04 Smooth Muscles
Vasoactive
Nitrates
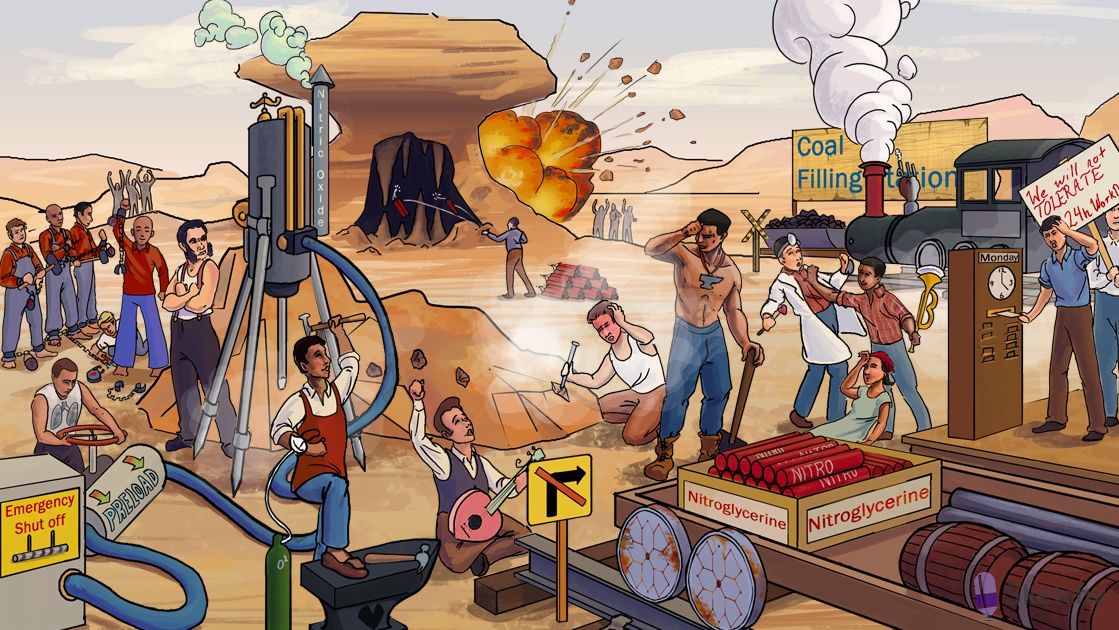

Dynamite: nitrates (e.g. nitroglycerine)
Nitric oxide exhaust: nitrates are metabolized and release nitric oxide
Grump: nitric oxide causes an increase in cGMP in vascular smooth muscle cells
Chains constricting pants/shirts: MLCK usually causes vasoconstriction
Cut P lock off chain: increased cGMP causes myosin light chain dephosphorylation, preventing its interaction with actin.
Dilated blue pants: nitrates cause venous dilation and increased venous capacitance
Modestly dilated red sleeves: nitrates cause some vasodilation of large arteries, but minimal dilation of arterioles
preload: Nitrates decrease preload

Folded tongue: sublingual administration of nitroglycerine avoids first pass metabolism (for acute symptom relief)
Anvil: antianginal therapy
Angina anvil:nitrates treat chronic stable angina
Discarded oxygen mask: nitrates reduce myocardial oxygen requirements
Anvil medal: nitrates treat Prinzmetal angina
Broken heart strings: nitrates are useful in acute coronary syndrome (ACS) (unstable angina, NSTEMI, STEMI)
Emergency shut-off: IV nitroglycerine can be used in hypertensive emergency
Wet lung spots: nitroglycerine is an acute treatment for pulmonary edema

Mouth cave: oral nitrate preparations have a longer duration of action
Single nitro stick in cave: isosorbide mononitrate (oral)
Double nitro stick in cave: isosorbide dinitrate (oral)
Big pile of dynamite: oral nitrate preparations require larger dosing

Fainting: nitrates can cause orthostatic hypotension (venous blood pool in extremities)
Heart reflex hammer: nitrate induced hypotension causes reflex tachycardia
muted beta bugle: beta blockers help prevent reflex sympathetic activation
Nitrates can cause throbbing headaches and flushing
Oxidized iron wheels: nitrates can cause methemoglobinemia
No tolerance for 24 hr work day: avoid tolerance with daily nitrate free intervals
"Monday disease" - with workplace nitrate exposure, tolerance disappears over weekend (decreased drug exposure at work) causing headache and dizziness recur on monday

