10 Intrinsic Hemolysis
PNH
Cause

normally complement does not lyse RBC

acquired: genetic mutation some point in life
GPI: anchors that attach DAF/CD59 to membrane
stem cell: RBC, platelets, WBC also involved
Pathogenesis, Symptoms
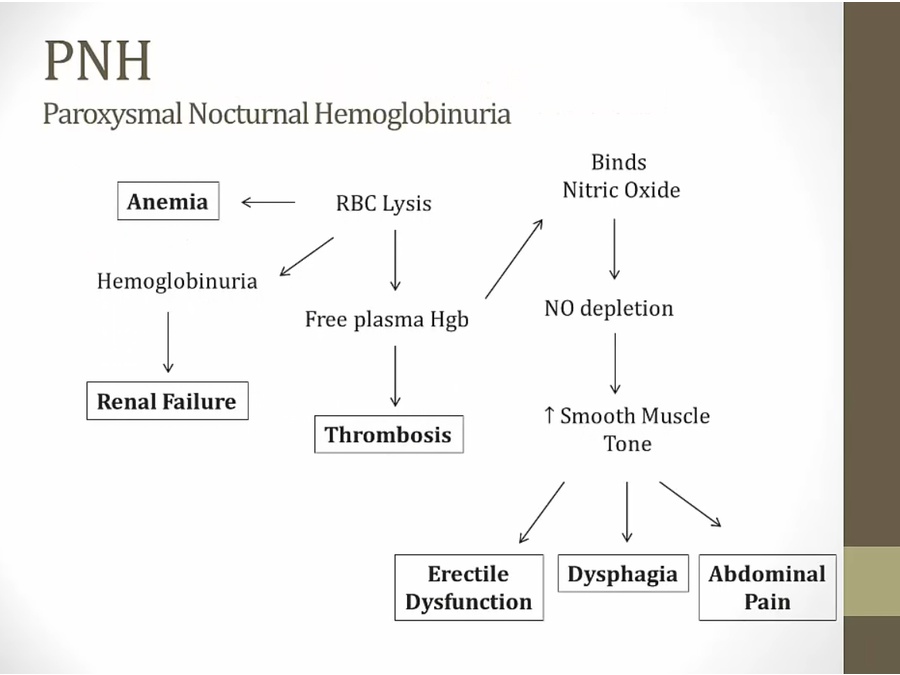
Free plasma Hgb thrombogenic, thrombosis
platelets lysed: spill granules
Priapism: sustained prolonged erection

paroxysmal: sudden
episodes at night when urine changes color

hypercoagulable
Diagnosis, treatment

antibodies not part of problem
Pyruvate Kinase Deficiency

when levels low, RBC most affected (require pyruvate kinase and glycolysis for anerobic)
no ATP, membrane fails
when problem with membrane, eaten in spleen

