Disorders Of Sexual Differentiation
Pseudohermaphroditism
_Male or female karyotype but ambiguous genitalia.,
_Caused by excess/deficient androgen:
Hypopituitarism
Congenital adrenal hyperplasia
Androgen insensitivity
5 alpha reductase deficiency
Aromatase deficiency..
Female Pseudohermaphroditism
_Is due to excessive and inappropriate exposure to androgenic steroids during early gestation (e.g, congenital adrenal hyperplasia or exogenous administration of androgens during pregnancy).,
Karyotype is 46, XX
Ovaries are present. No testes
External genitalia are virilized or ambiguous .,
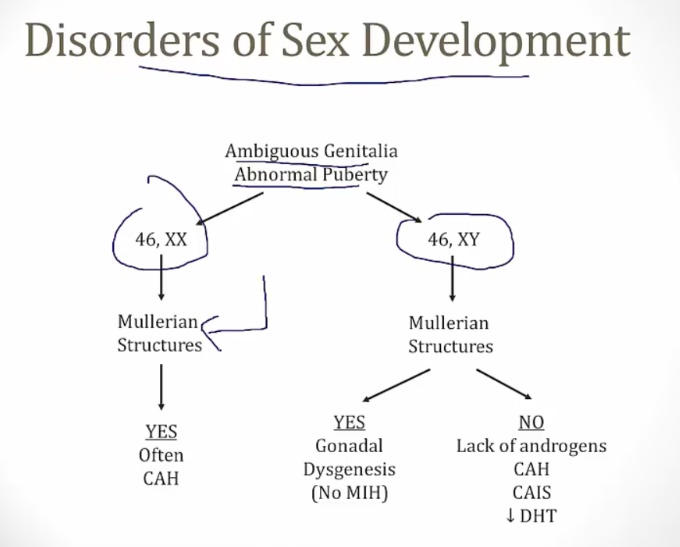
Male Pseudohermaphroditism
_Is most commonly caused by androgen insensitivity syndrome (testicular feminization).,
Karyotype is 46, XY
Testes are present
External genitalia are female or ambiguous.,

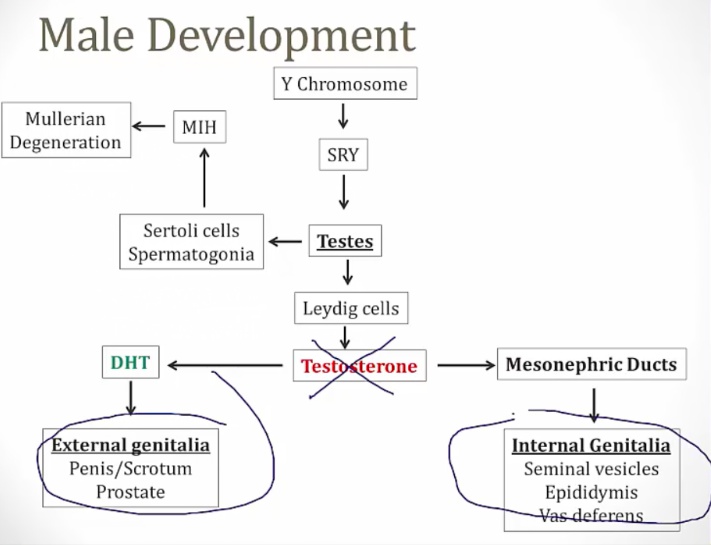
Androgen Insensitivity Syndrome
_Formerly testicular feminization.,
_Is due to impaired androgen receptors.,
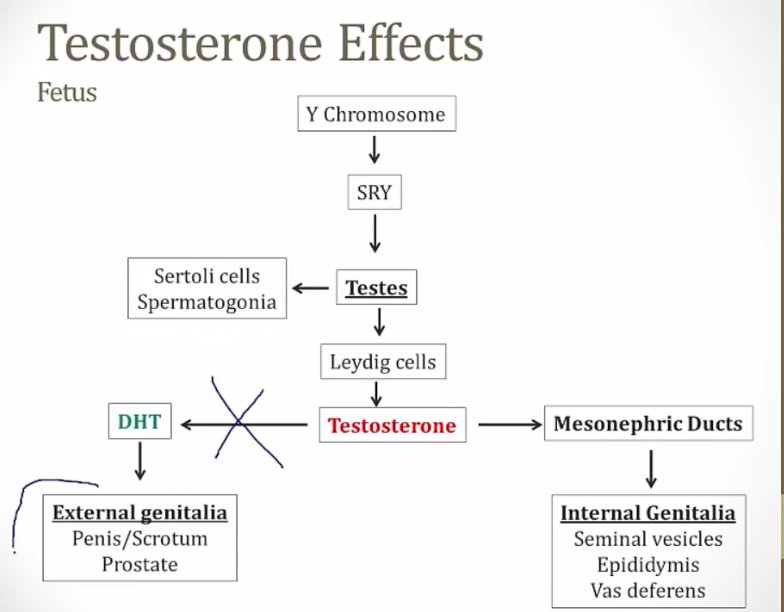
SRY gene is present: regression of Mullerian structures
Testosterone is present, receptor not responsive. No internal genitalia
No DHT, which is required for external male genitalia development.
