Chlamydia Trachomatis
_Obligate intracellular bacterium that makes it difficult to visualize on microscopy and gram stain.
On island, white: poor gram stain: 
_Cell wall lacks peptidoglycan due the absence of muramic acid, a component of bacterial cell walls. For this reason, penicillins are not very effective in treating infection.
No mermaid: 
_Causes:
Urethritis
Pelvic inflammatory disease (PID)
Chronic conjunctivitis
Lymphogranuloma venereum (LGV)
Neonatal pneumonia and conjunctivitis
Fitz-Hugh-Curtis syndrome

_Serovars D-K and serovars A-C of Chlamydia trachomatis are distinguishable by different clinical manifestations. Classically, infections “above the waist” are caused by serovars A-C, while infections “below the waist” are caused by serovars D-K.
Serovars A-C of Chlamydia trachomatis
_Are transmitted by hand-eye contact, causing:
Eye inflammation
Corneal vascularization and scarring
Blindness
Pirate eye patches and hand-eye contact
ABlindness See
Leading cause of world blindness. Leader 
Serovars D-K of Chlamydia trachomatis
_Infect columnar epithelium of the genitourinary tract, causing:
Urethritis
Cervicitis
Pelvic inflammatory disease
Fitz-Hugh–Curtis syndrome (perihepatitis)
Neonatal disease (conjunctivitis and atypical pneumonia)
Note: Because neonatal infections are acquired during passage through the birth canal, they usually involve these serovars, even though they occur “above the waist.”
Neonatal conjunctivitis with mermaid. Takes longer (1-2 weeks) to develop
PID symbol 
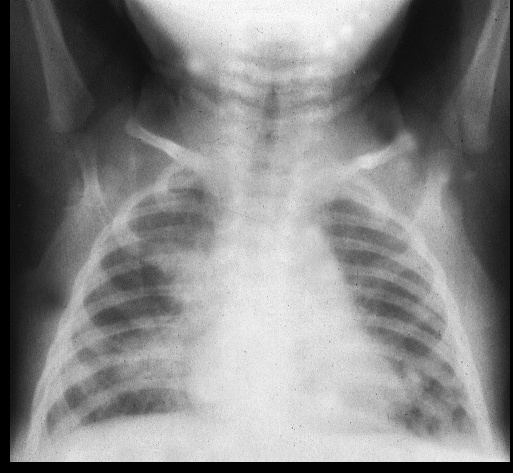
Neonatal conjunctivitis. Twelve-day-old with 5-day history of progressive lid swelling and discharge typical of chlamydial conjunctivitis.: 
Serovars L1-L3 of Chlamydia trachomatis
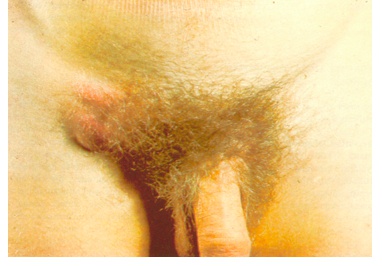
_Cause lymphogranuloma venereum, a necrotizing granulomatous inflammation of the inguinal lymphatics and lymph nodes. Lymphogranuloma venereum can present as painless genital ulcers and painful lymphadenopathy (buboes). Eventual resolution can result in fibrosis that can lead to rectal strictures with perianal involvement.
If untreated can lead to genital elephantiasis
Fever + leukocytosis
Painful lymphadenopathy on mermaid:

_ is sexually transmitted and often occurs in sexually active people and in neonates born vaginally to mothers with untreated C. trachomatis infection.
_Found in the genitourinary tract of infected, asymptomatic individuals. It can also be found in the eye, conjunctiva, and rectum.
_Enters epithelial cells as elementary bodies (EB) and is phagocytosed by macrophages, and forms reticulate bodies (RBs) that divide by binary fission and reorganize into EBs within cytoplasmic inclusions. Once the cell is filled with cytoplasmic inclusions, the cells burst and release elementary bodies to infect nearby cells. EBs are infectious but metabolically inert outside of a human cell.
Pearls: elementary bodies (enter); Clams: reticulte bodies: binary fission and replicate
Inclusion bodies under microscope: pile of pearls 
Cytoplasmic inclusion bodies in a patient with C. trachomatis: 
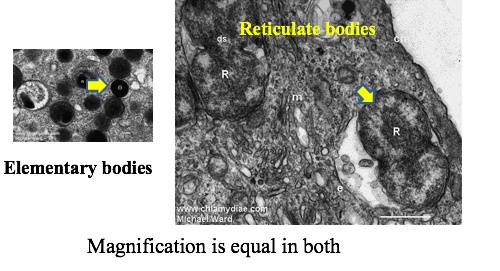
_ survives within an endosome in the cell by inhibiting fusion of the endosome to the lysosome.
_ Genital infection can present with lower abdominal pain, dysuria, and genital discharge.
Female patients typically present with
Mucopurulent vaginal discharge in cervicitis
Abdominopelvic pain in pelvic inflammatory disease
Dysuria in dysuria-pyuria syndrome
Females may have cervical ectopy (columnar epithelium in outer layer of cervix) and easily induced endocervical bleeding.
_Genital Male patients usually present with watery or mucous discharge. In addition they may present with dysuria in urethritis, and may have unilateral testicular pain in epididymitis.
In males with epididymitis, swelling of the epididymis may be accompanied by tenderness and palpable swelling.
Watery leakage; PID
_Rarely, patients develop reactive arthritis (a.k.a. Reiter’s Syndrome), a triad of arthritis, urethritis, and conjunctivitis. (“can’t see, can’t pee, can’t climb a tree.”) These symptoms may present in combination or individually.
Reactive arthritis: slap knee 
_In Pelvic inflammatory disease, the infection spreads to the fallopian tubes and can lead to infertility and ectopic pregnancies.
Fitz-Hugh Curtis syndrome
_Consists of infection of the liver capsule and peritoneal surfaces of the anterior right upper quadrant from Neisseria and Chlamydia spp.
_Acute symptoms manifest as a patchy purulent and fibrinous exudate known as “violin string” adhesions.
_Neonatal pneumonia and/or neonatal conjunctivitis occur due to untreated maternal Chlamydia trachomatis infection, as the baby is exposed to C. trachomatis in the vaginal canal during delivery.
_Vaginal or urethral swabs will show high levels of polymorphonuclear cells (PMNs) but, since Chlamydia trachomatis Gram stains poorly, no bacteria will appear on Gram stain.
Leukocytic uria
_In cases of dysuria, urinalysis will demonstrate pyuria but no bacteria on urinalysis or gram stain.
_Diagnosis is made with nucleic acid amplification testing (NAAT) of vaginal swabs or first-catch urine in men. Rectal or conjunctival sampling can also be done if infection is localized here.
Other diagnostic modalities include culture antigen testing and genetic probes.
gnat 
_Visualized with Giemsa stain.
Gems: 
_Uncomplicated Chlamydia trachomatis infection can be easily treated with oral azithromycin or doxycycline.
Doxycycline: cycle wheel
Macrolide: Ma-Crow 
Co-infection with Neisseria gonorrhoeae is common, so ceftriaxone MUST also be prescribed to treat gonorrhoea.
Gonorrhoea hat:
3 axes: 
Sexual partners are often asymptomatic (85% of infected people have no symptoms) and can often cause reinfection in the successfully treated patient. Partners must also be treated to prevent reinfection.
_Neonatal conjunctivitis and pneumonia are treated with oral erythromycin.
Last updated