42 Brain Tumors

in order of frequency
kids: most in posterior fossa near cerebellum


one of most common symptoms: headache

Adult
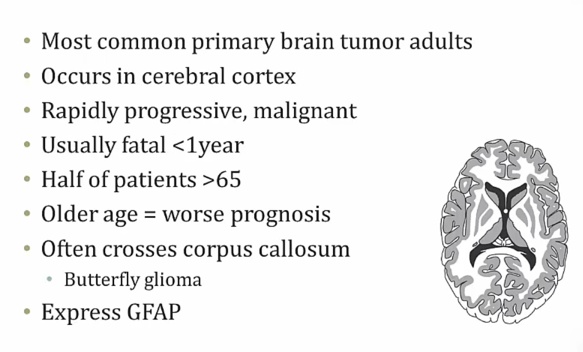
Glioblastoma
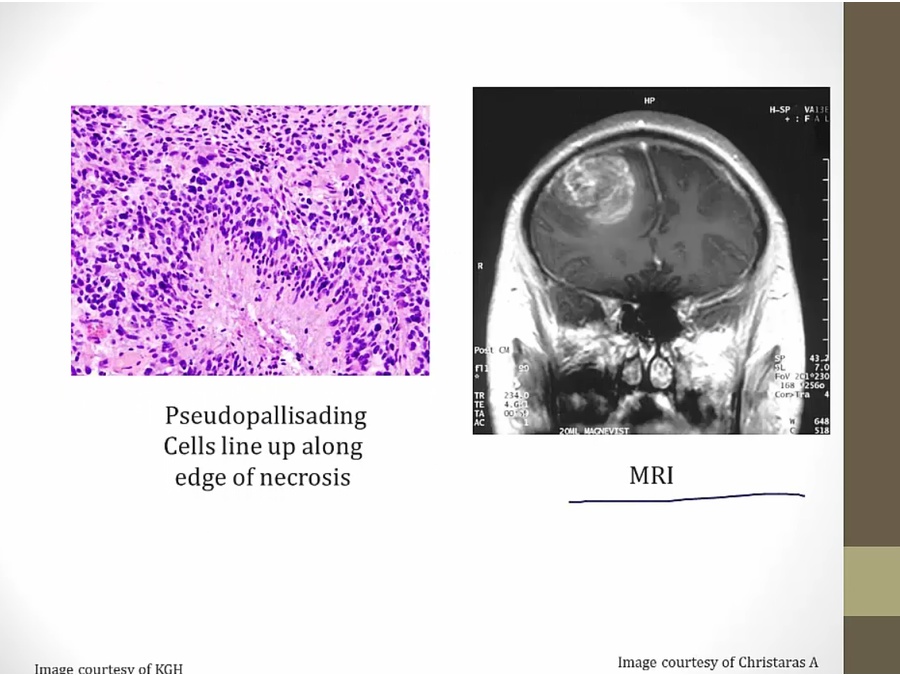
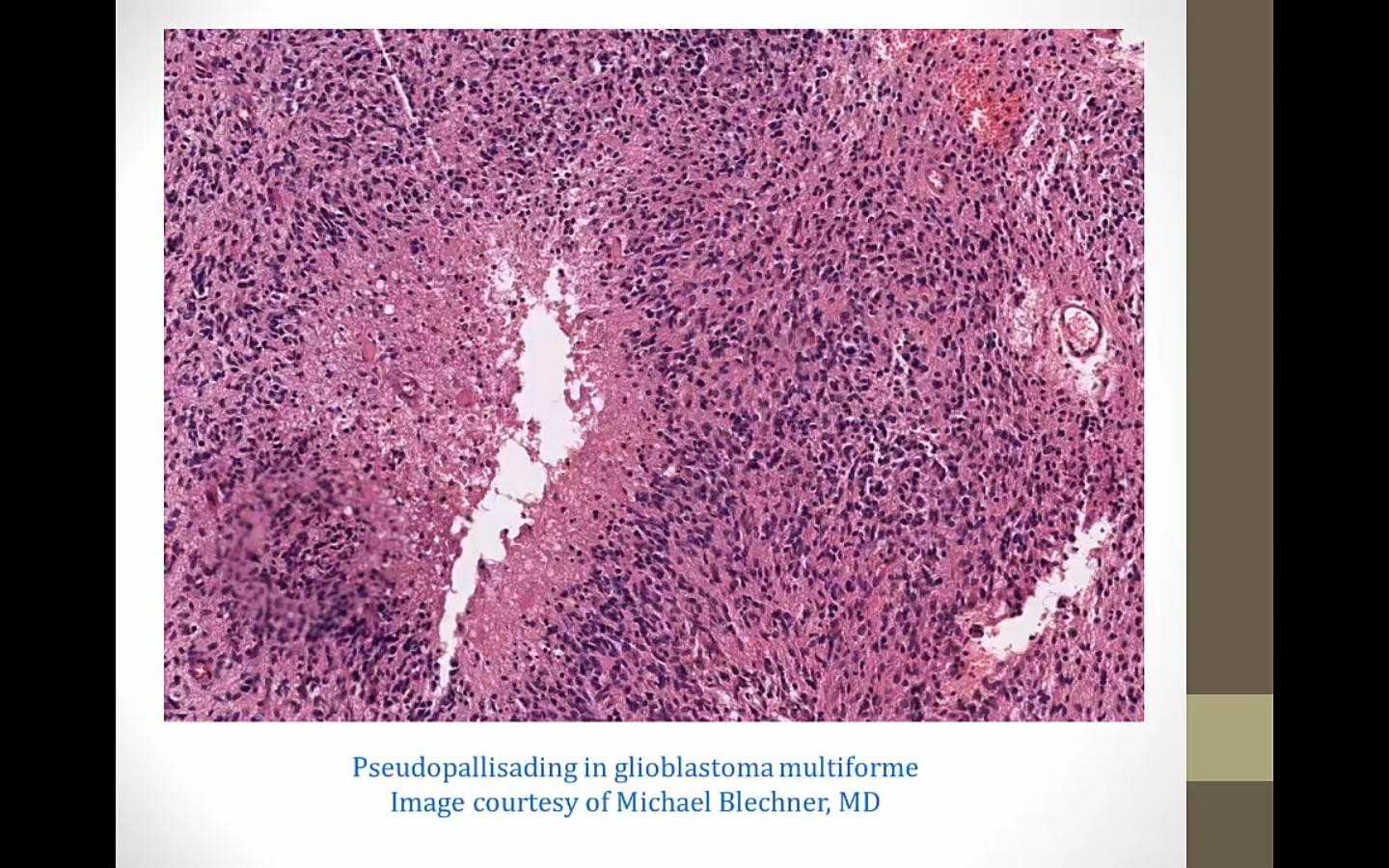
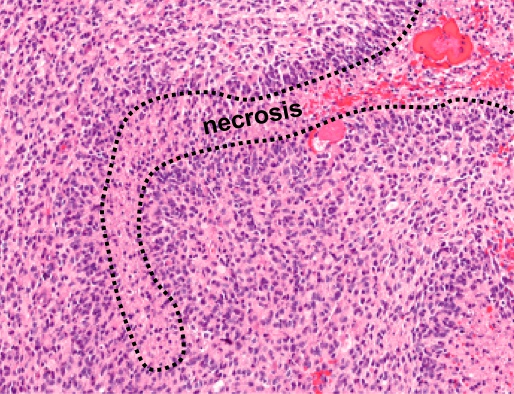
