31 Congenital Heart Disease
Cyanosis
[_](central vs peripheral cyanosis. 5T's of central cyanosis)..

central cyanosis: seen in congenital heart disease in babies
warm extremities: perfused with warm blood, just not enough O2

5 T's
Tetralogy
Pathogenesis
_..
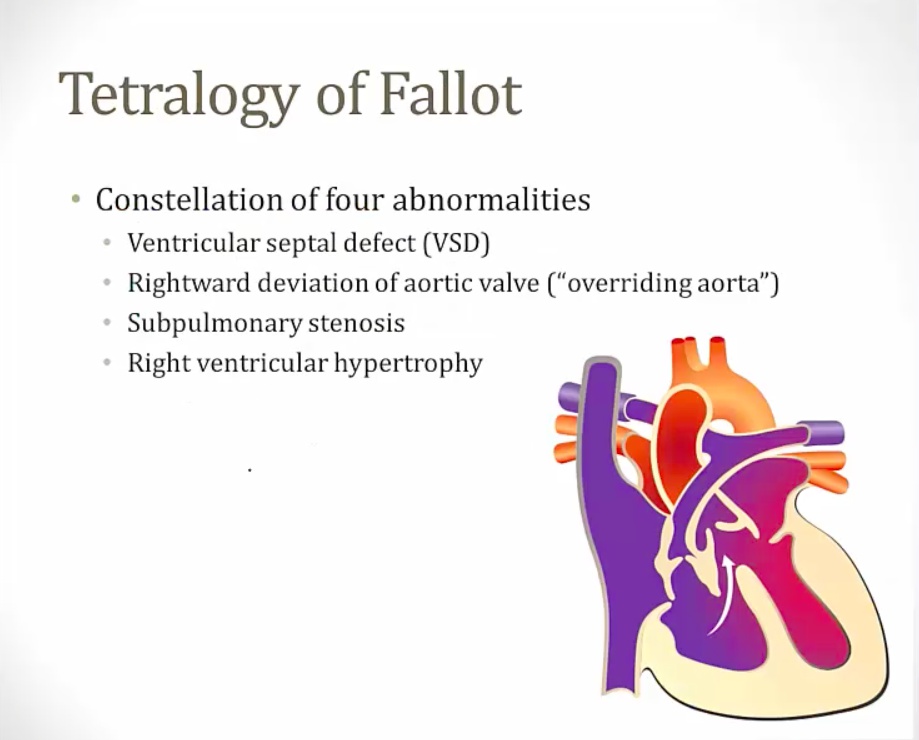
pic: aorta shifted to right, override ventricular septum with VSD, thick RV walls, stenotic PV
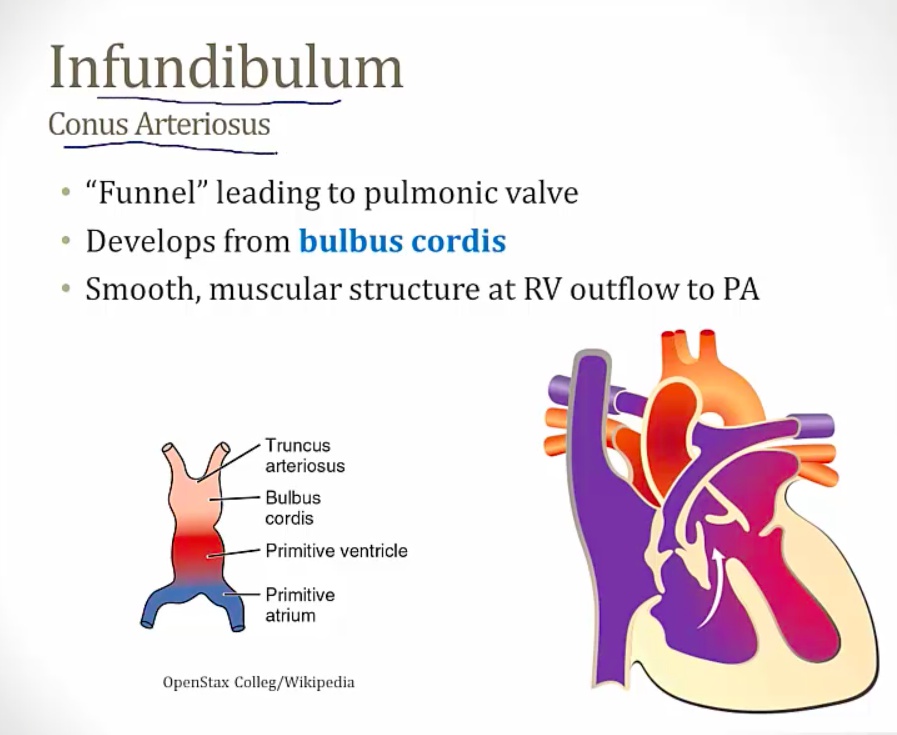
all abnormalities caused by infundibulum/conus arteriosus "monology of fallot"

pic: white infundibulum moving towards RV, dragging aorta with it to cause aorta to override RV, also creating VSD

