11 Microcytic Anemia
Measurements
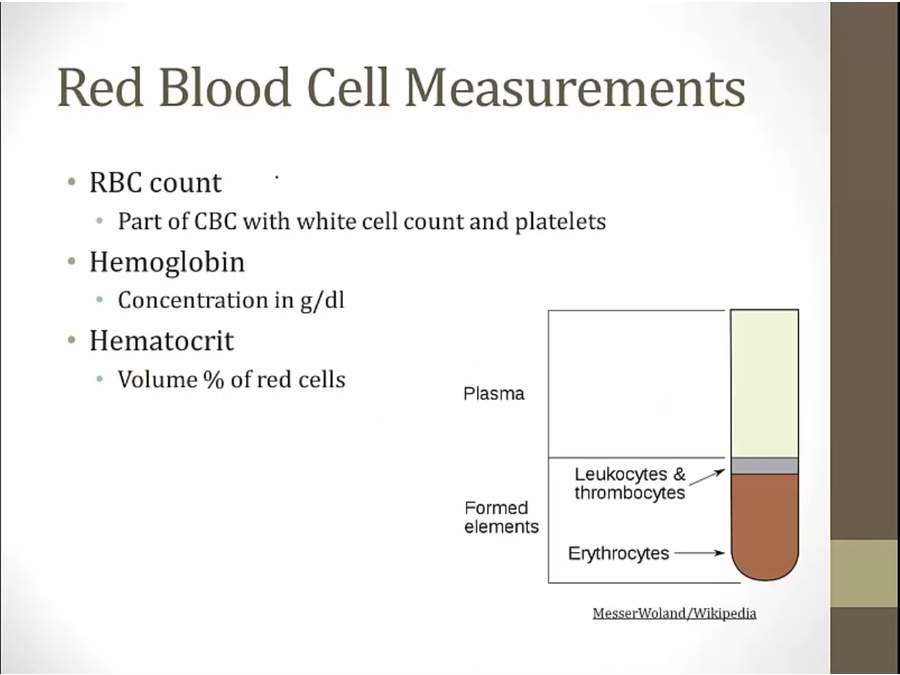
liquid plasma at top of tube
% occupied by red cells compared to whole = hematocrit


