35 Shock
_..

RV: contracts, generate high systolic
PA: same systolic, PV close and stop pressure drop at 10
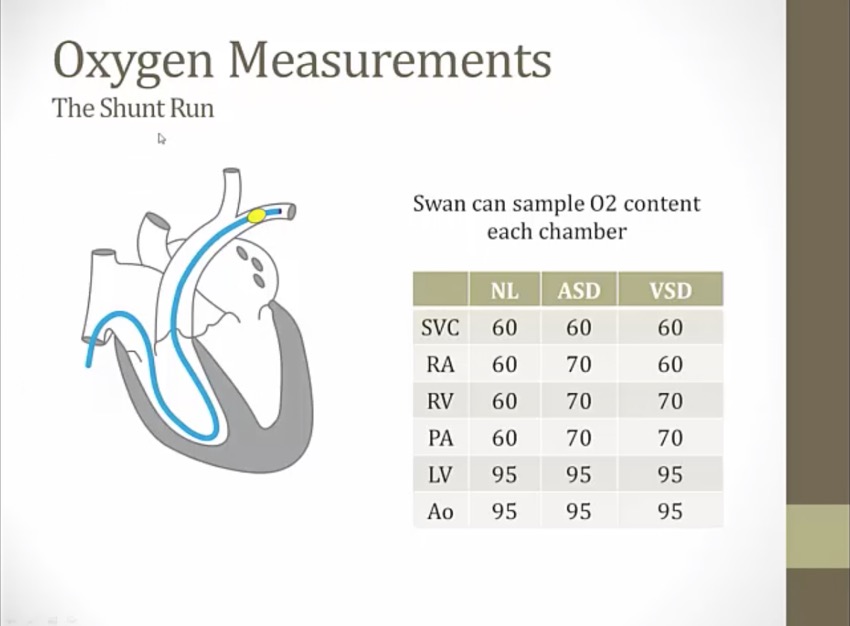
can also take blood sample and measure O2 sat

Swan-Ganz Catheter
_..
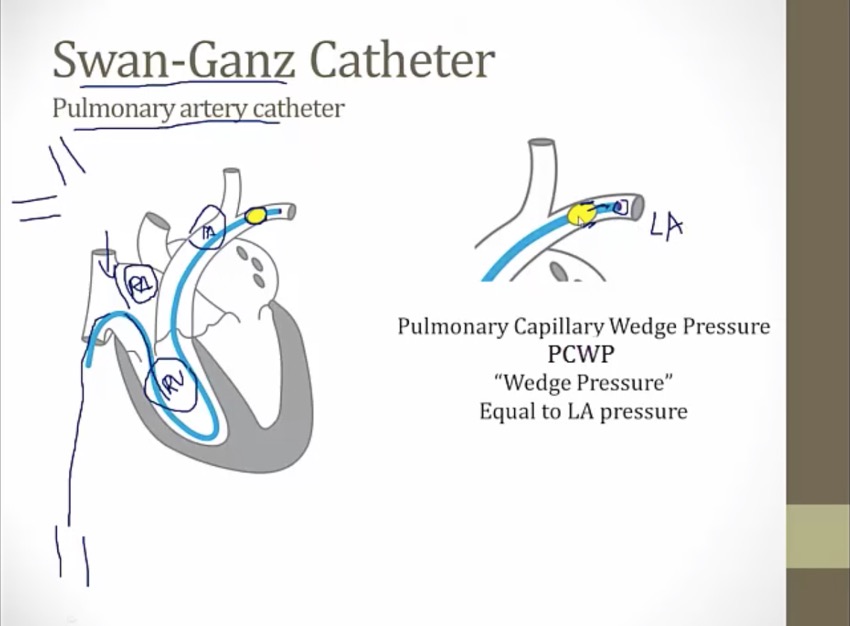
usually inserted into jugular vein or subclavian. Or femoral vein up to IVC
can be stopped in different chamber and measure pressure: RA, RV, PA, wedge pressure
PCWP: push balloon until it can't go any further, stuck in PA, tip of catheter just beyond balloon, measures LAP
