15 High Yield EKG
_..
P
QRS
Intervals
ST
P
_..

regular: spacing between QRS same


QRS
_..


Intervals
_..

atheletes (high vagal tones) and beta blockers prolong PR
ST
_..

Practice 1
_..

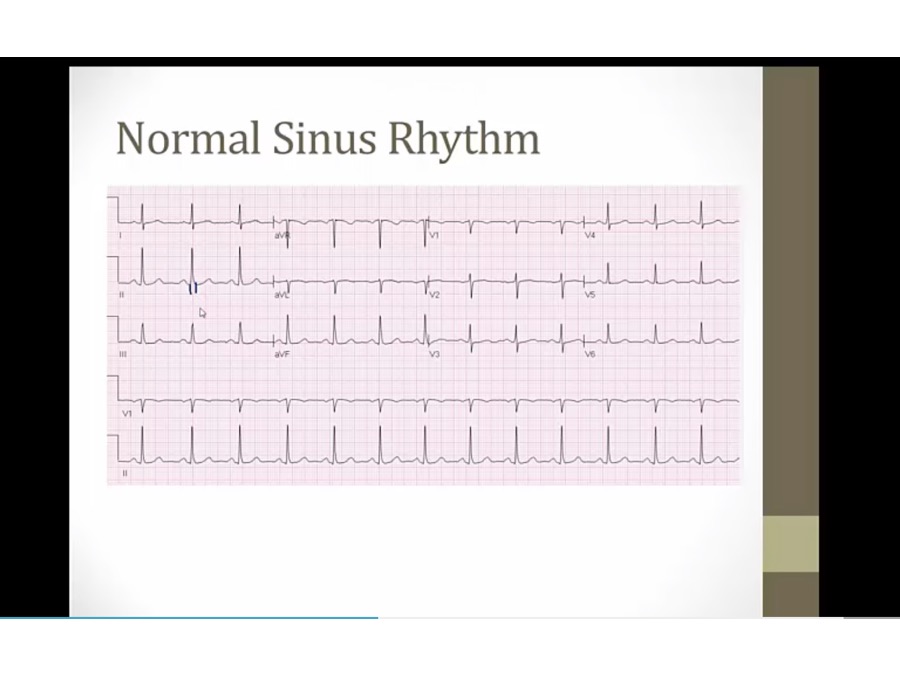
easily identifiable P
upright P in II, III, AVF: normal sinus P
QRS: regular
QRS: narrow
PR: less than 1 block
QT: less than half
ST: no significant depression, elevation