left: nuclei lining up (schwannoma, nuclei line up on their own)
pseudopallisading: nuclei lining up because being pushed by necrosis from middle
right: tumor invading cerebral cx.,
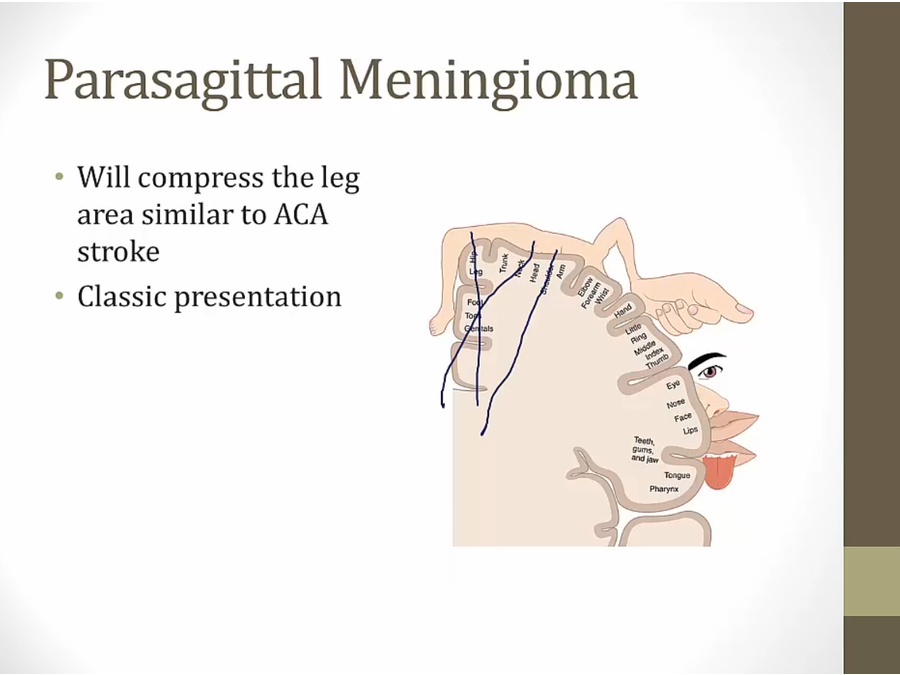
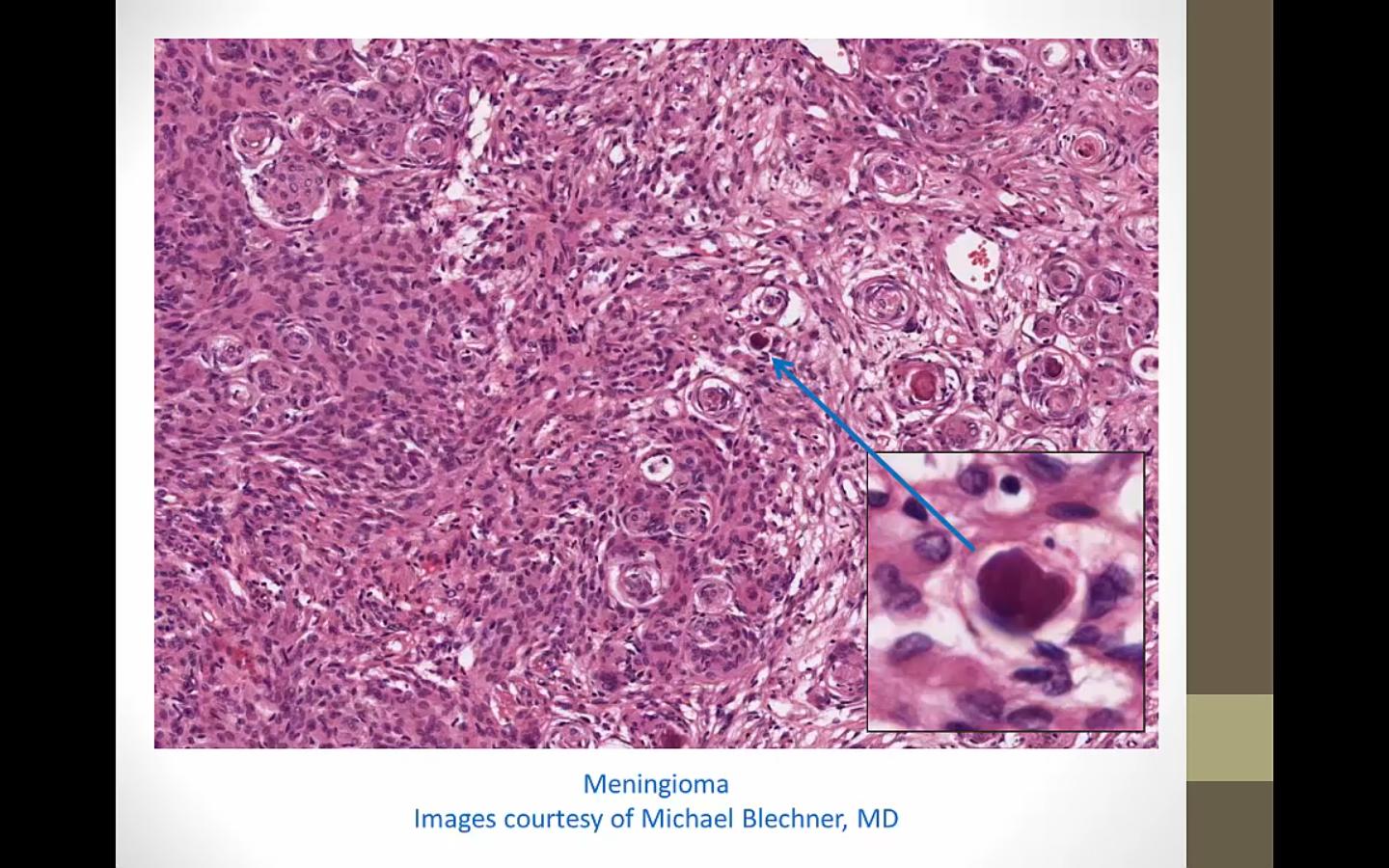
Meningioma

