11 Virus
RNA Positive Sense
_..
coin machine: Positive-sense mechanism of replication, uses host RNA polymerase. Insert coin and that's it
All + sense RNA replicate in cytoplasm, since host mRNA in cytoplas
Picorna Overview
_..

"Peak" = Picornaviridae
orange color, day time: Positive-sense RNA virus
statue of David: Naked virus
_..

poops: Fecal-oral transmission
coin machine: Positive-sense mechanism of replication, uses host RNA polymerase. Insert coin and that's it
ticket booth continuous ticket: Polyprotein product made at first
ticket booth broken tickets: Cleaved portion of polyprotein
All + sense RNA replicate in cytoplasm, since host mRNA in cytoplasm
_..

A: heptatitis A with A tag; liver spot: Hepatosplenomegaly
B: birds = entero
C: common cold = rhino; mud on rhino face: Upper respiratory infection
_..

enter aviary: Enteroviruses
flamingos: Poliovirus
cockatiels bird: Coxsackie A and B
echoing mockingbirds: Echovirus
_..

cage shaped like head, 100% aseptic sign: Aseptic meningitis (nonbacterial)
no added sugar: CSF glucose levels normal
no organisms: CSF shows no organisms
source of protein: CSF has elevated protein levels
child with helmet: Children most affected by meningitis
Polio
_..

flamingo: polio
orange color, sun: Positive-sense RNA virus
Pico baby = picornavirus
David: Naked virus
flamingo stable in acid pool: Acid stable; fecal oral transmission so must be resistant to acid
_..

eggs (virus) with orange plants (villi) : "Replication occurs in lymphoid tissue, such as Peyer's Patches"
sign: Peyer's patches, 2-3 weeks onset
bird with large anterior horn: Affects the anterior horn of the spinal cord
_..

flamingo bent leg: Asymmetrical paralysis, hyporeflexia
flamingo smoke air: Respiratory insufficiency
kid with helmet: Causes aseptic viral meningitis
_..

no treatment
sulky teenager with skull: Salk = killed vaccine, bypass GI tract via injection. Only forms IgG, no IgA
savin' a life: Sabin = live-attenuated vaccine
A in life: IgA response on top of IgG
Cox
_..

Cockatoos: cox virus
Pico counterpart = picornavirus
Positive-sense RNA virus
Naked virus
_..

Coxsackie A
bird seeds in mouth, hand, foot: Hand, foot and mouth disease
red bird seeds: Red vesicular rash
kid with helmet: Aseptic viral meningitis
girl in bathing suit: Infection common in summer months

_..

Coxsackie B
floppy bags of seeds: Dilated cardiomyopathy
zoo keeper grab: "Devil's grip = Bornholm's disease / pleurodynia" Strange sharp pain in unilateral lower chest
_..
supportive
Rhino
_..

Naked virus
Positive-sense RNA virus
pico rhino: picorna virus
lemon: Acid labile; can't resist stomach acid and can't transmit fecal-oral
tent with different colors: Rhinovirus has many different serotypes, no vaccine
_..

sneezing, please wash hands sign: Transmitted through fomites (dirty hands)
_..

mud on small rhino face/neck: Causes URI/common cold
camera: rhinovirus attach to host molecule ICAM-1
33: Grows best in cooler temperatures - around 33 degrees Celsius, upper respiratory tract where air flows better
Hep A
_..

Positive-sense RNA virus
Pico = picornavirus
A tag: "Hippo"titis A
Naked virus
_..

hippo stable on rock: Acid stable, make it through stomach
poop: Fecal-oral transmission
Contaminated water is a common source of infection in DEVELOPING countries
USA shellfish and fishing: Uncooked shellfish a common source of infection in DEVELOPED countries
backpack: Commonly seen in travelers to endemic areas
_..

inactivation sign: How to inactivate Hepatitis A
_..

Often silent but can cause acute
yellow guy: Jaundice, especially in adults
young kid not wearing yellow: Anicteric hepatitis in young children and infants
smoker: Smokers with Hep A develop an aversion to smoking
1 month sign: One month duration of symptoms
limit: Self-limiting
no carrying: No carrier state
_..

tranquilizer gun: Inactivated vaccine
Calicivirus
_..

Calicivirus: Cali Sea
Positive-sense RNA virus
Naked virus
1 long ticket: Produces one long polyprotein that is cleaved by viral proteases
_..

Narwhal: Norovirus is the most common Calicivirus
lots of kids: Young children = outbreaks common in daycare centers and schools
cruise scene: Responsible for over 90% of outbreaks of diarrheal illness on cruises
shellfish buffet: Consumption of shellfish is associated with Norovirus
liquid brown mud: Causes explosive watery diarrhea
Flavivirus
_..

New flavors: Flaviviruses
Positive-sense RNA virus
toga party with clothes: Enveloped virus
single straw: Non-segmented RNA
_..

dengue
yellow fever
west nile
Hep Sea: Hepatits C
_..

swimming dinghy: Dengue fever
Dengue Mosquitoes = Aedes Egyptei
2 broken oars: Type 2 dengue = break-bone fever
RBC's: Thrombocytopenia and hemorrhagic fever
blue/red ribbons off of boat look like blood vessels: Dengue fever can lead to renal failure, septic shock
floating down river: supportive treatment only

_..

yellow buffalo: Yellow fever
Aedes mosquito
liver shaped spot: Jaundice
buffalo hump: Backache
red stool: Bloody stool
large syringe: Live-attenuated vaccine for travelers
_..

Nile bird: West Nile virus = reservoir in birds
Mosquito vector
red turbans: Encephalitis
neck brace: Meningitis, rigidity
floppy drooping neck: Flaccid paralysis
flapping wings: Seizures
passed out bird: Coma
floating down: no treatment
Hep C
_..

FLAVIful Hep C = Hepatitis C is a Flavivirus
Positive-sense RNA virus
robe: Enveloped
C ring and out in sea: Hep C
"C" ear ring = Hep C
_..

bloody water: Transmitted in blood products (blood transfusion in 70s/80s)
needle in ear: Needle-sharing and needle sticks are sources of transmission
_..

liver spot: Hepatitis
yellow hippo: Jaundice
sign, C for chronic: 60-80% of Hepatitis C infections will become a chronic infection.
multicolored tent: Antigenic variability of envelope
no viewing: Hepatitis C lacks proof-reading, which is what leads to its antigenic variation
"No 3'- 5' exonuclease activity (proofreading) in the viral RNA polymerase"
_..

ALT rise/fall with tide: Acute infection characterized by a large rise and then fall in ALT. Usually will fall by 6 months.
salt precipitate on shore. 5 sided: Cryoglobulins seen in Hepatitis C. Cryoglobulins are serum proteins containing IgM that precipitate in cooler temperatures.
_..

corral: Can lead to fibrosis/cirrhosis
crab: Can lead to Hepatocellular Carcinoma
_..

ribs: Ribavirin used in combination therapy for Hepatitis C
walky talky with a, interference: Interferon Alpha (part of combination therapy)
meat cleaver: Can also use protease inhibitors to treat Hepatitis C.
Togavirus
_..

