01 Cardiac Embryology
Heart Embryology
Heart contraction
_Beginning as early as four weeks gestation.,
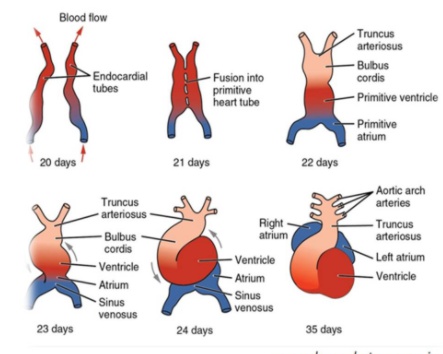
Primitive heart tube
_Formed from Lateral folding directing the endocardial heart tubes to fuse., 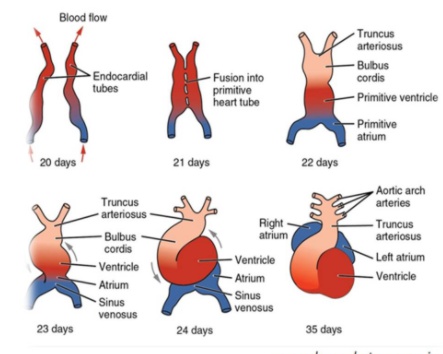
_The endocardium, myocardium, and epicardium of the heart are derived from mesoderm..
_EDC and aorticopulmonary septum derived from ectoderm, neural crest..
Cardiac looping
_ begins during the 4th week of gestation, and establishes a left-right polarity to the primitive heart tube. This process requires dynein., 
Heart beat
_During gestational week 6, transvaginal ultrasound may detect.,
Primitive heart tube
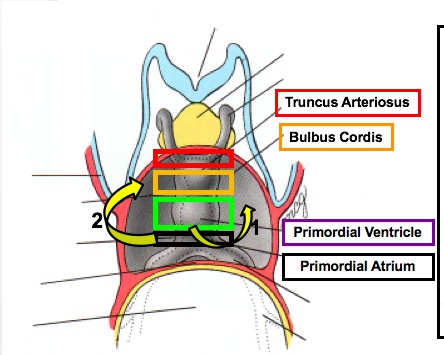
_Forms five dilations:
Truncus arteriosus
Bulbus cordis
Primitive ventricle
Primitive atrium
Sinus venosus (right and left horns).,
truncal-bulbar ridge top
