04 Pulmonary Circulation
_..


lower p: doesn't need to go as far
Blood O2 Content
_..

fetal: less blood to lungs, not important in womb

Diffusion
_..

more pressure difference of O2 in air/blood: more diffusion
more area: more diffusion
thickness: less diffusion

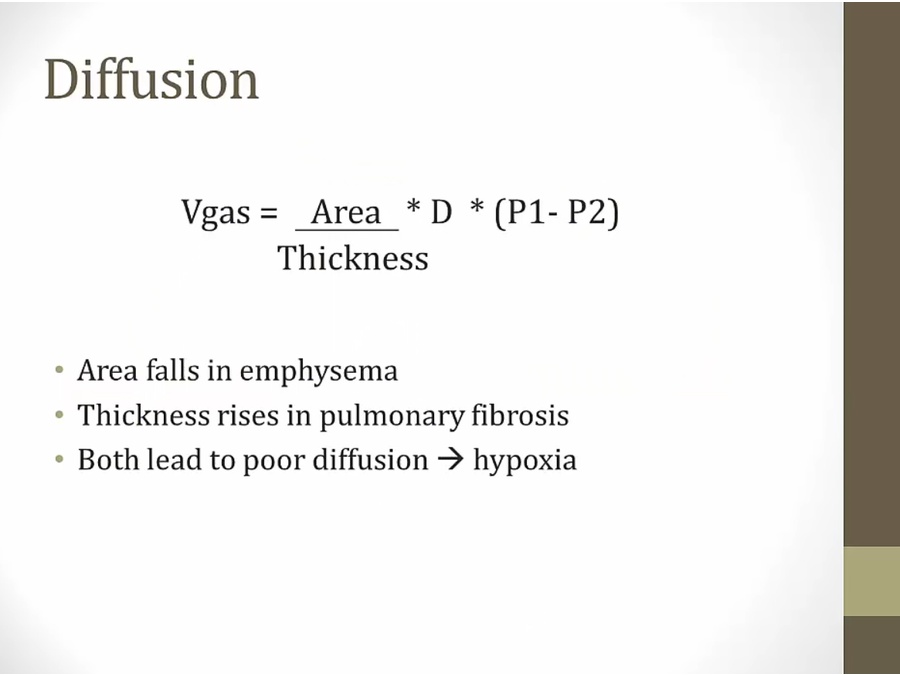
emphysema: alveoli destroyed, low DLCO
fibrosis: thicker, low DLCO
diffusion of CO same as DLCO
Diffusion-Perfusion
_..
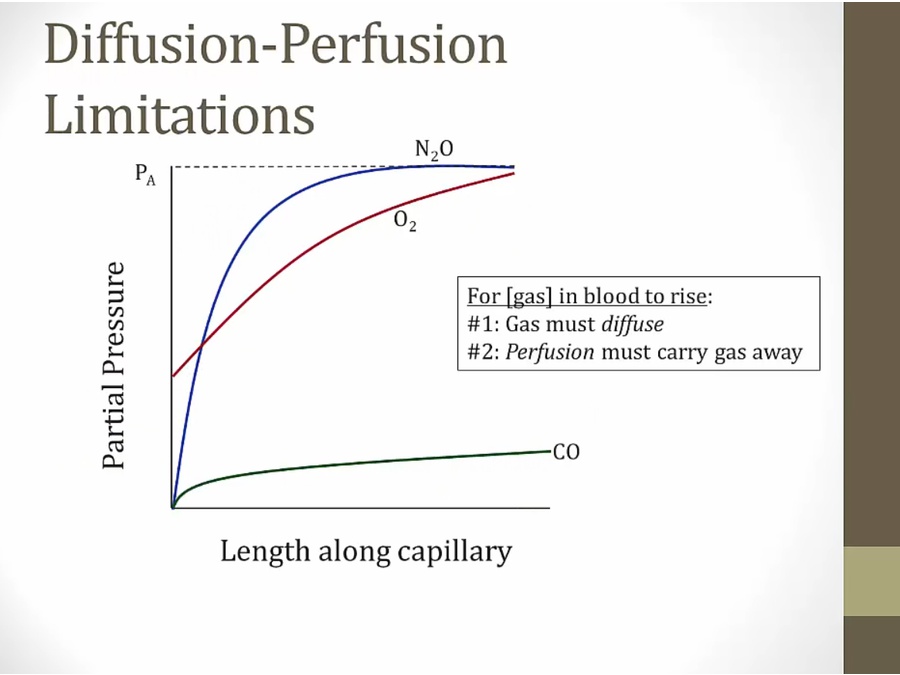
infuse 3 gases into lungs at Pa concentration, ideally reach Pa concentration
N2O: at length 0, no N2O diffuse into blood; diffusion rises very rapidly along capillary length to max value
CO: rises slowly, never gets to maximum concentration
O2: some O2 from veins at length 0, rise relatively rapidly until max value

gas must diffuse through and get carried away

N2O: barrier not a factor
N2O rapidly diffuse through
only determination for rate of rise of N2O is how fast blood flowing, carrying away molecules, rapid rise in partial pressure

barrier is major factor for diffusion
slow rise
diffusion main factor. Perfusion not a factor


N2O: only thing slow or speeds up concentration is blood flow rate
O2: same
CO: uptake limited by diffusion
_..

