03 B Cells
_..

BCR
_..
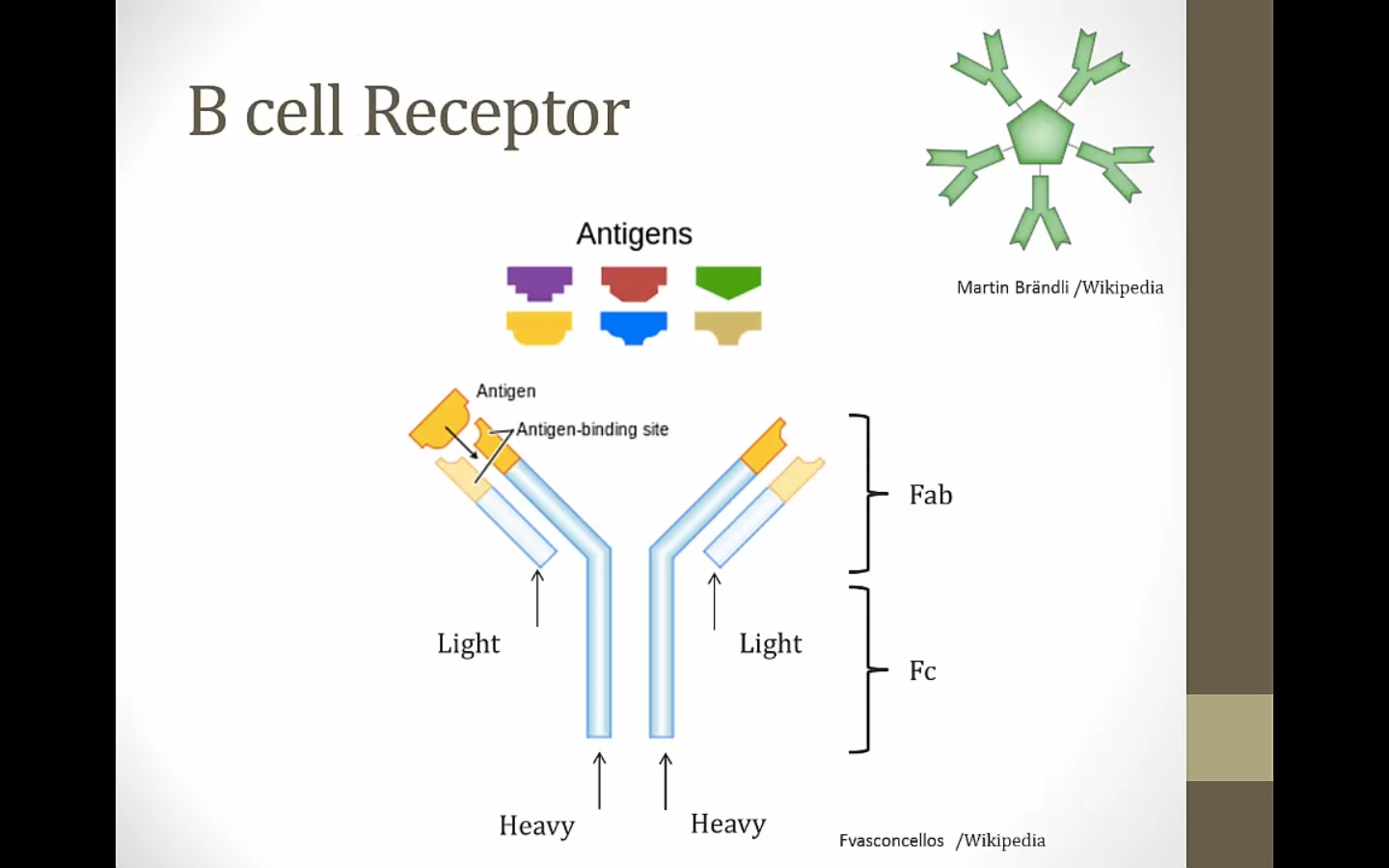
FAB: fragment antigen binding
FC: constant
Made of monomer IgM antibody

purple: variable regions. Vary from 1 B cell to another
light chain: 1 constant region; heavy chain 3 constant regions
variable regions end in nitrogen groups; constant end in carboxyl group
Connected by disulfide bridges
macrophage Fc/protein A binds CH2-CH3 region
Heavy chain
_..

Activation
_..

_..