Positive-sense RNA virus
scene outside nucleus dome: replication in cytoplasm
toga: Toga viruses are enveloped
_..

man hitting head on arbor: Arbovirus
Rubies = rubella
Arbovirus
_..

man hitting head on arbor: Arbovirus
mosquitos around head: Arthropod vector
compass and horse: Western, Eastern, and Venezuelan equine encephalitis
turban: Encephalitis, neuro symptoms
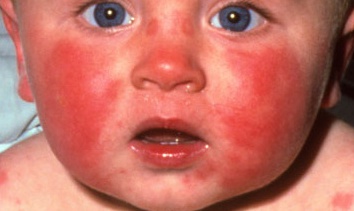
Rubella
_..

Rubies = rubella
aka German measles
water droplets: Spread via respiratory droplets
torches: transplacental transmission, TORCHeS infection
tickets: Long polyprotein precursor cleaved by viral proteases
immigrant: usually unvaccinated
_..

child king: Rubella is a childhood exanthem (rash)
grabbing back of neck: tender Postauricular and occipital lymphadenopathy
rubies falling off crown: Rash starts at the head and moves downward

_..

open aqueductus arteriosis: Patent ductus arteriosis
sculptures with creepy blank eyes: Congenital cataracts
covering ear: Sensorineural deafness
blue gems: Purpuric blueberry muffin rash
yellow babies: Jaundice


_..

kneeling adults: Arthritis in adults
_..

live puppet show for children: MMR = live-attenuated vaccine
pregnant puppy without syringe: Pregnant women should not be given MMR vaccine
200 ticket count: HIV positive patients should receive the vaccine only if CD4 count is over 200
Corona
_..

Positive-sense RNA virus
crown: "Corona" virus
robe: Encapsulated virus
spiraling road: Helical capsid
sneezing: Causes the common cold
red/enflamed respiratory tract: SARS or MERS = acute bronchitis can lead to acute respiratory distress syndrome
king out in field with castle (nucleus) in back: replicate in cytoplasm
Retrovirus
_..
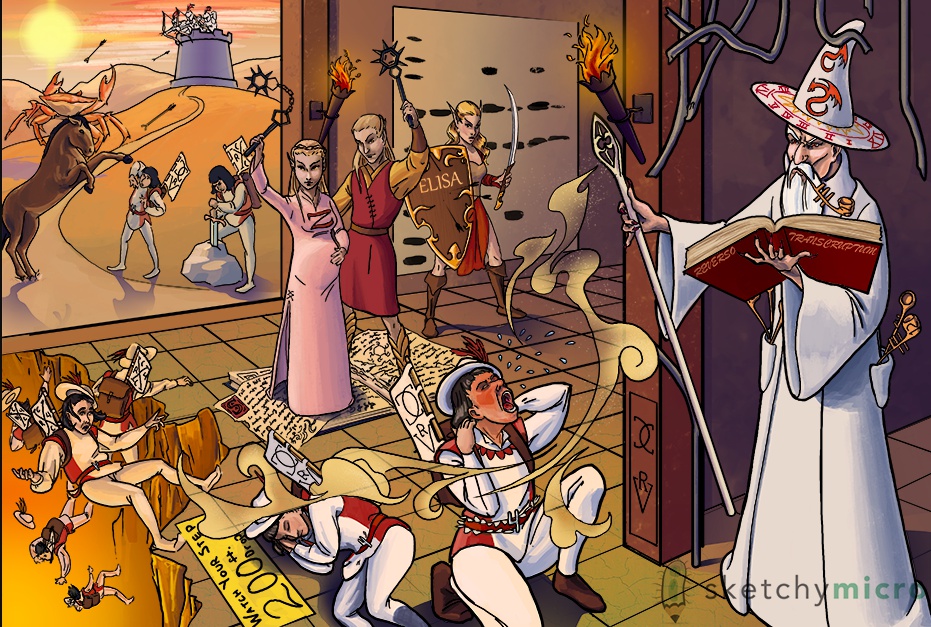

wizard: HIV
staph: immunocompromised
orange sun: + sense RNA
robe: enveloped
2 orange dragon hat: diploid RNA positive virus. 2 RNA in each virion
replicate in nucleus
_..

round 24h sundial: gag gene = p24, capsule for RNA strands
pipe: env protein = gp 41, 120
pipe in mouth: gp41 transmembrane protein
pipe in pocket sticking out: gp120 outer protein
reverso transcriptum book: pol = reverse transcriptase
_..

transmission: sexual and blood
torches: TORCH infection
_..

busted jail: initially infects macrophages
esquire helper with 4 buckles: infects helper T cells, especially CD4
CCR5/CXCR4 flag: gain entry via CCR5 early and CXCR4 late
_..

1st esquire crying and touching back neck: prodrome involves flu/mono like symptoms with cervical LAD
mouth open: enlarged tonsils
pearls around waist: LAD
red faced/sweaty: fever
sleeping esquire: latent period lasting up to 10 years
Steep cliff with 200 ft: steep drop below CD4 200 develops into AIDS
AIDS also defined if above 200 but with aids defining illness
_..

large crab marching up to archers in stronghold (B cells in lymphoma): AIDS can cause Diffused Large B Cell Lymphoma
_..

She elf with ELiSA shield standing in front: ELISA screening for antibody
tabestry: confirmed with Western blot for antibody
vertical transmission: neonates will always be positive because has maternal antibody; use HIV RNA/DNA nucleic acid amplification to find virus itself
TCR used to track progression of CD count
_..

pregnant elf swinging nucleotide shaped chain: NRTI backbone of retroviral therapy; nucleotide analog, halts prolongation
Z: zidovudine, good for pregnancy, labor, post partum
He Elf holding mace without chain: NNRTI, doesn't incorporate in to chain but still inhibit transcriptase
both elves standing on book: both inhibit reverse transcriptase
esquire can't pull sword: protease inhibitors
Mare on hind legs crushing esquire: CCR5 inhibitor
RNA Negative Sense
_..
RNA must be transcribed to + sense first, thus must bring own RNA polymerase
all are single stranded except Reovirus
All replicate in cytoplasm, except orthomyxovirus
_..
BOAR: bunya, ortho, arena, reovirus are segmented. Only segmented can have antigenic shift
Orthomyxovirus
_..

Orthodontist: ortho
yellow moon: Negative-sense RNA
Warm / Orange hues = RNA
robe: Enveloped
octopus repilcates in helmet: Orthomyxovirus is the ONLY RNA virus that replicates in the nucleus.
Octopus legs = 8 segments in Orthomyxovirus
water droplets: respiratory transmission
_..

