Cholinometics
Cholinomimetics

mimic Ach of sympathetic nervous
Acetyl-Cola: acetylcholine receptor agonists
Mime drinking cola: cholinomimetics

Smoker: nicotinic acetylcholine receptor:
Ganglia-like transformers (wire to wire) near smoker: nicotinic acetylcholine receptors are found on autonomic ganglia
Outlet near smoker: nicotinic acetylcholine receptors are found on skeletal muscle motor end plates
Adrenal beanie on smoker: nicotinic acetylcholine receptors are found in the adrenal gland
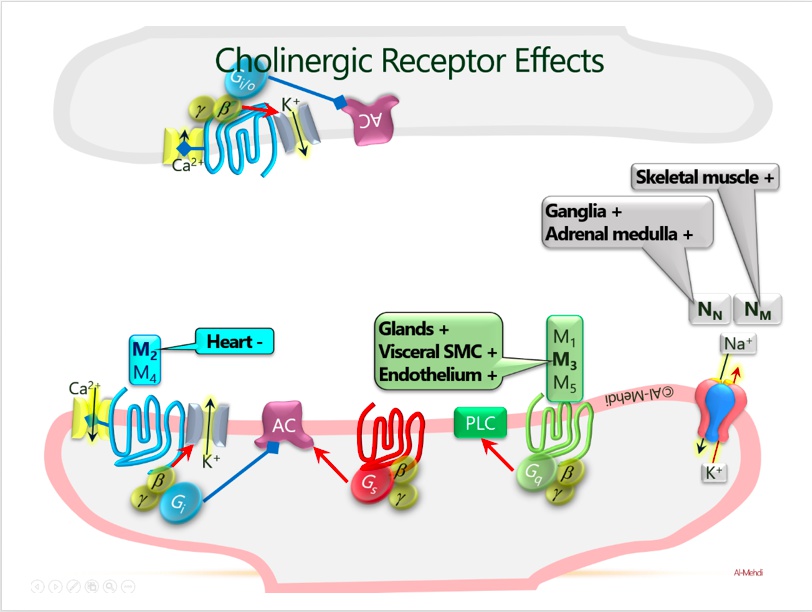
Motorcycle parking spots: muscarinic acetylcholine receptors (M1, M2, M3) (smooth muscles):
Brain helmet: M1 receptors are found in nerves and the CNS
Top of heart with atria visible and with jewels: M2 receptors are found in the atria, the SA and AV node. Ventricle is innervated by sympathetic not para sympathetic
Glandular sponge: M3 receptors are found on glands
Smooth muscle stripes: smooth muscle contains M3 receptors


Ion Channel news behind smoker: nicotinic receptors act as ion channels


QIQ store: M1, M2, and M3 are coupled to Gq, Gi, and Gq, respectively
3 "dags": M1 and M3 are coupled to Gq proteins which activate the IP3-DAG cascade, increase in Ca
Packed up camp tent: M2 is coupled to a Gi protein which decreases cAMP
Dilated nitric oxide exhaust: M3 receptor activation -> nitric oxide release in vascular smooth muscle cells-> increased cGMP and vasodilation
Constricted clogged pipe: atherosclerosis-> vascular epithelial damage-> direct muscarinic receptor activation-> vasoconstriction


Beth with cola: bethanechol (a cholinomimetic)
Cement pouring from colon spout: muscarinic agonists (e.g. bethanechol) increase secretion and motor activity of the gut
"Do Not Obstruct": bethanechol is used to treat non-obstructive gastrointestinal dysmotility (e.g post-op ileus, neurogenic ileus)
Beth using bladder hose: bethanechol treats urinary retention