No right turn: nitrates should be avoided in right sided MI (reduce right ventricular preload, use IV fluid to enhance preload)
Fill* station on blocked track: patients on PDE-5 inhibitors (e.g. sildenafil) should avoid nitrate therapy for 24 hrs, avoid severe hypotension
Obstructed heart smokestack: nitrates are contraindicated with hypertrophic obstructive cardiomyopathy (HOCM), worsens on decreased preload
Migraine
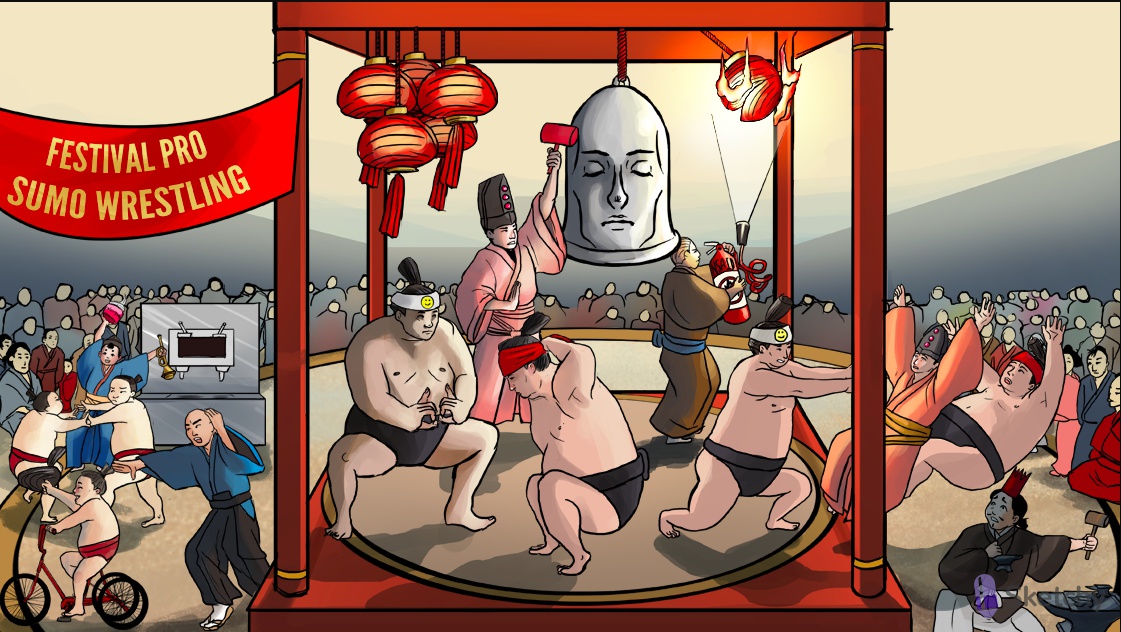
Pounding head shaped bell: migraine therapy
Three gems on hat: migraine pain due to activation of trigeminal nerve afferents in the meninges
Dilated sleeves: trigeminal afferents release vasoactive peptides (e.g. CGRP, substance P, neurokinin A) onto meningeal vessels -> vasodilation and protein extravasation

Sumowrestler: triptans (e.g. sumatriptan) are an acute treatment for migraines
"b" and "d" shaped fingers: triptans (e.g. sumatriptan) are 5-HT1b and 5-HT1d receptor agonists
Smiley face on headband: 5-HT1b and 5-HT1d receptors are located on the meningeal vessels
Tightening red headband: triptans (e.g. sumatriptan) cause vasoconstriction of cerebral and meningeal vessels. Decreases stretch of pain receptors
Sumo taking out the 3 gems: triptans also activate 5-HT1b and 5-HT1d receptors on the trigeminal nerve, preventing release of vasoactive peptides
Hair stem: triptans also activate 5-HT1b and 5-HT1d receptors in the brain stem, inhibiting pain pathways

Constricted coronary crown: triptans can cause coronary vasospasm
Anvil in the sumo's shadow: triptans are contraindicated in patients with angina
Anvil medals in the sumo's shadow: triptans are a known trigger of Prinzmetal angina