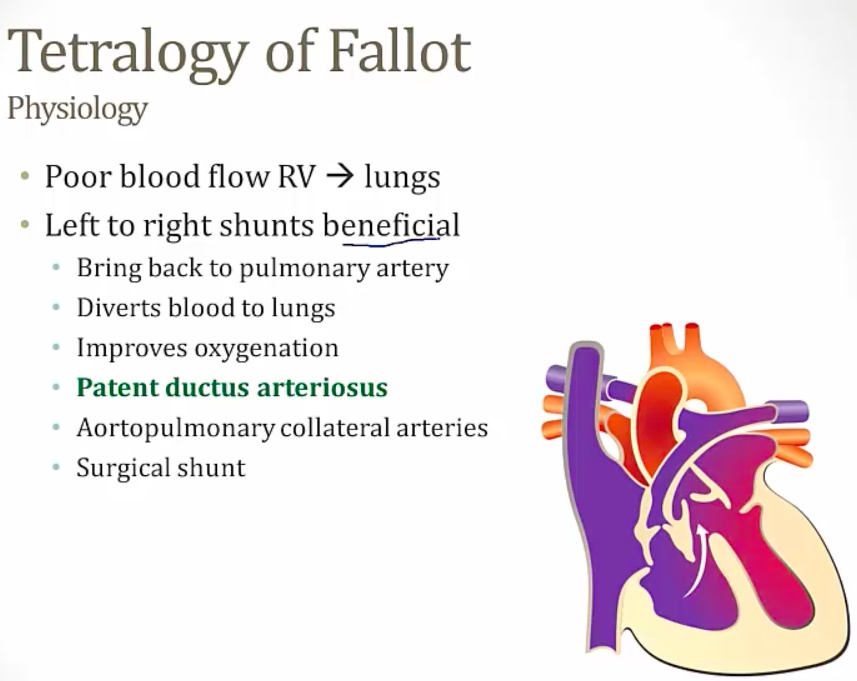
restricts flow of pulmonary artery

deoxygenated blood diverted away from lung to LV and systemic circulation
pink tets: mild obstruction, less cyanosis
Symptoms
_..

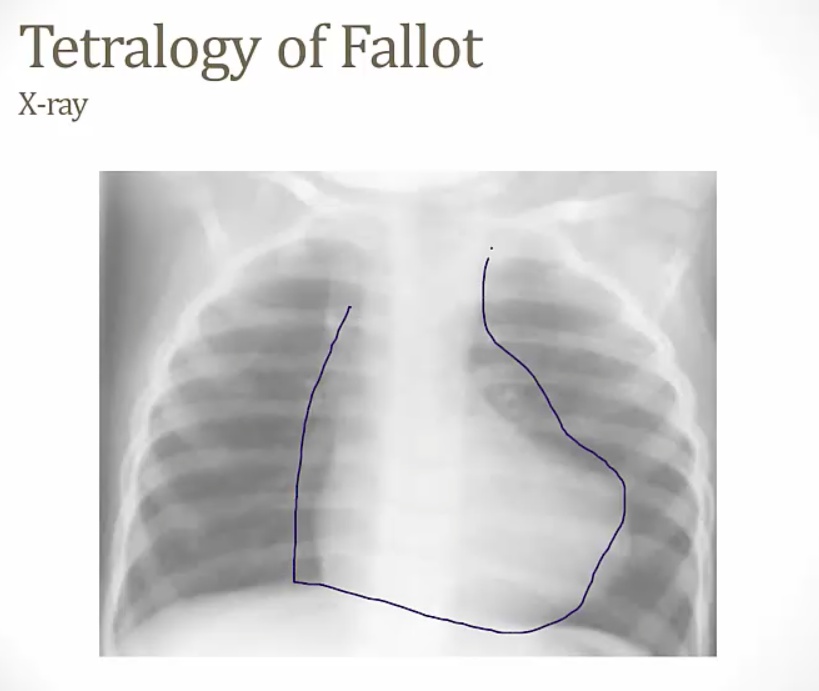
boot shaped heart
hypertrophic RV and apex misplaced