not in brain tissue itself, can attach to dura with tail

if large enough: seizures
tumor expresses estrogen receptors
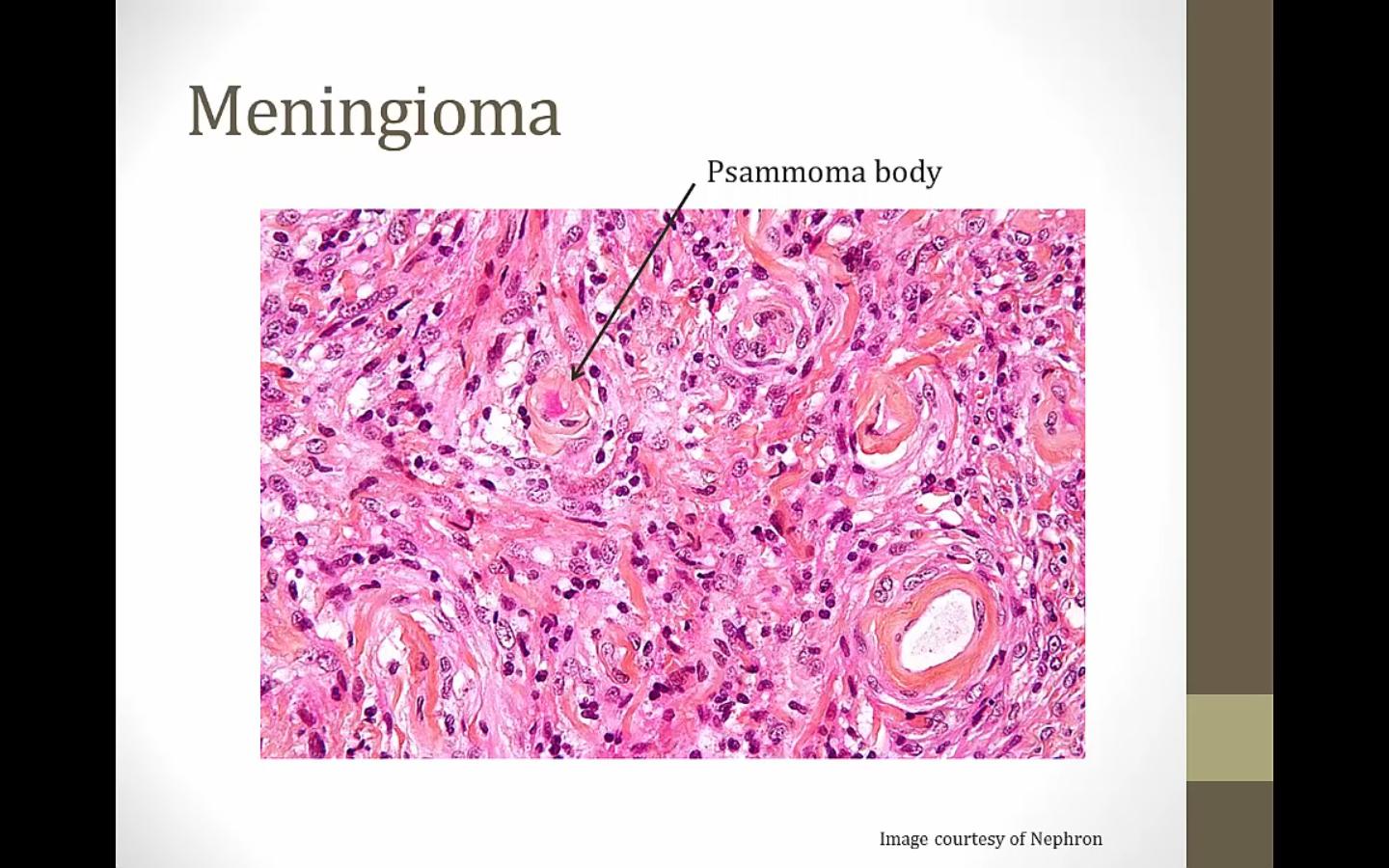