Result: female external genitalia with scant sexual hair and a rudimentary vagina; uterus and fallopian tubes are absent.,
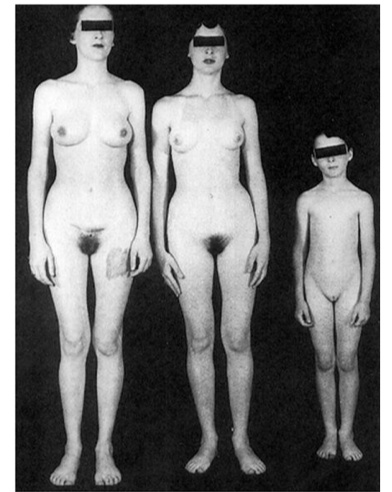
At birth:
No ovaries; testes formed in utero and undescended (SRY gene) (inguinal mass)
No uterus/fallopian tube (MIH from sertoli cells)
female external genitalia (no testosterone)
Puberty:
Appears female with amenorrhea
Breasts develop (testosterone to estrogen)
No armpit/pubic hair (lack testosterone) (differentiate from imperforate hymen that has hair)
Amenorrhea (no uterus)
No cervix and rudimentary vagina on exam
Testes in abdomen or labia majora.,
_Methods for diagnosis:
Karyotyping
Androgen receptor mutation analysis
Normal FSH levels
Increased levels of testosterone, LH, and estrogen..
_Orchidectomy is recommended in patients to reduce the risk of malignancy.,
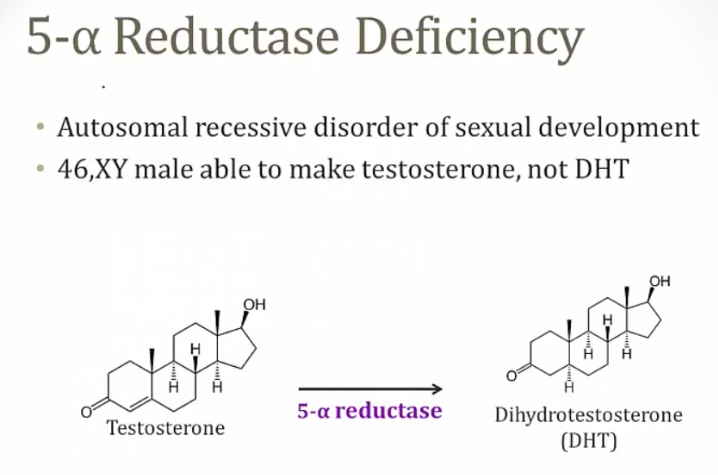
5-a reductase deficiency
_An autosomal recessive disorder resulting in an inability to convert testosterone to dihydrotestosterone (DHT).,
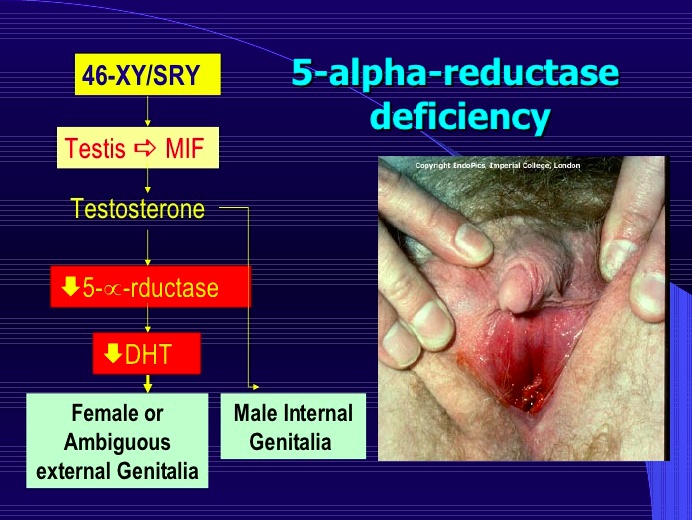
_At birth:
Normal internal genitalia (epididymis, vas, seminal)
ambiguous genitalia (blind ending vagina) until puberty
however the external genitalia are female and patients are often raised as females
can have hypospadias (small penis)
During puberty:
Female masculinize due to Leydig cells making more testosterone
Normal testosterone serum level
Absent uterus, blind vagina, undescended testes
Masculinization and virilization of the external genitalia (enlargement of the phallus, increases in body hair and muscularity, voice deepening, no breast development) occurs due to increasing levels of testosterone
grows a penis at puberty.,
Internal genitalia are normal: presence of the SRY gene on the Y chromosome encodes Leydig cells which produce normal levels of testosterone that stimulate development of Wolffian structures. They also encode for Sertoli cells, which produce AMH/MIF that leads to normal regression of the Mullerian duct structures.