knit femoral arteries when squatting

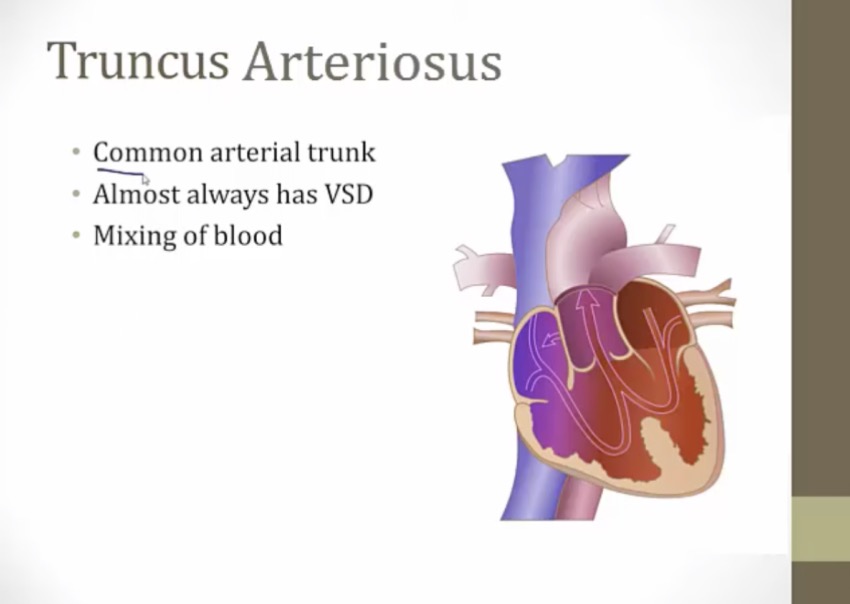
Truncus Arteriosus
_..
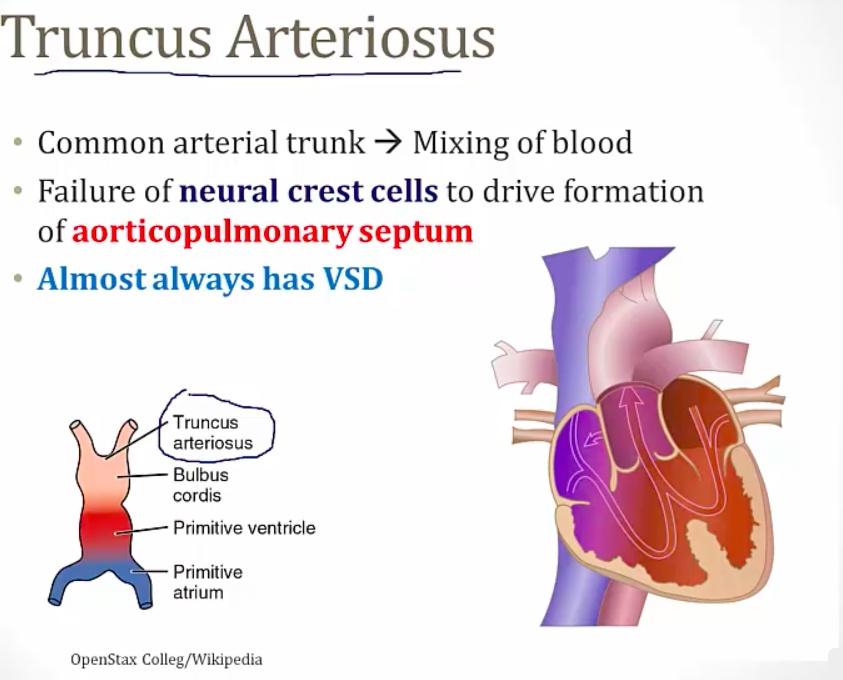
normally truncus divides into aorta or PA
persists = common trunk
mixing of blood = cyanosis
Transposition of great vessels
_..
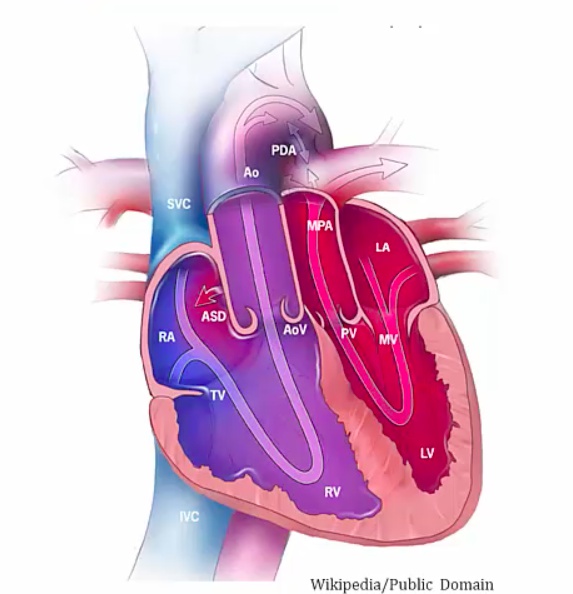
switched aorta and PA

