04 Adrenal Disorders
Overview
Adrenal disorders are divided into 4 types:
Excess cortisol: Cushing's
Insufficient cortisol: adrenal insufficiency
Excess mineralocorticoids: aldosteronism
Tumors: pheochromocytoma, paraganglioma, neuroblastoma, adenomas..
Management
Cushing's
[_](Cushing's syndrome is)Syndrome with excess cortisol.,
Cause
[_](Cushing's disease, most common cause)Most common cause:..

[_](Cushing's syndrome types)Types of Cushing's syndrome..
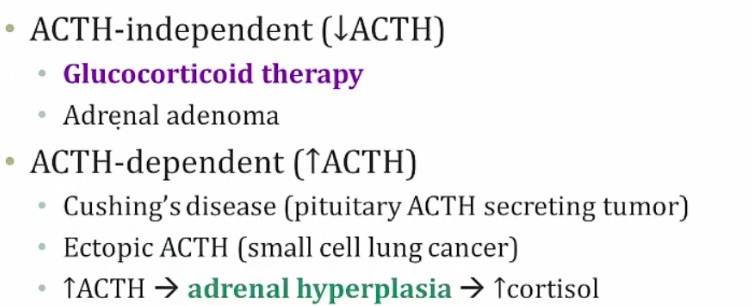
ACTH-independent: either exogenous cortisol (steroid) therapy or adrenal adnenoma producing cortisol. In this case, there would be a low ACTH from pituitary because of negative feedback
ACTH-dependent: tumors secreting ACTH. Could be Cushing's disease (pituitary ACTH tumor) or small cell lung cancer
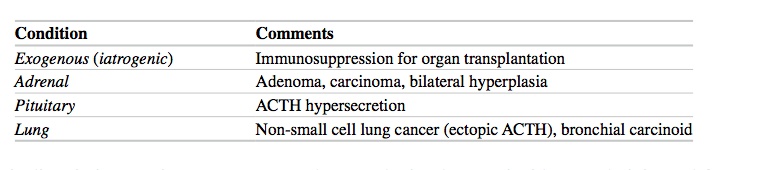
[_](Causes of Cushing's and gross size)
With exogenous, there's bilateral atrophy. In primary adenoma, there is 1 large and 1 small adrenal. Paraneoplastic and ACTH secreting must be distinguished because both have enlargement..
_The decreased ACTH levels can lead to bilateral adrenal atrophy..
[_](Skin pigmentation happens in which type of Cushing's syndrome?)Only happens in ACTH dependent. Can be Cushing's disease (pituitary ACTH tumor) or small cell lung cancer..

ACTH Indepent Examples
[_](ACTH dependent Cushing's disease examples).,
An ACTH-secreting pituitary adenoma
Paraneoplastic syndromes (e.g. renal cell carcinoma, small cell lung cancer, bronchial carcinoids, neural tumors)
Symptoms
[_](Cushing's syndrome main symptoms)Symptoms are:
The usual high cortisol and associated symptoms
Low FH/LSH and associated symptoms
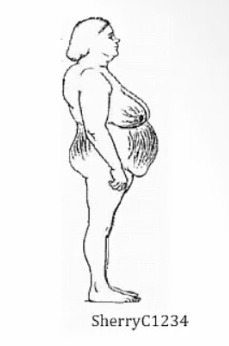
Stimulation of adipocytes and obesity
Thinning of skin