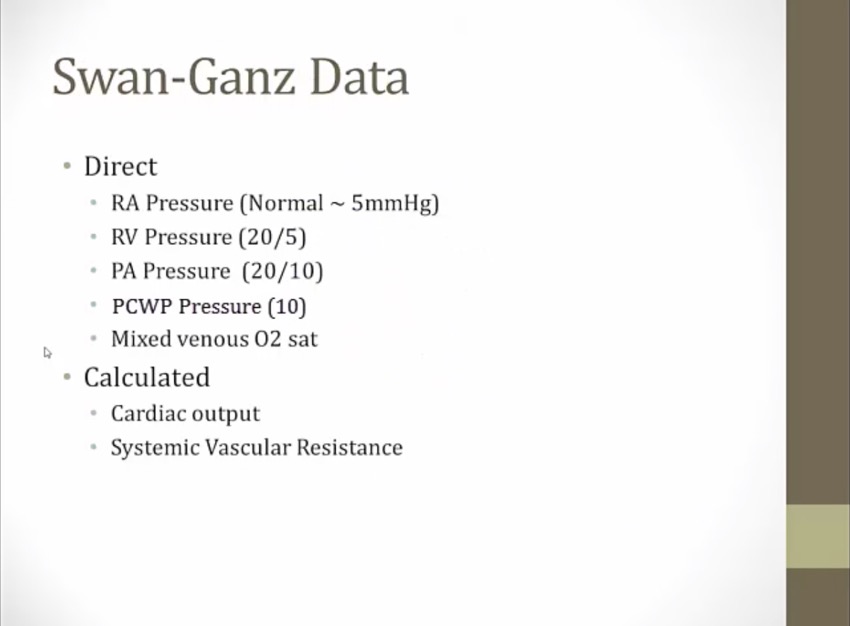
total hemodynamic assessment from swan-ganz
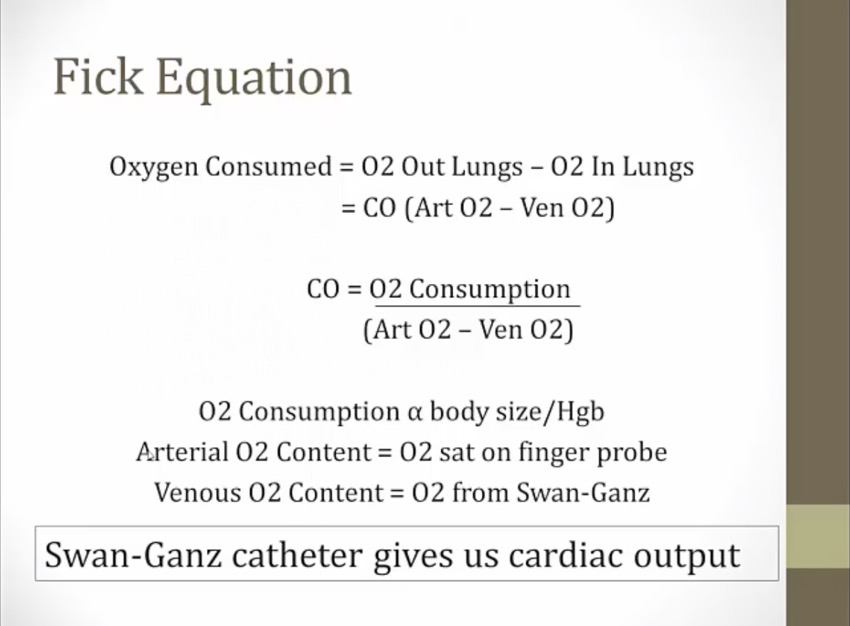
O2 consumption, arterial and venous O2 can all be found from swan ganz catheter

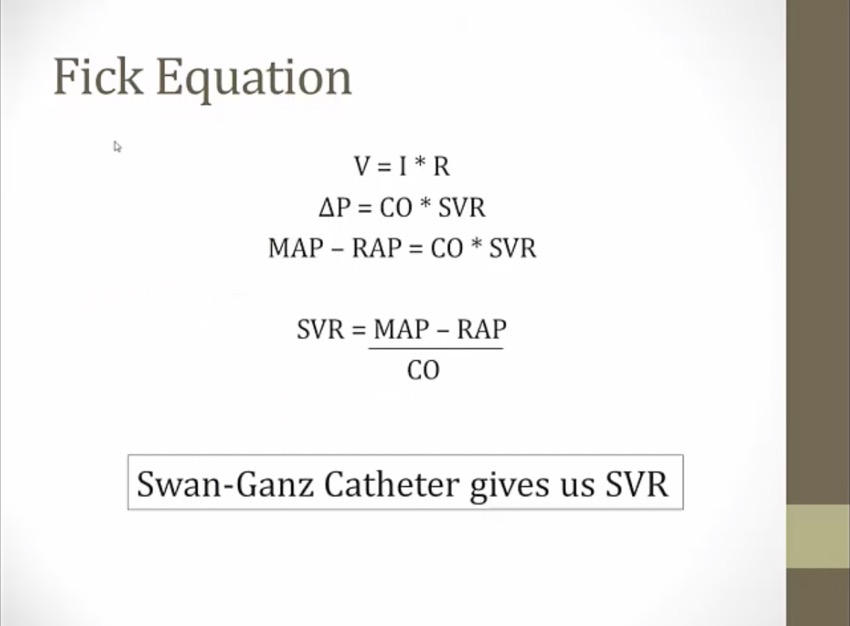
MAP: pressure leaving heart
RAP: pressure returning to heart
Shock
_..


cardiogenic: weak heart can't pump
insensible loss: lose fluid in lungs/diarrhea/vomiting, not sensed by body compared to flood loss through kidney
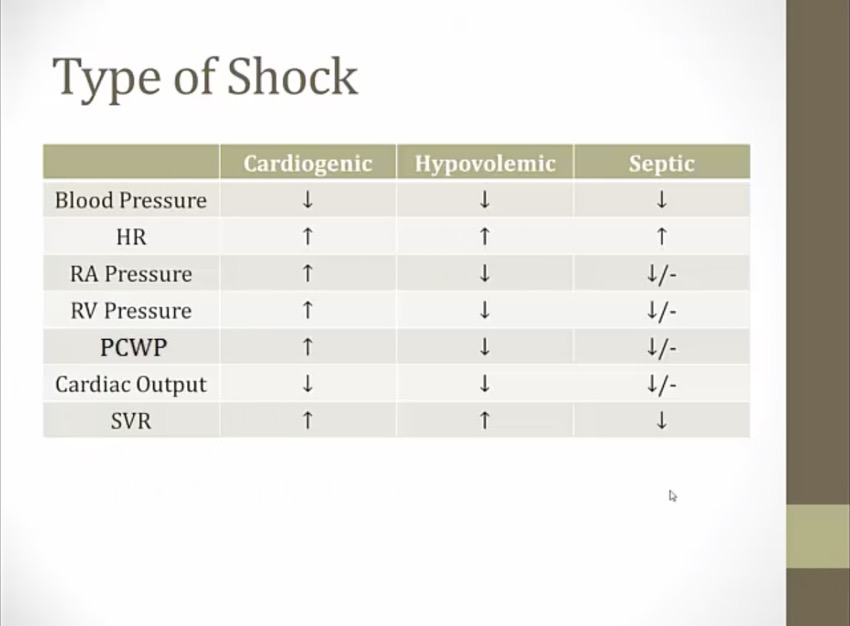
high HR: body response to increased sympathetic drive
cardiogenic: hallmark low CO from weak muscle, blood back flow to all heart chambers
hypovolemic: low CO, all low chamber pressure from low blood volume
septic: hallmark low SVR, early dilation of veins = all low pressure, in hospital may be normal from IV fluid

Equalization of Pressures
_..

tamponade: effusion of blood
pericardial constriction: constricting sac
restrictive cardiomyopathy: infiltrative substance


Valvular Disease
_..