Lantern cluster: triptans (and inhaled oxygen) are also an acute treatment for cluster headaches
Fire extinguisher: NSAIDs are an acute treatment for migraine

Calci-Yum icecream nozzles: calcium channel blockers can be used for migraine prophylaxis
Muted beta bugle: beta blockers can be used for migraine prophylaxis
festiVAL PRO: valproic acid (an antiepileptic) can be used for migraine prophylaxis
Toupee: topiramate (an antiepileptic) can be used for migraine prophylaxis
Tricycle: tricyclic antidepressants (e.g. amitriptyline) can be used for migraine prophylaxis
Prostaglandins
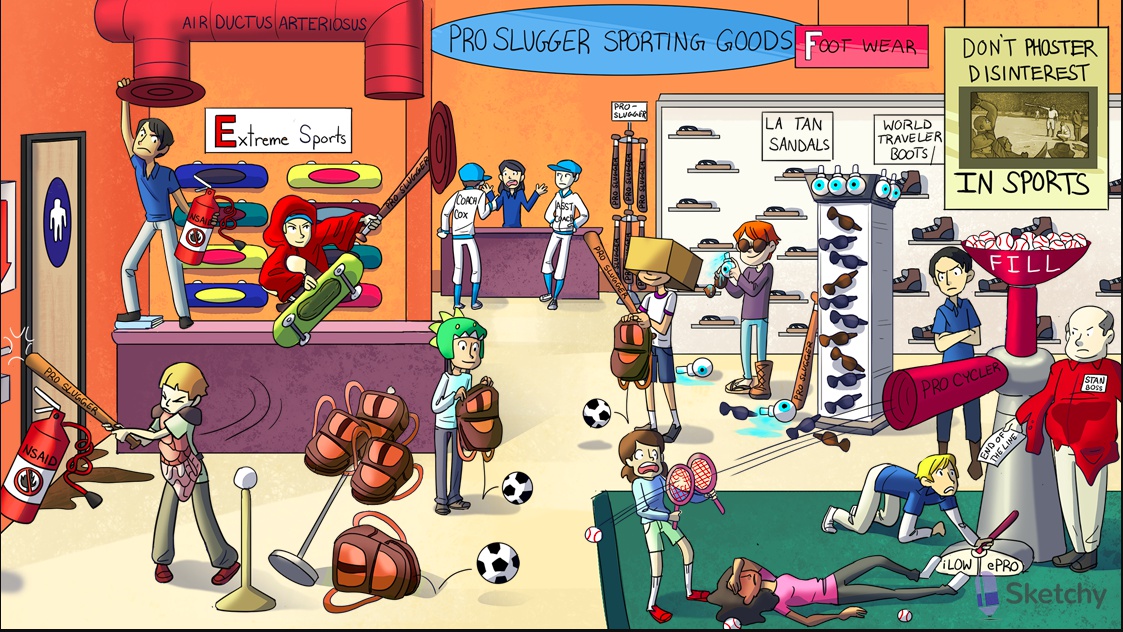

Head and assistant coaches: COX-1 and COX-2 produce prostanoids (e.g. prostaglandins)
Pro slugger: prostaglandins

"E": PGE1 and PGE2
Dill pickle: alprostadil (PGE1)
Erect bat: alprostadil treats erectile dysfunction
Dilated red sleeves: alprostadil is a vasodilator
Opening air duct: alprostadil maintains patent ductus arteriosus
Closing air duct: NSAIDs (e.g. indomethacin) promote closure of ductus arteriosus
Missed swing: misoprostol (PGE1)
Gastric protective equipment: misoprostol promotes protective mucus secretion by gastric mucosa
Missed swing hitting fire extinguisher: misoprostol can prevent NSAID-induced peptic ulcer
Opening uterus bag: misoprostol promotes uterine contraction to facilitate labor or terminate pregnancy
Flooded bathroom: misoprostol can cause diarrhea
Dino helmet: dinoprostone (PGE2)
Opening uterus bag: dinoprostone promotes uterine contraction and ripens the cervix to facilitate labor or terminate pregnancy

