14 Allergies
Acute
path: IgE mediated, exposure to trigger causes mast cell cross linking/degranulation. Histamine releases that mediates reaction
3 types for acute:
anaphylaxis
urticaria
Angioedema
Anaphylaxis
symptoms: urticaria (rash) all over body + hypotension, wheezing, loss of airway
diagnosis: clinical
treatment
epinephrine 1:1000 IM ASAP
H1/H2 blockers for histamine relief
Steroids: lessen immune reaction
Urticaria
symptoms: wheal, whelt, erythema, no hypotension
diagnosis: clinical
treatment
usually self limiting: observe, topical antihistamines
rule out anaphylaxis
Case: someone with bee sting. Treat anaphylaxis if present. Otherwise treat urticaria
Angioedema
symptoms: Swelling airway and wheezing. No hypotension or rash
Always with ACE I use
diagnosis: clinical
treatment
secure airway
H1/H2 blockers
Steroids
rule out C1 esterase deficiencies: give FFP
Chronic
allergic rhinitis
allergic conjunctivitis
Allergic Rhinitis
Triggers: seasonal (weed, pollon) or perinneal (around all the time, smoking, dusts, pets)
symptoms
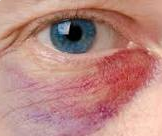
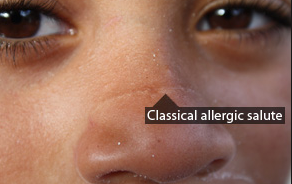
allergic shiners and salute
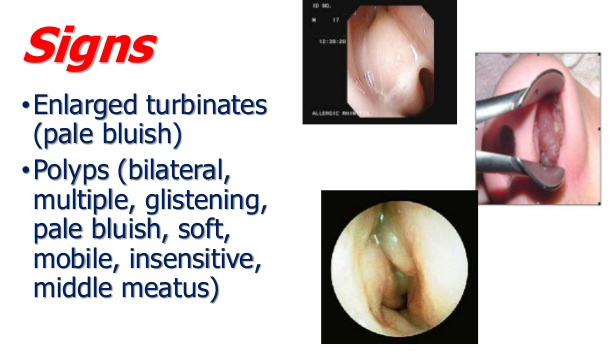
pale, boggy mucosa; polyps in nose
cobblestoning from postnasal drip
diagnosis
clinical only
RAST and skin testing only when refractory or for desensitization
treatment
avoiding triggers
intranasal steroids
H2 > H1
Allergic Rhinitis
pale, boggy mucosa, and polyps:
cobblestoning:

Allergic rhinitis
Allergic shiners are dark circles under the eyes caused by congestion of the nose and sinuses. They're usually described as dark, shadowy pigments that resemble bruises:
The allergic salute is the characteristic and sometimes habitual gesture of wiping and/or rubbing the nose in an upwards
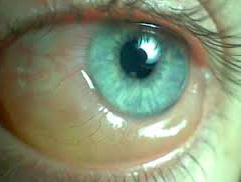
Allergic Conjunctivitis
same path, diagnosis, treatment as rhinitis
symptoms: shiners, injection, chemises (swelling)
Food allergies
Usually outgrow: wheat, soy, milk, eggs
May carry throughout life and cause anaphylaxis: shellfish, nuts
symptoms: NVD, look for other allergy signs (asthma, atopic dermatitis). Can cause anaphylaxis
diagnosis: food trial: withdraw all agents, introduce one at a time
treatment: avoid triggers, epi
Milk Protein Allergy
path allergy to soy
symptoms: NVD, bloody bowel movement. Failure to thrive despite feeding adequate amounts
diagnosis: clinical
treatment: change formula to cow's milk, breastfeed, hydrolyzed formula
Last updated