11 RTA
_..


many times asymptomatic, discovered on routine blood work
changes bicarb level: non-anion gap
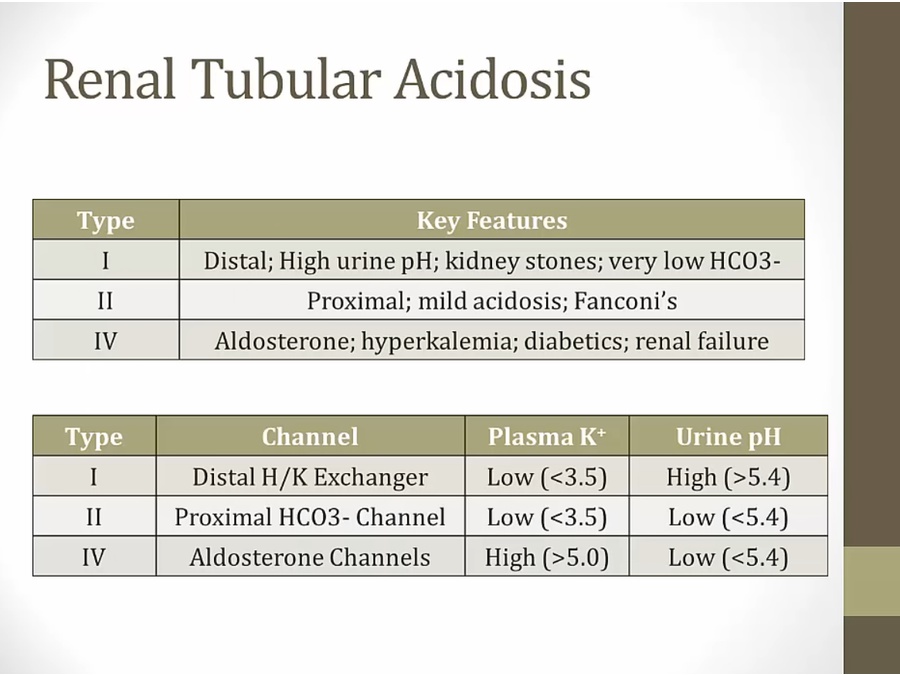
Type 1
_..

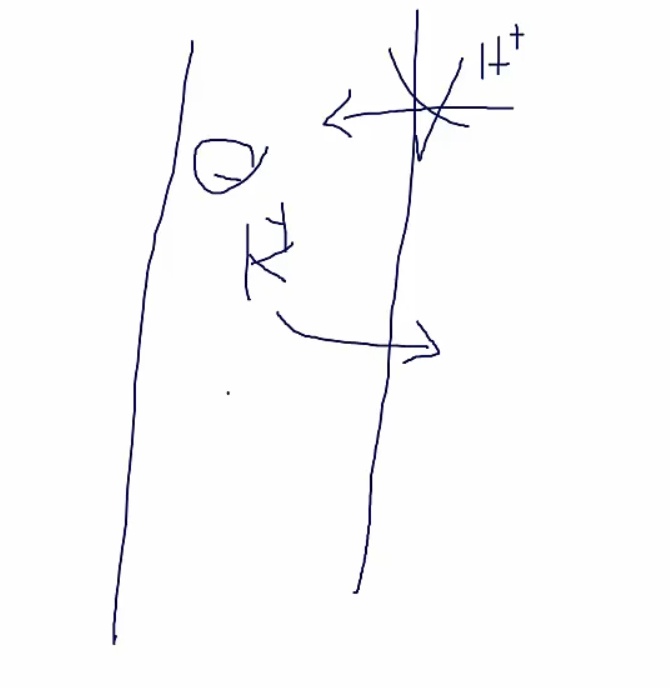
H channel defect, can't secrete H
K held in lumen, no absorption
_..

in metabolic acidosis, urine should be low to excrete H
if high pH, there's defect excreting H
_..

bilateral stones: think distal RTA
Calcium binds to negative albumin, competing with hydrogen ions
Alkalosis: less H+ competing, more Ca binding, which decreases free calcium levels.
Acidosis, increase H+ competing, less Ca binding, resulting in increased free calcium levels

_..