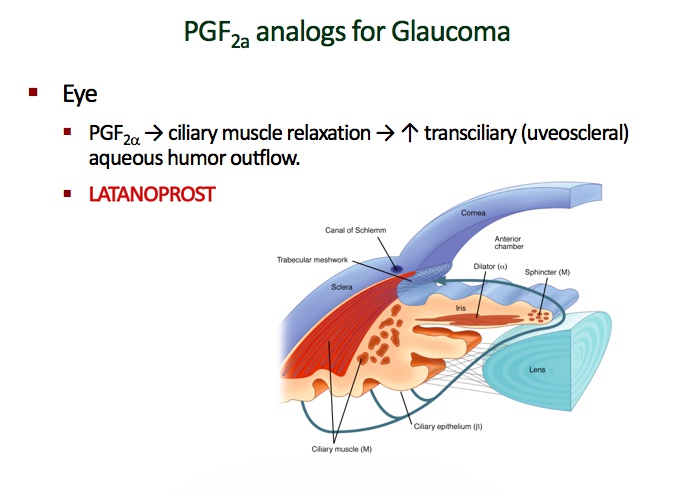
"F": PGF2a
Cardboard box: carboprost (PGF2a)
Opening uterus bag: carboprost promotes uterine contraction to control postpartum hemorrhage or terminate pregnancy
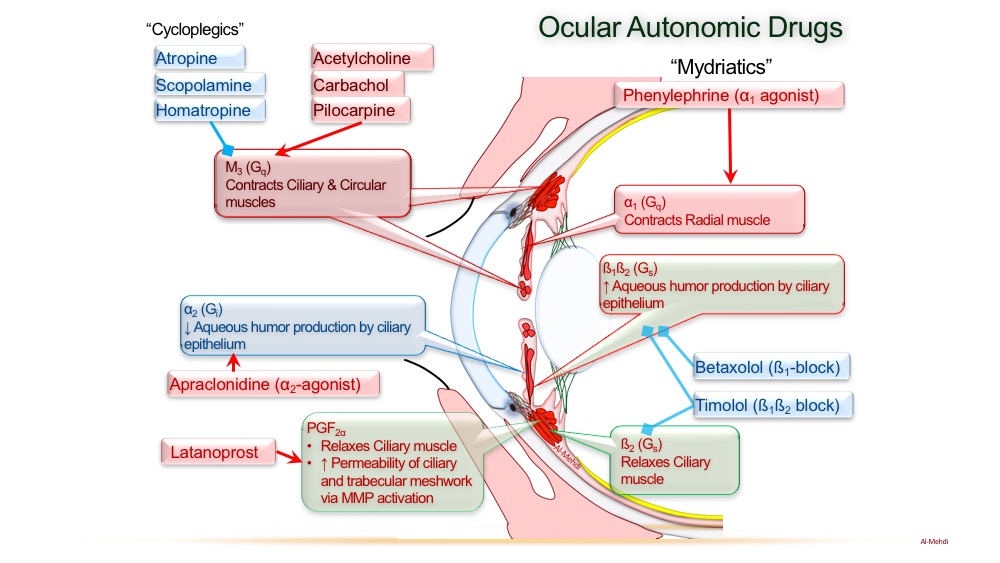
LA tan sandals: latanoprost (PGF2a)
World traveler boots: travoprost (PGF2a)
Leaking eyeballs: latanoprost and travoprost treat glaucoma by increasing aqueous humor outflow (not production)
Brown sunglasses: latanoprost and travoprost can produce brown pigmentation in iris

High tension pulmonary rackets: pulmonary hypertension
Dilated pro-cycler: prostacyclin analogs cause vasodilation (e.g. iloprost, epoprostenol)
iLOW - ePRO setting: iloprost and epoprostenol (prostacyclin analogs) treat pulmonary hypertension
Fainting: iloprost and epoprostenol may cause flushing, headache, hypotension

FILL: -fill suffix of phosphodiesterase isoform 5 (PDE-5) inhibitors (e.g. sildenafil, tadalafil)
Don't phoster disinterest: phosphodiesterase isoform 5 (PDE-5) inhibitors (e.g. sildenafil tadalafil
Grump: PDE-5 inhibitors increase cGMP
Erect bat: PDE-5 inhibitors (e.g. sildenafil, tadalafil) treat pulmonary hypertension and erectile dysfunction