relative position normal
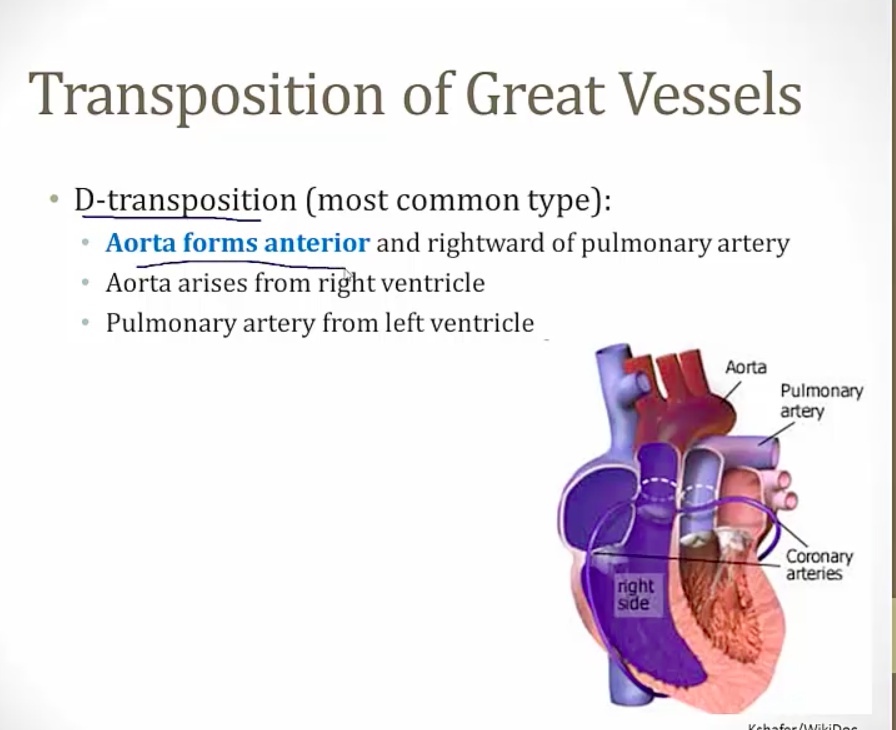

D transposition
VSD: allow RV/LV mix
PDA: allow Ao PA mix

rare variant
RV fail from not being able to take aorta pressure

transposition most common
Tricuspid Atresia
_..
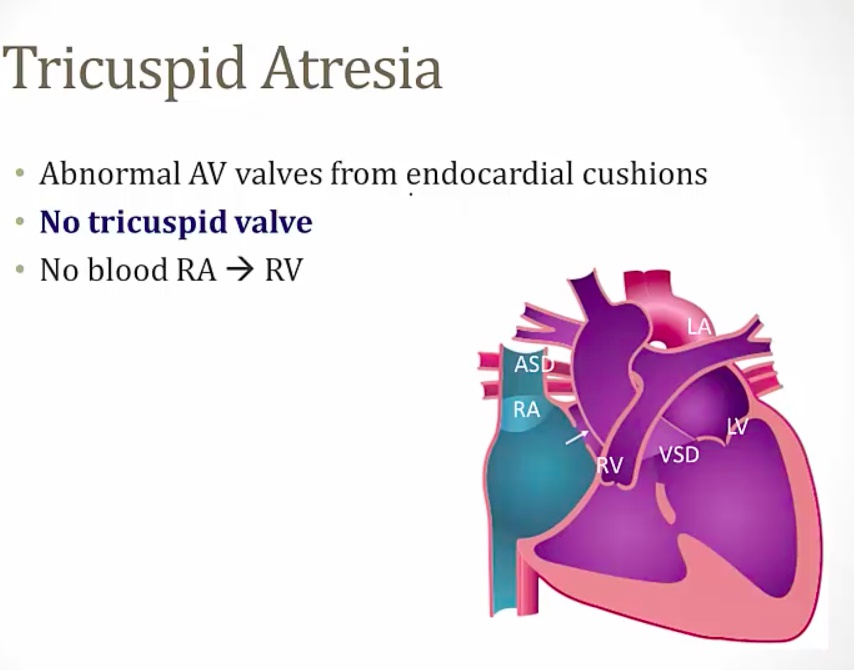