Ca deposits
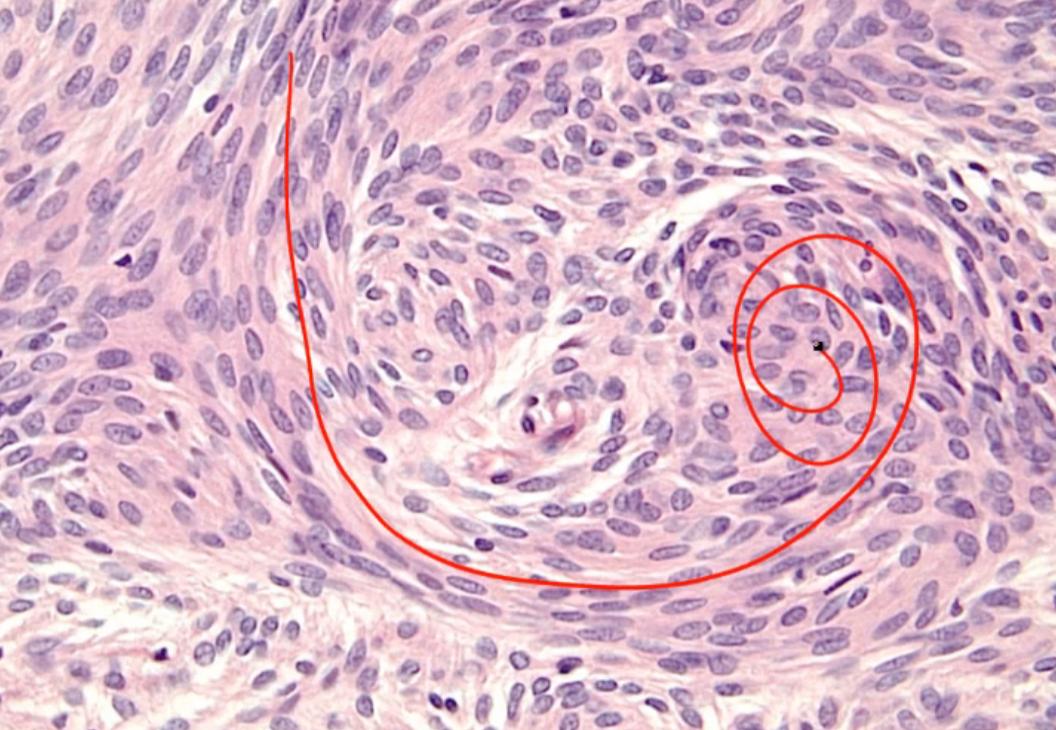
whorled appearance
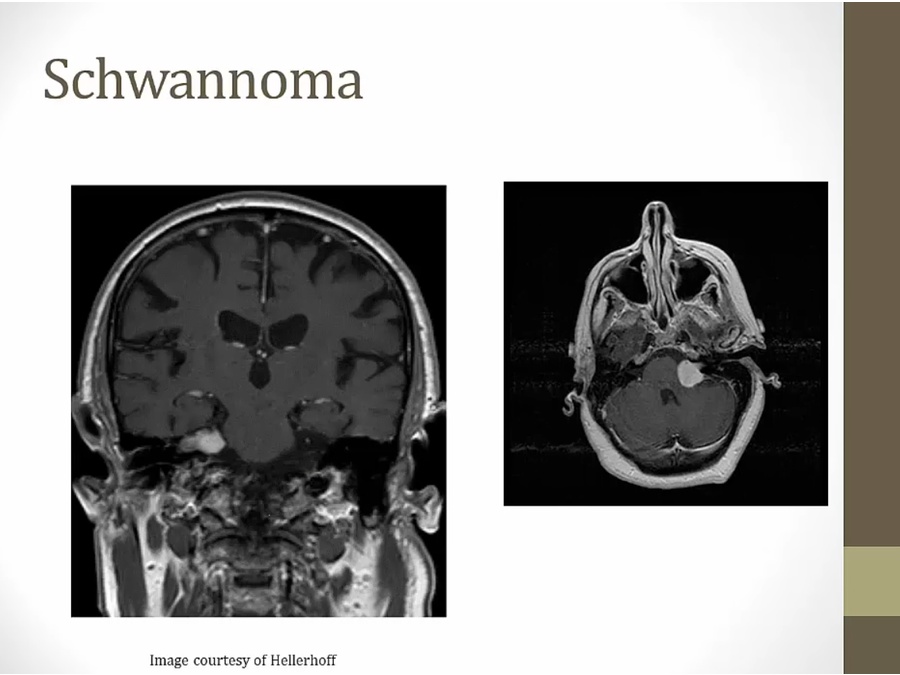
Schwannoma