Pile o' carp: pilocarpine (a cholinomimetic)
Dripping carp mouths: pilocarpine increases salivation
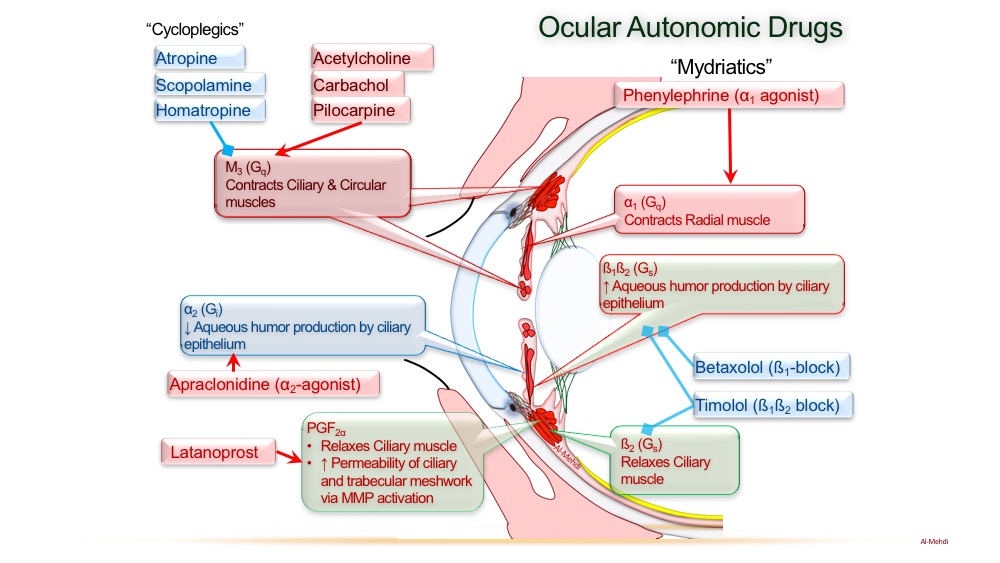
Round glass: muscarinic agonists (e.g. pilocarpine) cause accommodation of the lens
Smooth muscle crane with net zonules: pilocarpine contracts the ciliary muscle, zonular fibers relax, lens become spherical shaped, reduce intraocular pressure, increasing aqueous humor outflow (useful to treat glaucoma).
Constricted hood: pilocarpine activates the sphincter pupillae muscle to cause pupillary constriction (useful in acute angle-closure glaucoma)

Carbon fumes from smoker: carbachol is both a muscarinic and nicotinic agonist
Constricted hood blocking carbon fumes: carbachol causes pupillary constriction (useful in acute angle-closure glaucoma)


Marathon: methacholine (a cholinomimetic)
Challenge: methacholine challenge instigates asthma for pulmonary testing
Wheezing man: cholinomimetics (e.g. methacholine) contract bronchial smooth muscle which may exacerbate asthma or COPD

1-800-VERY-CLEAN: varenicline (a nicotinic receptor partial agonist) is used for smoking cessation
Acetylcholinesterase Inhibitors

Indirect view of Acetyl-cola mime: indirect cholinomimetics (inhibit acetylcholinesterase)
Dumpster of acetyl-cola bottles: acetylcholinesterase degrades acetylcholine (ACh)
Knocked over dumpster with acetyl-cola spilling out: acetylcholinesterase inhibitors increase synaptic concentrations of ACh
ANTI-ESTablishment: anti-cholinesterase, a.k.a. acetylcholinesterase inhibitor
STIGMA: "c-stigmine"d drug suffix of acetylcholinesterase inhibitors

Skeletal muscle brick wall: acetylcholinesterase inhibitors enhance effects of ACh at the NMJ (increase activity of NICOTINIC ACh receptors)
Electrical end plate: motor endplate (at the NMJ), increase contraction

GRAVIS graffiti: myasthenia gravis (MG)-> antibodies against nicotinic ACh receptors at motor endplate (skeletal muscle NMJ)
Graffiti covering electrical end plates: MG causes progressive proximal weakness, ptosis, diplopia (inactivated nicotinic ACh receptors at motor endplate)

