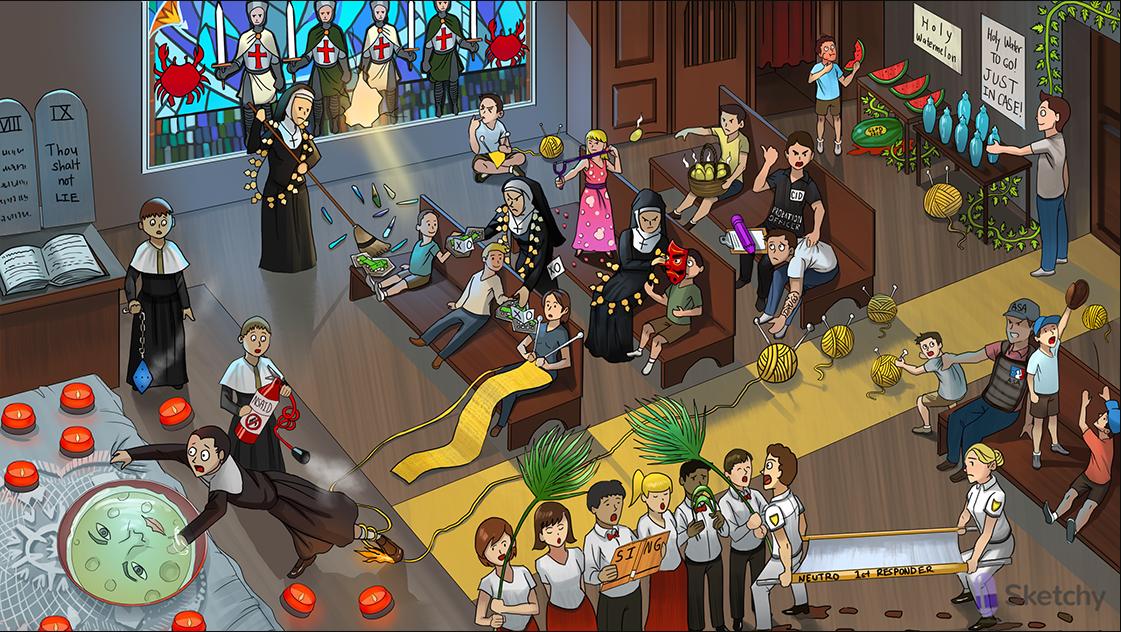

Knitting needles: uric acid crystals
Yellow center aisle: renal tubule
Uric acid yarn in the center aisle: uric acid excretion by kidney
Purine-shaped collection plate: purines (purine metabolism produces uric acid)
Small kid passing XO note: hypoxanthine (purines are converted into hypoxanthine)]
XO love letter: xanthine oxidase (converts hypoxanthine to xanthine)
Larger kid passing XO note: xanthine
XO love letter: xanthine oxidase (converts xanthine to uric acid)


Tripping over yarn: acute gout with inflammation, gout crystals cause PGE production and neutrophil chemotaxis

Fire extinguisher: NSAIDs (e.g. indomethacin) treat acute gout
Moon face: glucocorticoids (e.g. oral prednisone) treat acute gout (Cushing's disease moon face)
Choir sing: colchicine treats acute gout
Spindly palm fronds: spindle apparatus microtubules
Binding palm fronds: colchicine binds intracellular tubulin preventing polymerization of microtubules
First responders blocked by choir: colchicine disrupts the cytoskeleton of neutrophils thereby inhibiting neutrophil migration, phagocytosis, and degranulation

Muddy floor: colchicine can cause diarrhea (brush border epithelium high mitosis rate affected)

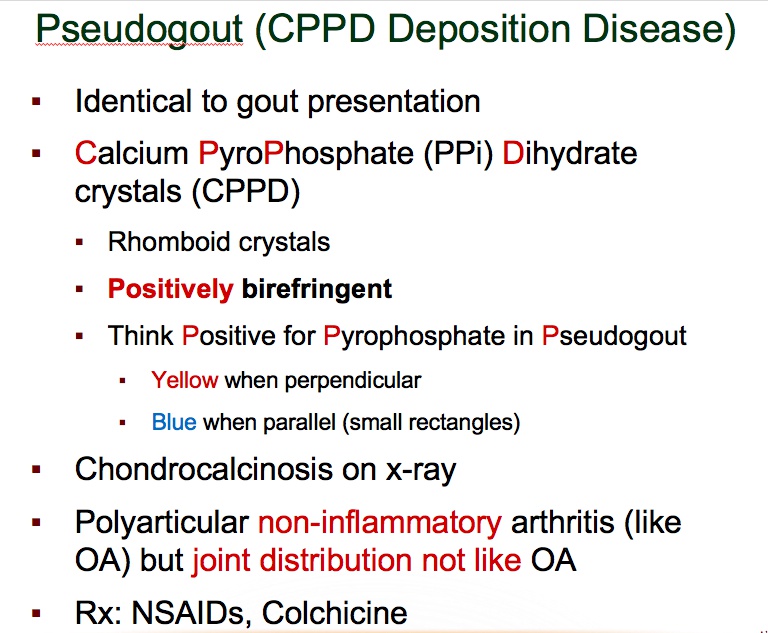
Lying: pseudogout (acute treatment is similar to acute gout - NSAIDs, glucocorticoids, colchicine)
Blue-rhomboid incense holder: pseudogout is positively birefringent (blue under polarized light) and forms rhomboid-shaped crystals