left horn/left side: coronary sinus
right horn: RA 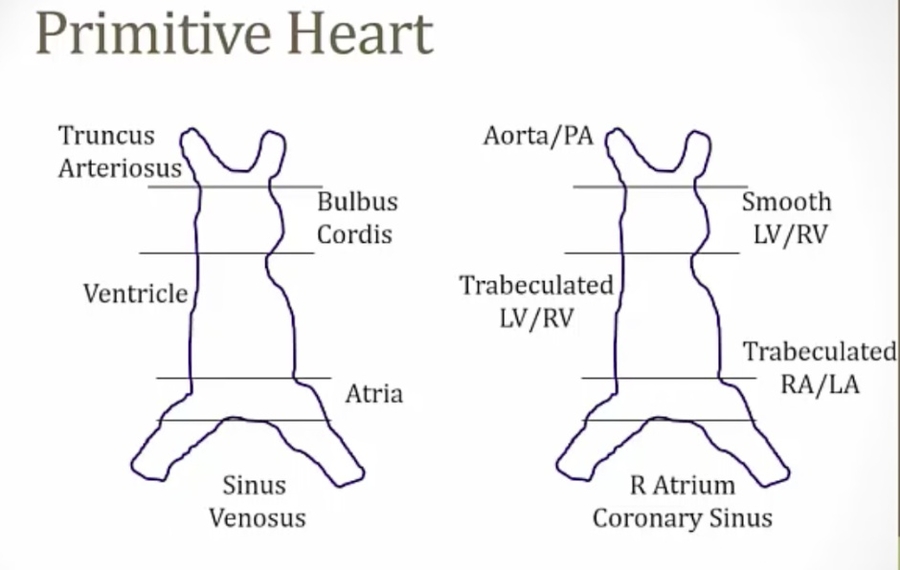
Truncus arteriosus
_Develops into the ascending aorta and pulmonary trunk., 
Bulbus cordis
_Develops into the conus arteriosus (smooth part of the right ventricle) and the aortic vestibule (smooth part of left ventricle)., 

_ smooth part of right ventricle., _ smooth part of left ventricle., _ aka conus arteriosus.,
Primitive ventricle
_Develops into trabeculated part of right and left ventricles., 
Primitve atrium
_Develops into the muscular (trabeculated) part of right and left atrium and the septum primum., 
Left horn of sinus venous
_Develops into the coronary sinus., (left side) 
Right horn of sinus venous
_Develops into the smooth part of the right atrium., (right side) 
Crista Terminalis
_The junction of the trabeculated and smooth parts of the right atrium.,
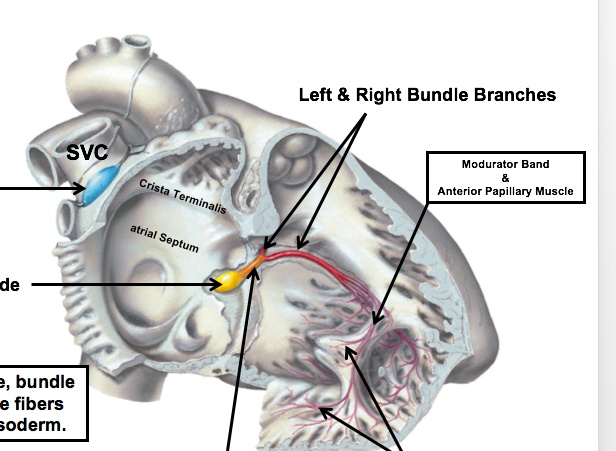
Superior Vena Cava