Heme aquarium and stuck together RBC's: Hemagglutinin (HA) is a virulence factor for Orthomyxovirus. Glycoprotein, binds SA on RBC, cause RBC to clump together
plants in tank: Sialic acid residues - carbohydrate chains to which the virus attaches.
Scalpel missing from Nurse Assistant tray= symbol for Neuraminidase (NA), a virulence factor of Influenza
scalpel: Neuraminidase (NA) cleaves silica acid to free newly formed viral particles
shell with 2 M ridges: M2 Protein = Allows virus to manipulate pH for viral uncoating.
_..

Doktor drift: Antigenic Drift = point mutations that cause seasonal flu or epidemics. "DoKtor" has a point mutation. Slightly altered each year.
Night Shift with falling H with reassortment at bottom: Antigenic Shift = segment rearrangements in HA and NA that cause Pandemics. The "H" in "Shift" has fallen to become recombined with other Influenza H's and N's.
_..

Fluoride on wall: Influenza is an Orthomyxoviridae
ABC: Influenza types A, B and C. A is most important with shift and drift. B is just drift
_..

Multicolored curtains: Antigenic variation
Multicolored suckers: H1, H2, H3, etc. Determines cell tropism and which cells can bind to
NA and HA from swine, avian and human influenza viruses can undergo reassortment during antigenic shifts to form pandemics.
_..

Manta dining = A-Manta-Dine (Amantadine) is an M2 protein inhibitor, thus preventing viral uncoating.
Tammy V = Tamiflu (Oseltamivir / Anamivir ). V = "-vir"
Tamiflu (Oseltamivir) is an NA inhibitor (Tammy is putting caps on the NA scalpels)
_..

Dec - Feb most common infection. Give vaccine in October to allow immune buildup
_..

syringe impale pirate skeleton: Killed vaccine given IM
bubbles up through nose: Live vaccine is intranasal
_..

lung chest: pneumonia major complication. (Case: elderly with flu develop productive cough later)
Golden staff: Staph Aureus is a common pathogen in superimposed bacterial pneumonia. However, Strep Pneumo is still the most common!
influenza associated with Guillou-Barre syndrome. Boy grabbing leg of bear to illustrate ascending paralysis.
[_](reye's syndrome cause and symptoms)..

aspirin uncouples oxidative phosphorylation in hepatic mitochondria: extensive damage
Sun with rays: "Rays = Reye's syndrome "
fat cow with liver spot: "Fatty liver seen in Reye's syndrome"
man with turban: "Encephalitis seen in Reye's syndrome"
sun: fever
"Beware of giving Aspirin to a child with influenza. They may develop Reye's syndrome."
Paramyxovirus
_..
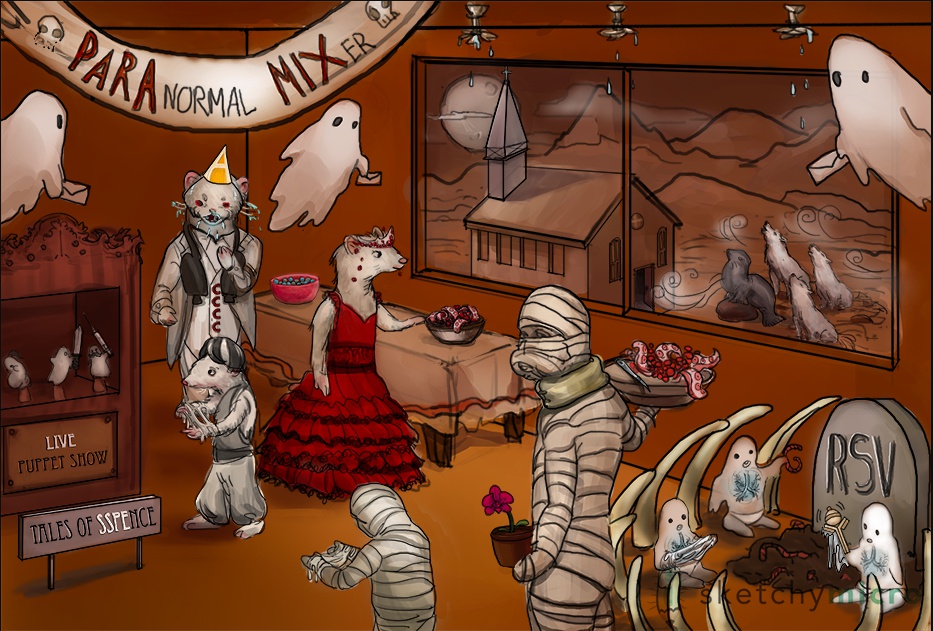

paranormal mixer: paramyxovirus
Negative-sense RNA virus
ghost robes with envelopes: Enveloped virus
sprinkler droplets: Transmitted by respiratory droplets
_..

live puppet show: MMR: Live attenuated vaccine
"Don't give MMR to pregnant women."
_..

Weasels represent Measles, aka rubeola
Mumps mummy: mumps
RSV tombstone: Respiratory Syncytial Virus
parainfluenza seal: Seal bark cough seen in Croup (caused by parainfluenza virus)
_..

Weasels represent Measles
Ruby-"Hola" dress = Rubeola
"4 C's of prodrome (early symptoms) = Cough, Coryza, Conjunctivitis, Koplik Spots"
coughing: cough
drippy nose: coryza (runny/stuffy nose)
red eyes
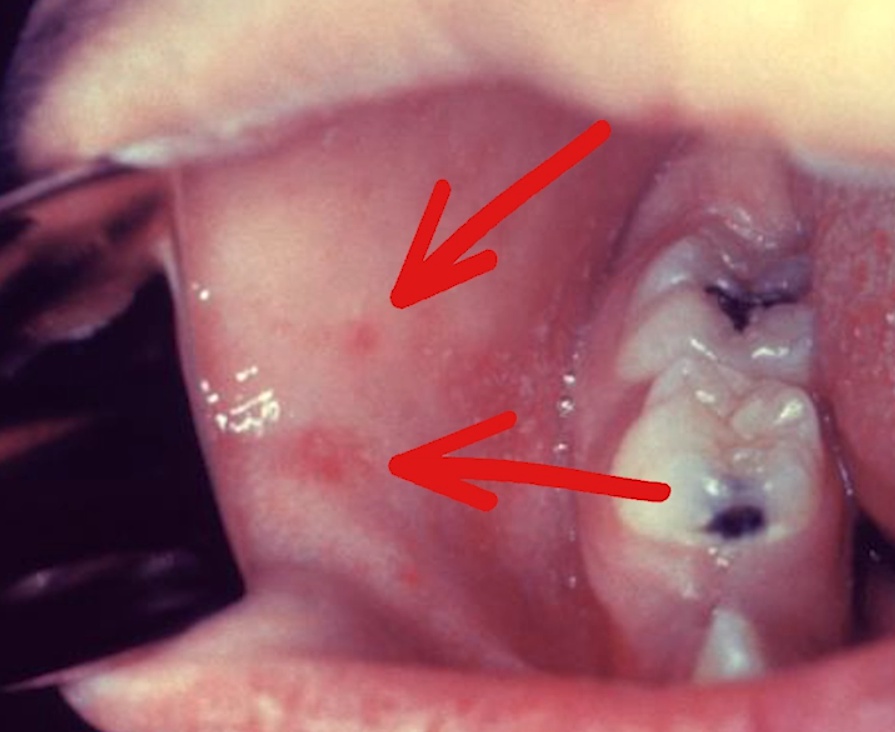
blue and white candies: Koplik spots = bluish white spots on buccal mucosa
sweating: High Fever (>40, 104), last 4 days
late:
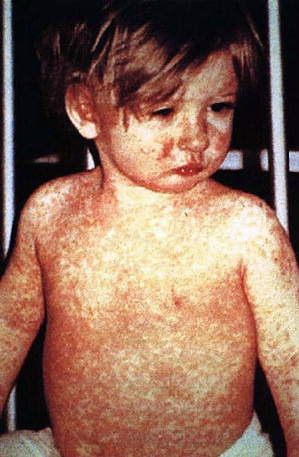
rash on lady on right: Rash starts after initial symptoms
Rubies falling off: Rash starts from face and moves downward
solid flamingo dress: Rash becomes confluent (starts as dots and blend in together)
_..

