37 Seizures

Workup

blood work for electrolytes
cardiac syncope can mimic seizure
brain imaging for tumors/strokes
LP: meningitis, encephalitis
EEG
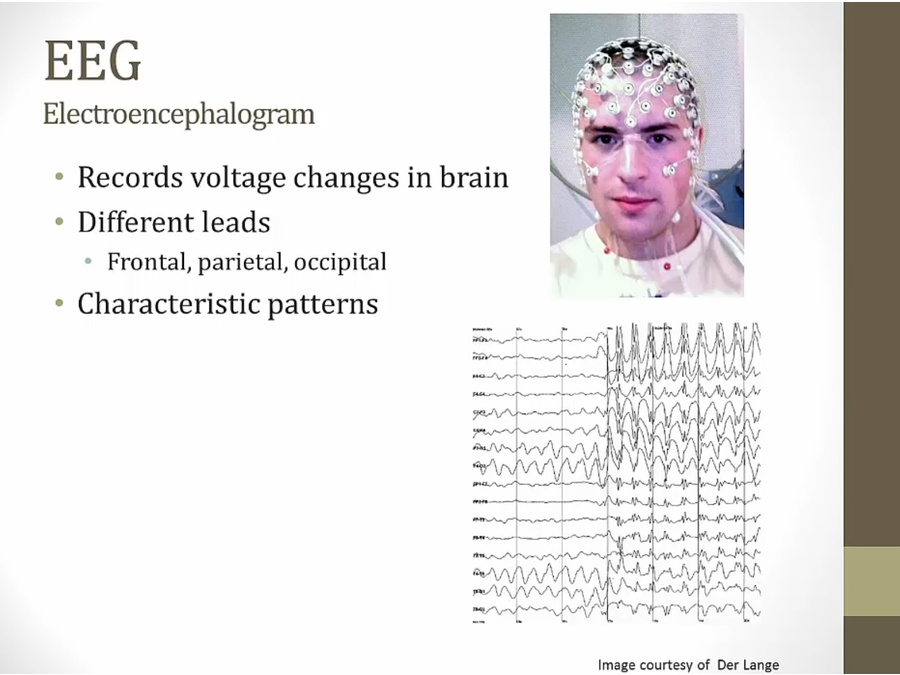
Types

simple: motor contraction, abnormal sensation
complex: motor, sensory, consciousness altered
petit mal: common in children, loss awareness of surroundings briefly
grand mal: classic seizure, collapse, shake
atonic: stiff once, then flaccid, collapse, mimic cardiac syncope
myotonic/myoclonic: rhythmic jerking of a certain area, drop objects, twitches, not as severe as tonic clonic
clonic tonic clonic: jerk once, multiple jerks fuse into clonic, then tonic, then clonic
secondary generalized: starts out as partial then become generalized
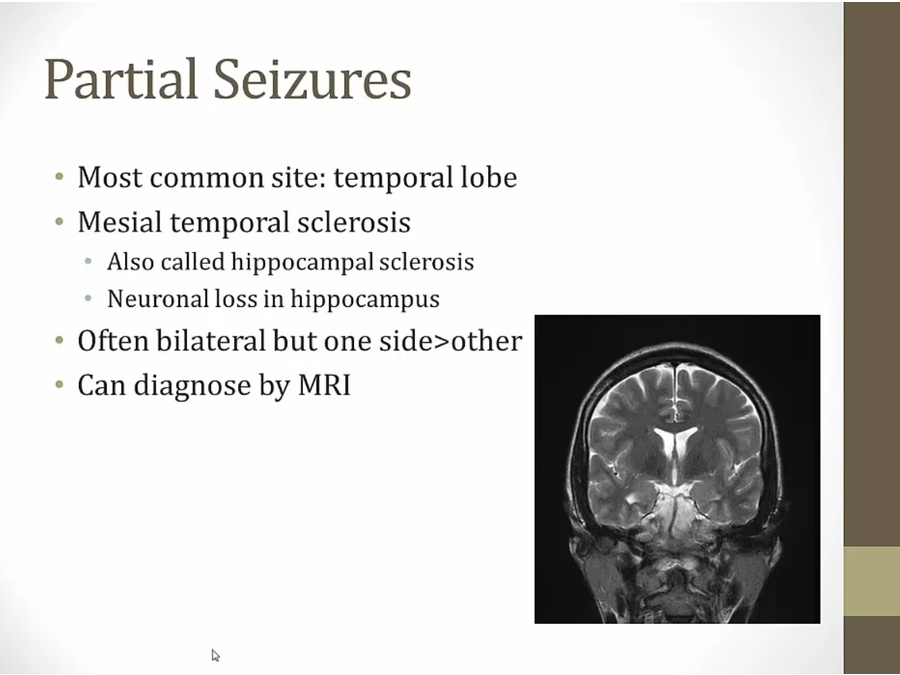
hippocampal sclerosis: loss neuron in hippocampus
MRI: white spot on right side of temporal hippocampus
Symptoms
.  - muscles can contract, relax, spasm - feel, see, smell things not there - mild: loss of awareness for a few minutes, aka absence seizures - severe: pt collapse and shakes   - classic: epigastric rising, precede temporal lobe epilepsy - piloerection: skin standing on edge