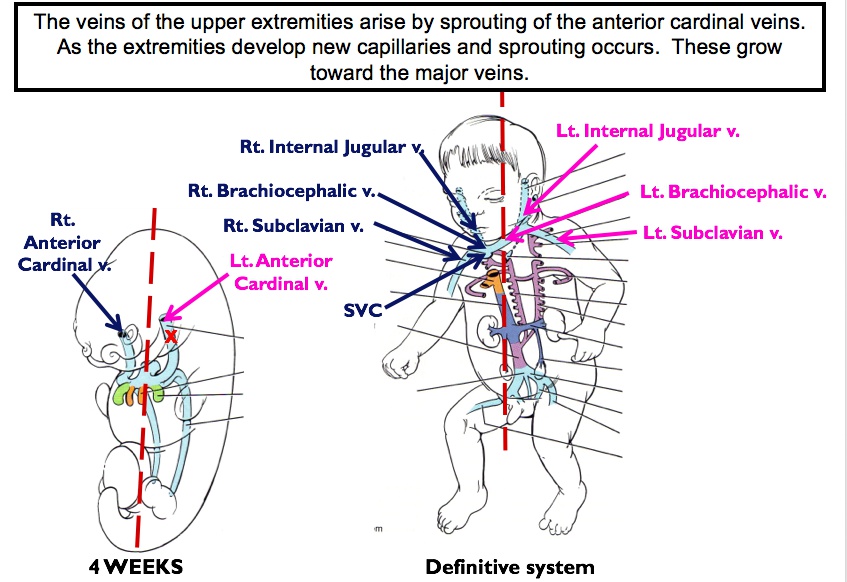
_Structures from outside the heart tube help form the adult heart structure, such as the right common cardinal vein and right anterior cardinal vein which develop into the superior vena cava., 
Primitive pulmonary vein
_Derives the smooth part of the left atrium.,
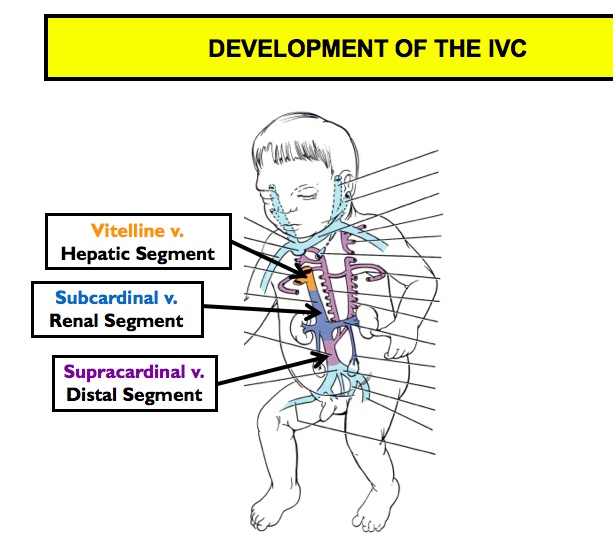
Inferior Vena Cava
_Derived from:
Vitelline veins
Posterior cardinal veins
Subcardinal veins
Supracardinal veins.,

Aorticopulmonary septum
_Neural crest cells migrate from the hindbrain to the primitive heart tube (Truncal bulbar ridge), which ultimately forms this., 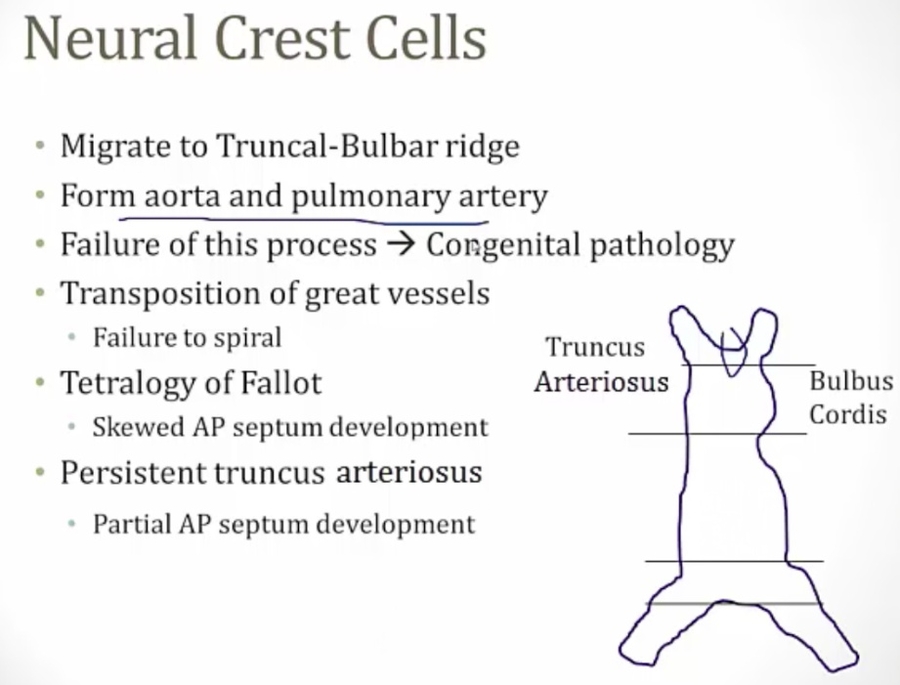
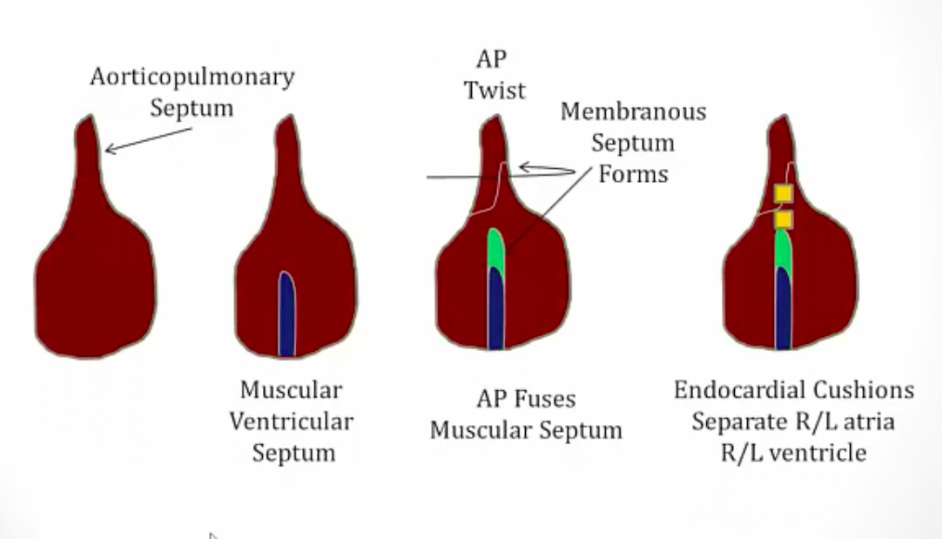
_Develops spirally, creating the anterior-posterior relationship between the ascending aorta and pulmonary trunk.,
EDC of outflow tract
_Derives the aortic and pulmonary valves.,
EDC of atrioventricular canal
