Vaccines
Overview
Do not memorize schedule
Understand how many vaccines they need and what to do if behind schedule
When in doubt: give vaccine
Active Vaccine
Antibody against antigens include:
organism pieces
toxins
toxoid: look like toxins (e.g. tetanus toxoid vaccine)
Passive Vaccine
Includes:
maternal to fetus
IVIG
Herd immunity
if enough people get vaccined in the community, disease disappears
Vaccine Reactions
Allergies
Egg Allergies
Do not give Yellow fever vaccine
Safe to give MMRV (MMR, varicella) vaccines
Safe to give Flu vaccines now
Vaccines contraindicated in cases of neomycin allergy include:
IPV
MMR
Varicella
Hepatitis A
The vaccines for rotavirus and meningococcus are contraindicated in cases of latex allergy.
Live attenuated
Immunocompromised: AIDS, transplants, biologics drugs (Etanercept), pregnant women
MMRV
Flu, intranasal
Normal Reaction
If temp < 104
Erythema
Consolable
Abnormal Reaction
temp > or = 104
Inconsolable
frank anaphylaxis
Scenarios
Sick: give vaccine
family history: give vaccine
autism: give vaccine
Individual Vaccines
Hep B
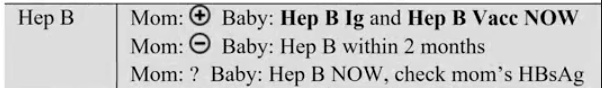
prevent vertical transmission via IVIG and hep B vaccine immediately (both within 12 hours)
mom -: start Hep B series
mom unknown: give hep B within 12 hours, test mom, if positive, give HBIG within 7 days
DTaP

DTaP: 5 doses. Big D = bigger dose
TdaP: 1 dose after 11, every 10 years
Td: booster, can be given instead of TdaP
HiB

Getting Hib does not give immunity
MMRV

Pneumococcal

mostly for adults
kids: if sickle cell or asplenic
Meningitis

every one gets, especially if shared space (college, military)
HPV

Hep A, B

Flu

Diseases shouldn't see
Tetanus
cause: dirty wound from rusty metal puncture
symptoms: lock jaw, spastic paralysis, die
diagnosis: clinical
treatment: intubate, sedate, muscle relaxers, paralytics, IV antibiotics (metronidazole)
prevention: Tdap, Td booster, tetanus IVIG
get 3 doses as adult (tdap, dtap, td, tt; 1 must be in adulthood), get every 10 years
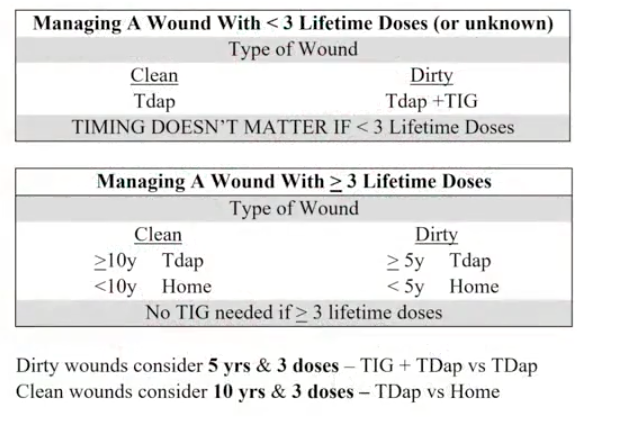
dirty wound: metal, dirt, feces, soil, saliva
if more than 10 years since last dose: give tdap. Can also use Td
Diptheria
Symptoms: Fever; dysphasia, dyspnea from pseudomembrane (do not try to peel)
Diagnosis: clinical
Treatment: secure airway (intubate), anti-toxins,IV antibiotics
Pertussis
Symptoms: 3 phases
Catarrhal: nonspecific symptoms looks like cold, infectious
Paroxysmal: coughs followed by wheezing on inspiration (whooping cough)
Resolution:
Diagnosis: clinical
Treatment: supportive, erythromycin
Rotavirus
oral vaccine
CI in anyone with
intussuception
Immunodeficiencies such as SCID (live, attenuated vaccine)
latex allergies
Last updated