locate more peripherally
S100 marker of schwann cells
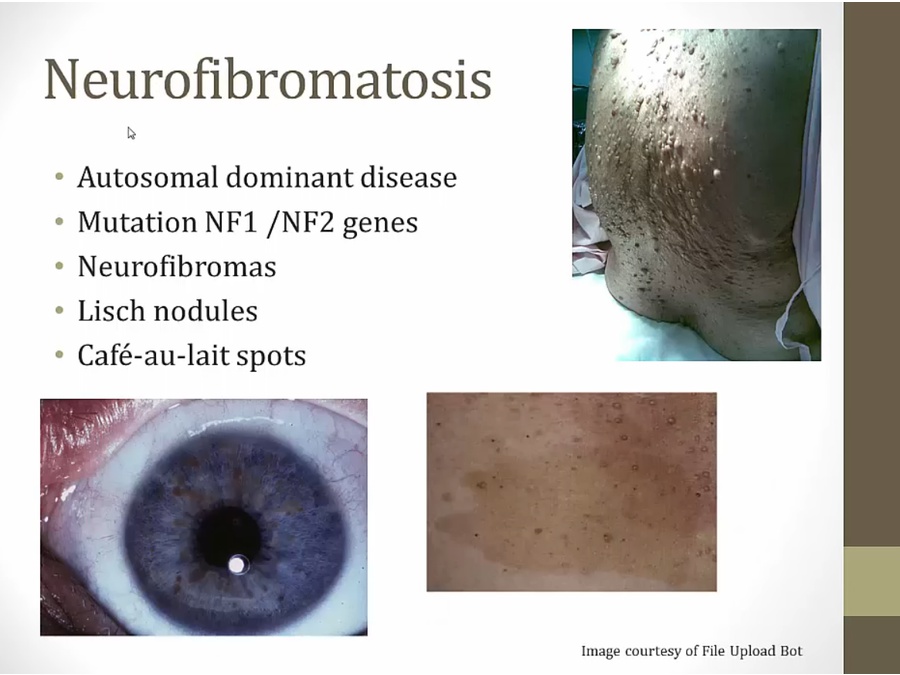
Neurofibromatosis
association with schwannomma
diffused neurofibromas: upper right, diffused skin nodules all over body
lower right: cafe au lait, like coffee spilled on skin
lower left: lisch nodules, brown spots
neurofibromas: neural crest origin

type 2: almost all get bilateral schwannomas (deaf)
MISME: multiple tumors
Oligodendroglioma
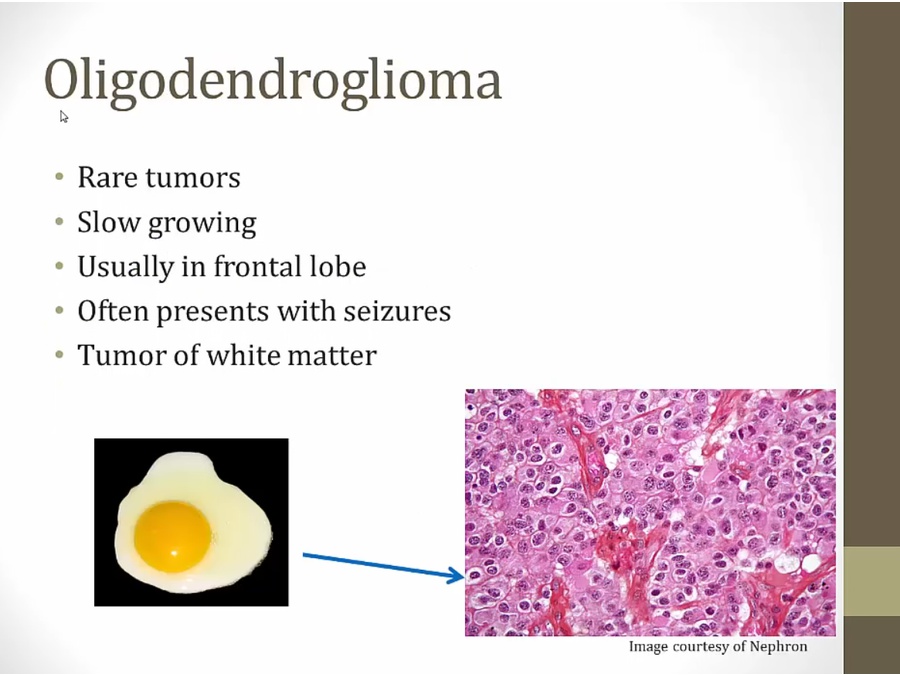
calcified tumors present in frontal lobe, presenting with seizures
oligodendrocytes myelinate axons in white matter
fried egg appearance