average RBC

MCV: mean amount of volume in RBC, not total volume
MCHC: ratio of MCH/MCV

MCV most important
iron deficiency/anemia of chronic disease: both microcytic and normocytic
Microcytic Anemia
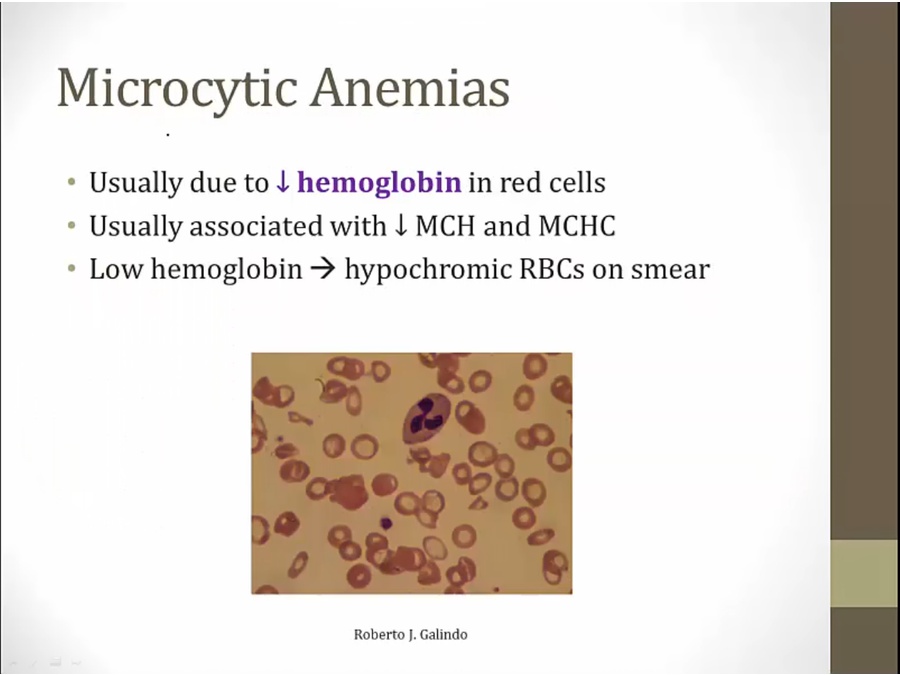
when not enough hemoglobin, RBC precursor undergoes extra devision, smaller RBC
histology: larger pale areas
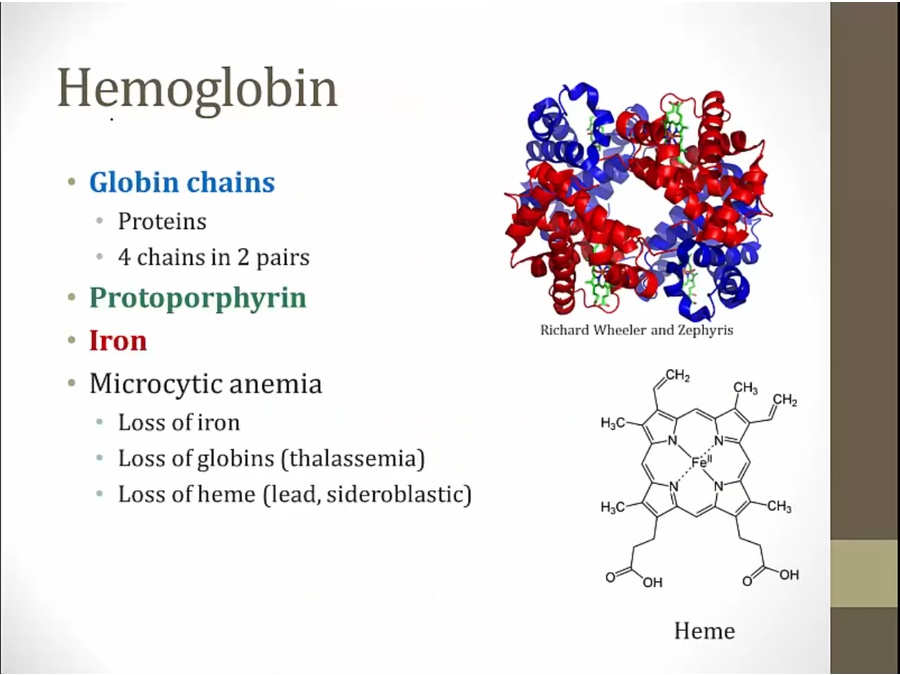
if any of the 3 main components deficient, anemia
protoporphyrin: surrounds iron in heme
loss of heme: lead poisoning, sideroblastic anemia