_Lab findings:
Testosterone and estrogen levels are normal
LH may be normal or increased.,
_Diagnosis is done by:
Karyotyping
Abdominopelvic ultrasound for presence of female or male internal structures
Elevated serum ratio of testosterone to DHT (hallmark of diagnosis).,
_Treatment includes two phases:
Phase 1: gender assignment and surgical correction for desired sex
Phase 2: hormone replacement therapy that can be tailored to the chosen sex..
Aromatase Deficiency
_The inability to synthesize estrogens from androgens.,
_Masculinization of female (46, XX) infants produces ambiguous genitalia
High serum testosterone and androstenedione
Can present with maternal virilization during pregnancy due to the fetal androgens crossing the placenta.,
True Hermaphroditism
_Previously known as True Hermaphroditism.,
_Defined by the presence of both testicular and ovarian tissues in a single individual. This affects the development of external and internal genitalia in a variable manner.,
_Various genes have been implicate, including:
RSPO1 gene
SRY gene
DMRT gene.,
_A 46, XX karyotype is most commonly seen. The 47, XXY karyotype can also be seen, but it is less common..
_Patients are born with ambiguous genitalia. Most patients will undergo breast development during puberty. Physical exam findings include:
Uterine abnormalities
Abnormal vagina
Chordee penis (if penis is present)
Urogenital sinus
Hypospadias
Bifid scrotal folds.,
_Diagnosis:
Chromosomal analysis
Hormone testing
Imaging to find occult gonads..
Definitive diagnosis can be made with gonadal biopsy.
_Treatment options involves:
Sex hormone replacement if delayed puberty is seen
Surgery may be indicated to reinforce the decided upon gender assignment..
Sex Chromosome Disorder
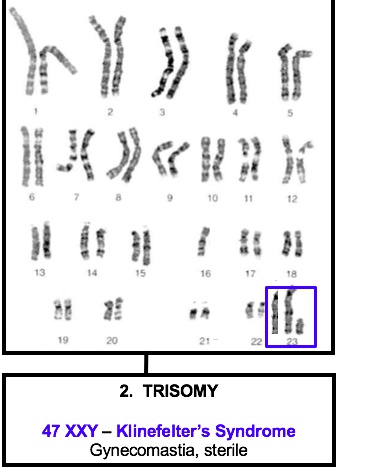
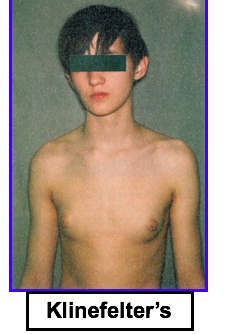
Klinefelter’s syndrome
_47, XXY males is a sex chromosome disorder caused by meiotic non-disjunction (most commonly in meiosis I).,
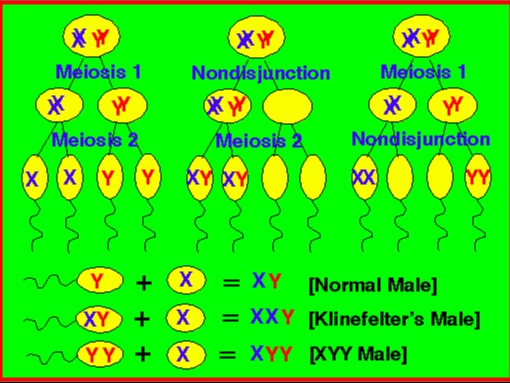
_The manifestations are the result of the following hormonal abnormalities:
Dysgenesis of the seminiferous tubules: no inhibin and high FSH
Damaged Leydig cell: no testosterone
Increase in FSH: increased aromatase synthesis, conversion to estrogen.,
The primary reason for hypogonadism and feminization is that testosterone does not have a normal interaction with androgen receptors, which along with increased conversion into estradiol, causes hypogonadism and feminization.