_Derives the mitral and tricuspid valves. Endocardial cushion seprates atria from ventricle.,
Heart Septum Formation
_Aka ostium primum.,
_Aka ostium secundum.,
Septum Primum
_Foramen primum is the first foramen. During the 4th gestational week, a septum separating the primitive atrium begins expanding from the superior interatrial space towards the endocardial cushions, forming septum primum.. 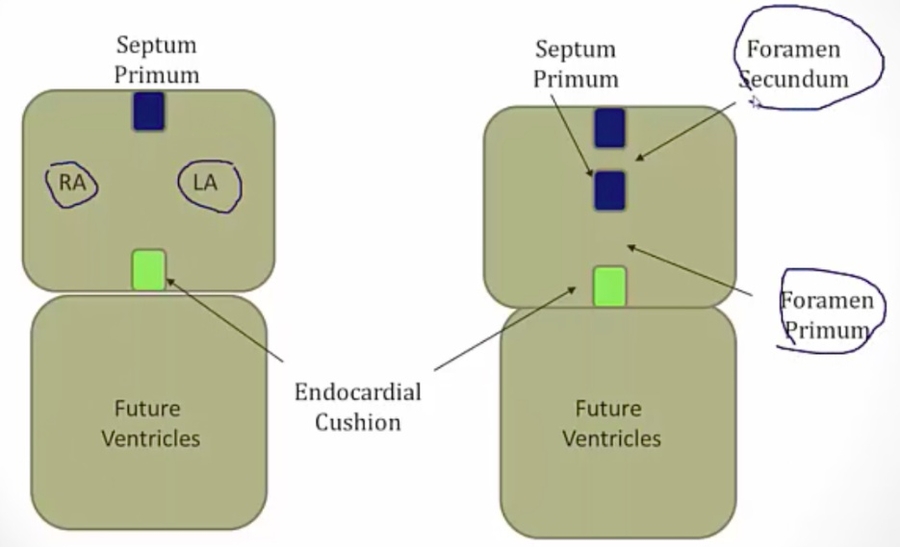
_The septum primum does not completely close against the endocardial cushions, leaving the initial opening, foramen primum. The septum primum then develops perforations that join to form foramen secundum. Septum foramen now has two holes in it.. 
Septum secundum and foramen ovale
_The septum secundum grows to the right of the septum primum from top and bottom, forming a partial barrier between the right and left atria. The opening in that barrier is the foramen ovale..