Iron Deficiency
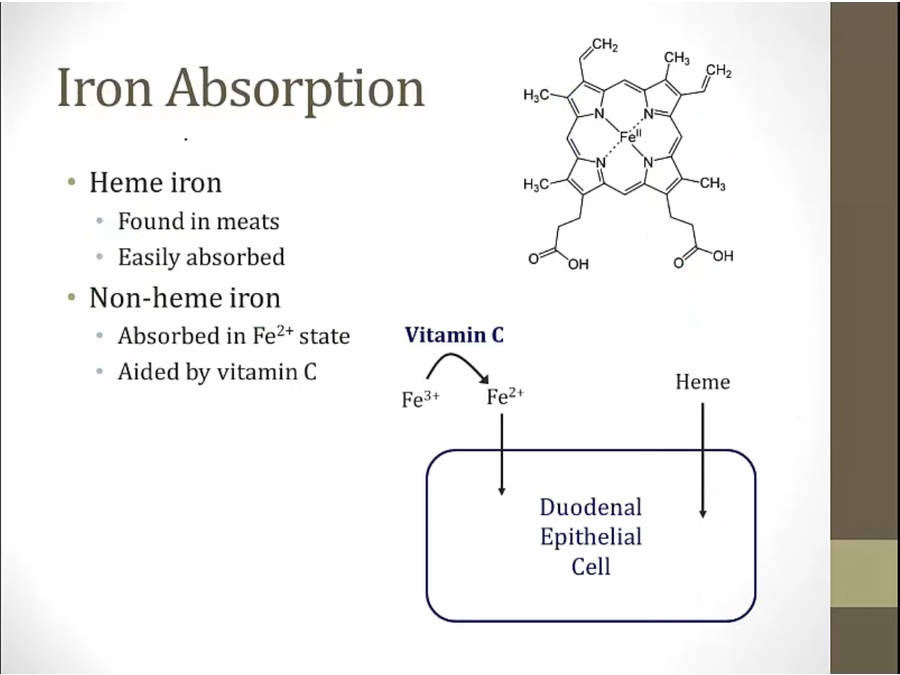
absorbed in 2 forms
heme: iron in center of heme, found in flesh of other animals
absorbed in duodenum
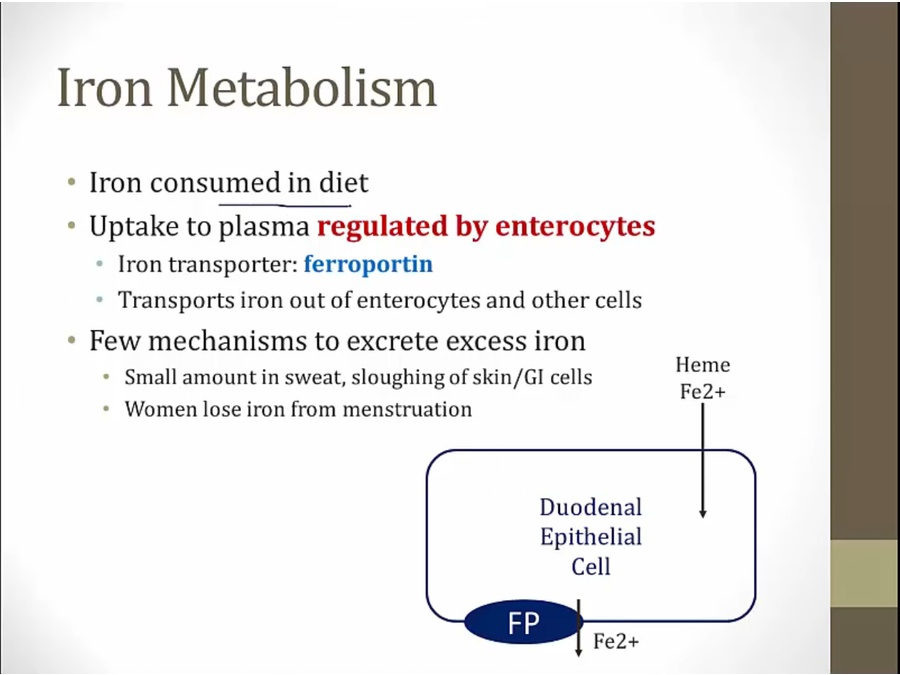
enterocyte uptake main way of regulation
ferroportin controls amt of iron released from duodenal cells into body