disease severity based on how low enzyme activity is
G6PD Deficiency

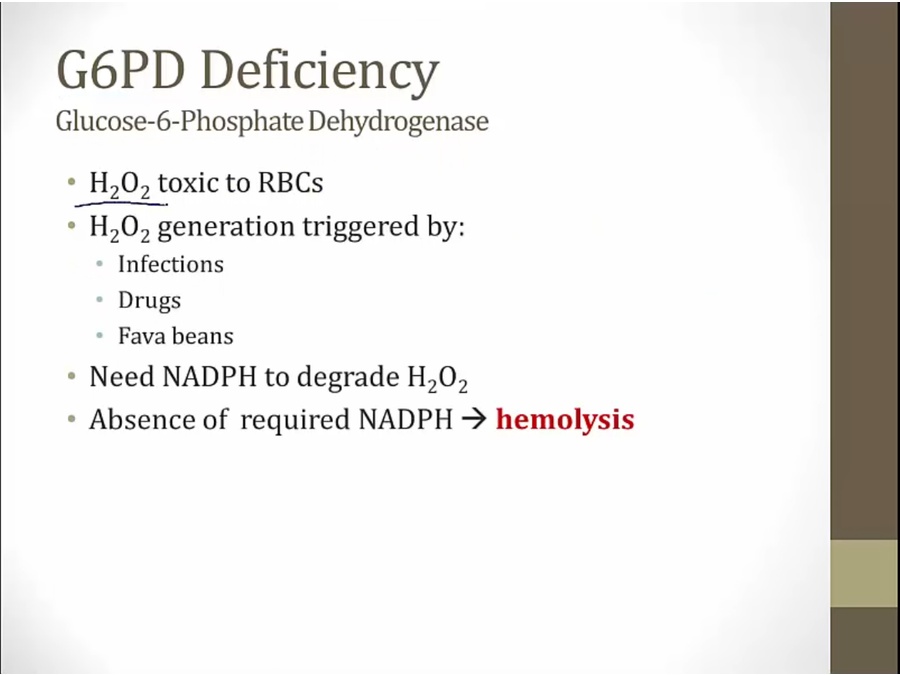
especially fava beans

antimalarials can trigger hemolysis

know the countries
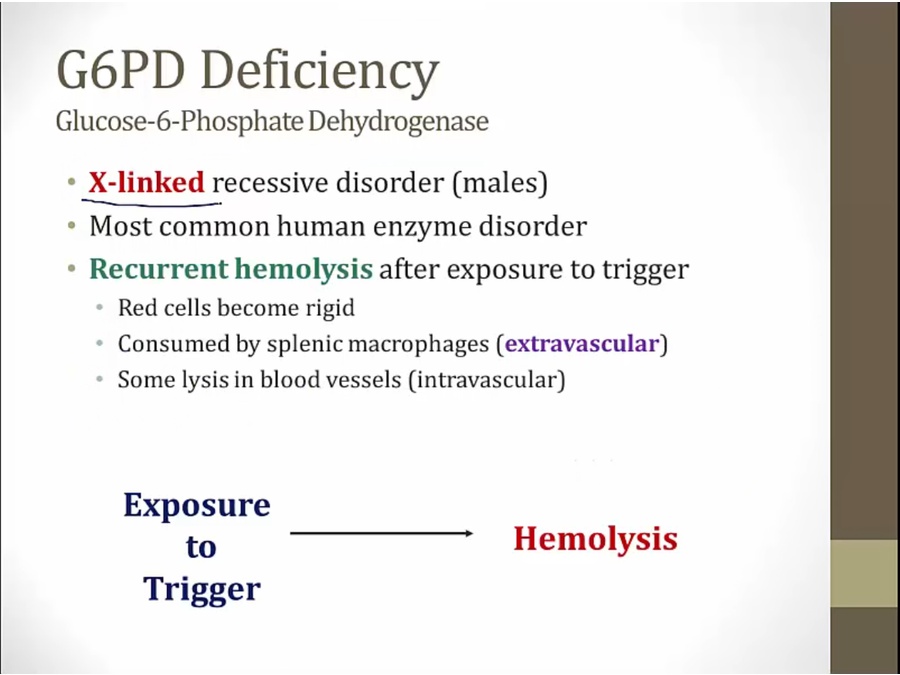
Can't make ATP, RBC become rigid, cannot maintain membrane
most extravascular
some become so damaged/rigid: intravascular


Bite and seeds: bite cells and Heinz bodies seen in RBCs
Broken G6PD-free fruit: hemolytic anemia in G6PD deficiency

Bite and seeds: bite cells and Heinz bodies seen in RBCs
Broken G6PD-free fruit: dapsone can cause hemolytic anemia in G6PD deficiency