Boss man Stan: bosentan treats pulmonary hypertension
End o' the line: bosentan is an endothelin inhibitor
Dilated red sleeves: bosentan (an endothelin inhibitor) causes vasodilation
Liver spot: bosentan is associated with fatal hepatotoxicity
Allergy and Pulmonary
Histamines
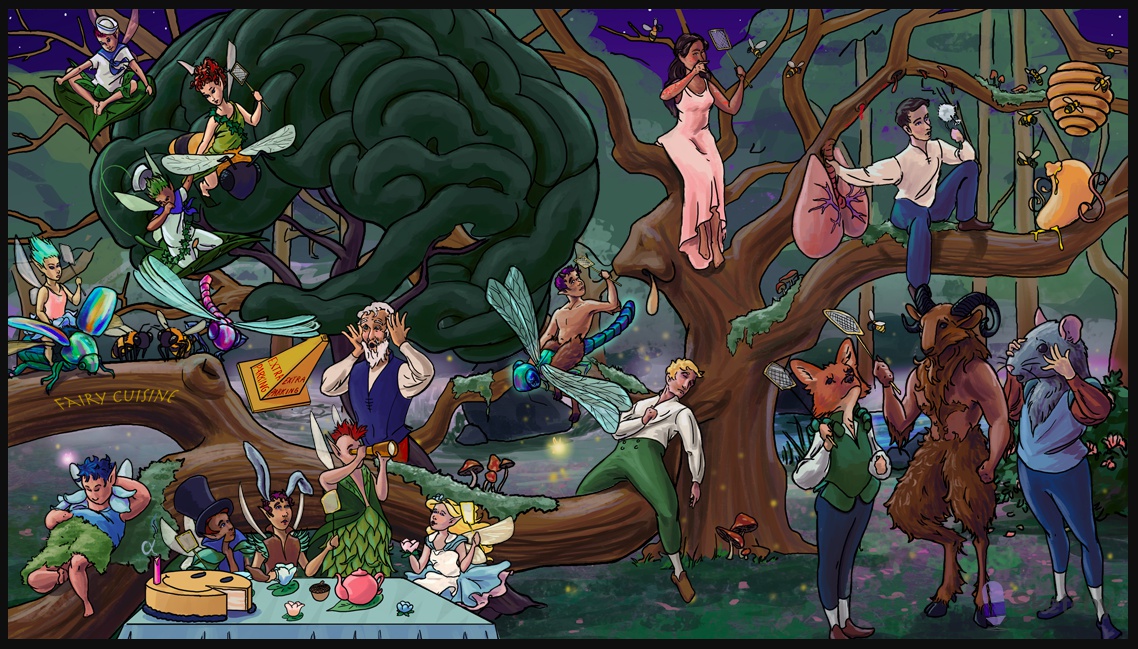

beehive: histamine sequestered inside the granules of mast cells
"Q" dandelion: H1 histamine receptor is coupled to Gq protein (mediates allergic inflammation)
Honeypot with 2 "S" handles: H2 histamine receptor is coupled to Gs protein, increased cAMP
Golden gastric honey looks like stomach: H2 histamine receptor mediates gastric acid secretion
Dripping nose sap: histamine increases nasal and bronchial mucus production (H1 receptor activation)
Dripping vascular sap: histamine increases vascular permeability (H1 receptor activation) (urticaria/hives)
Constricted lung branch: histamine causes constriction of bronchial smooth muscle (H1 receptor activation)
Brain tree: histamine functions as a neurotransmitter (H1 receptor regulates sleep and arousal)
fairy rubbing nose: allergic rhinitis

Bee swatter: H1 receptor blocker (antihistamine) treats allergy
Dragonfly fairy: diphenhydramine and dimenhydrinate (1st-generation H1 receptor blockers)
Color fairy: chlorpheniramine (1st-generation H1 receptor blocker)
Fairy cuiSINE: hydroxyZINE, mecliZINE, promethaZINE (1st-generation H1 receptor blockers)

Fairy dust and dander: histamine mediates type-1 allergic reaction -> hives, allergic rhinitis (H1 receptor blockers are first line therapy)
Seasick fairy sailors: 1st-generation H1-blockers treat vestibular nausea or motion sickness (lipophilic -> enter CNS -> act on vestibular system and brainstem)
Falling "extra parking" cone: 1st-generation H1-blockers treat extrapyramidal side effects caused by antipsychotics, e.g. acute dystonia (antimuscarinic effects re-establish dopaminergic-cholinergic balance)