% sat: iron/TIBC
Cause


new born babies deplete iron store from mother in 6 months of age

loss of acid: gastrectomy/PPI

loss most common cause
colon cancer: very important/dangerous. Initial presentation
unexplained iron deficiency anemia: colon cancer workup

losing more iron than taking in
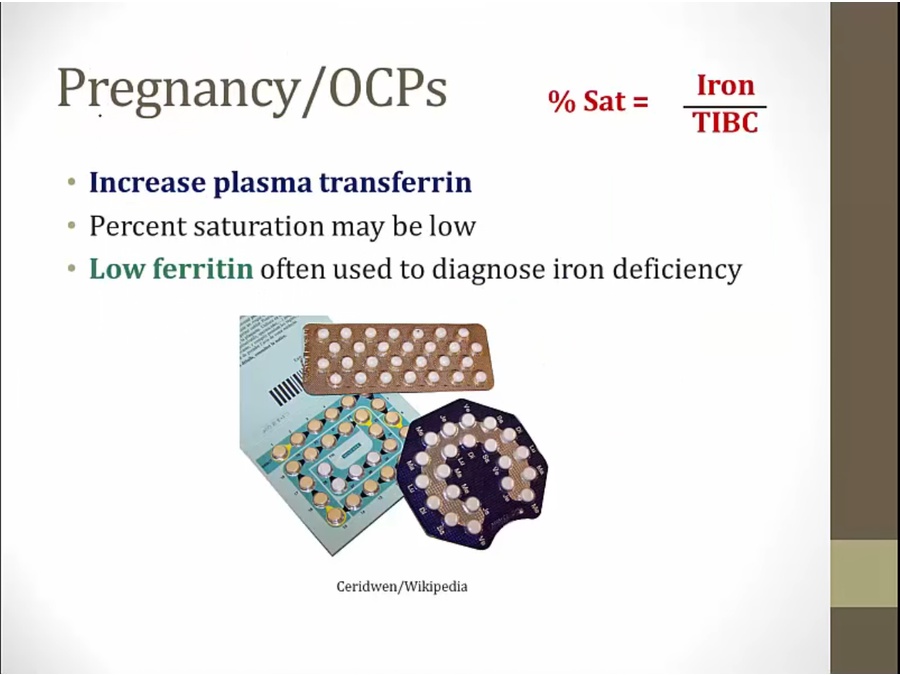
% sat low under pregnancy/OCP use, misleading for iron deficiency anemia
use ferritin for diagnosis in pregnancy/OCP

Pathogenesis

1st thing: deplete body storage
eventually ferritin storage depleted, and serum iron begin to drop
Diagnosis

fewer RBC produced
everything is low
initially make fewer RBC but maintain size
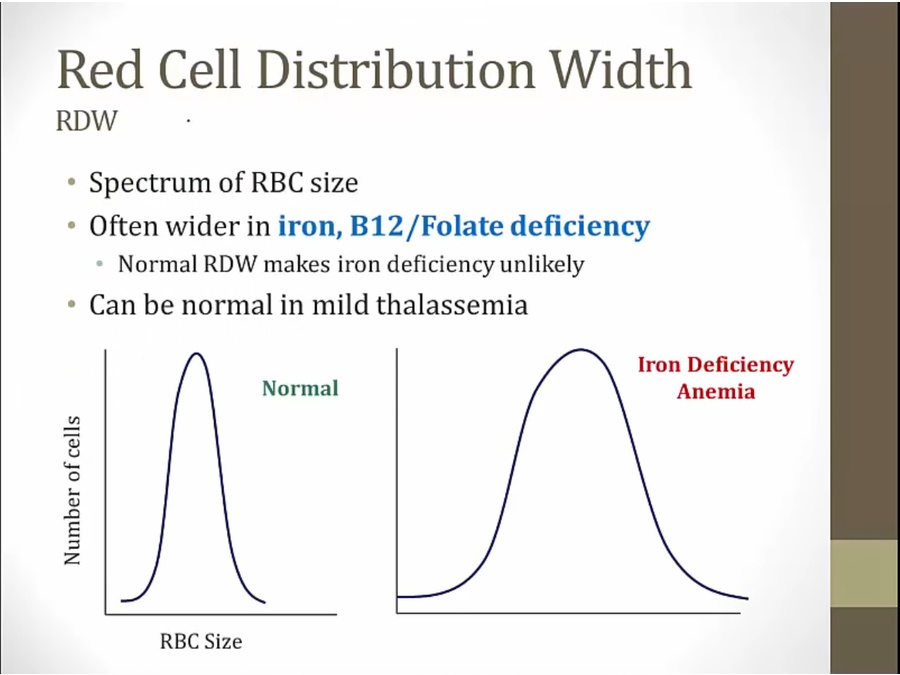
some cells find iron to form normal amount of hemoglobin = normal in size
other cells deficient in iron = small
can be seen in any nutritionally caused anemia
thalassemia: normal, deficient production of globin chain, all RBC same problem