in reality, simple, partial seizures

especially after grand mal or tonic
differentiate from cardiac syncope: faint from heart problem, become immediate aware after gain of consciousness
seizure: period of confusion
Causes

most don't have chronic seizure disorders
lack of sleep: can have single seizures
Juvenile Myoclonic Epilepsy

wake up in morning, one of muscles jerking
Childhood Absence Epilepsy

stare into space for moments
good prognosis
classic presentation: child appear to not pay attention
know EEG
Febrile

Eclampsia

late pregnancy
Treatment

status epilepticus: emergency, can cause other symptoms
prevent frequent seizures
Breaking Seizures

if lorazepam not working, administer phenytoin, fosphenytoin
if still not working, phenobarbital
last line: general anesthesia

Preventing

oral drugs to take chronically
Na necessary for depolarization of neurons
Carbamazepine


always monitor drug levels

misdiagnosed as URI
Ethosuximide

very unique MOA
Phenobarbital
Phenytoin
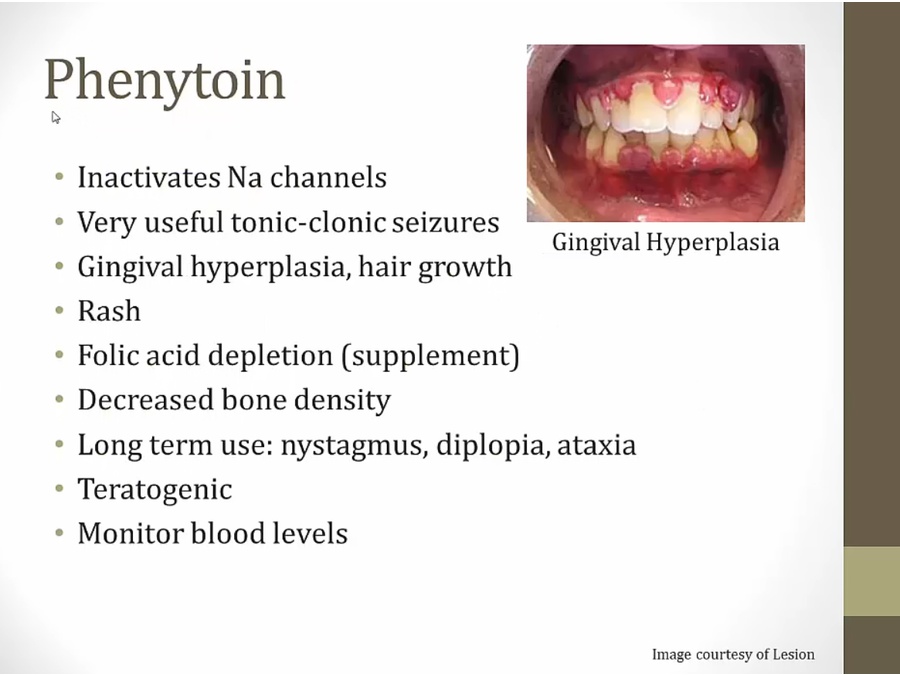

low dose: small rise in lvls, drug quick to metabolize
both inducer and metabolized by P450
0 order kinetics
Valproic Acid

Levetiracetam

very effective
phenytoin and levetiracetam most common
Others

Gabapentin: first thought to affect GABA, but actually affect Ca

Topiramate: also migraine drug, causes foggy mind, more Ca in urine = stones
Drug SE
Teratogenicity

Last updated