Community PRIDE: PYRIDOstigmine (acetylcholinesterase inhibitor used as long-term treatment for MG)
Removing graffiti on end plates: acetylcholinesterase inhibitors increase ACh at NMJ endplate to outcompete MG antibodies
Neon sign STIGMA: neostigmine (acetylcholinesterase inhibitor used as treatment for MG)
Phone booth: edrophonium (acetylcholinesterase inhibitor that transiently reverses symptoms of MG)
Quarters only: pyridostigmine, neostigmine and edrophonium are quaternary amines and do not penetrate the CNS

Phone wire tension: tensilon test -> edrophonium reverses (positive) or fails to reverse (negative) muscle weakness
Phone in working order: edrophonium REVERSES muscle weakness in undertreated MG patients (POSITIVE tensilon test)
Phone out of order, with anti-esterase graffiti: edrophonium FAILS to reverse muscle weakness during cholinergic crisis (NEGATIVE tensilon test)

CURARE crayons stuck in end plate: nondepolarizing neuromuscular blocking agents (e.g. tubocurarine, pancuronium, cisatracurium) inhibit nicotinic ACh receptors at NMJ endplate (for inducing paralysis in surgery)
Neon sign store owner kicking out CURARE crayon kid: acetylcholinesterase inhibitors (e.g neostigmine) reverse nondepolarizing neuromuscular blockade

SUCKS: succinylcholine is a depolarizing neuromuscular blocking agent (nicotinic ACh receptor AGONIST)
PHASE-1 cleanup crew getting shocked: initial PHASE-1 of depolarizing blockade is IRREVERSIBLE (acetylcholinesterase inhibitors potentiate blockade). Continuous depolarize: unresponsive muscles

Bladder hose: acetylcholinesterase inhibitors can be used to treat urinary retention (muscarinic activation of detrusor)

PHYS ED center: PHYSostigmine (acetylcholinesterase inhibitor with CENTRAL effects) Cross BBB
Atropine in Wonderland: atropine overdose -> "mad as a hatter, hot as a hare, blind as a bat" (reversed by physostigmine)
Deadly nightshade: belladonna flower is a naturally occurring form of atropine (overdose reversed by physostigmine) (work in a garden then present with symptoms)
GYM weeds: Jimson weed is a naturally occurring form of atropine (overdose reversed by physostigmine)
PHYS ED teacher reprimanding atropine "cartist"d: physostigmine reverses atropine overdose (peripheral and CENTRAL effects)

"Your brain on drugs": physostigmine (and organophosphates) enters CNS to reverse atropine and cause central cholinergic effects

DUMBBELS: acetylcholinesterase inhibitor toxicity (Diarrhea, Urination, Miosis, Bronchospasm Bradycardia, Lacrimation, Salivation)
Weak nicotine kid: acetylcholinesterase inhibitor toxicity includes flaccid paralysis (NMJ nicotinic ACh receptor over-activation)

THIOL spray: thiosulfate insecticides (parathion, malathion, echothiophate) are organophosphates, a type of acetylcholinesterase inhibitor (also includes nerve agents and herbicides)
Green fumes: organophosphates are a major cause of acute cholinergic toxicity (DUMBBELS)

Closing LID on TOXIC spray: praLIDoxime reverses organophosphate toxicity (DUMBBELS)
New toxic waste dumpsters: pralidoxime regenerates acetylcholinesterase at muscarinic and NICOTINIC receptors (reverses cholinergic toxicity INCLUDING FLACCID PARALYSIS)
Atropine Alice is in your head: atropine reverses both peripheral and CENTRAL muscarinic toxicity from organophosphate poisoning (pralidoxime is peripheral only) (atropine only M, but not reverse paralysis; pralidoxime reverses )

Old pest-control man: "caging" of the organophosphate-cholinesterase complex leads to irreversible binding
Corroded dumpster: pralidoxime is ineffective once aging of organophosphate- cholinesterase complex has occurred

Alzheimer's GALA: galantamine (acetylcholinesterase inhibitor used to treat Alzheimer's disease)
REVERSE the STIGMA: rivastigmine (acetylcholinesterase inhibitor used to treat Alzheimer's disease)
Done with brain puzzle: donepezil (acetylcholinesterase inhibitor used to treat Alzheimer's disease)
Brain puzzle: galantamine, rivastigmine, and donepezil penetrate the CNS
Antimuscarinics