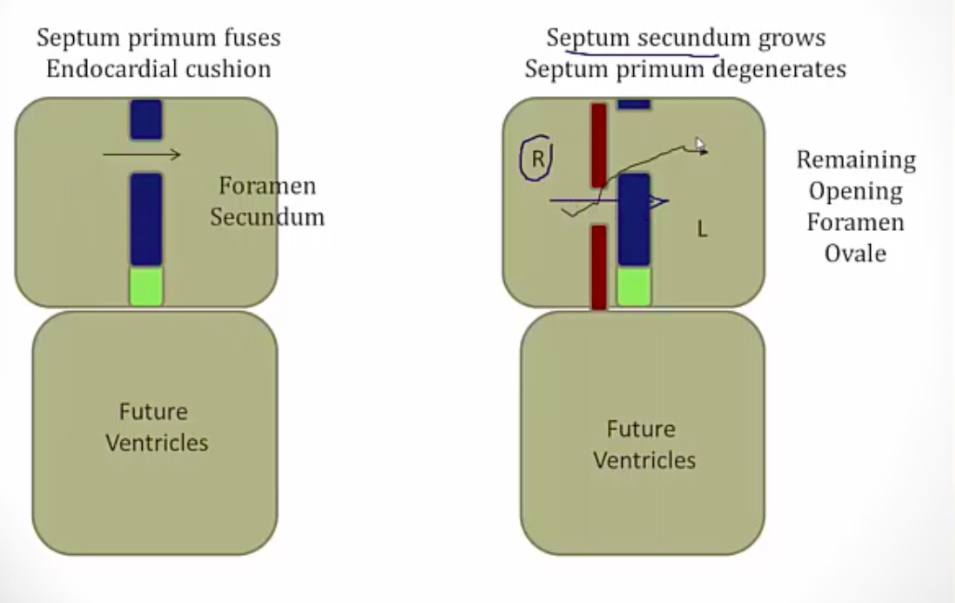
Foramen ovale
_The opening in the septum secundum.,
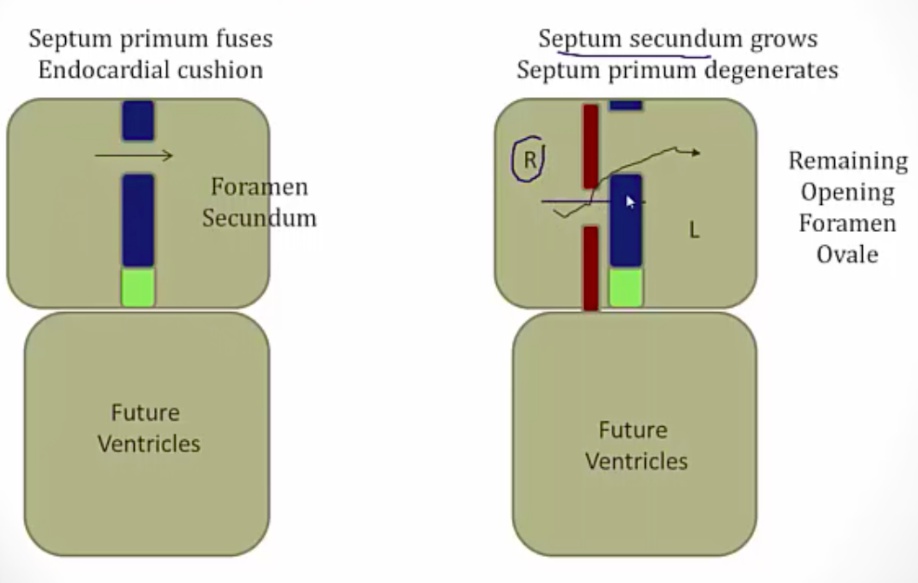
_Maintains blood flow from the right atrium to the left atrium.,
Fetal Circulation vs Changes in circulation at birth
_During fetal circulation, the lungs are filled with fluid (high resistance). Oxygenated blood are carried through umbilical vein and travel straight to RA, bypassing liver via ductus venosus. Blood in RA bypasses lung via foramen ovale. Some blood that goes to RV bypasses lung via ductus arteriosus from PA to aorta..