pneumonia tie: pneumonia is a complication of measles
turban, tales of SSPEnce: Subacute Sclerosing Panencephalitis (SSPE) (inflammation and sclerosing of brain caused by persistent measles). Child with measles or unvaccinated develop neuro (myoclonus, personality change, seizures, ataxia, coma) symptoms 15 years later.
_..

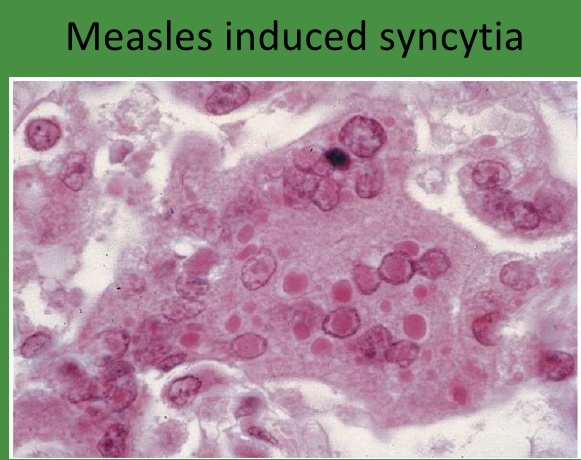
sticky hands: Fusion protein is a virulence factor for measles, multinucleated giant cell found in lymphoid tissues
yummy tentacles with stuck together berries: Hemagglutinin (HA) is a virulence factor for measles
No NA
_..

A party hat: Vitamin A reduces morbidity and mortality from measles. Pneumonia especially.
_..

Mumps mummy: mumps
big cheeks: Parotitis
single orchid: Orchitis, inflammation of epididymis, unilateral
neck brace: Meningitis
pancreatitis
_..

tentacles: Hemagglutinin (HA) = = mumps virulence factor
mummy child sticky hands: Mumps vaccine, Fusion protein = mumps virulence factor
scalpel: Neuraminidase (NA) = mumps virulence factor
_..

RSV tombstone: Respiratory Syncytial Virus
little ghosts: infants < 6 months
G shaped worm: Virus attaches to G protein to infect epithelial cells
sticky hand: Fusion protein = RSV virulence factor

_..

bronchiole trees: RSV causes bronchiolitis and pneumonia in infants.
Ribs: Ribavirin (nucleoside analog) for adults,but not for children or pregnant women.
extra pale baby with IgG toy: Give Palivizumab to premature and high-risk infants. Palivizumab (IgG shaped rattle) is an antibody against the RSV fusion protein (slime)
_..

parainfluenza seal: Seal bark cough seen in Croup (caused by parainfluenza virus)
wind blowing in: Inspiratory stridor seen in Croup
church with steeple: Patients with Croup will often have a "steeple sign" on Chest X-ray, narrowing of subglottic region
Three wolves = Parainfluenza has all THREE virulence factors. HA, NA and Fusion proteins.


aka laryngotrachealbronchitis.,
Rhabdovirus
_..
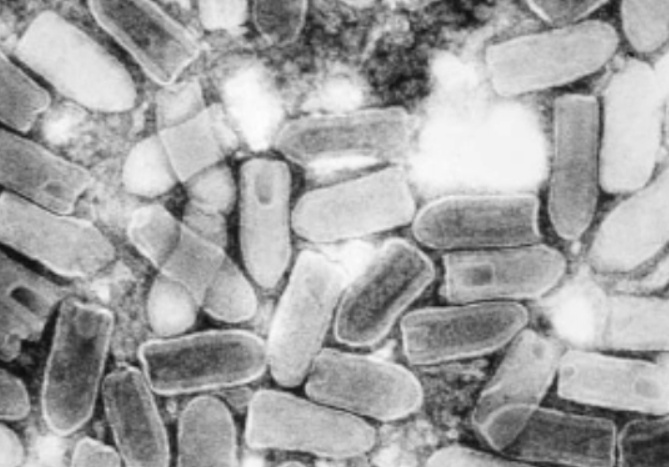
rabies
_..

Negative-sense
Orange / warm hues = RNA virus
hoodie: Enveloped
bullet collar: Bullet-shaped virus
curly tail: Helical capsid
_..

bats: #1 carrier in US
fox, skunk, rodents: Carriers
transmission: bite
_..

nicotine cigar: Nicotine = Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptors. The receptors in the motor-endplate that the virus binds to during infection
cola cans: Acetyl Cola = Acetylcholine. Rhabdovirus binds to Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptors
socket behind dog: Binds to receptors in the postsynaptic motor endplate
bullets travel backwards to car: Virus moves retrograde along peripheral nerve
puppy replicas underneath car motor: Replicates in motor neurons
roots of trees behind tree: Virus spreads to Dorsal Root Ganglia
_..

thief sweating with turban: Encephalitis and Fever
drooling/foaming at mouth
_..

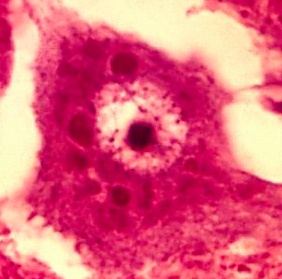
pink spots on Integrity boat: Negri Bodies = Eosinophilic (pink), cytoplasmic inclusions
bungee cords on purkinje looking tree: Negri bodies seen in Purkinje cells (Bungee cords)
red in tree: Eosinophilic negri bodies in Purkinje cells
seahorse: Negri bodies in hippocampus (greek for seahorse)
pyramid canopy: Negri bodies in Pyramidal cells in Hippocampus

_..

key chains with antibody keys: Passive immunization for post-exposure prophylaxis. Give Rhabdovirus immunoglobulins
tranquilizer gun with skull: Killed vaccine for active immunity
Filovirus
_..