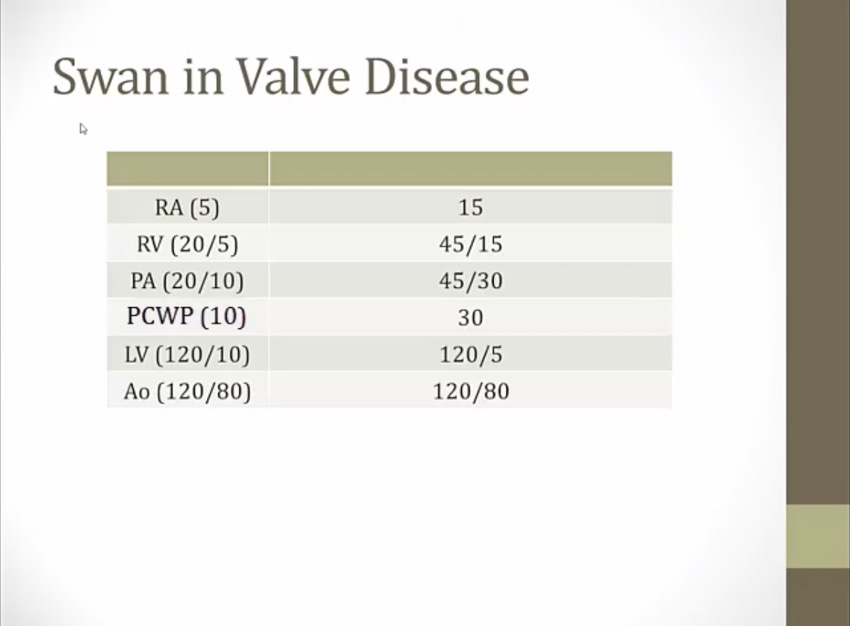
mitral stenosis
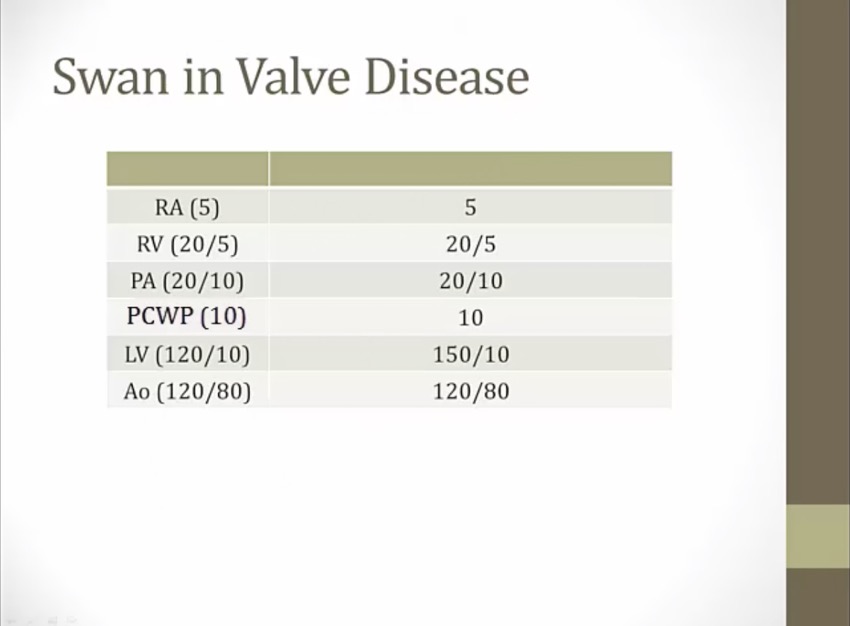
aortic stenosis, high LV systolic pressure
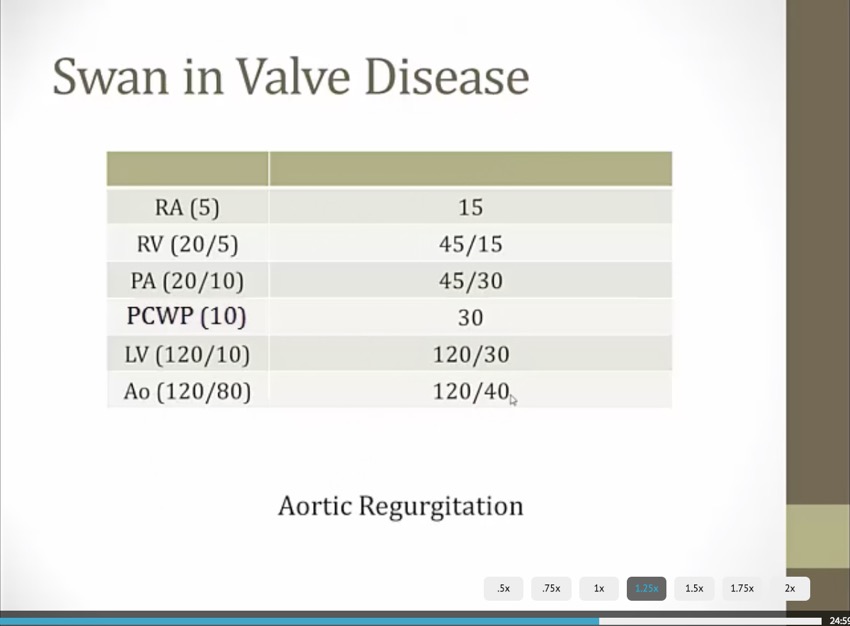
wide pulse pressure