"Color queen" - chloroquine, beads join together as polymer, blocking plasmodium heme polymerase. High resistance
"Primal queen" - primaquine, can cause anemia in G6PD deficiency
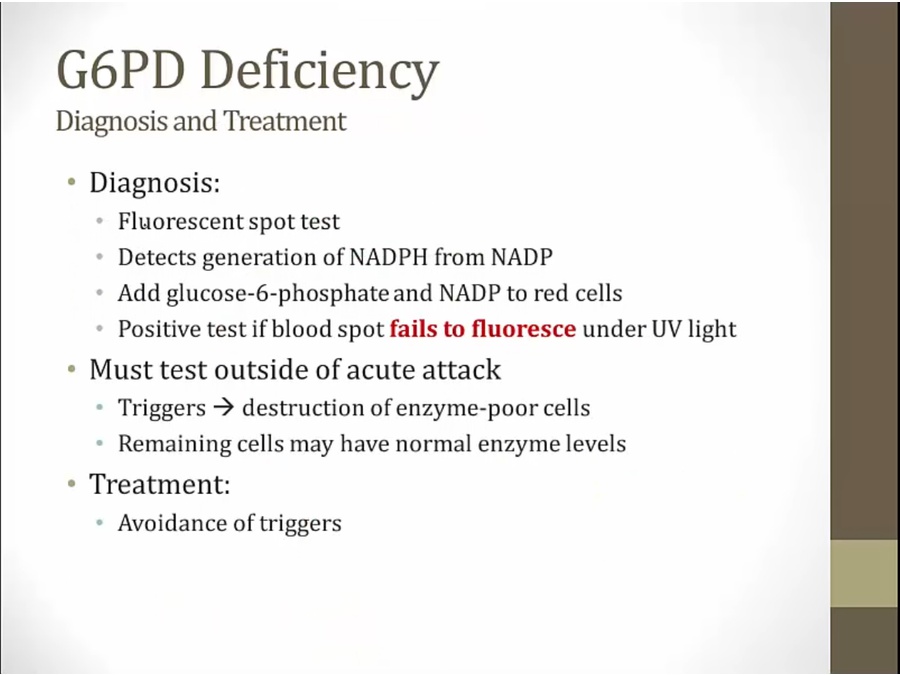
fluorescent spot: screening test
pts unable to generate NADPH
normal: generate NADPH, fluoresce
must test when not having acute attack

Hereditary Spherocytosis
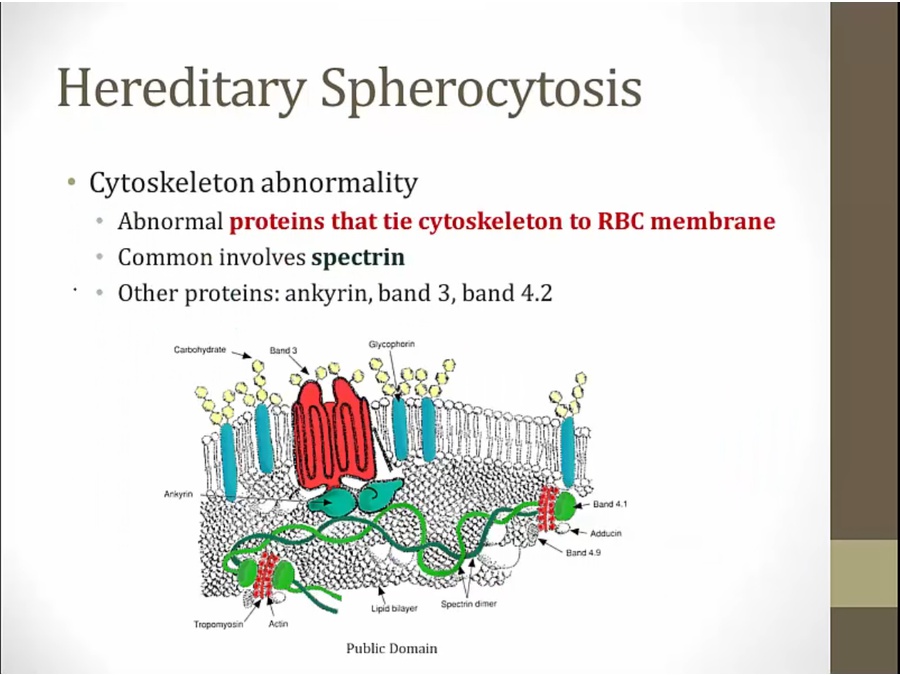
proteins give RBC biconcave shape and flexibility
abnormal: rigid membrane
spectrin for spherocytosis