Soccer field: filovirus
Negative-sense RNA virus
orange lights: RNA (orange) with helical capsid
jersy: Enveloped virus
_..

bats: Bats may be the viral reservoir
monkeys: Possibly transmitted via primates
medics on field: Transmitted to healthcare workers through exposure to bodily fluids
_..

marburg player: Marburg virus
goal: Ebooooooooooooooooooola, Ebola
_..

sweating goalie: Fever
rashes: Petechial rash
pool of blood: Hemorrhagic fever
blood spots: End-organ failure within days
lightning bolt: Hemorrhagic (hypovolemic) shock
Bunyavirus
_..

Paul bunyan = bunyavirus
Orange hues = RNA virus
Negative sense
robe: Enveloped. Gold = Specifically obtained from Golgi body
3 tree trunks: Segmented virus with three segments (BOAR)
3 stumps with rings inside: circular segments
_..

arbo in background: Arboviruses (California Encephalitis and Rift Valley Fever)
rodents: Hantavirus are roden born
_..

Haunted = Hantavirus
mouse running away: Reservoir is the deer mouse
mouse feces: Transmitted via rodent urine/feces
sweaty chest: Pulmonary capillary leak
kidney water bottle leaking without top: Pre-renal azotemia
sweating with blood dripping: Hemorrhagic fever
_..

California rift valley school: California Encephalitis, Rift Valley Fever
mosquitos: Arboviruses are transmitted by the Aedes Mosquito
shaking: Seizures
turban: Encephalitis
Myalgia/fever
Arenavirus
_..

Arena: arenavirus
Negative-sense RNA virus
robe: Enveloped virus
1 sword in each hand, ambidextrous: Ambisense = can encode its RNA both positively and negatively
spiral banners: Helical capsid
Two rings = 2 RNA segments (BOAR)
_..

sandy floor: Grainy appearance on electron microscopy

_..

rodents: Rodent transmission
_..

LCV sign: Lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus (LCV)
turban: Meningoencephalitis
sweating: Fever
fire spear: Inactivated by heat
reflect shield: Inactivated by irradiation
Reovirus
_..

Rio Grande: Reovirus
David: Naked virus
DNA rope: Double-stranded RNA virus, no positive or negative sense
11 boats = 11 RNA segments (BOAR)
_..

rotating propeller: Rotavirus
welcome to colorado sign with tick: Colorado tick virus
_..

brown water: Rotavirus causes watery diarrhea
Nine SPeed 4 stroke: NSP4 toxin causes secretory diarrhea
Chlo-rider: NSP4 toxin causes chloride permeability, water secretion
snow caps: More common in winter months
kid contestants: Children are at risk for rotavirus infection, especially in daycare
#1 sign: Rotavirus = #1 cause of severe diarrhea in infants and children
water bottle: Treatment = oral rehydration
_..

welcome to colorado sign with tick: Colorado tick virus
kid sweating, vomiting, on ground: Colorado tick virus causes myalgia, fevers, and vomiting
_..

live camera crew with mic to mouth: Live-attenuated oral vaccine
telescope: Vaccine side effect = intussusception: telescoping of the bowel, due to enlargement of Peyer's Patches

Enveloped virus
Double-stranded, linear DNA virus
Intranuclear inclusion bodies (Cowdry bodies)
Vertical transmission (TORCHeS infection)
Gingivostomatitis is first sign of HSV-1
Herpes labialis, or "cold sores"
Keratoconjunctivitis
Serpiginous corneal ulcers on Fluorescein slit lamp exam
HSV-1 causes temporal lobe encephalitis
#1 cause of sporadic encephalitis in the United States
HSV-1 latent in trigeminal ganglia
"Dew drops on a rose petal" appearance = vesicles on an erythematous base
Herpetic whitlow, more common in dentists (HSV-1 and 2)
Erythema multiforme may appear 1-2 weeks after infection
Painful inguinal lymphadenopathy associated with HSV-2
HSV-2 latent in sacral ganglia
HSV-2 may cause aseptic meningitis in adolescents and adults
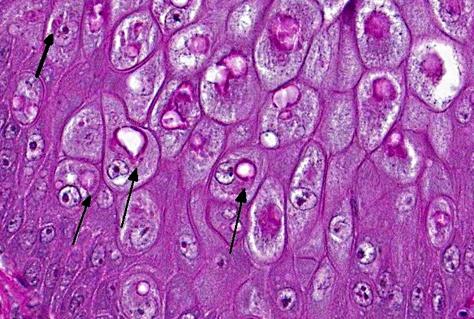
Tzanck smear = multinucleated giant cells
Acyclovir or valacyclovir to prevent breakouts
DNA Virus
EBV
_..
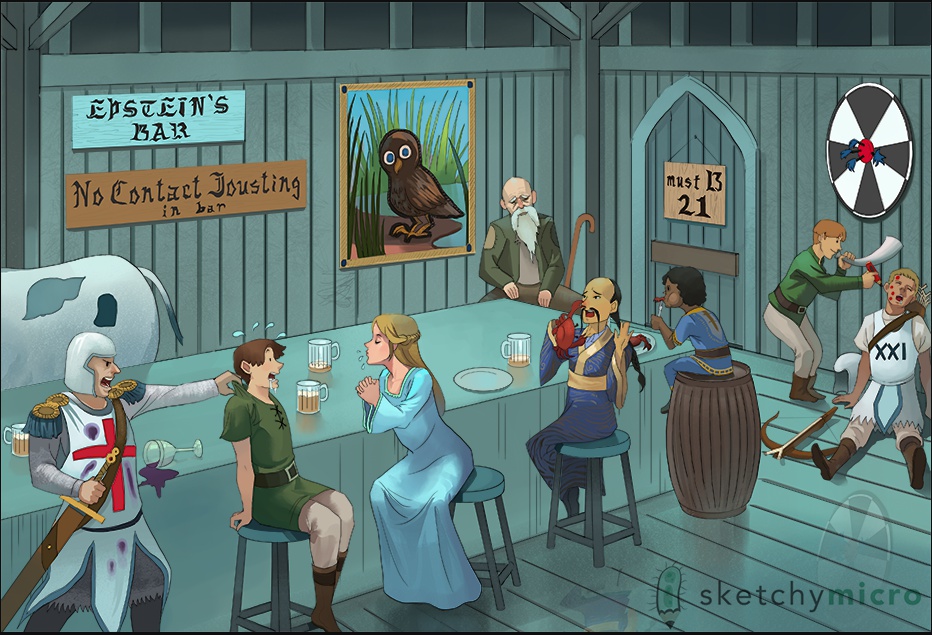