blood spilling out of aorta in diastole
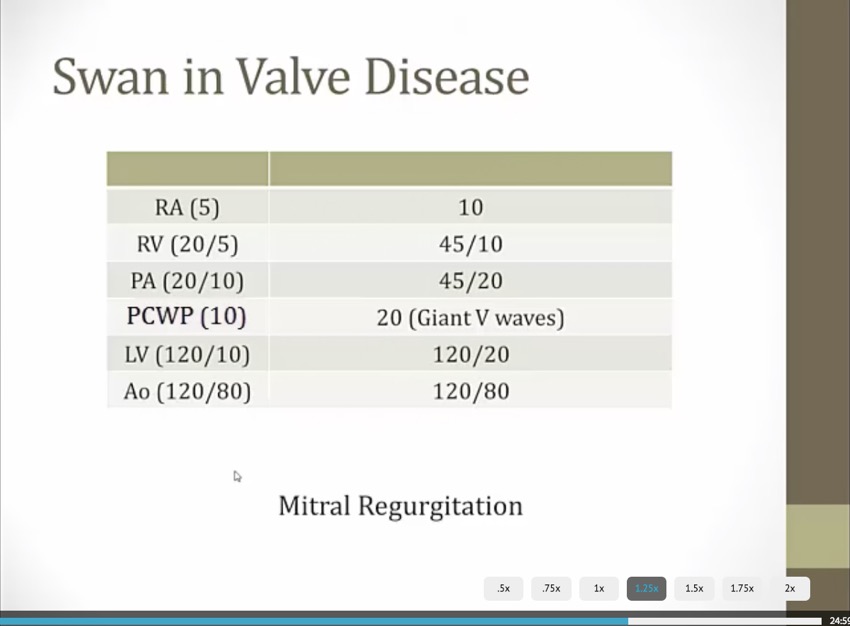
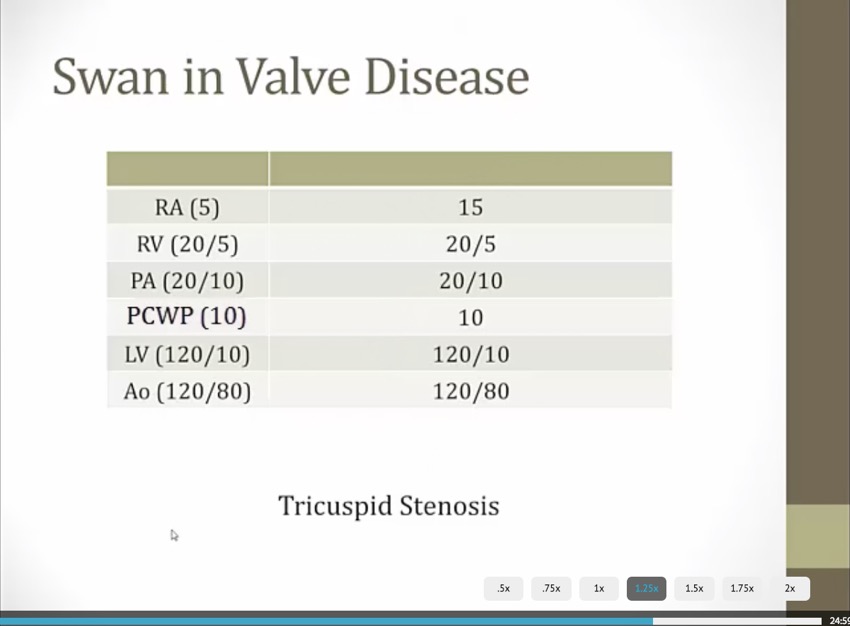
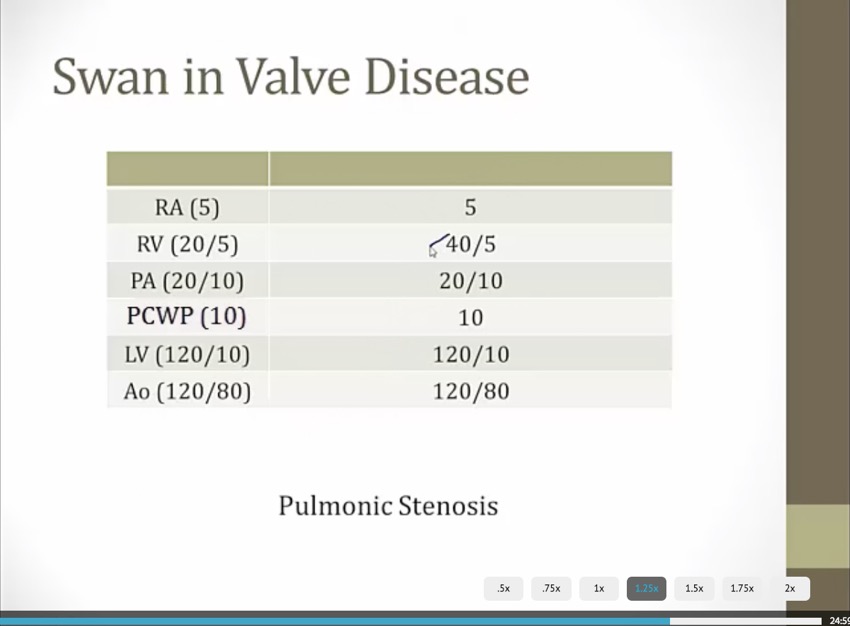
RV and PA systolic should be equal