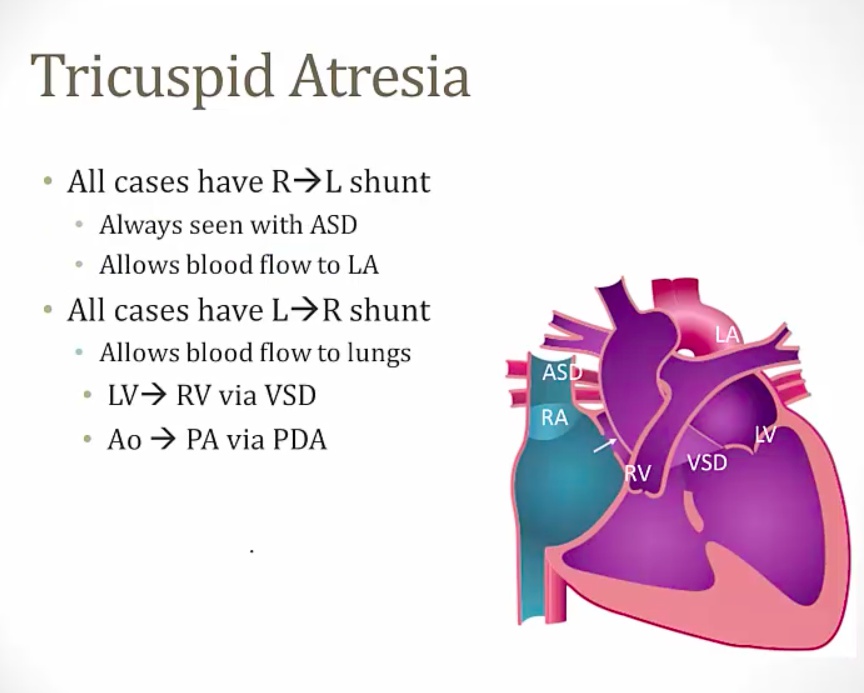
only case to be compatible with life
2 shunts to allow blood flow
TAPVR
_..

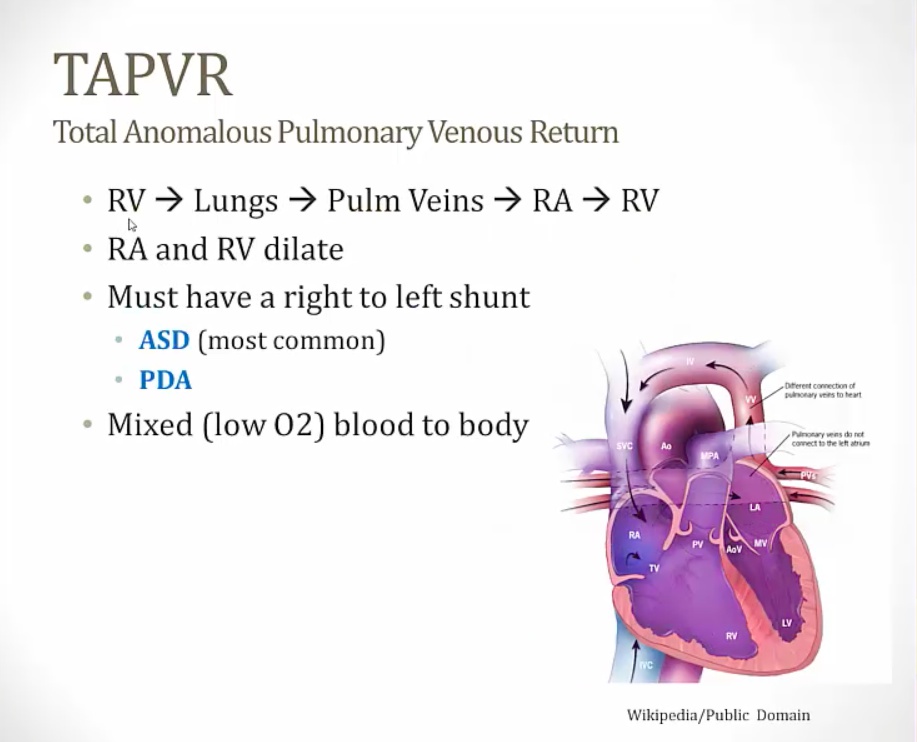
mixed blood with low O2, cyanosis
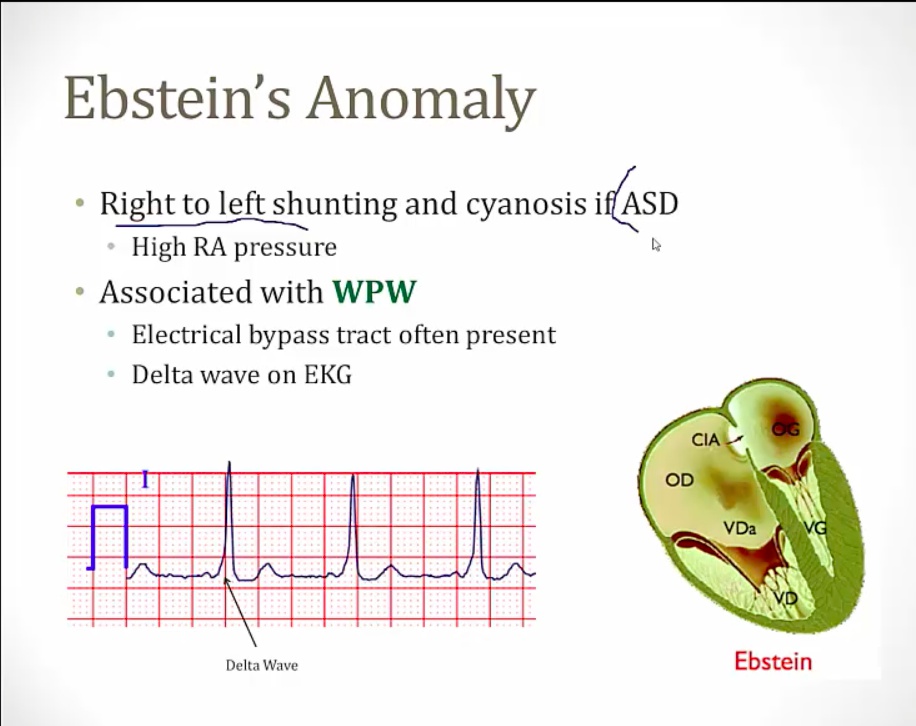
Ebstein's
[_](Ebstein's is, characteristics, cause, EKG)..