Ebstein Bar: EBV, also Herpes virus
blue color: Epstein-Barr virus = double-stranded DNA virus
EBV causes mono
saliva girl: Primarily transmitted through saliva, kissing disease
Cytomegalovirus and Epstein-Barr virus are members of the Herpesviridae family. All viruses within this family contain an icosahedral core surrounded by a lipoprotein envelope and have double-stranded, linear DNA. These are the only viruses to acquire their envelopes by budding from the nuclear membrane.
_..

sleeping archer: EBV remains latent in B cells
must B 21: EBV envelope glycoprotein binds CD21 (c3b) to infect B cell
_..

sweating: Fever
grabbed neck: Tender posterior lymphadenopathy (can also be generalized)
cow spot: Splenomegaly more common
drooling: Pharyngitis (severe sore throat) and tonsillar exudates
fatigue
_..

strep pneumo: children, adolescence; mono: asymptomatic in young age (late teens, adults symptomatic)
Pencil drawing rash: If mistakenly given amoxicillin or ampicillin for strep pneumo, can develop maculopapular rash
_..

Owl sitting in weeds: Hodgkin lymphoma = Reed-Sternberg cells that look like "owl's eyes"
AA bar kid with swelling jaw: Endemic or African Burkitt lymphoma = large jaw lesion and swelling
crab pinching nose: Nasopharyngeal carcinoma associated with Asian patients with EBV
bearded man with cane: Oral hairy leukoplakia in HIV patients, non-cancerous lesion; can't scrape off

left: CMV; right: EBV


_..

reacting T knight with 8's: Reactive cytotoxic CD8+ T cells (Downey, or atypical cells) lymphocytosis, seen on blood smear (stain on cloth)
Atypical lymphocytes good response. Kills B cells and prevent lymphoma.
dart sport: Monospot test = rapid diagnosis. Clumped IgM

_..

No contact: Warn patients to not participate in contact sports, splenic rupture
CMV
_..

Mega lo prices: Cyto"Mega-Lo" Virus
Blue = DNA virus, replicate inside nucleus, since host DNA inside nucleus
Herpes figure: Member of the Herpesvirus family
Cytomegalovirus and Epstein-Barr virus are members of the Herpesviridae family. All viruses within this family contain an icosahedral core surrounded by a lipoprotein envelope and have double-stranded, linear DNA. These are the only viruses to acquire their envelopes by budding from the nuclear membrane.
_..

sleeping man next to archers and knights: Can be latent in B and T cells (mononuclear cells)
cages: Can be latent in macrophages
cane waking up: reactivation in immunosuppressed
_..

blood, sexual contact, saliva, breast milk
torches: TORCHeS infection
Also in utero
_..

blueberry muffin: Blueberry muffin rash in congenital CMV (thrombocytopenia causing petechiae rash, same as rubella)
cataracts
cow: Hepatosplenomegaly and Jaundice in Congenital CMV
covering ears: Sensorineural hearing loss
large helmet symbol: Ventriculomegaly in Congenital CMV
milk on ventricles: Periventricular calcifications
slipping man: Seizures in Congenital CMV due to changes in brain structure
80-90% off: 80-90% of those with congenital CMV infections are asymptomatic
_..

balloon animal in water: Hydrops fetalis, heart failure leading to severe edema with fluid accumulation in multiple compartments, spontaneous abortion. In utero transmission
Number 1 shirt: CMV is the #1 cause of mental retardation due to a viral infection. Also #1 cause of virus induced hearing loss.,

_..

Butcher: Transplant patients
Butcher coughing with lung stains: Transplant patients at risk for CMV pneumonia
old man with cane: CMV in AIDS patients
Charity drive 50c: CMV infections in CD4 counts < 50
pizza pie: CMV retinitis causes "pizza pie" appearance on ophthalmoscopy; blind spot, flashing lights
conveyer belt with ulcers: Linear ulcerations scene in CMV esophagitis (singular, deep, linear compared to multiple/shallow in herpes)
bags with red dots: CMV colitis

_..

"Owl O cereal = Owl's eye inclusions seen in CMV"
no mo spot: Monospot test will be negative in patients with CMV and mononucleosis-like symptoms

left: CMV; right: EBV

_..

Green for G, cans only: Ganciclovir
UL97 sticker: UL97 Kinase gene mutation leads to resistance to Ganciclovir, use foscarnet
Fast car net = Foscarnet for patients with resistance to Ganciclovir
_..

mom screaming: Pharyngitis seen in CMV infection in adults (similar to the pharyngitis of mono)
Lymphadenopathy seen in CMV infection in adults (similar to the lymphadenopathy seen in mono)
Varicella
_..

zeus: zoster
Hermes: Herpes virus family
robe: Enveloped Virus
_..

torch: Vertical transmission (TORCHeS infection)
kid squirting droplets: Respiratory droplet transmission
_..

doll with small arms, stuffing coming out, blind: Congenital varicella syndrome = limb hypoplasia, cutaneous dermatomal scarring, blindness
chicken: Chicken pox
shingles on roof: Herpes zoster, or shingles, is reactivated form
_..

doll with small arms, stuffing coming out, blind: Congenital varicella syndrome = limb hypoplasia, cutaneous dermatomal scarring, blindness
_..

chicken: Chicken pox
sweating and touching head: Fever and headache
kid squirting droplets: Respiratory droplet transmission
rose petals: Vesicular "dew drops on a rose petal" lesions, same as herpes simplex
All ages: Lesions in different stages of healing (smallpox: all at same stage)
tank: Tzanck smear = multinucleated giant cells

_..

adult: Pneumonia complication
red turban with cane: Encephalitis, especially in immunocompromised
_..

live show: Live-attenuated vaccine for children
live show > 60: Live-attenuated zoster vaccine recommended for adults over 60 (don't give to immunocompromised)
Max occupant 200: HIV patients with CD4 count >200 may be given shingles vaccine
_..

recycle bin: Acyclovir treatment for children ages 12+, adults, and immunocompromised
family: Famciclovir treatment for shingles
violet cycling bin: Valacyclovir also treatment for shingles
_..

sleeping on tree roots in back: Latent in dorsal root ganglia
elderly with canes: Reactivation occurs with emotional stress, aging, or immunocompromised state
_..