osteoporosis
very common in women

fat growth
Moon face: round like the moon


cortisol inhibits fibroblasts/collagen
Most easily seen with forearm..
Diagnosis
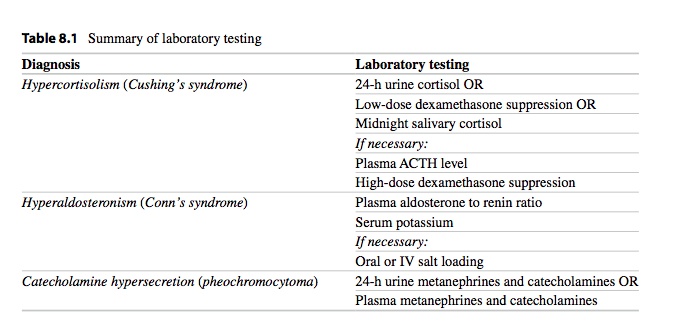
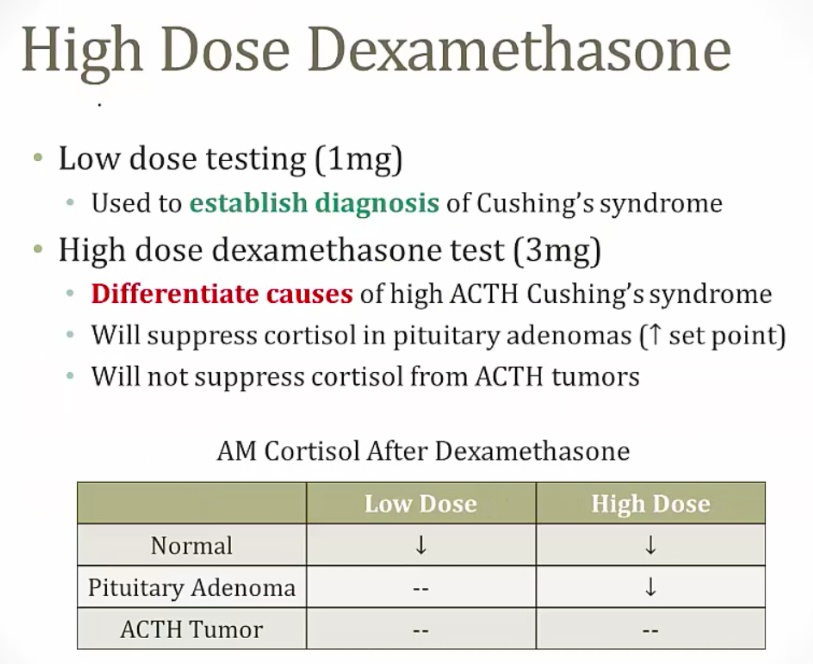
[_](Cushing's syndrome steps for diagnosis)Steps for diagnosing Cushing's:..
Diagnosis Cushing's via 24 hour cortisol level or low dose dexamethasone suppression test
Find cause by measuring ACTH
If high ACTH, use high dose dexamethasone to differentiate between pituitary or ACTH tumors
[_](Why can't you measure plasma cortisol to diagnosis Cushing's?)

..
Step 1, diagnosis Cushing's
[_](Cushing's diagnosis labs)

Can also use low dose dexamethasone suppression test..
Low dose dexamethasone suppression test
Diagnosis for Cushing's syndrome..

Step 2, find cause
[_](Cushing's diagnosis. Determine cause between ACTH dependent and independent)
 ..
..
Step 3, Pituitary vs ACTH
[_](Cushing's diagnosis, differentiate between ACTH tumor and pituitary adenoma)
Pitutary adenoma still responds to negative feedback from cortisol
If pituitary adenoma: confirm with MRI..
Treatment
[_](Cushing's treatment)
 ..
..
 ..
..
Adrenal Insufficiency
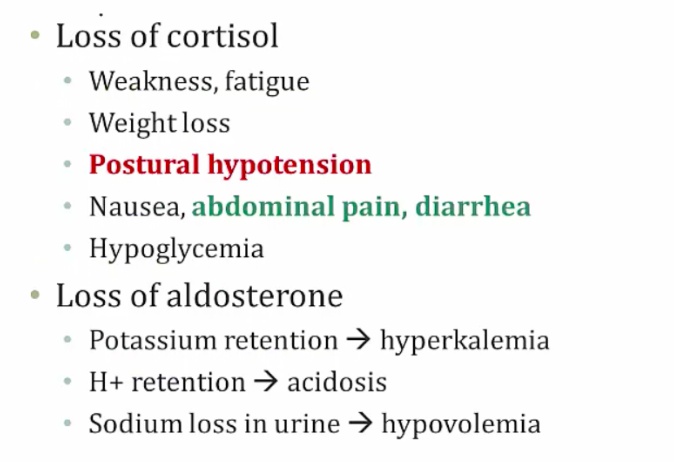
_Insuficient cortisol, aldosterone.,