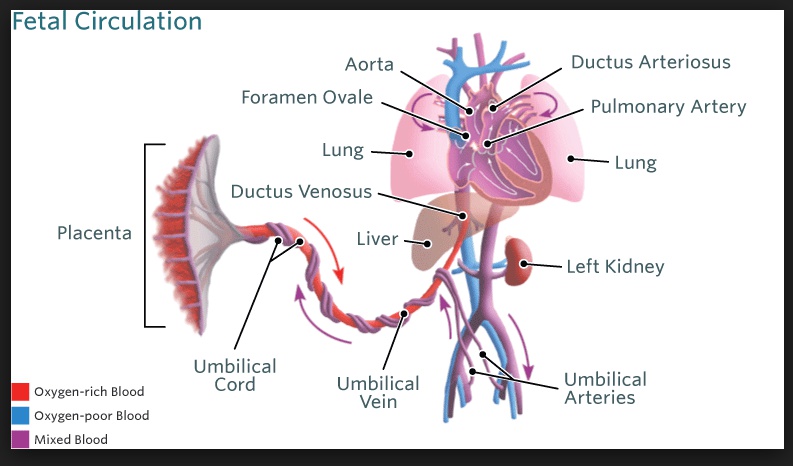
_At birth, fluid is pushed out of lung (pulmonary resistance drops). More blood goes to the lungs and thus the left atrium. LA pressure becomes higher than RA. At the same time, closure of umbilical vein decrases RA pressure. This closes the foramen ovale, forming fossa ovalis..
Ductus Arteriosus
_Maintained by low O2, high PGE. Low PGE closes ductus..
Ventricular septum development
_The muscular interventricular septum develops first, originating from the floor of the primitive ventricle and extending towards the endocardial cushions but leaves a space forming the interventricular foramen.
The membranous interventricular septum forms when the aorticopulmonary septum rotates and fuses with the muscular interventricular septum.
The membranous IV septum is formed by the fusion of bulbar ridge (part of aorticopulmonary septum) and endocardial cushions
Typically, the rotation of the aorticopulmonary septum and formation of the membranous interventricular septum closes the interventricular foramen.. 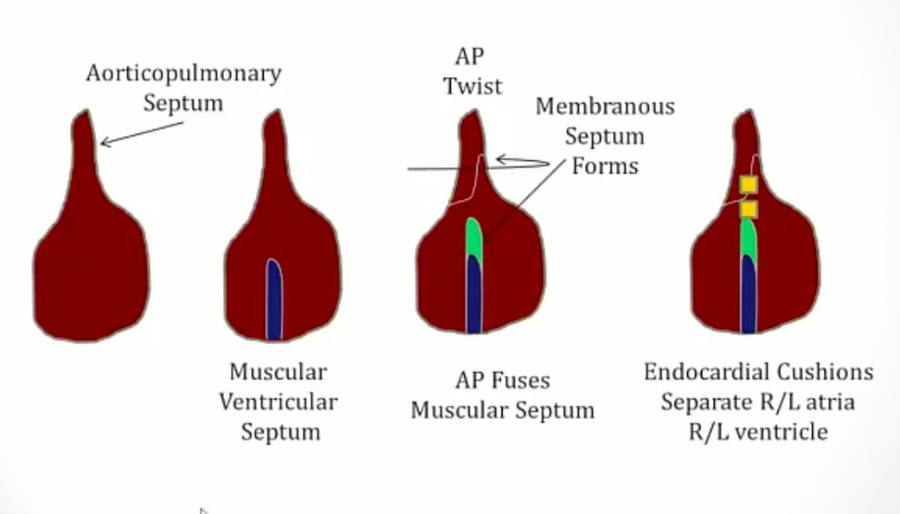
Last updated