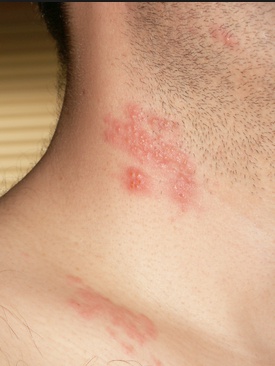
shingles on roof: Herpes zoster, or shingles, is reactivated form
rose petals on shirt: Herpes zoster, or shingles, has "dew drop on a rose petal" appearance with dermatomal distribution (trave down sensory ganglia on reactivation)
If rash crosses midline = disseminated VZV in immunocompromised patients
stabbed in chest: Extremely painful rash
shirtless with lightning bolt: Postherpetic neuralgia = pain after rash subsides
red eye patch: Herpes zoster opthalmicus = vision loss possible if V1 affected (case: immunocompromised with vesicles on forehead and blindness in one eye)
Roseola
_..

Roses: Roseola
6th disease: 6th in childhood (Ro- six- ola)
Hermes with 6: HHV-6 is in the Herpes Virus family = double-stranded DNA virus
Esquire with 4: HHV6 infects CD4 cells, can cause immunosuppression
_..

child in arm: Affects children ages 6 months to 2 years, and is usually self limiting
sweating with 4 suns: Roseola, or exanthema subitem, is characterized by a high fever generally lasting 4 days, followed by rash
trembling esquire: Children with roseola can develop febrile seizures (very high fever > 104)
blue fire cooled and lace covering everything but face: After fever, a diffuse lacy body rash occurs that spares the face
Kaposi
_..

Kate's posies: Kaposi
Hermes with 8: Human herpes virus 8 causes Kaposi sarcoma
HHV-8 = double-stranded DNA virus
_..

sexual contact, kissing, especially gay men
AIDS ribbon and cane: AIDS and immunosuppressed associated with Kaposi sarcoma
"Russian rhododendrons" = higher incidence in Russian men
"African azaleas" = endemic in areas of Africa
_..

Veg Fertilizer: Causes dysregulation of VEG-F
red hose and red branching plant: Causes proliferation of vasculature (color)
flower petals on nose/extremities: Causes violacious lesions on nose, extremities, and mucous membranes; maybe present as patch, plaque, macule, nodule
colon covering: Lesions can be found within the GI tract (spindle shaped cells)
violet flowers on ceiling: Kaposi lesions most commonly occur on the hard palate
B rating and medieval archer: Infection of B cells can cause Primary Effusion Lymphoma (B-cell lymphoma)


_..

lepard: Differentiate Kaposi (lymphocytic infiltrate, viral) from bacillary angiomatosis caused by bartonella (neutrophilic infiltrate, bacterial)
Polyomavirus
_..
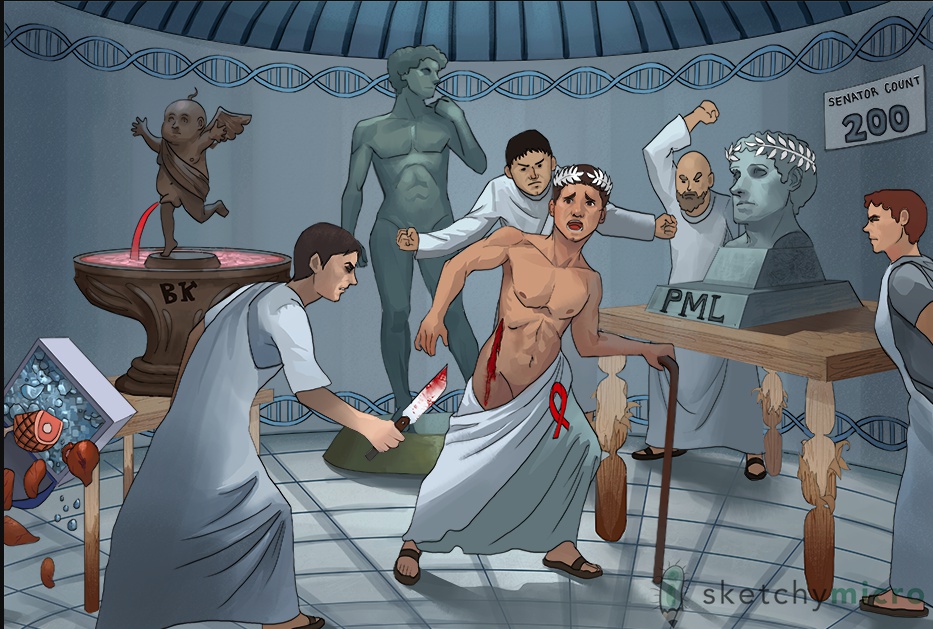

JC (julius caesar) and BK (Brutus's knife)
_..

politicians: Polyomavirus
round room: Circular, double-stranded DNA virus
David: Naked virus
_..

Julius Caesar with toga falling off = JC virus
PML: JC virus causes Progressive Multifocal Leukoencephalopathy (PML)
senator count 200 and cane: JC virus reactivated in HIV positive patients with CD4 count <200
white crown leaves: Non-enhancing multifocal brain lesions in white matter (toxoplasma: ring enhancing lesions)
white leaves: white matter affected
peeling legs of table: Leukoencephalopathy is a demyelinating process
pts die in a few months
Nonenhancing:

Enhancing:

_..

"Brutus's knife = BK virus"
organs falling: BK nephropathy in transplant patients
stabbed in flank: BK virus causes nephropathy
BK fountain with red stream: BK virus causes hemorrhagic cystitis (hematuria)
Papillomavirus

Anogenital cancers
These characters represent HPV 1-4
Verruca vulgaris = common wart
Represent HPV 6 and 11
Laryngeal papillomatosis - caused by HPV 6 and 11
Anogenital warts (condyloma acuminata) - from sexual transmission
Accumulating bugs in jar = Condyloma Acuminata
HPV 16, 18, 31, 33 increase risk for anogenital cancers
HPV 16 (age at which people can drive)
HPV 18 (age at which people can vote)
E6 gene disrupts P53 tumor suppressor
Gardasil an inactivated subunit vaccine covers HPV 6,11,16,18 (all the people enclosed within the fence)
Naked virus
circular virus
Blue colors = DNA virus
E7 gene (straw shaped like a 7) disrupts RB tumor suppressor (Root Beer)
P53 (the crab cracker) arrests cell cycle at G1/S phase to prevent abherrant replication
Koilocytes - atypical cells seen on pap smear
Pap smear
Immunocompromised (AIDS patients) at risk of developing these cancers
Parvovirus
_..

B19 bomber: Parvovirus B19
David: Naked virus
tiny town: Parvo virus is the smallest DNA virus… what a quaint little town
single runway: Single-stranded DNA virus
_..

water gun: Respiratory droplet transmission
torch: Vertical transmission (TORCHeS infection)
_..

balloon baby: Hydrops fetalis in utero, fetal anemia and resulting CHF from heart pumping harder
slapped kid with 5 fingers: "Slapped cheek" rash = Fifth's disease, aka erythema infectiosum (low grade fever, then slapped cheek, then rash downward)
plane with red on nose and point downward: Lacy rash starts on the face and moves downward
adult kneeling on floor: Joint pain, arthritis, and edema in adults
communist plane with sickle with plastic bone and web: Aplastic anemia in sickle cell patients, only left is adipocytes (cobweb look)


Adenovirus
_..