cyanosis and HF from tricuspid regurge

Pulmonary Atresia
_..

in utero not a problem
VSD: allows blood to exit ventricle
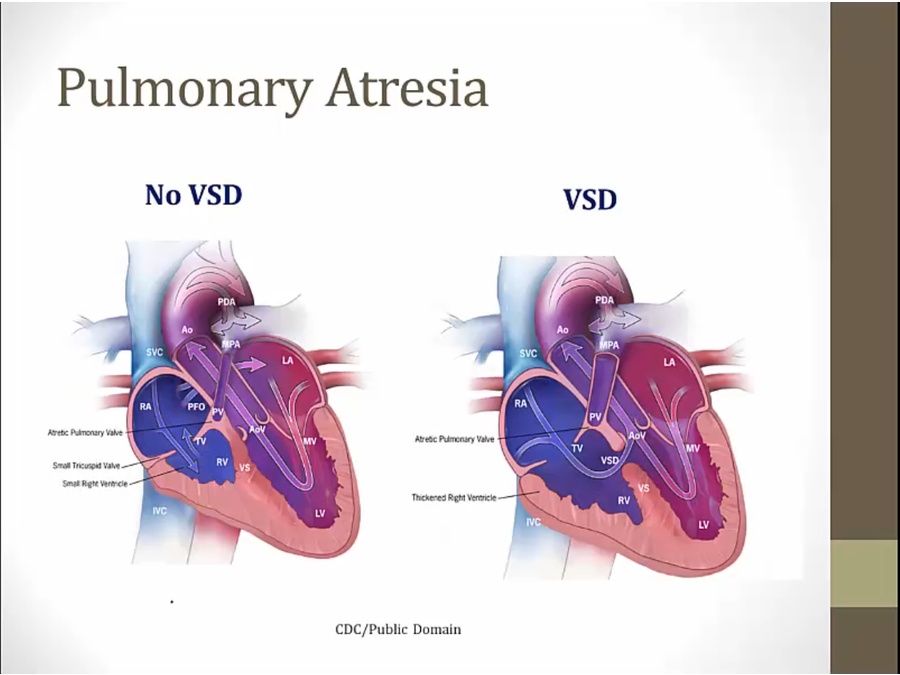