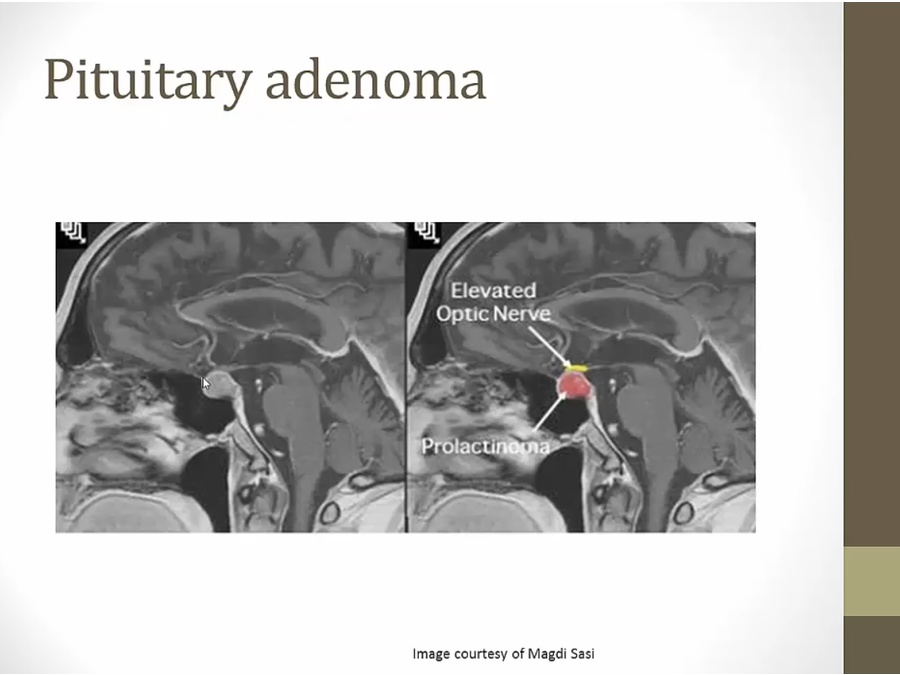
Pituitary Adnoma
Cavernous Hemangioma
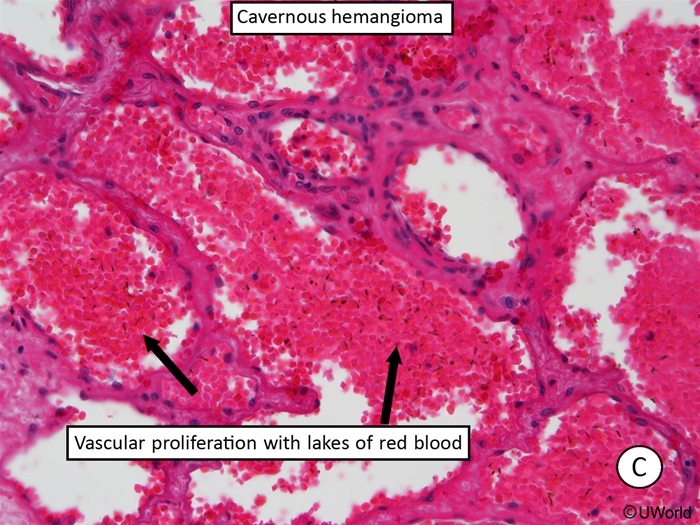
Cavernous hemangiomas are vascular malformations that frequently involve the deeper tissues of the body, such as the liver and brain. Gross examination of hemangiomas reveals a "mulberry-like" appearance due to their purple vascular clusters. Histologically, they are composed of abnormal, dilated blood vessels with a thin adventitia lacking elastic fibers and smooth muscle. The reduced structural support gives them a tendency to leak, causing recurrent hemorrhage.
Most patients with cavernous hemangiomas are asymptomatic, although hemangiomas in the brain may cause neurologic deficits and seizures due to compression of the surrounding tissue and irritation from recurrent bleeding. Surgical resection is indicated for lesions causing intractable epilepsy or progressive neurologic deficits.
Childhood Tumors
most common to least common
Pilocytic astrocytoma

derived from astrocytes
cerebellar dysfunction: ataxia, loss of balance
top right: rosenthal fibers (long red lines), seen anytime gliosis (growth of glial cells)
GFAP: Glial fibrillary acidic protein, expressed in astrocytes
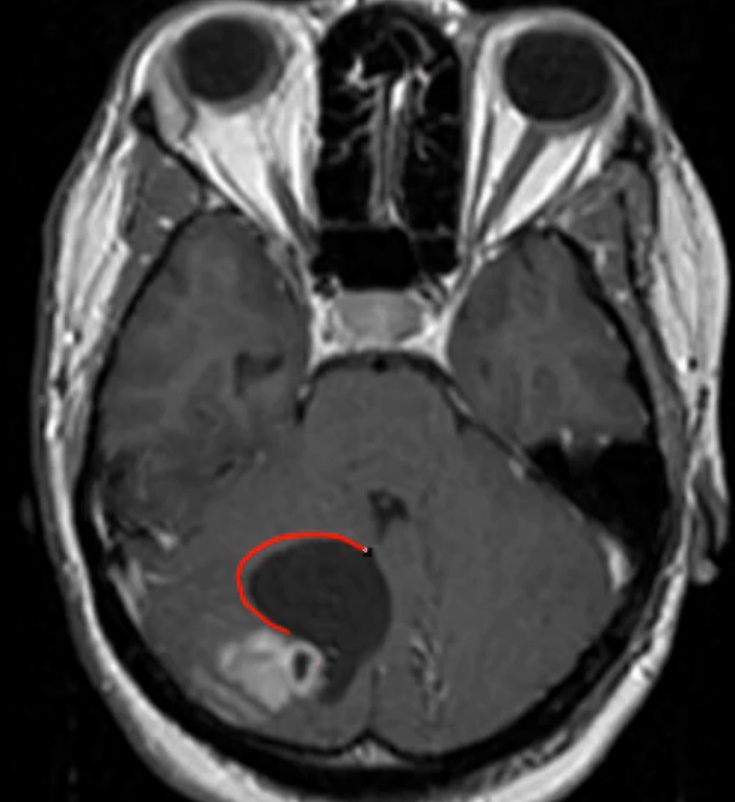
cystic lesion with nodule growing on its wall
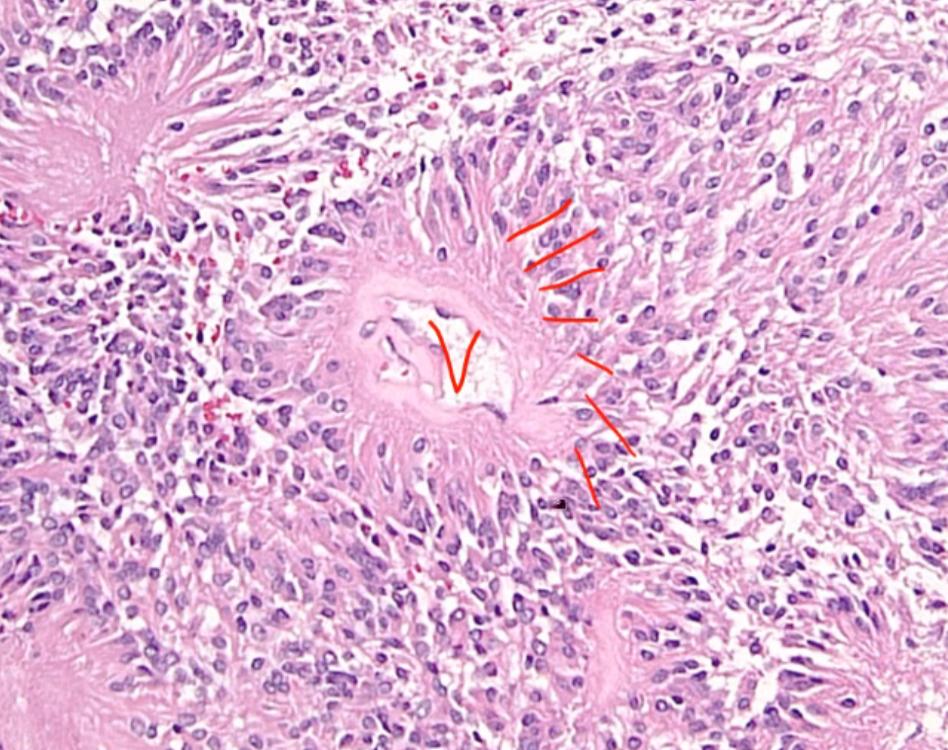
Medulloblastoma