B cell crosslinked by antigen
Second signal required in addition to crosslinking
MHC 2 binds TCR and CD4
CD40 binds CD40L: class switching
B7 binds CD28: T cytokine secretion

_..
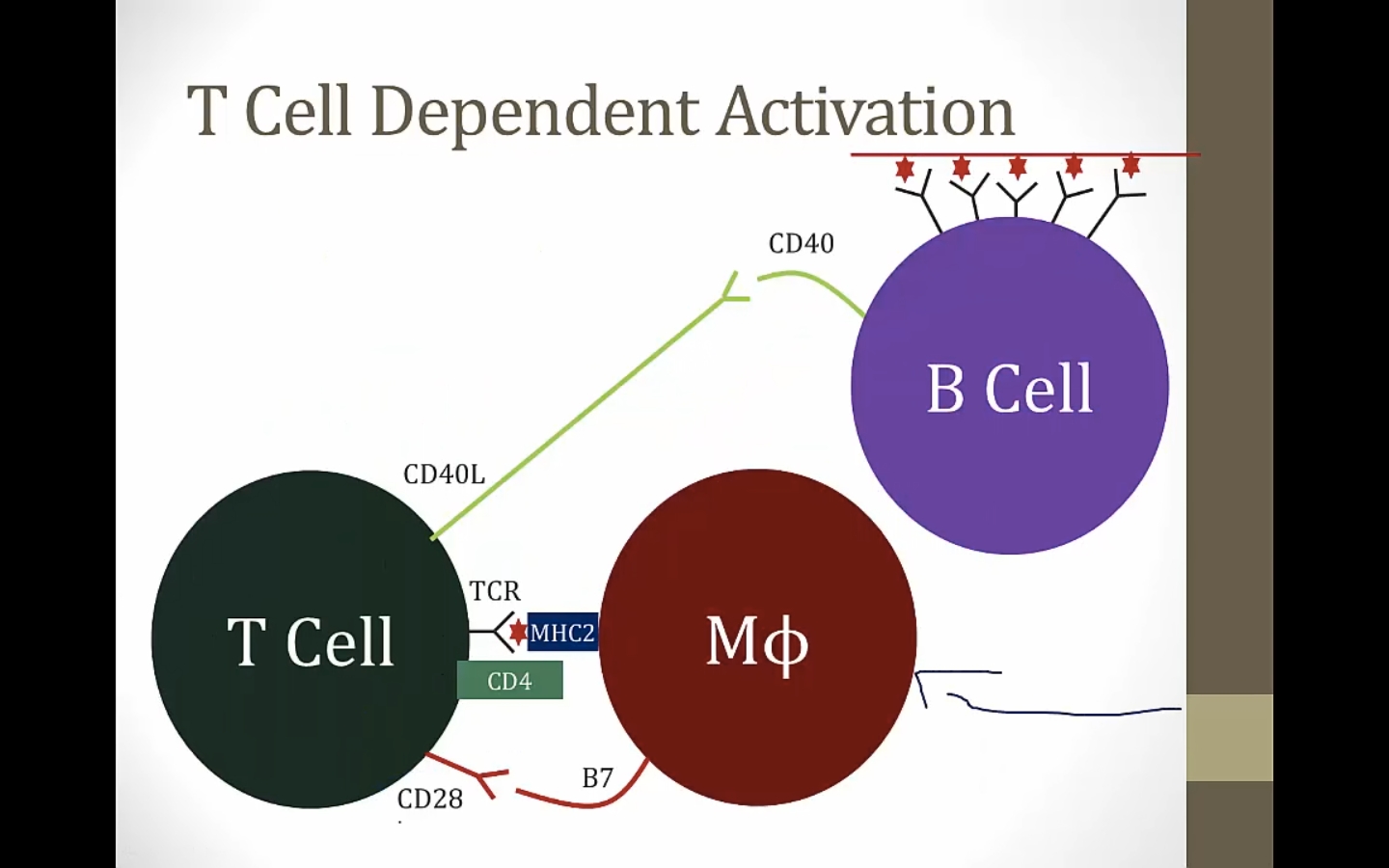
macrophage antigen presenting instead
T Independent
_..

so many antigen on surface, B cell activated without T
_..

Conjugated Vaccine
_..


Surface Proteins
_..
CD21 receptor for complement, receptor for EBV
Antibody
_..

_..

Protein A
_..

prevents opsonization:
Class Switching
_..

only change Fc portion, not FAB portion

Cm and Cd closes
Cm and Cd spliced out; B starts to make Cy (IgG), Ca, Ce
IgM
_..

Classical pathway: 2 C1 molecules bind together to Fc of IgM; easy to bind because so many IgM Fc together
Prevents attachment: very large and clumps on to pathogens
Weak opsonin: too big; macrophages can't get to Fc
IgG
_..

macrophages bind to Fc very easily

IgA
_..

secretory component in middle of 2 IgA
linked by secretory: can't complement


IgA Protease
_..

IgE
_..