problem lies in chronic extravascular hemolysis, not O2 carrying capacity
Diagnosis
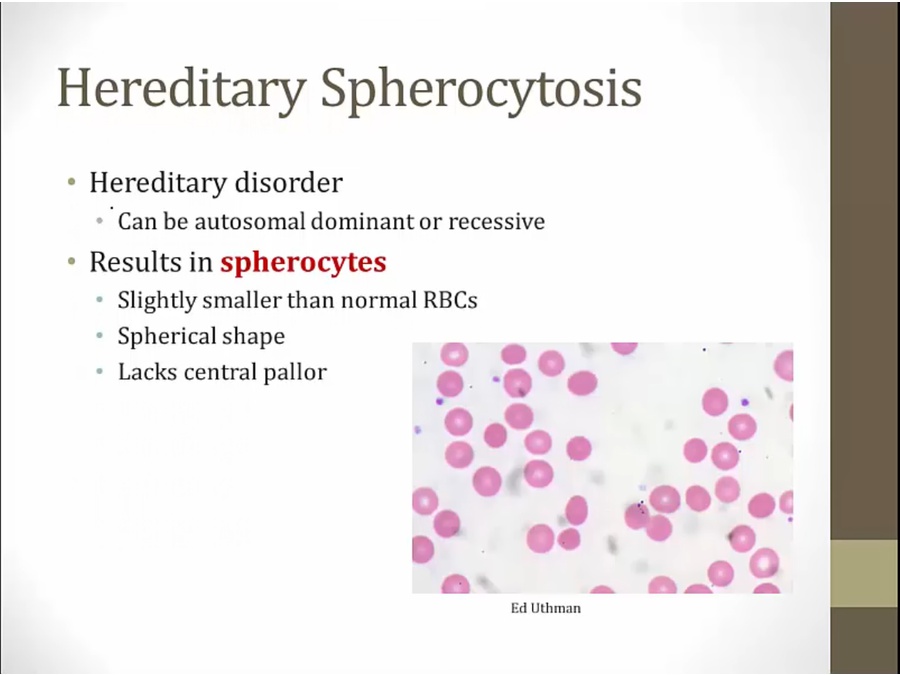

progressive loss of cell membrane as RBC circulate in vasculature
RDW: red cell distribution width
normally: narrow, some small/large cells. Most are in middle
Spherocytosis: large spectrum of RBC sizes

material density goes up
MCHC: mean corpuscular hemoglobin concentration
MCV: mean corpuscular volume: average size of RBCs
chronic hemolysis: more reticulocytes, high MCV

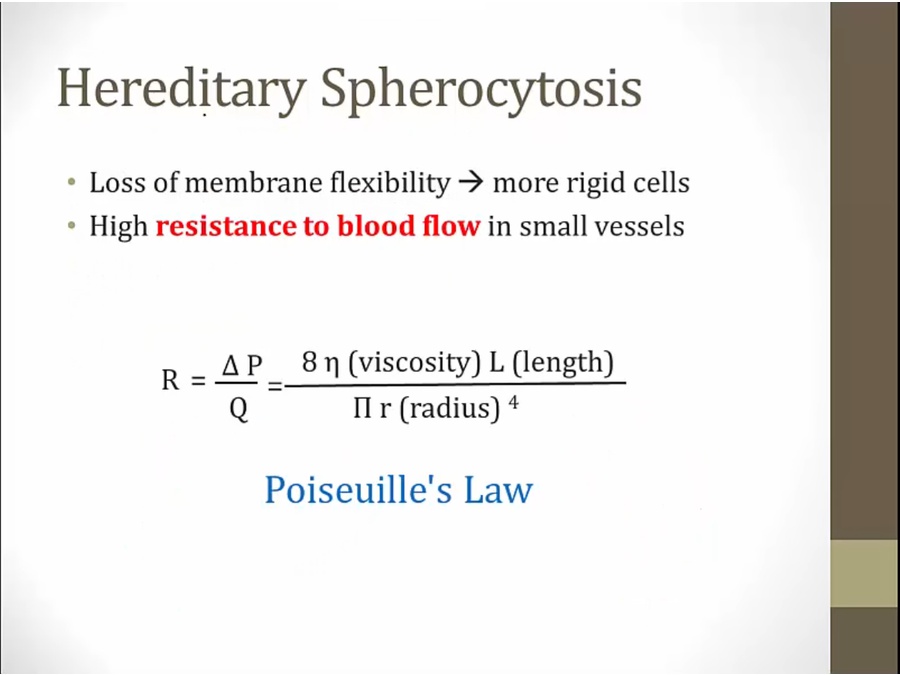
viscosity of blood go up with rigid cells

no spherocytes in G6PD with infection


Last updated