Motorcycle parking spots: muscarinic acetylcholine receptors (M1, M2, M3)
Reversing into motorcycle parking spot: muscarinic antagonists reversibly block muscarinic receptors
Blocked tweedleDUMBBELS: antimuscarinics block the muscarinic effects of diarrhea, urination, miosis, bronchospasm, bradycardia, lacrimation, salivation
Blocked acetyl-cola bottle: antimuscarinics block the action of acetylcholine at M receptors

Alice: atropine (antimuscarinic)
Belladonna flower - a natural antimuscarinic alkaloid
Jimson weed - a natural antimuscarinic alkaloid

TeleSCOPE: scopolamine (antimuscarinic)
Seasick sailor outfit: scopolamine is used to treat motion sickness (vestibular nausea)
Eyepatch: scopolamine transdermal patch is used to treat motion sickness
CNS hat: antimuscarinics (e.g. scopolamine) cross the blood-brain barrier and inhibits central M1 receptors

Heart with jewel nodes: antimuscarinics block parasympathetic activation of M2 receptors on the SA and AV nodes (increased heart rate, increased AV conduction). Parasympa slows HR/AV conduction. Inhibition results in opposite
Elevated heart watch: antimuscarinics (e.g. atropine) increase heart rate (useful in the treatment of bradycardia)
Heart shield: heart block (atrioventricular block)
Falling heart shields: antimuscarinics (e.g. atropine) increase AV conduction (useful in the treatment of heart block)

Cat-ipra-tio-tropillar: ipratropium and tiotropium (M3 muscarinic antagonists)
Puffing: ipratropium and tiotropium are inhaled antimuscarinic bronchodilators
Blue bloater with pink puffer: ipratropium and tiotropium are useful in the management of COPD (antagonize M3 receptors -> bronchodilation, decreased secretions)
Long lasting TIO smoke rings: tiotropium dissociates more slowly from the M3 receptor (longer bronchodilator action)

Ox butler: oxybutynin (M3 muscarinic antagonist)
Turtle butler: tolterodine (M3 muscarinic antagonist)
Turning off bladder: oxybutynin and tolterodine treat incontinence (antagonize M3 receptors -> relax smooth muscle in ureters and bladder wall)

CENTER over M1: M1 muscarinic receptors are found in the CNS
PARKING over M1: M1 receptor antagonists can reduce tremors and rigidity in Parkinson's disease
Benz parked in M1: benztropine (centrally acting M1 muscarinic antagonist)
Tri-hex car parked in M1: trihexyphenidyl (centrally acting M1 muscarinic antagonist)
Shaking antenna: centrally acting antimuscarinics (e.g. benztropine, trihexyphenidyl) treat tremor and rigidity in Parkinson's (block excess cholinergic activity)
Cogwheel: excessive M1 activation is associated with cogwheel rigidity in Parkinson's disease
Falling "cextra parking" cone: antimuscarinics treat extrapyramidal side effects caused by antipsychotics: e.g. dystonia, akathisia, parkinsonism (re-establish dopaminergic- cholinergic balance)

Hot as a hare: antimuscarinics inhibit M3 receptors on sweat glands -> decreased sweating -> hyperthermia
Dry as a cracker: antimuscarinics decrease salivation and lacrimation -> dry mouth and eyes
Blind as a bat: antimuscarinics cause mydriasis and cycloplegia-> blurred vision
High-pressure as a kettle: antimuscarinics cause mydriasis -> decreased outflow of aqueous humor -> acute angle closure glaucoma
Mad as a hatter: antimuscarinics cross the BBB and antagonize central M1 receptors -> sedation, agitation, hallucination, coma (especially in elderly patients)
Cycloplegia is paralysis of the ciliary muscle of the eye, resulting in a loss of accommodation
Large pupil gazing into the distance: antimuscarinics cause pupillary dilation (mydriasis) and cycloplegia (inability to accommodate the lens for near vision)

Last updated