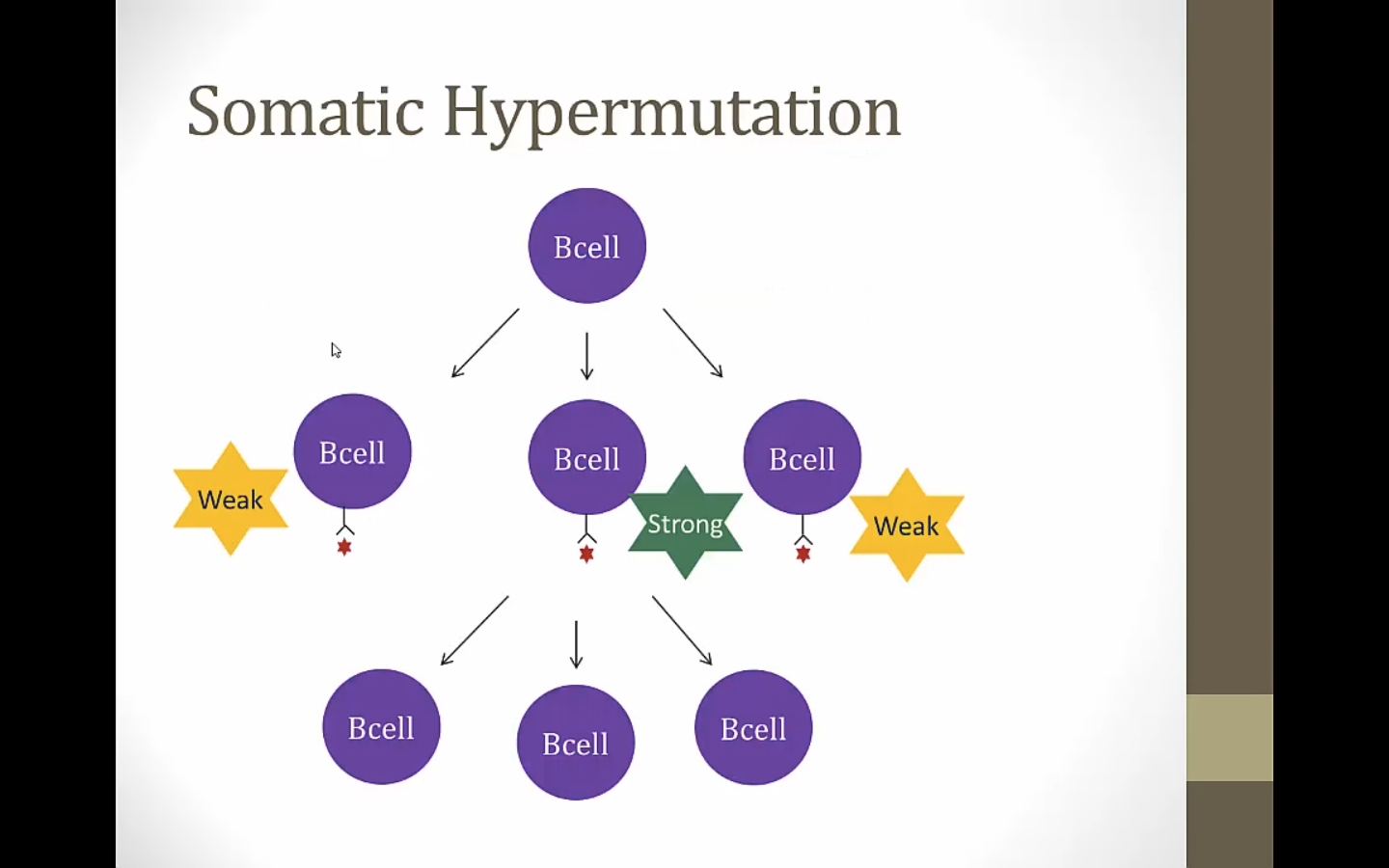
Somatic Hypermutation
_..

Happens during proliferation after activation
Stronger binding will proliferate the most
B Cell Fate
_..


Development Timeline
_..

Vaccines
_..
active
passive
Active
_..

_..

Live attenuated: T cell mediated response
Killed: antibodies against HA antigens of virus
Inactivated viral vaccines do not infect host cells and therefore do not enter the MHC class I antigen-processing pathway, which is normally required for the generation of a significant CD8+ cell-mediated immune response. In contrast, live-attenuated viral vaccines strongly stimulate the MHC class I antigen-processing pathway and can generate cytotoxic CD8+ T lymphocytes that kill infected cells.
_..

Passive
_..

give if suspicion for rabies, tetanus: neutralize before infection happens
Last updated