Practice 2

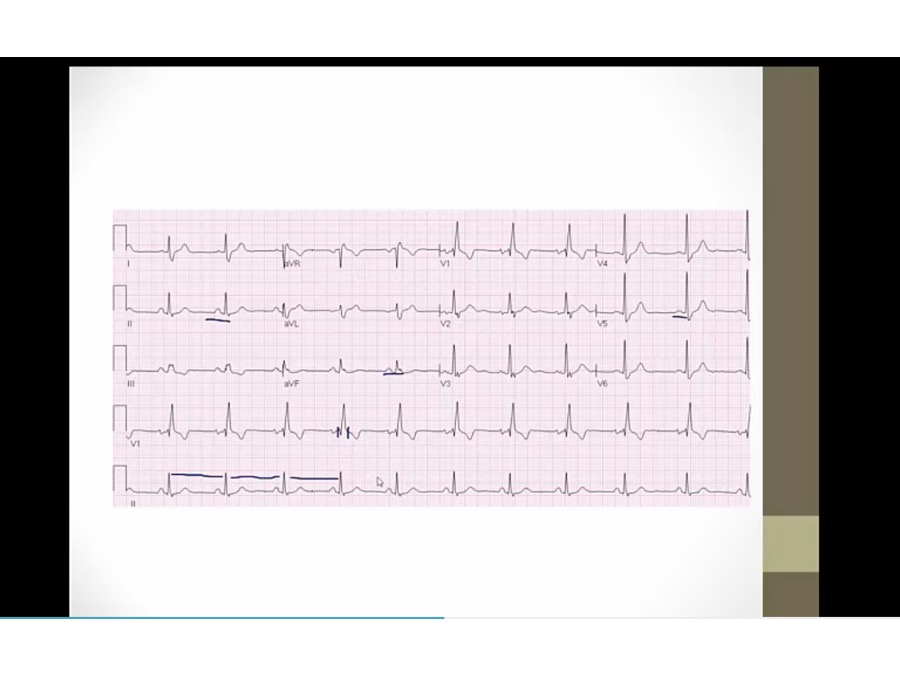
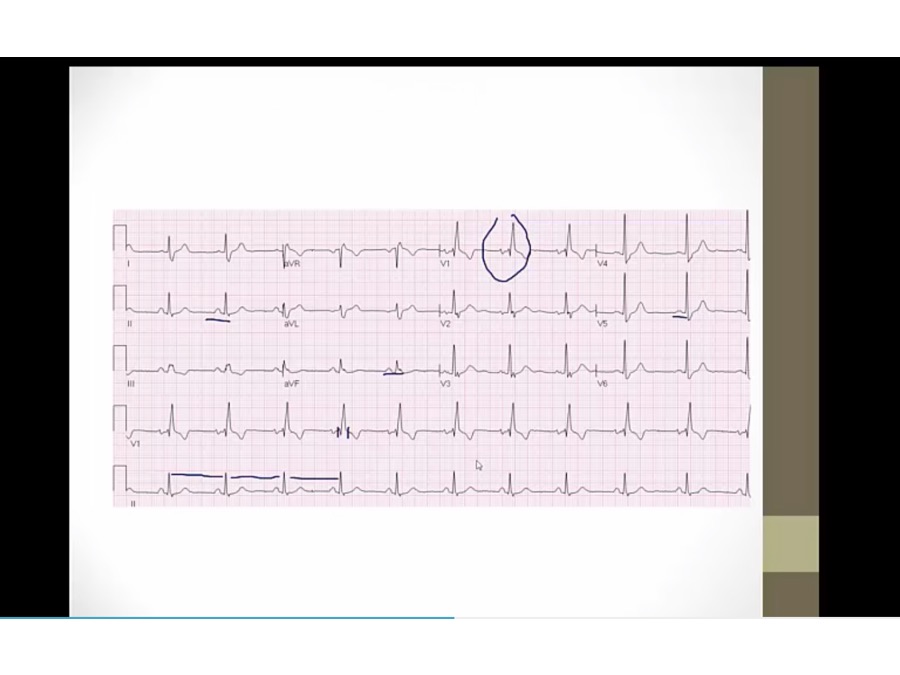
P: upright in II, III, AVF, normal sinus P
RR: regular QRS
QRS: wide in V1, upright QRS in V1 RBBB
PR: not prolonged
QT: less than 1/2
ST: T inversion in V1, normal in RBBB







Practice 2

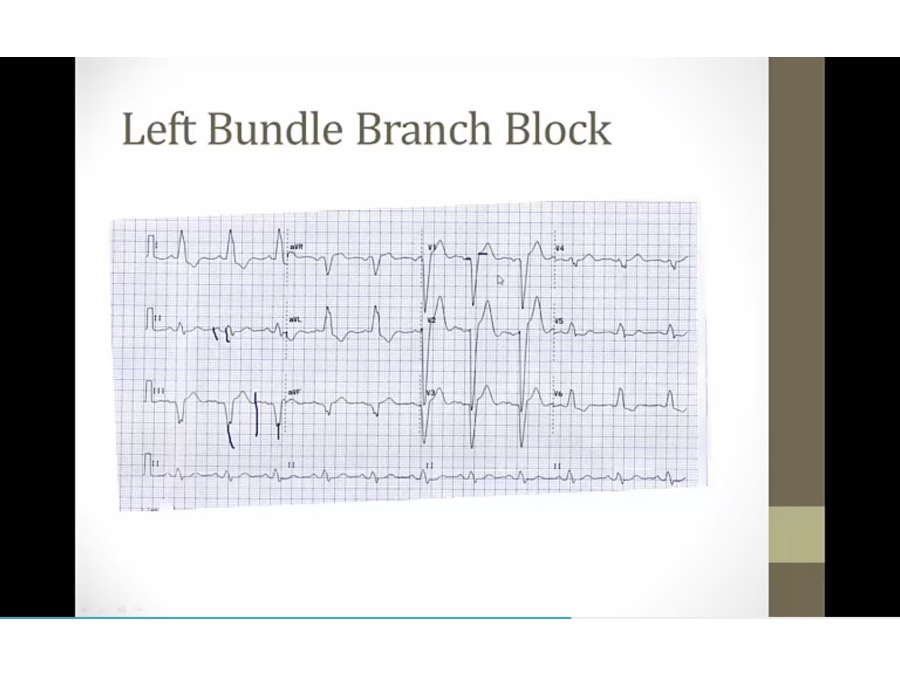
P upright in II, III, AVF, sinus
QRS wide, negative V1, LBBB
peaked T and ST elevation in V1-3: common
T inversion 1, L, V5, V6: normal in LBBB