In contrast with primary adrenocortical insufficiency (Addison’s disease), secondary adrenocortical insufficiency has:
No hyperpigmentation: since ACTH levels are low, melanocyte-stimulating hormone is not elevated as in Addison's disease
No hyperkalemia: aldosterone synthesis is preserved, and release is regulated by the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system..
Metyrapone test
[_](Metyrapone test. What's is used for and explain result)
To determine the cause of the defect and confirm the diagnosis, a metyrapone test may be performed. Metyrapone inhibits 11-β-hydroxylase, which is responsible for the conversion of 11-deoxycortisol into cortisol.
In a patient with a fully intact HPA axis, metyrapone administration will result in increased ACTH levels and increased 11-deoxycortisol levels.
In primary adrenocortical insufficiency, metyrapone administration will result in increased ACTH levels and no change in 11-deoxycortisol levels.
In secondary adrenocortical insufficiency, metyrapone administration will not change levels of ACTH or 11-deoxycortisol.
 ..
..
Primary Adrenal Insufficiency
_Diagnosis: cortisol and ACTH levels.
Cosyntropin (synthetic ACTH) should result in a brisk increase in cortisol levels. An abnormal cosyntropin (ACTH) stimulation test implies a subnormal response of plasma cortisol following cosyntropin administration, and it is definitive and diagnostic of primary adrenocortical insufficiency..
Symptoms
.,
Skin hyperpigmentation (buccal mucosa, skin creases) occurs because elevated ACTH occurs alongside elevated melanocyte-stimulating hormone (MSH) because pro-opiomelanocortin (POMC) is the shared precursor molecule for MSH and ACTH (as well as beta-endorphin).
_In primary insufficiency, hormone replacement of glucocorticoids, mineralocorticoids, and in some cases androgens, is indicated.
Glucocorticoid (hydrocortisone and prednisone- dosage often needs to be adjusted when initiating treatment)
Mineralocorticoid (fludrocortisone- dosage tailored to manage blood pressure and fluid balance)
Androgens (dihydroepiandrosterone (DHEA)- recommended for some women to improve libido and well-being)..
Tertiary Adrenal Insufficiency
_Rapid cessation of chronic high-dose glucocorticoids can cause this.,
_In secondary/tertiary insufficiency, only glucocorticoid replacement is necessary. Aldosterone deficiency is not an issue because aldosterone secretion is regulated predominantly by angiotensin II (not ACTH). Skin hyperpigmentation (the result of increased ACTH release) is also not an issue in secondary/tertiary insufficiency..
Excess Mineralcorticoids
_Primary vs secondary:
PRA: Plasma renin activity
PAC: Plasma aldosterone concentration..


_Diagnosis method..

Primary Aldosteronism
_Cause:.,

_Labs..


_Symptoms:
Classic: young age hypertension (not expected)
Hypokalemia: weakness, muscle cramps (unreliable finding because diet)..

_Treatment..

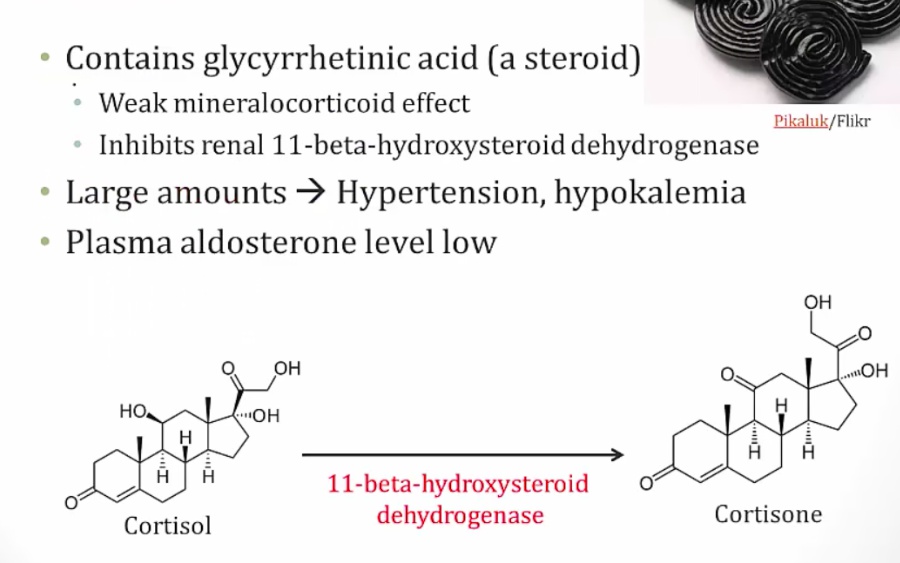
Aka apparent mineralcorticoid excess
Eat a lot of licorice = looks like hyperaldosteronism
Cortisol makes aldosterone and is broken down into cortisone
Licorice inhibits the breakdown = more cortisol = more aldosterone
Lower plasma aldosterone..
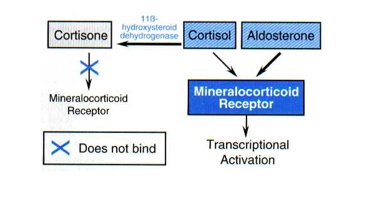
11B HSD
_Degrades cortisol in adrenal gland and kidney to protect from aldosterone effects.,
Conn Syndrome
_Aldosterone producing adenoma.,
Secondary Hyperaldosteronism
_Cause.,

_Labs..