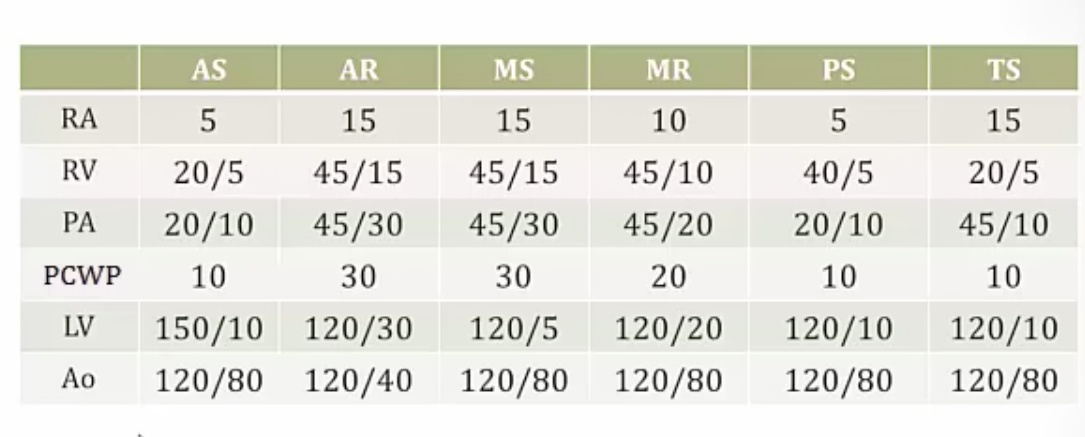
start with aorta and work backwards, find first chamber with high pressure
MR: no aortic regurgitation with low diastolic pressure
Shunt Run
Last updated