Sleeping under brain tree: 1st-generation H1-blockers cause drowsiness (lipophilic -> cross BBB -> central effects)
Antimuscarinic tea party: 1st-generation H1-blockers antagonize peripheral and central muscarinic receptors (e.g. pupillary dilation, dry mouth, urinary retention, constipation, exacerbation of glaucoma, and delirium)
Cut smiley face cake: 1st-generation H1-blockers antagonize serotonin receptors in the CNS
Stuffed fairy: 1st-generation H1-blockers stimulate appetite and weight gain (anti- serotonergic effects)
Extinguished single alpha candle, fainted fairy: 1st-generation H1-blockers antagonize alpha-1 receptors -> dizziness and hypotension
Delirious elderly man: 1st-generation H1-blockers cause cognitive impairment in the elderly (central antihistamine and antimuscarinic effects)

Fox, satyr, and rat: 2nd-generation H1-blockers: fexofenadine, cetirizine, loratidine
Fox, satyr, and rat stand outside of brain tree: 2nd-generation H1-blockers are less lipophilic -> do not cross BBB -> less sedating (also less antimuscarinic, antiserotonergic, or anti-alpha adrenergic properties)
Asthma Drugs
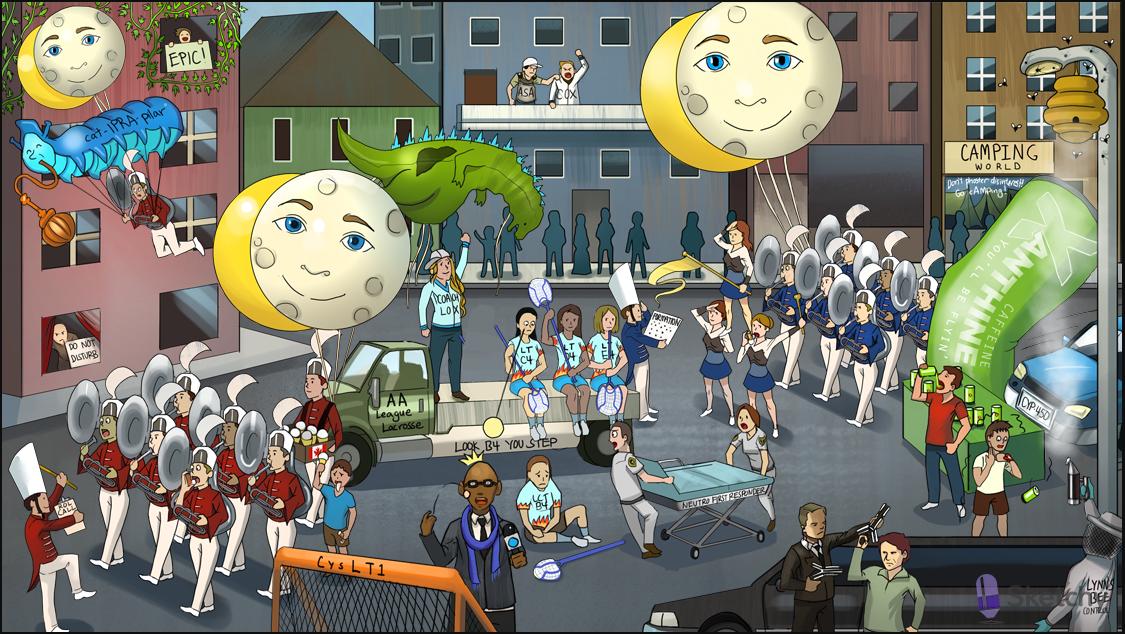

Dilated beta 2 tuba: selective beta-2 agonists (e.g. albuterol) treat bronchoconstriction in asthma
ROL call: "-rol" suffix of the selective beta-2 agonists (e.g. albuterol, pirbuterol)
"Do not disturb": terbutaline (a selective beta-2 agonist) treats bronchoconstriction in asthma
Inhaler: selective beta-2 agonists (e.g. albuterol) are available as metered dose inhalers for acute symptom relief
Moon face: inhaled corticosteroids (e.g. beclomethasone, budesonide, fluticasone) can be added as daily maintenance therapy for persistent symptoms
Moon eclipsing inflammatory sun: corticosteroids treat asthma by blocking later inflammation and cellular infiltration
Canadian snow: Candida albicans
Snow cone tongue: inhaled corticosteroids (e.g. beclomethasone, budesonide, fluticasone) can cause oropharyngeal candidiasis