not enough iron around: elevated protoporphyrin levels

hemochromatosis: iron overload
Treatment

Anemia of Chronic Diseases

mild anemia
severe anemia: unlikely microcytic

rising cytokines
RBC don't live as long
EPO rise higher in iron deficiency anemia compared to rise in chronic disease anemia

ferroportin lets iron out in enterocytes and macrophages
rise in ferritin: opposite of iron deficiency

Diagnosis

in real life: ferritin is acute phase reactant, increase not representative. Step 1, ferritin is chronic disease
TIBC: low, total body storage is high

hemochromatosis: iron overload
Lead Poisoning

battery: classic
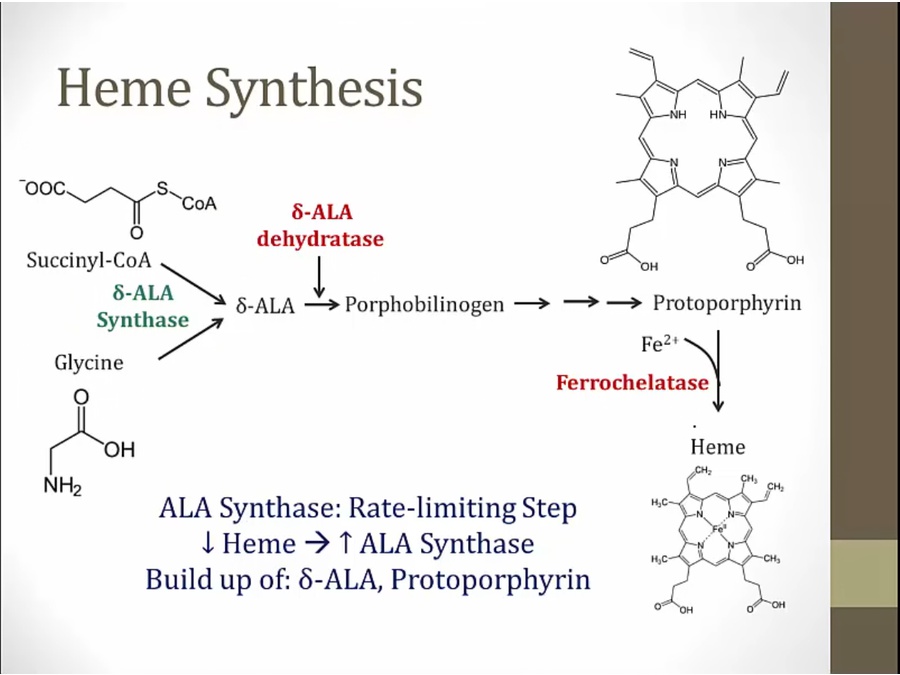
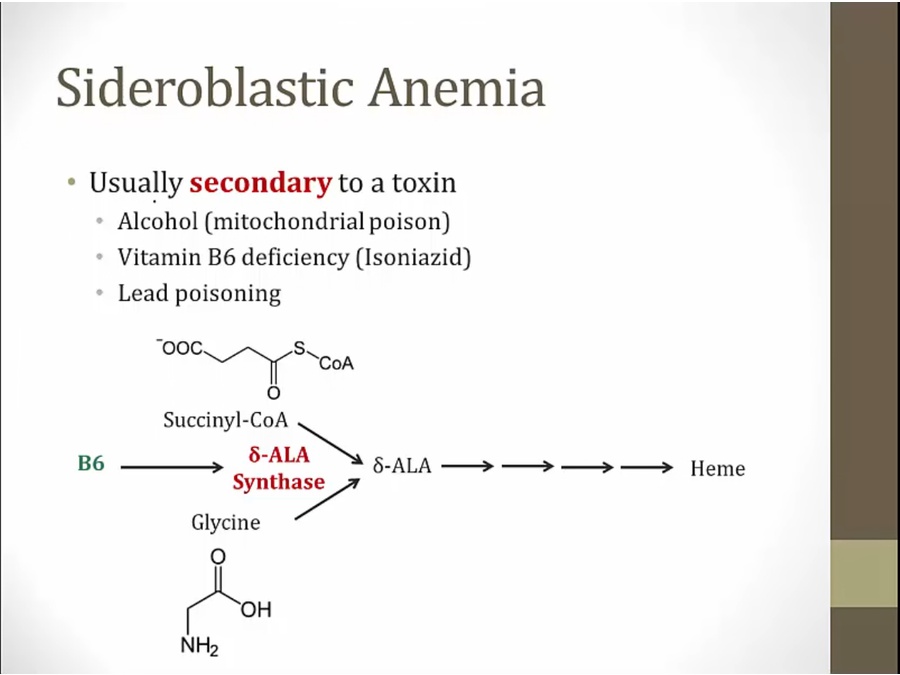
heme derived from succinyl coa and glycine
inhibition of D-ala dehydratase and ferrochelatase: low Heme
increased activity of ALA synthase: build up of D-ALA