Tumors
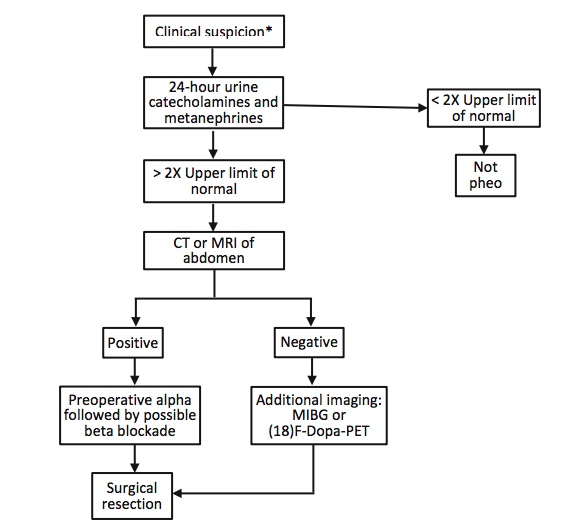
Pheochromocytoma
_..

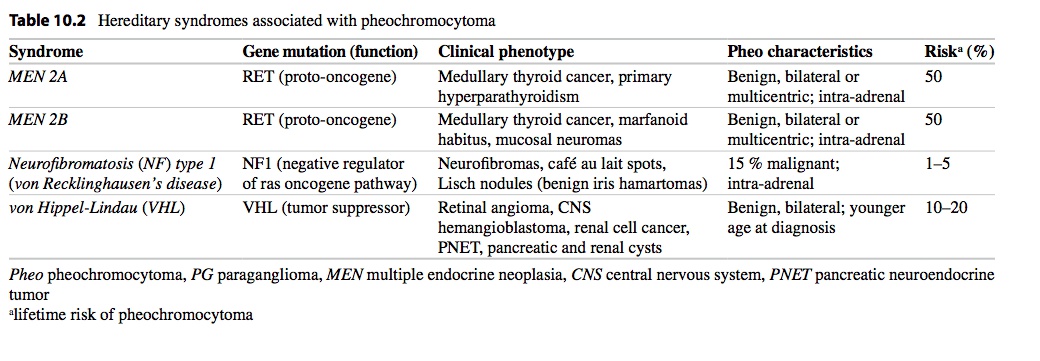

.,

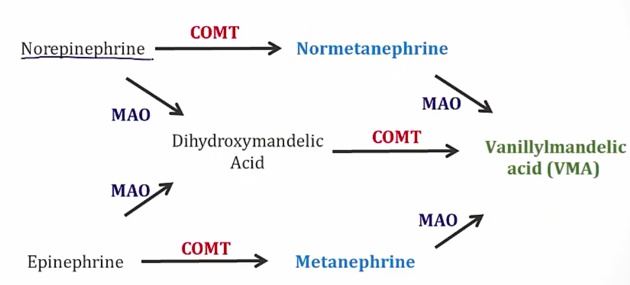

.,
_..
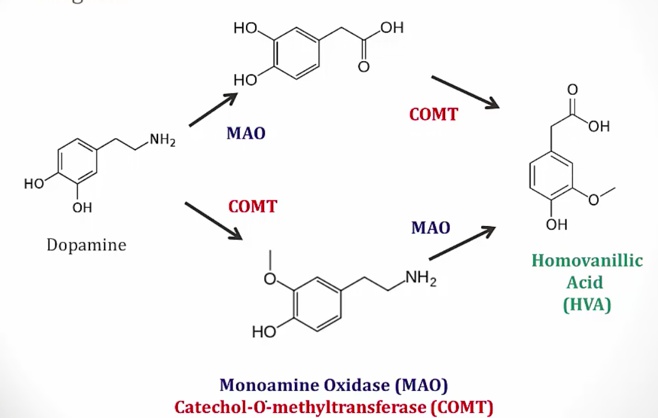
_..