second most common
can't stand/sit up without falling
neuroectoderm embryonic structures, thus more often in children
association with Turcot Syndrome
PNET: tumor suppressor gene

hearing loss, neurocognitive impairment
noncommunicating hydrocephalus
can cause cauda equina syndrome

left: rosettes, circulation orientation of flowers
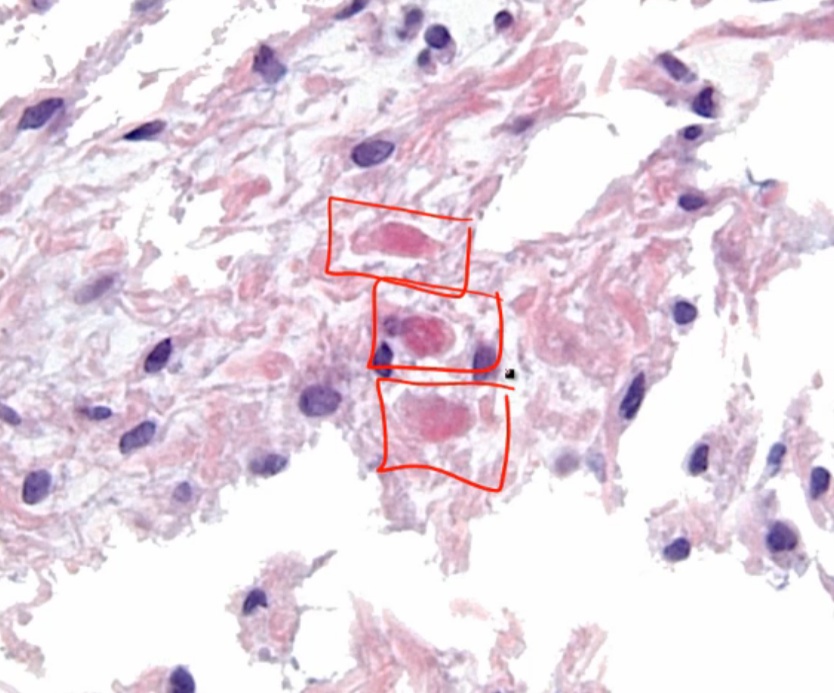
Ependymoma
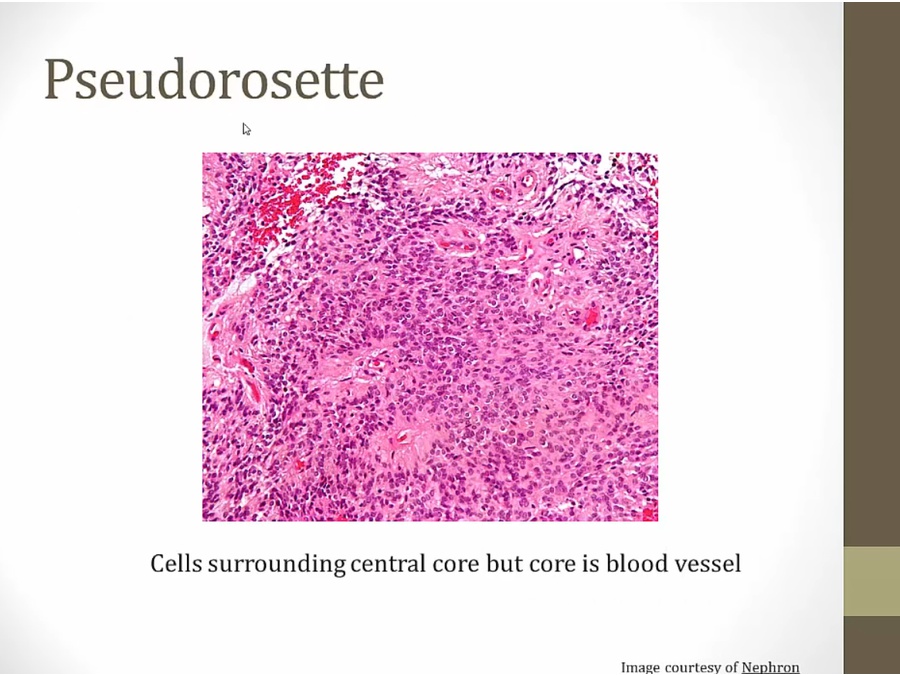
curcles of cell surrounding blood vessel as central core
Hemangioblastoma
EPO
VHL.,