Lion's den: Adenolions = adenovirus
Cool, blue tones = DNA virus
Naked virus
_..

dripping water: Transmitted in respiratory droplets
poop: Fecal-Oral transmission
kids: Children commonly affected.
Camo = Outbreaks known to occur in military barracks
red pool: Public swimming pool outbreaks
_..

red cave with lions yarning : most common cause of Tonsilitis / Adenitis
hematuria: Adenovirus causes hemorrhagic cystitis
red eyes in cave: Adenovirus causes conjunctivitis (pink eye)
enteric adenovirus: cause of intussusception
_..

camo with gun: Military recruits may be administered a live vaccine.
live lions: Live vaccine
Poxvirus
_..

boxes: poxvirus
blue color: DNA virus
dumbells: Dumbell shaped core
world's largest: Largest known DNA virus
workers make own envelops: Poxviruses make their own envelopes
workers stuffing packages: "Poxvirus has a special DNA-dependent RNA polymerase" (RNA polymerase that reads DNA). Only DNA virus that replicates in cytoplasm.

_..

map HQ nucleus, G across world: Guarnieri bodies, or inclusion bodies, type B inclusions, are sites of viral replication in the cytoplasm
_..

small box: Small pox
udder styrofoam unit: Cowpox = contact with infected cow udders
snail mail with shell: Molluscum contagiosum = flesh-colored, dome shaped, umbilicated skin lesions
_..

small box: Small pox
same day shipping: Same age lesions
_..

snail mail with shell: Molluscum contagiosum = flesh-colored, dome shaped, umbilicated skin lesions
kid with stamps: Umbilicated lesions on trunk in children (dimples in middle)
cane: Diffuse molluscum contagiousum infection in adults suggests an HIV infection. Healthy adult has 1 lesion

Hep B
_..
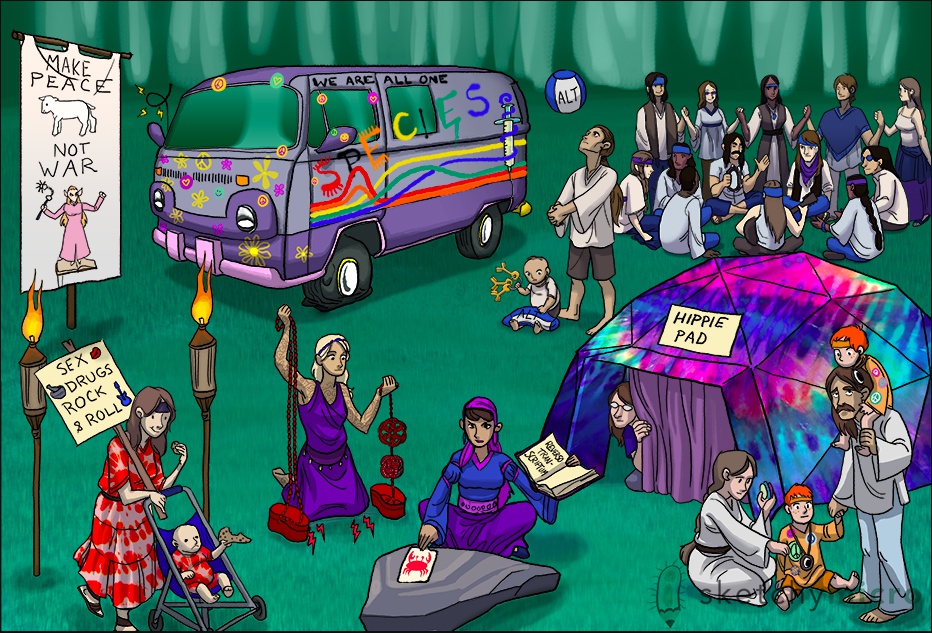

Hippies: Hep B
Hippo van = Causes hepatitis
Hippie Pad: Hepadenavirus family
clothes: Enveloped
blue colors. Circle of people with incomplete outer circle: Partially double-stranded DNA Virus
_..

Hippies outside and inside dome: Intranuclear and Cytoplasmic Replication
spell book: Uses a reverse transcriptase. RNA Dependent DNA Polymerase. DNA to single RNA to double DNA. Does not incorporate in host DNA

_..

Sex/drugs/rock and roll: Transmitted via sex (HCV rare with sex) and blood products (IV drug use, needle sticks or transfusions)
baby with blood: Transmitted during delivery from mixing of blood. Does not cross placenta because large
torches: TORCH infection
_..

baby 90% cookie: 90% of neonatal infections progress to chronic infections
mother 10% cookid: 10% of adult infections progress to chronic infections
_..

red beads: Polyarteritis Nodosa
rash on body: Rash (purpuric macules). Urticaria vasculitis
kneeling: Arthralgias. Serum sickness like syndrome
compared with HCV (usually asymptomatic)
kidney boxes: Kidney disease (secondary to Polyarteritis Nodosa)
thick knots in string: Associated with membranous glomerulonephritis
3 string: Associated with membranoproliferative glomerulonephritis. Tram track appearance
rock liver and crab: Chronic infection may lead to cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma.
_..

high ALT ball: ALT rises during acute infection and then falls after symptomatic phase is over in chronic. In viral hepatitis ALT>AST. (alcoholic AST > ALT)
deflated ALT: ALT often normal in neonatal hepatitis
_..

S: HbSAg (Hep B Surface antigen) = First marker of infection
E: HBeAg (Hep b E antigen) - Sign of increased infectivity.
flat tire: Symptomatic phase. Patient will be positive for HBsAg or HBeAg.
C in window: Anti-HBc (Core antibodies) - First detectable antibody. On the window, signifying that it may be the only antibody/antigen detectable during the window period.
E: Anti-HBe
S: Anti-HBs (Surface antibodies). If positive, indicative of recovery from infection. No longer infection, acute or chronic
Blue around syringe: An immunized person will only test positive for Anti-HBs (surface antibodies). Will not be positive for Anti-HBc or Anti-HBe.
_..

orange children with clothes and moon: Hep D = RNA negative, enveloped
headbands: Circular genome
_..

mom attaching antigen: Hep D requires HBsAg to be infectious
kid holding dad's hand: Co-infection of Hep D and Hep B occurs at same time. Better prognosis.
kid on shoulder: Hep D after Hep B infection. Superinfection = Worse prognosis (as noted by grimacing father).
_..

lamb: Lamivudine
elf with nucleoide: "NRTI's"
interference: Interferon alpha
keys to hippie van: IgG antibodies - Give at risk infants anti-hep b immunoglobulins along with passive vaccination.
Last updated