protoporphyrin: also used to screen iron deficiency

Symptoms



DMSA aka succimer
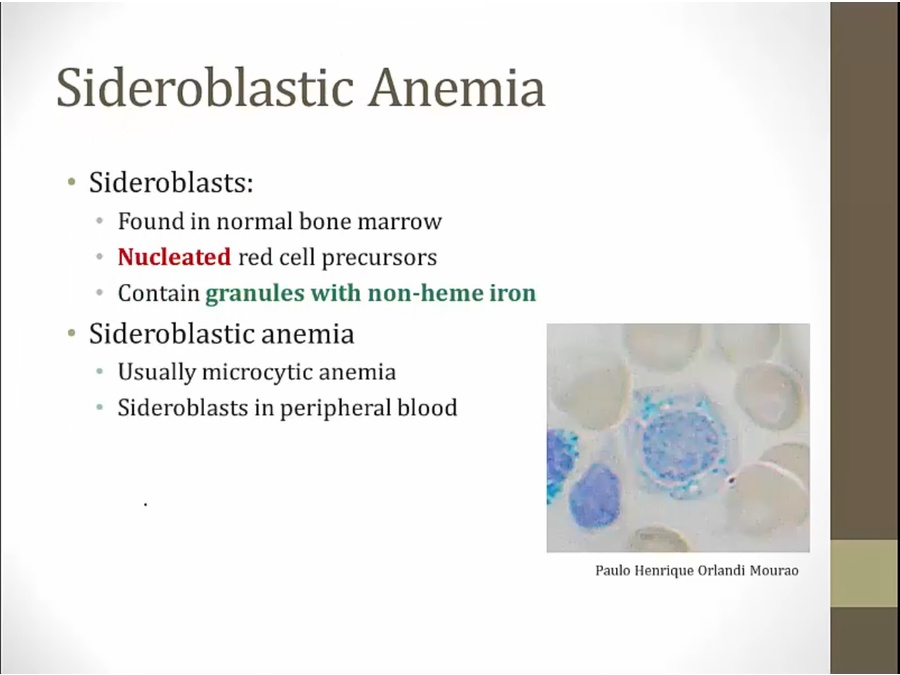
Sideroblastic anemia

B6 co factor
lead poisoning: underproduction of protoporphyrin

B6 activates available ALA synthase
Diagnosis

lead poisoning sideroblastic: can have high protoporphyrin
Last updated