08 Spinal Cord Syndromes
Polio

.,


Werdnig-hoffman disease

.,
similar to polio without virus
MS

.,
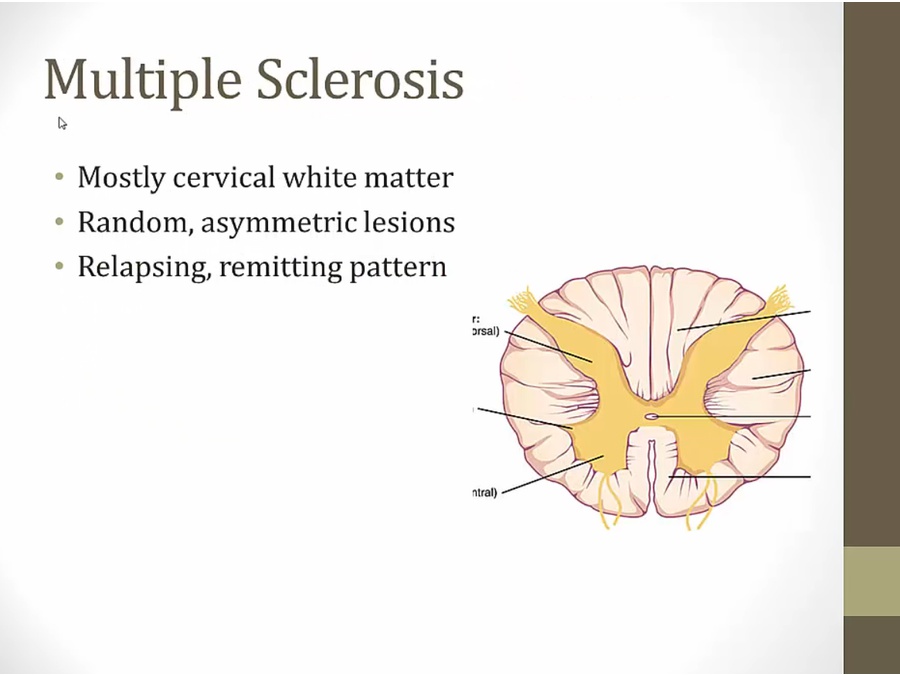
symptoms in one region of body, go away and come back in another region
ALS

.,

both lower/upper lost

progressive dysphagia until feeding tube, can't clear aspirations
free radical scavenger enzyme


ASA Occlusion
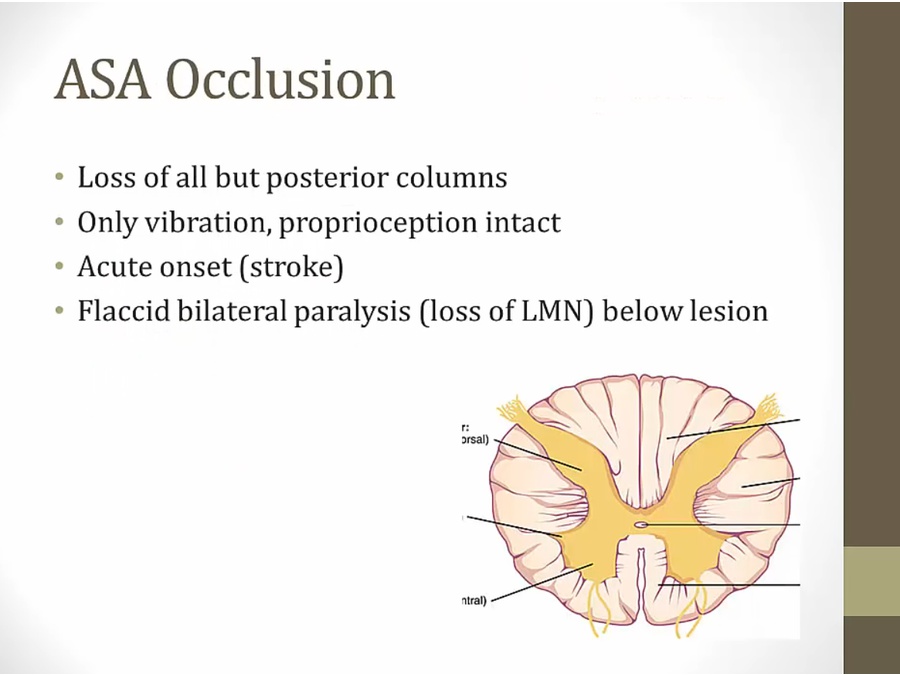
The ASA is particularly dependent on blood supply from the radicular arteries that originate from the thoracic aorta, such as the artery of Adamkiewicz. Thoracic aortic surgery can result in reduced blood flow through the radicular arteries (eg, from aortic cross-clamping and/or systemic hypotension) and consequently lead to anterior spinal cord infarction.
Tabes Dorsalis