Practice 4

no clear P waves, afib
irregularly irregular: QRS closer in some, farther apart in others

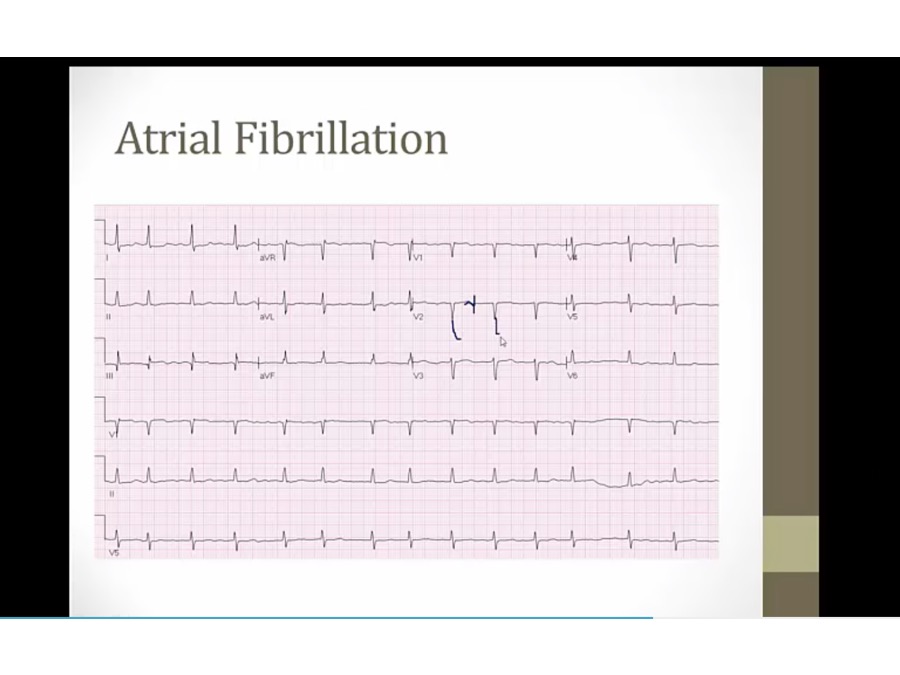

Practice 5

sawtooth, aflut
Practice 6

ventricle contracts on its own
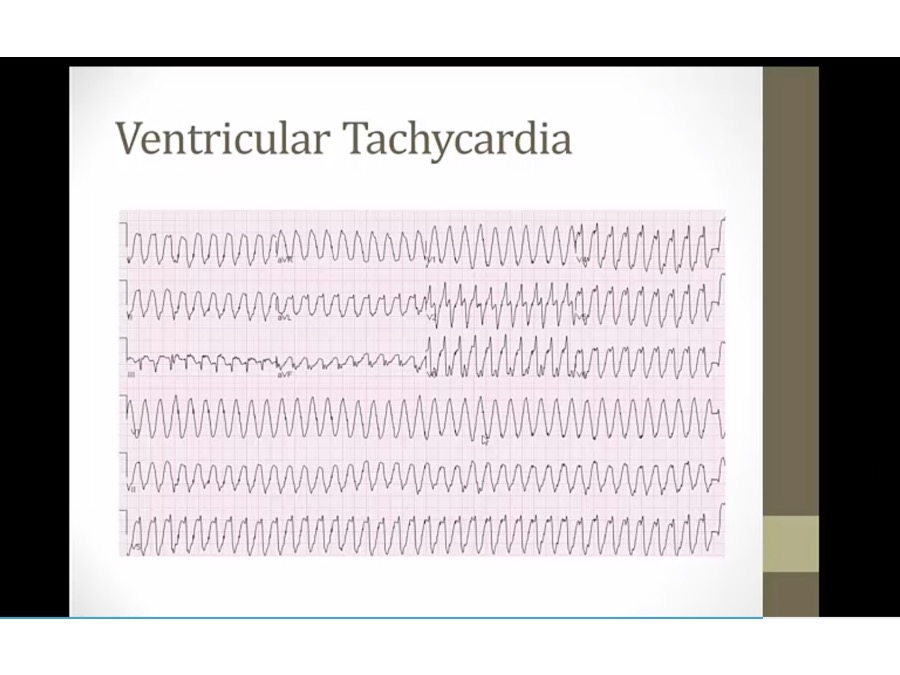
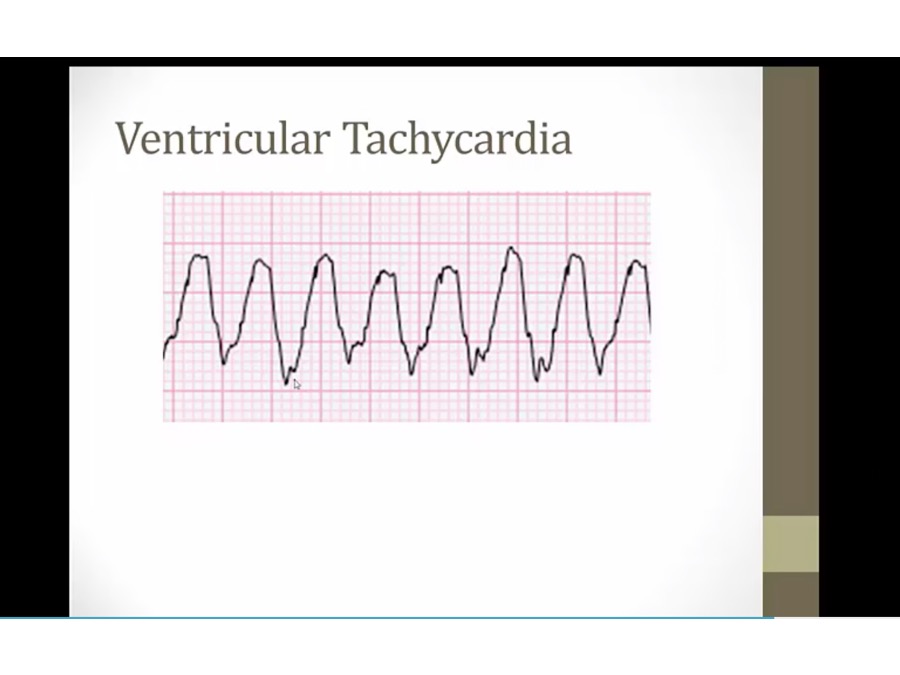