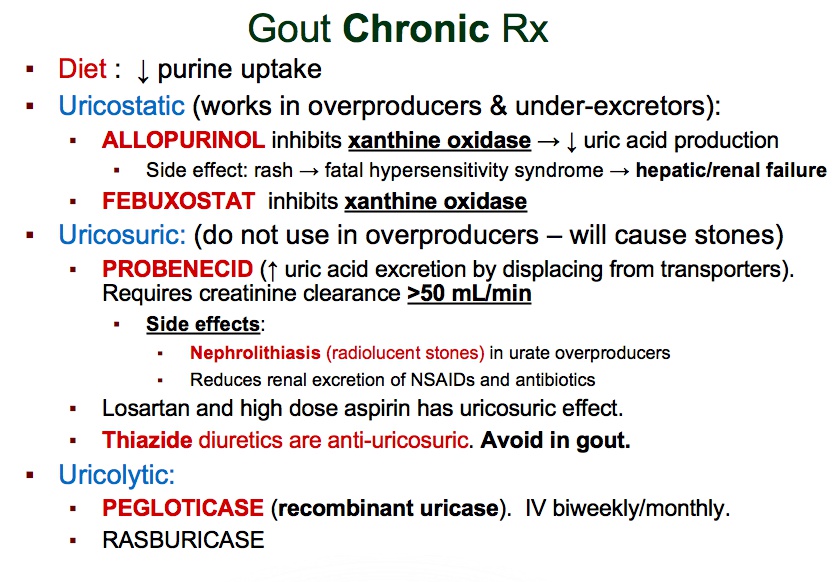
Pure nun: allopurinol manages chronic gout
Nun grabbing XO notes: allopurinol inhibits xanthine oxidase
Stopped XO note: febuxostat (chronic gout therapy) inhibits xanthine oxidase

Shattered cancer crab glass: uric acid crystals can form in tumor lysis syndrome after starting cytotoxic chemotherapy
White T-cell crusaders: tumor lysis syndrome is most common with treatment of lymphoma and acute lymphoblastic leukemia
Nun sweeping crystals: allopurinol prevent uric acid crystal deposition in setting of tumor lysis syndrome
Needle in flesh: Lesch-Nyhan syndrome (associated with hyperuricemia) is managed with allopurinol

Concentrated purine beads: allopurinol inhibits breakdown of purine analogs (e.g. 6- mercaptopurine and azathioprine) increasing risk of toxicity
Sloughed off red mask: allopurinol can cause Stevens-Johnson syndrome
Eo-slingshot granules: eosinophilia
Eosinophilic dress: allopurinol can cause drug reaction with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms (DRESS syndrome)

Probation officer Cid: probenecid (a uricosuric agent) manages chronic gout
Cid’s purple pencil: probenecid prevents renal excretion of penicillin
Preventing punk from grabbing yarn: probenecid decreases renal tubular reabsorption of uric acid
Accumulating yarn and needles: probenecid can increase the risk of renal stone formation due to increased uric acid excretion
"Drugs” tattoo: probenecid can inhibit the excretion of many drugs
Rotten sulfa eggs: probenecid is a sulfa drug


ASA umpire: aspirin
Preventing son from grabbing yarn: aspirin at high doses prevents reabsorption of uric acid
Little ASA umpire catching yarn: aspirin at low doses inhibits uric acid excretion
Do not use aspirin for acute gout treatment

Holy water: pegloticase converts uric acid into water soluble allantoin
“just in case”: pegloticase (recombinant uricase) can be used in chronic gout management
Ivy: pegloticase is administered IV, SE too much
Watermelon with bite: pegloticase can cause hemolysis in G6PD deficiency (bite cells)
Choking kid: pegloticase can cause anaphylaxis

Last updated