.,
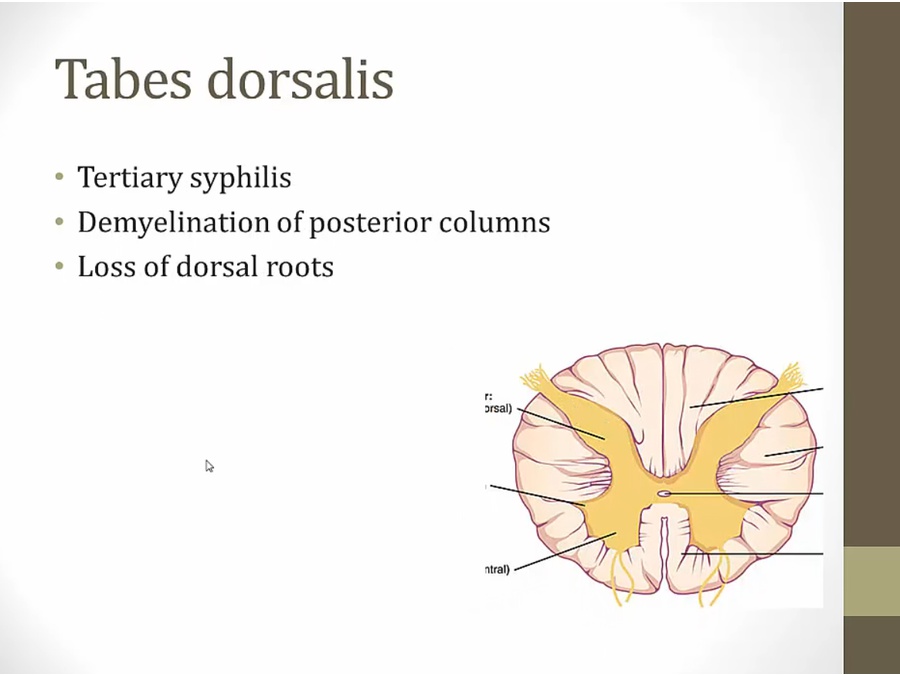
lose proprioception/balance: ataxic
also lose dorsal roots: lose reflexes

Syringomyelia

.,
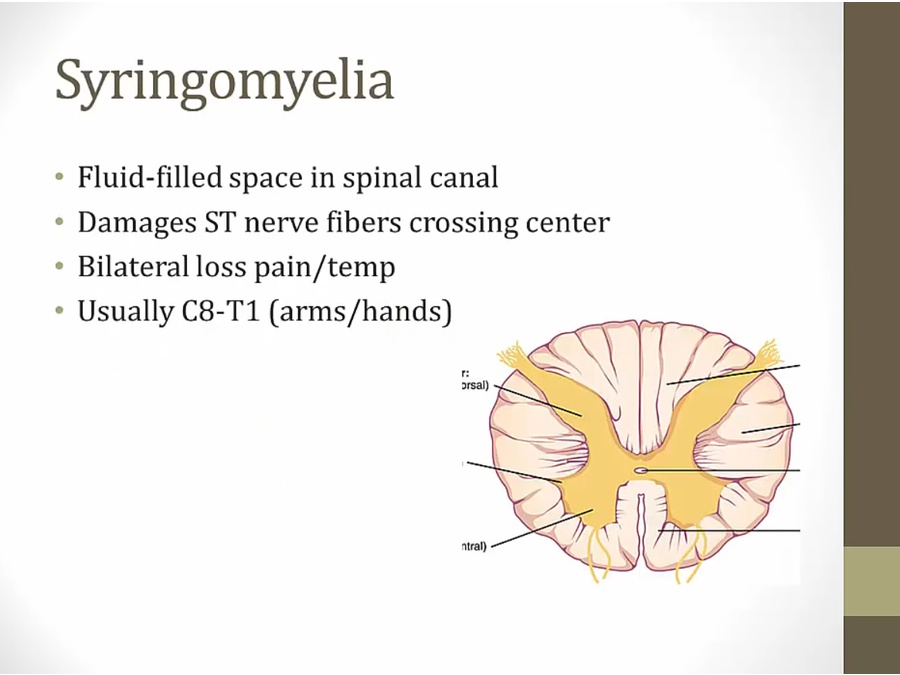




Central cord syndrome (CCS) typically occurs with hyperextension injuries in elderly patients with pre-existing degenerative changes in the cervical spine.
Can also be from whiplash injury from MVA
Subacute Combined Degeneration