buried P waves at different rate as QRS (AV dissociation)


VFib
_..

top: VFIB, cardiac arrest
PAC, PVC
_..
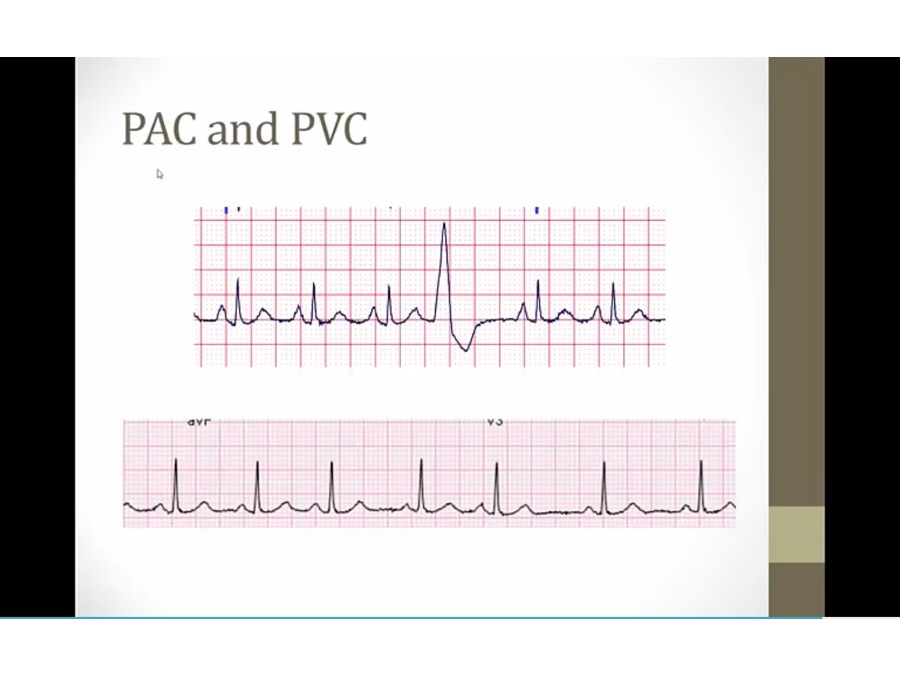
top: early wide QRS, PVC, something stimulated ventricles to contract on its own (high catecholamines, infection, surgery)
bottom: early narrow QRS with compensatory pause after

Last updated