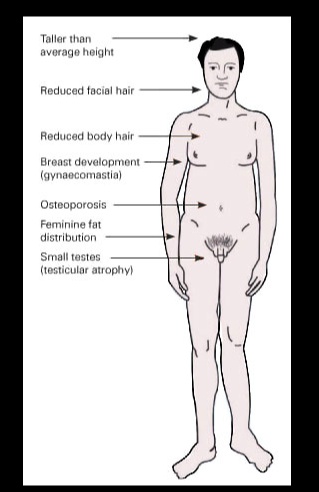
_The clinical presentation is variable, but includes:
Low testosterone: Testicular atrophy, infertility
High estrogen: Eunuchoid appearance (wide hips and gynecomastia), Female distribution of body hair
Long extremities
Low testosterone: Lack of male secondary sex characteristics (deep voice, beard, male pubic hair distribution)
May present with developmental delay.,
_Diagnosis is confirmed with a karyotype showing 47, XXY.,
Buccal smear preps usually show a Barr body (an inactivated X chromosome).
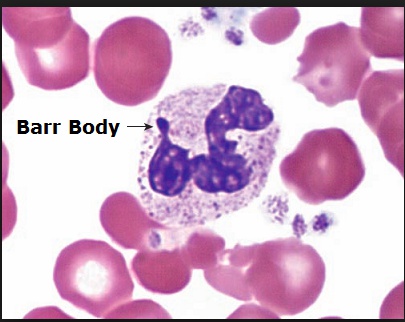
_Patients often have complications including:
Increased incidence of Type II Diabetes Mellitus and metabolic syndrome
Mitral valve prolapse
Osteoporosis/Bone Fractures.,
_Can be managed with the following:
Testosterone replacement therapy
Surgical removal of breast tissue
Psychiatric therapy to assist the patient with coping..
Turner
_45, XO females, is the most common genetic cause of primary amenorrhea.,
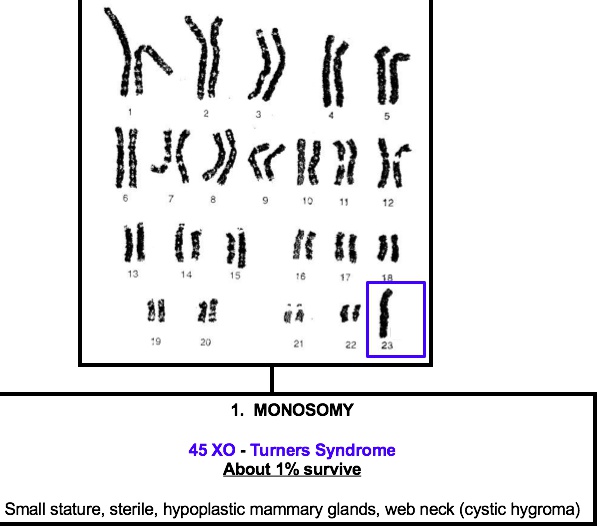
_Can be caused by:
Meiotic non-disjunction (60% of cases): 45,XO
Mosaicism (30% of cases): 45,XO/46,XX
Structural abnormalities of the X chromosomes (10% of cases)..

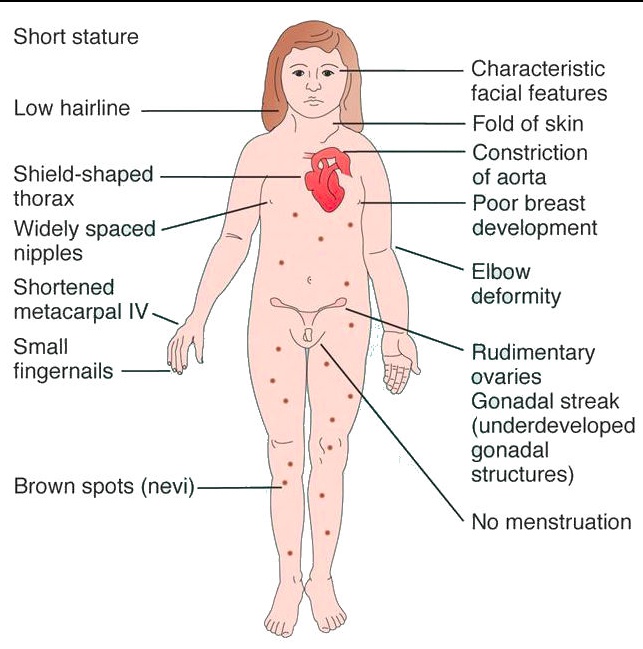
_The clinical presentation includes the following:
Short stature (<5 feet) due to deletion of second SHOX gene on the X chromosome
Streak gonads (ovaries are replaced with fibrous tissue)
Infertility
Menopause before menarche
Broad chest with widely-spaced nipples
Webbing of the neck (cystic hygroma) with a low hairline
Lymphedema in the hands and feet
Abnormal development of female secondary sex characteristics.,
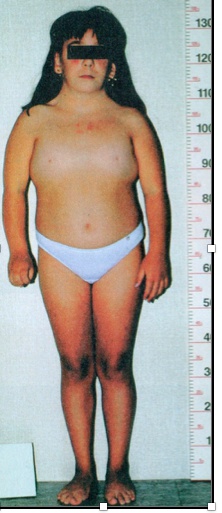
cystic hygroma: lymphatic systems not completely developed swollen areas, neck
_Hormonal testing would reveal:
Decreased estrogen and progesterone
Increased FSH and LH..