Paraganglioma

.,
Neuroblastoma
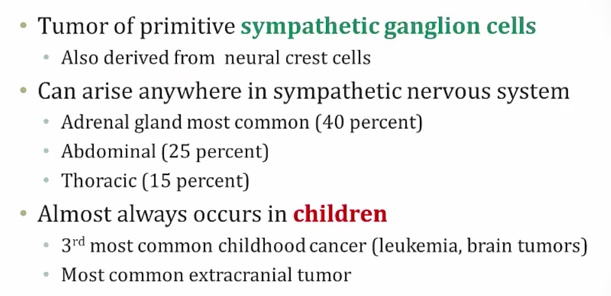
.,

.,

.,
MIBG

.,
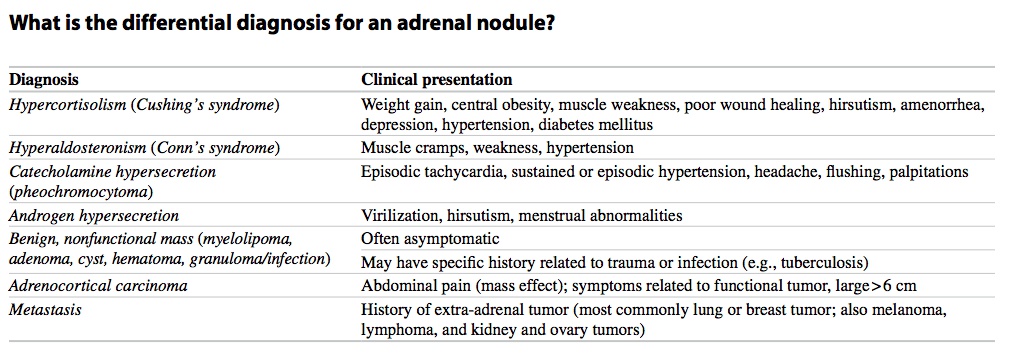
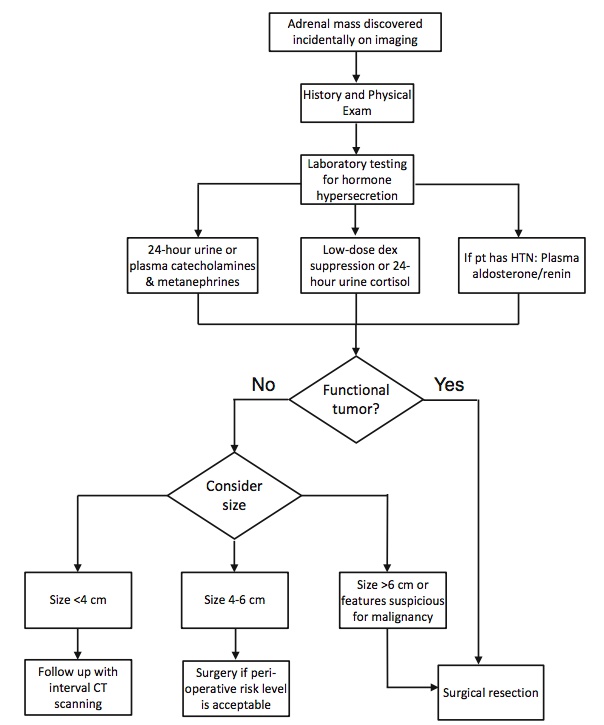
Incidental, nonfunctional adenoma
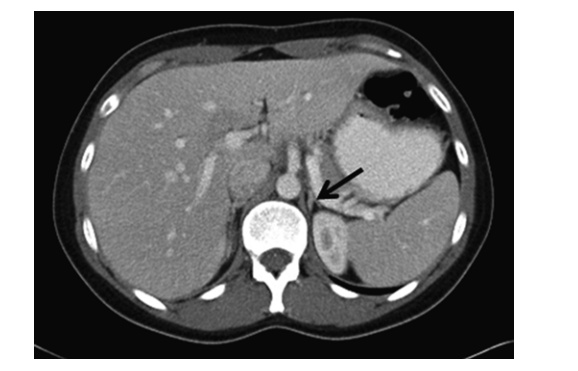
An incidentaloma is an incidentally discovered mass seen on imaging performed for an unrelated reason. Approximately 5 % of patients who undergo an abdominal CT scan will have an incidentally discovered adrenal mass. The incidence increases with patient age, with up to 10 % of patients having adrenal nodules on autopsy studies.
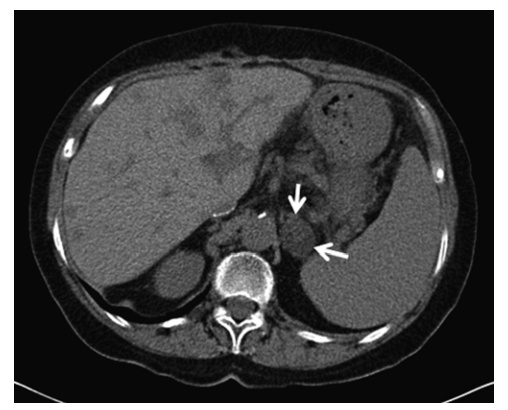
Cortical Carcinoma
fdsafdsafds.,
fdadsafds
fdsafdsad
Last updated