.,



Tabes Dorsalis plus UMN symptoms
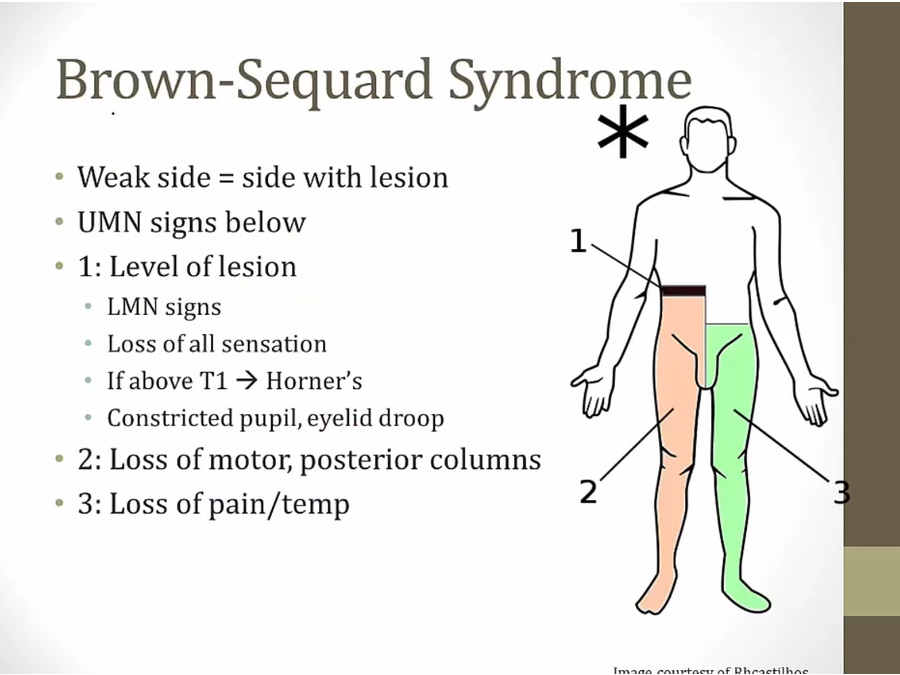
Brown Sequard

.,


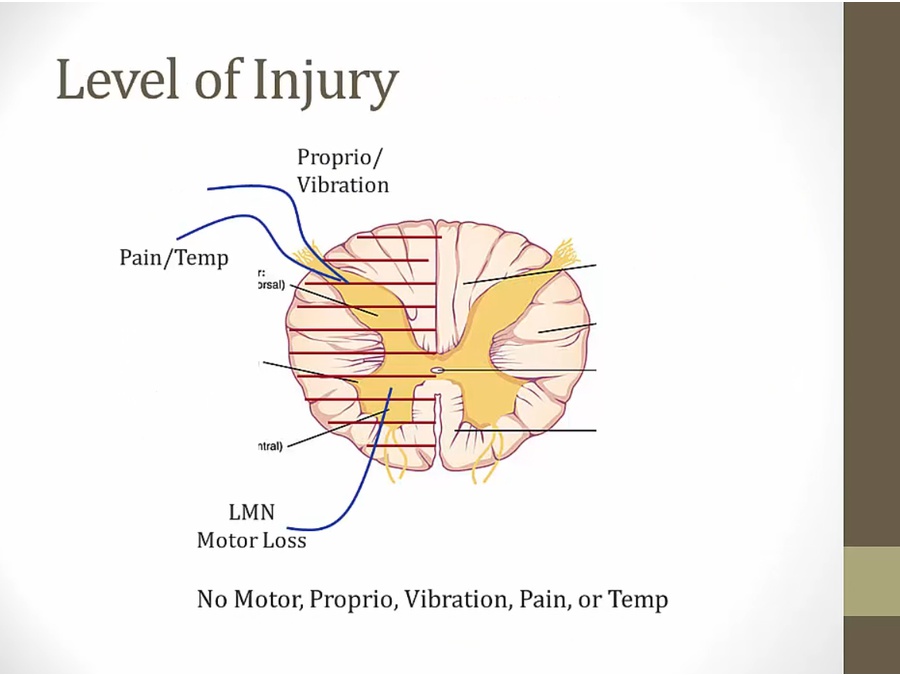
complete sensory loss

Cauda Equina


normal babinski because nerves in cauda equina are LMN, not UMN
Conus Medullaris

Overview
Disease
Location
Symptoms
Polio
ventral horn
loss reflex, LMN signs
MS
Varies
Varies
ALS
corticospinal, ventral horn
UMN/LMN
ASA Occlusion
all spinal cord, no DCML
LMN signs, DCML intact
Syphillis
DCML, dorsal root
loss reflex, gait, +Romberg, pupil, strength intact
Syringomyelia
White commissure
Pain/temp bilateral
B12 deficiency
DCML, corticospinal
UMN, ataxia,
Brown Sequard
Cauda Equina
LMN signs, saddle anesthesia
Conus Medullaris
UMN, saddle anesthesia, impotence
Last updated