_Complications associated include:
Preductal coarctation of the aorta
Bicuspid aortic valve
Hypothyroidism
Horseshoe kidney
Ovarian dysgerminoma..
_Pharmacological treatment includes:
Growth hormone to correct short stature
Estrogen therapy in order to achieve adult sexual development..
_Although rare, pregnancy is possible in some patients with Turner Syndrome. In those cases, they must become pregnant via in vitro fertilization using donor oocytes, exogenous estradiol-17beta and progesterone. It is important to remember that although these patients do not have working ovaries, in most cases they do have a normal uterus with an endometrium that responds normally estrogen; thus making pregnancy possible..
Double Y
_47, XYY is found in 1:1000 males and is often undetected.,
_Is caused by a random event of paternal nondisjunction during anaphase II of meiosis II..

_ patients will be phenotypically normal, but will present with tall stature and severe acne.
Normal testosterone levels, and most have normal sexual development and normal fertility.
Typically have normal behavior and intelligence. However, in some cases they have been associated with aggressive behavior, learning disability, and autism spectrum disorders.,
Fragile X
_The second most common genetic cause of intellectual disability (Down syndrome is the most common).,
_Is caused by expanded trinucleotide CGG repeats in the promoter segment of the FMR1 gene. The expanded promoter segment enhances methylation leading to silencing of the FMR1 gene.,
Silencing of the FMR1 gene leads to decreased synthesis of FMRP protein
Lack of FMRP is what causes the clinical symptoms seen in Fragile X syndrome
_Is more common in males and presents with:
Macro-orchidism (enlarged testes)
Large jaw
Large everted ears
Mental retardation
The most common cardiac complication is mitral valve prolapse.,
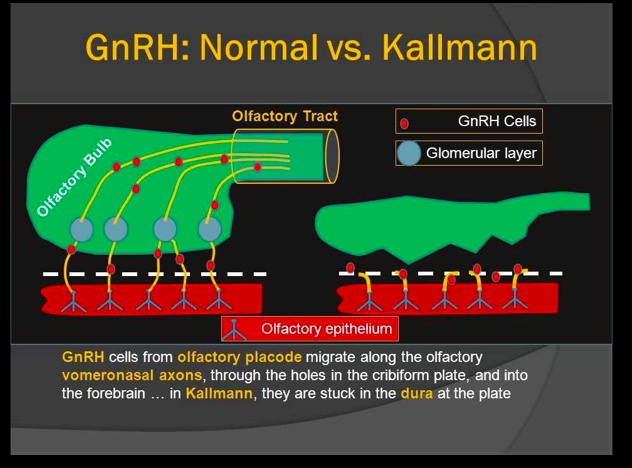
Kallmann syndrome
_A form of hypogonadotropic hypogonadism, which results in a failure to complete puberty.,
_It is associated with anosmia.,
_Is also known as hypogonadotropic hypogonadism with anosmia.,
_Is caused by failed migration of GnRH neurons from the olfactory placode to the hypothalamus, which results in improper development of the olfactory bulb (explains the anosmia).
Without GnRH neurons, the hypothalamus synthesizes and secretes decreased amounts of GnRH leading to decreased LH, FSH, and testosterone/estrogen (which accounts for hypogonadism).,
_Presents with the following symptoms:
Anosmia
Lack of secondary sex characteristics
Lack of testicular development in males
Infertility (low sperm count in males; primary amenorrhea in females)
Failure to start/complete puberty.,
_Is treated with sex hormone replacement therapy in order to achieve normal adult sexual development in patients. Puberty can be induced with the administration of LH and FSH..
Last updated