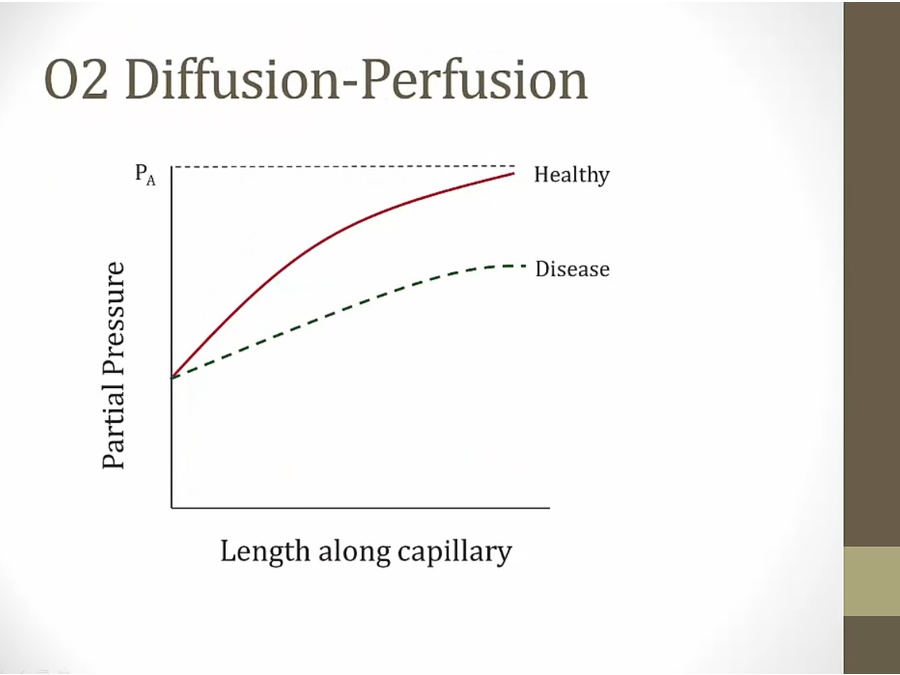
diffusion limited
concentration of O2 in blood falls = hypoxemic

at rest: blood flows slowly, lots of time to pick up O2
exercise: blood flow faster, gets further before reach maximum, but still does even in patients exercising
exercise alone should not make someone hypoxemic
Pulmonary Resistance
_..
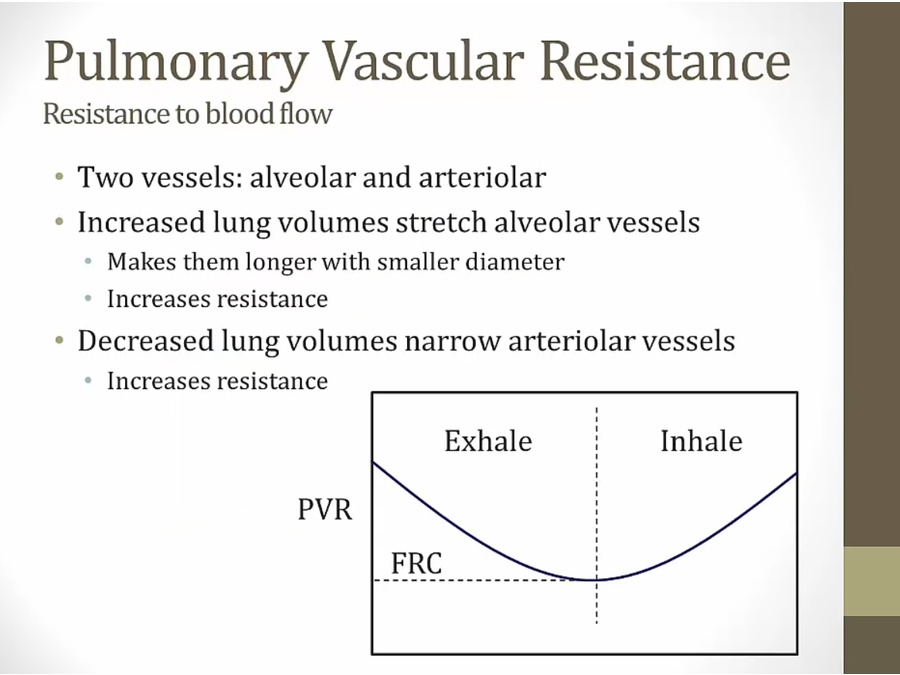
alveolar: blood supplying alveolus
arteriolar: blood supplying lung parts outside alveoli
inhale: increase resistance from alveolar vessels
exhale: increase resistance from arteriolar vessels
FRC: lowest point of pulmonary vascular resistance
Pulmonary Hypertension
_..


_..

right heart cath: cath into PA from heart
_..

V: energy needed to drive flow
I: how fast you want to go
R: resistance to flow
Ppa high in pulmonary hypertension, if any of the variables increased

high CO: increase flow through lungs
most common cause of PHTN nothing to do with lungs but with left heart

chronic hypoxia vasoconstrict

_..


Epoprostenol: IV, must infuse constantly, cumbersome
Last updated