very very high yield: sjogren or RA

1 shaped acid tube: renal tubular acidosis (RTA) type 1 is cumulative toxicity of amphotericin
Depleted potassium banana peel: RTA type 1 is associated with hypokalemia
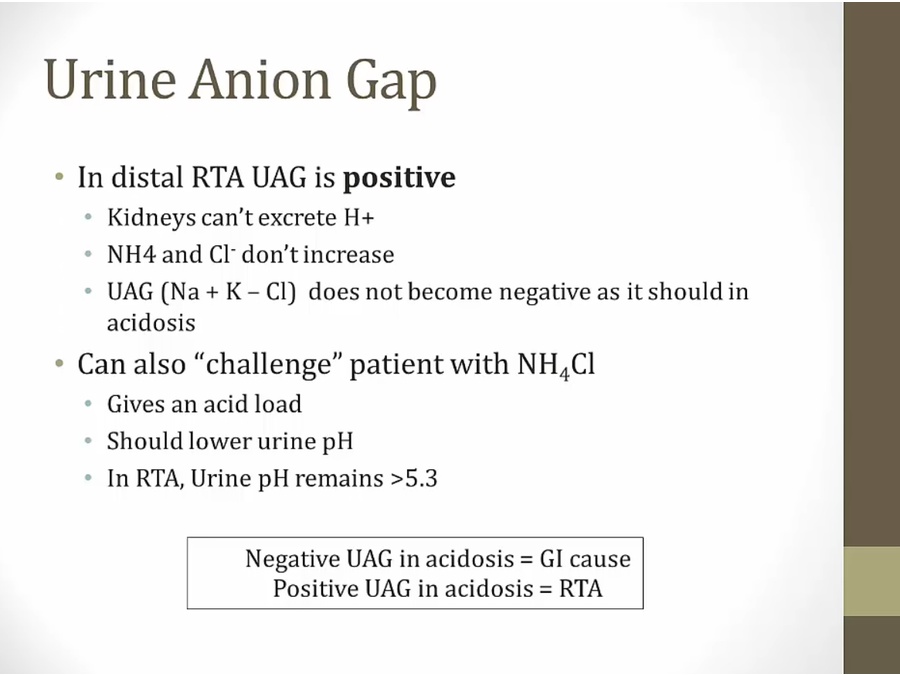
Urine Anion Gap
_..

urinary anion gap equation different from plasma anion gap
urine Cl goes up, UAG becomes negative
_..

_..
Type 2
_..


Fan cone: Fanconi syndrome (type 2 RTA) associated with use of expired tetracyclines
_..

Type 4
_..

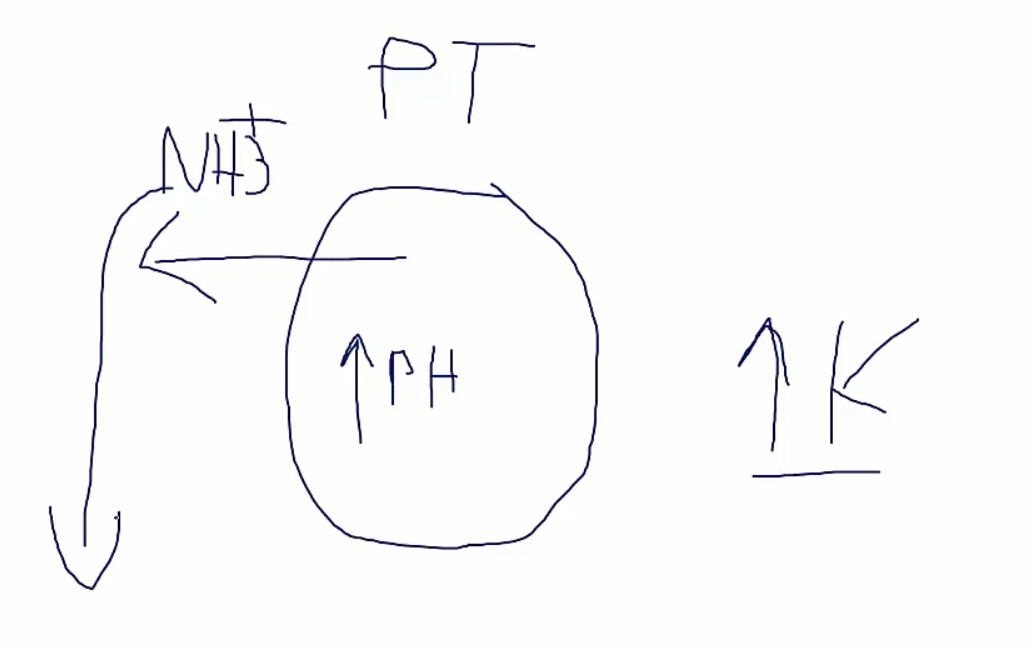
aldosterone doesn't work > hyperkalemia
hyperkalemia > increased K into cell, increased H out of cell> high pH in PCT cells
high pH > unable to excrete H and NH3
Inadequate amount of NH3 available for buffering of protons. Even if only a few protons are secreted distally, urinary pH will fall in the absence of buffers.
_..

diabetic renal: less renin production from renal insufficiency
ace/ARB: less aldosterone
bactrim: disrupt K excretion
Hyperkalemic RTA is commonly seen in elderly patients who have poorly controlled diabetes with damage to the juxtaglomerular apparatus, which causes a state of hyporeninemic hypoaldosteronism.

ACE I: high potassium cup

Depleted mineral mine: NSAIDs can cause hypoaldosteronism (decreased mineralocorticoids)
Big K: NSAID induced hypoaldosteronism can cause hyperkalemia. Type 4 RTA

Mad scientist with 4 tubes of acid: Type IV renal tubular acidosis (RTA)
K shape: Type IV RTA leads to hyperkalemia
Elevated bananas: K+ sparing diuretics can cause hyperkalemia
Acid spill into intracellular space: K+ sparing diuretics cause a normal anion gap metabolic acidosis (by decreasing the function of the H+ATPase)
4 acid tubes: K+ sparing diuretics inhibit the effects of aldosterone in the collecting duct causing a type 4 renal tubular acidosis (RTA)
Big K: type 4 RTA is associated with hyperkalemia

Depleted mineral mine: heparin can cause hypoaldosteronism (a mineralocorticoid)
Big K: heparin induced hypoaldosteronism (Type 4 RTA) causes hyperkalemia
_..

fludrocortisone: synthetic aldosterone
_..
Last updated