Craniopharyngioma

occur above sella tursica

calcified and look like teeth because derived from mouth tissues
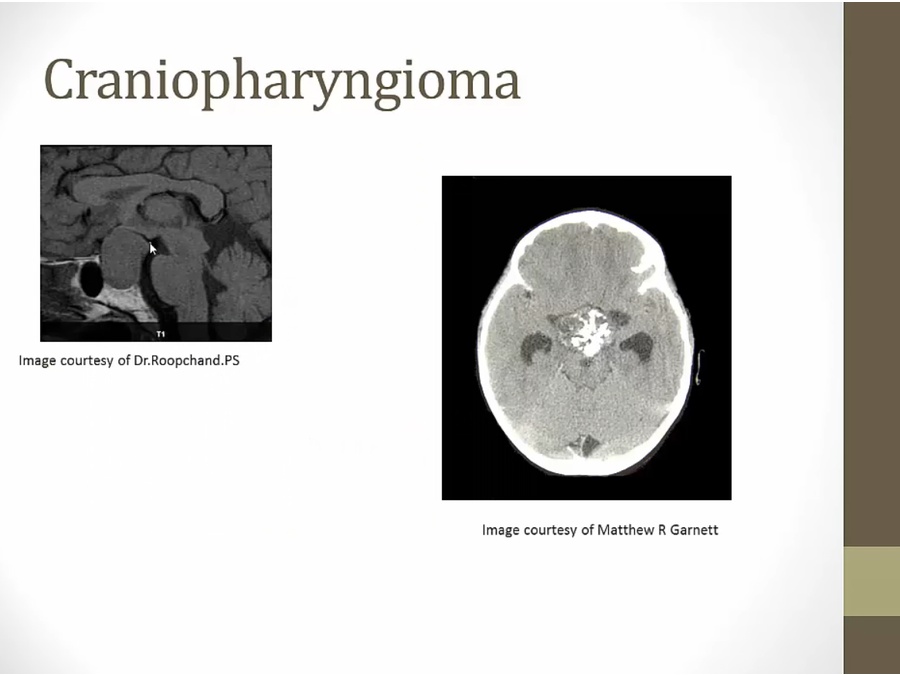
right: Ca inside
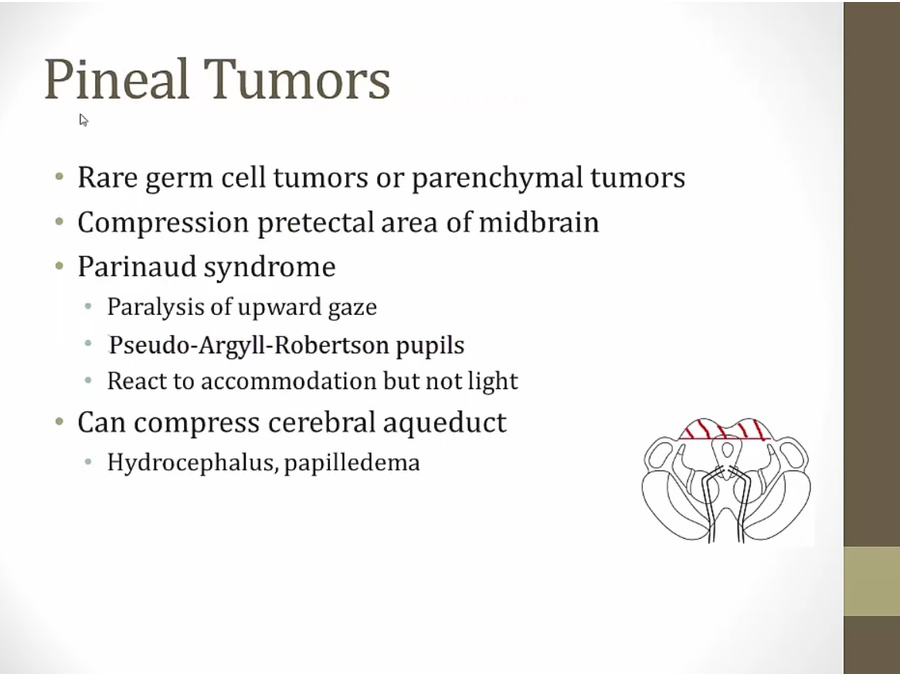
Pineal tumor
Histology and markers
craniopharyngioma
meningioma
glioblastoma, pseudopallisading
oligodengroglioma, fried egg
rosenthal fibers, pilocytic astrocytoma
rosettes, medulloblastoma
pseudorossettes, ependymoma
Schwannoma
craniopharyngioma
meningioma
Last updated