Trichomonas Vaginalis
_Sexually transmitted flagellated protozoa responsible for the urogenital infection known as trichomoniasis. 
_Can be distinguished from other flagellated protozoa in that it lacks a cyst form
– the organism is sexually transmitted and rarely leaves its host.
_Women can become an asymptomatic carrier or present with acute vaginitis (burning, pruritis, dysuria, and frequency).
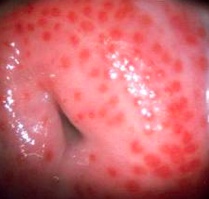
Vaginal exam of women infected shows an erythematous, "strawberry" cervix.
Produces a green, foul-smelling vaginal discharge. (frothy discharge)
yellow/green lights, cervix painting, foul smelling fire

_Men infected are usually asymptomatic and often spontaneously resolves. Symptomatic patients may present with signs of urethritis. 
_Diagnosis is made via laboratory testing that may include
Visualization of pear-shaped flagellated trichomonads on wet mount
motile trophozoites (classically called "corkscrew" motility) due to flagellated movement.
Positive culture
Positive nucleic acid amplification test
Rapid antigen or DNA hybridization probe test



 A vaginal wet mount (or vaginal smear or wet prep) is a gynecologic test wherein a sample of vaginal discharge is observed by wet mount microscopy by placing the specimen on a glass slide and mixing with a salt solution.
A vaginal wet mount (or vaginal smear or wet prep) is a gynecologic test wherein a sample of vaginal discharge is observed by wet mount microscopy by placing the specimen on a glass slide and mixing with a salt solution.
_Vaginal pH in the setting is > 4.5. In contrast, vaginal pH is normal (4.0 - 4.5) in the setting of Candida vulvovaginitis. 
_Treatment includes metronidazole to both the affected individual and their sexual partners. 
Trichomonas vs gardnerella
_Key distinguishing features of each infection are listed below:
Trichomonas vaginalis
Gardnerella vaginalis
Symptoms
Itching & burning
Non-painful
Discharge color
Green
Grey
Discharge smell
Foul
Fishy
Microscopy findings
Motile trophozoites
Clue cells
Last updated