AA league: arachidonic acid (AA) is the precursor of leukotrienes (and prostanoid) synthesis
Lacrosse Coach Lox: lipoxygenase (LOX) converts AA into leukotrienes
Lacrosse players: leukotrienes LTB4, C4, D4, and E4 are important regulators of inflammation
B4 attracting first-responders: LTB4 is a chemoattractant for inflammatory cells (e.g. neutrophils
First responders: neutrophils
Hand clamping lacrosse stick bronchi: LTC4, D4, E4 increase airway vascular permeability, mucus production, and bronchoconstriction
Lacrosse goal CysLT1: receptor for LTD4 (most potent bronchoconstrictor)

Monte the broadcaster: "-kast" suffix of LTD4-receptor antagonists (e.g. montelukast, zafirlukast)
Blocked D4 shot: LTD4-receptor antagonists (e.g. montelukast, zafirlukast) are an alternative therapy for mild persistent asthma
Dilated scarf: LTD4-receptor antagonists cause bronchodilation
Open mouth: LTD4-receptor antagonists are administered orally
Godzilla falling on Coach Lox: zileuton (a direct lipoxygenase inhibitor) is an alternative therapy for mild persistent asthma
Liver spot: zileuton has a risk of hepatotoxicity

ASA umpire grabbing Coach Cox: inhibition of COX shifts the AA metabolism to the LOX leukotriene pathway (exaggerated in aspirin-induced asthma)

Salute formation: salmeterol and formoterol (long acting beta-2 agonists) treat moderate or severe persistent asthma
Long tapering flag: salmeterol and formoterol (beta-2 agonists) have a long duration of action
Inhaler: long acting beta-2 agonists (salmeterol, formoterol) are administered as a daily controller inhaler
Higher moon face: an increased dose of inhaled corticosteroids treats moderate or severe persistent asthma
Xanthine energy drink: methylxanthines (e.g. theophylline) are an alternative therapy for mild to severe persistent asthma

Xanthine energy drink: methylxanthines (e.g. theophylline) are an alternative therapy for mild to severe persistent asthma
"flyin'": theophylline (a methylxanthine)
Caffeine: methylxanthines are related to caffeine
"Don't phoster disinterest": methylxanthines (e.g. theophylline) are phosphodiesterase inhibitors
"Camping'": methylxanthines increase cAMP, bronchodilation
Open mouth: theophylline is administered orally

Shaking kid: methylxanthines (e.g. theophylline) have CNS side effects including nervousness and tremor
Holding up heart watch: methylxanthines (e.g. theophylline) can cause tachycardia
Chrome bumper hitting energy drinks: methylxanthines (e.g. theophylline) are metabolized by the cytochrome P-450 system
Treat overdose with activated charcoal

Bee hive: mast cell degranulation is important to the pathogenesis of asthma
IgE gun shooting hive: antigen binding to IgE on mast cells causes degranulation and release of inflammatory mediators (e.g. histamine)
Limousine: omalizumab (an anti-IgE monoclonal antibody) is an adjunctive therapy for moderate or severe persistent asthma
Grabbing end of IgE gun: omalizumab is a monoclonal antibody directed against the Fc portion of IgE, preventing mast cell sensitization
chrome Lynn's bee control dispenser: cromolyn sodium
Bee sedating smoke: cromolyn sulfate inhibits mast cell degranulation (preventing release of histamine)

Beta-2 tuba: inhaled short-short acting beta-2 agonists (e.g. albuterol) treat an acute severe asthma exacerbation
Moon face: systemic corticosteroids treat acute severe asthma exacerbation
Ivy: corticosteroids are administered IV or orally during an acute severe asthma exacerbation
Cat-ipra-pillar: nebulized ipratropium bromide (anticholinergic) can be added to treat an acute severe asthma exacerbation
Epic: subcutaneous or intramuscular epinephrine can be used to treat an acute severe asthma exacerbation
Last updated