keeps connection open
Conotruncal Heart Defect
_..
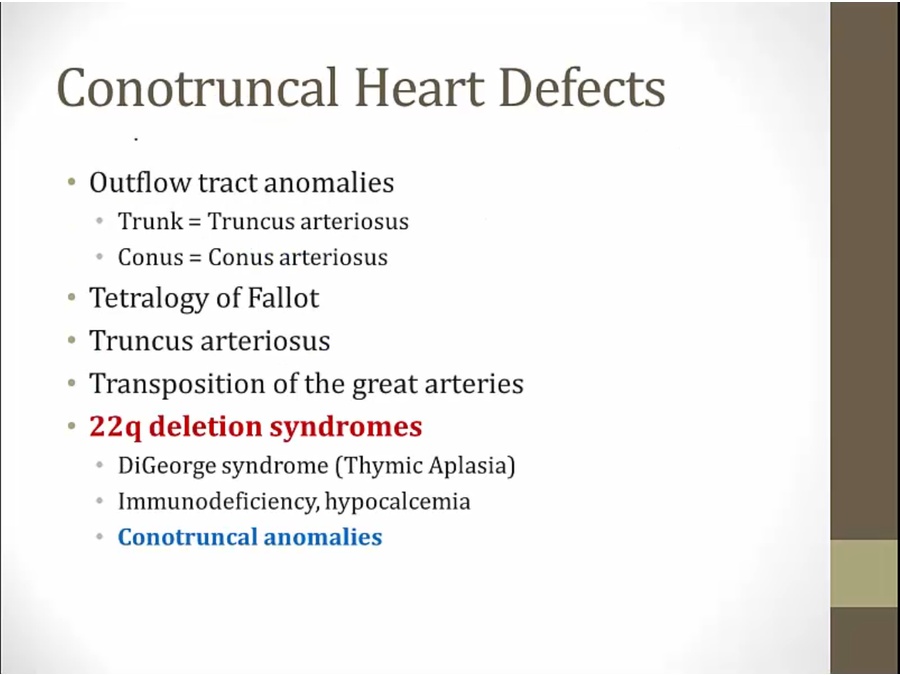
arteriosus: form outflow of LV and RV
classic: DiGeorge, develop any conotruncal problems
Coarctation
_..
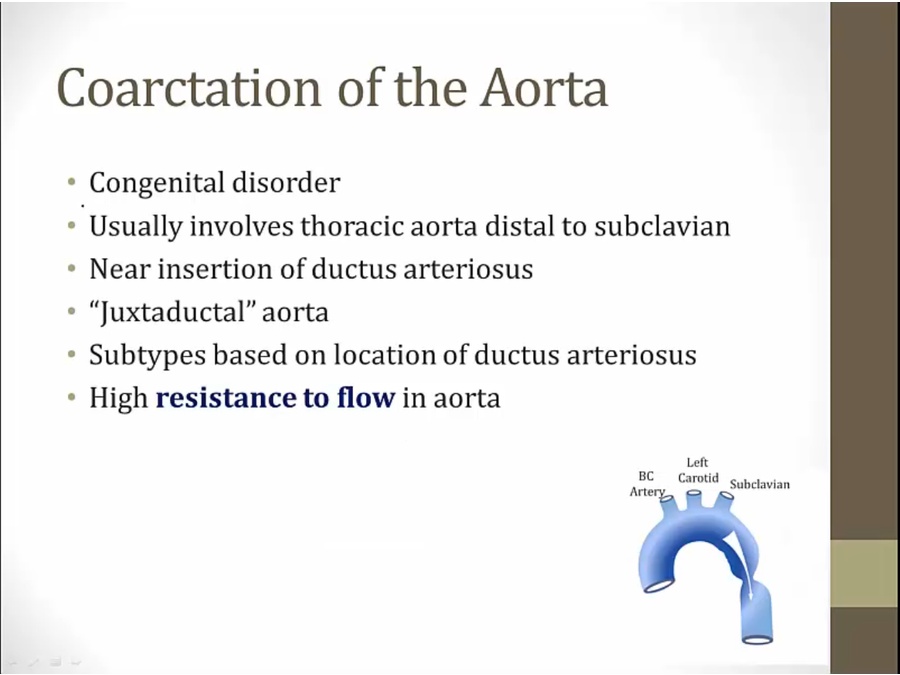

preductal: before ductus arteriosus insertion
Preductal
_..
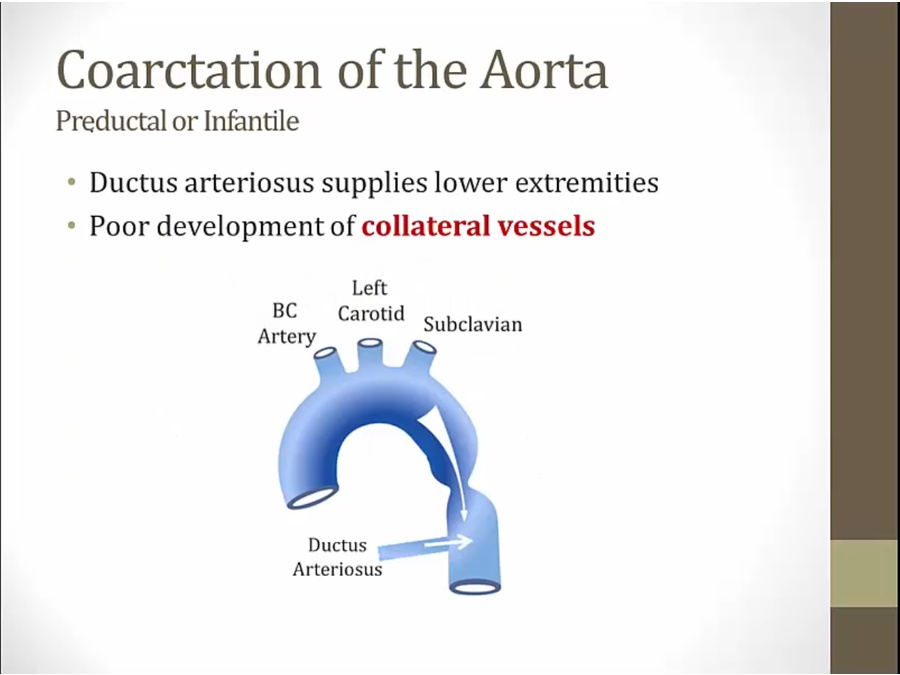
DA supplying lower body = no need for collateral vessel development in womb

cyanosis: blood bypass lung via DA and to lower extremities

all blood has to go through narrowing
baby into heart failure/shock in day 2 of life


narrowing of aorta usually in thoracic region
Postductal
_..
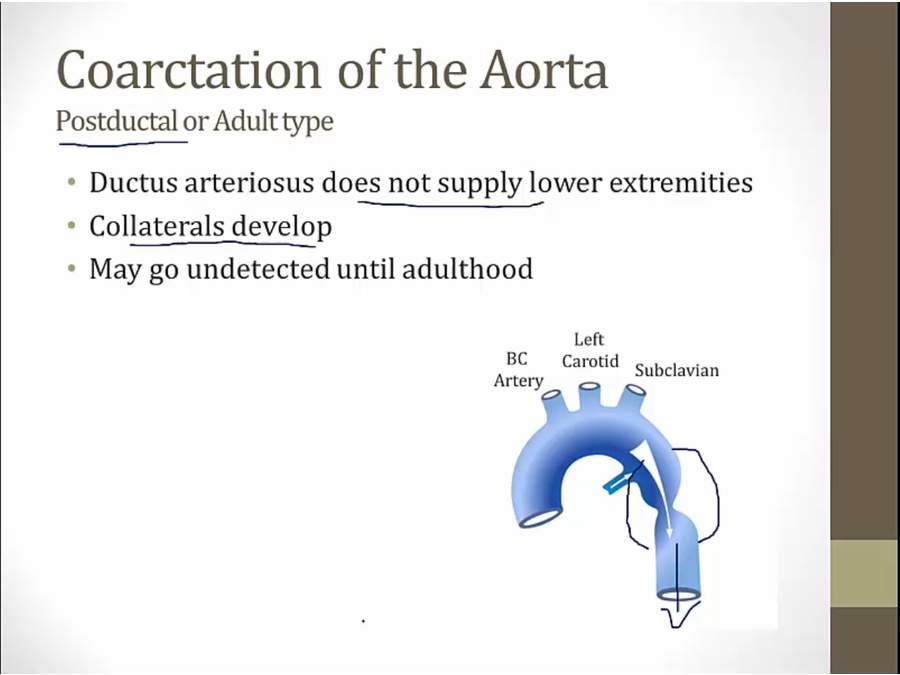
good: no HF in babies
bad: asymptomatic until adult

delay between when feel brachial vs femoral pulse

young person with htn
rarely, poor blood flow to lower body: pain/ischemia with walking


xray: aortic knob and below

not flushed in upper extremities or cyanotic in lower extremities because of autoregulation

endovascular infection: infection inside vascular tree
endocarditis: heart valves
endarteritis: artery
_..


coarctation part of a bigger problem of vasculature
Last updated