33 Antihypertensives
_..
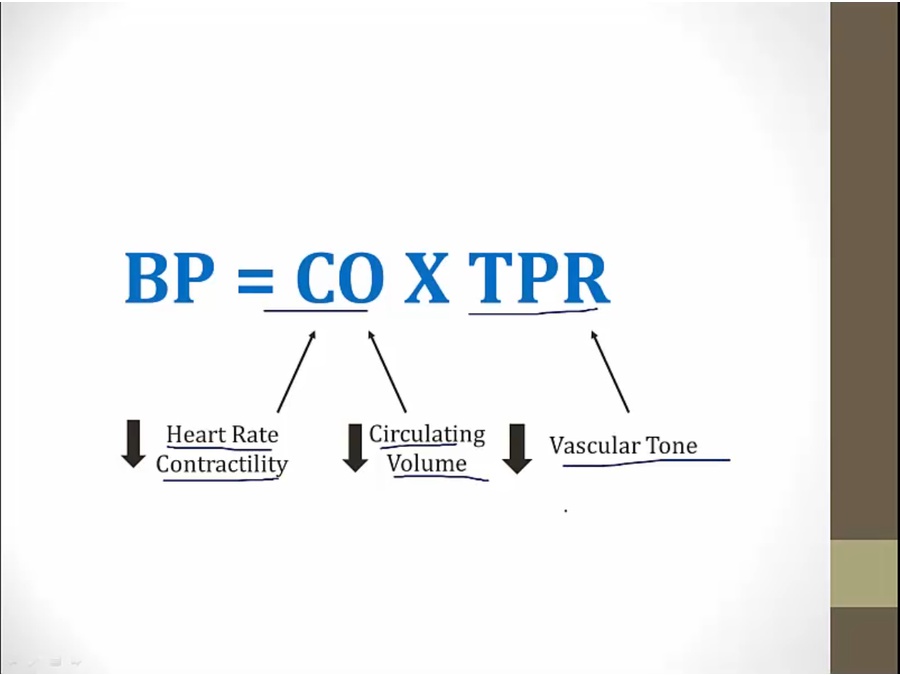
antihypertensives work by either decreasing CO or decrease TPR
Beta Blockers
_..

do not want to block b2


not really used for hypertension
b1 blockade: general lower BP, including portal system
b2 increase flow to liver, block to decrease flow

carvedilol: clinical trial shows benefit, not because of special receptor

at low sympathetic level, higher activation of beta receptor than sympathetic activity, thus agonist
high level, lower activation of beta receptor than sympathetic, thus blocker
_..

fatigue, etc: blunt CNS activity
hyperlipidemia not clinically relevant

given because many benefits
diabetics often hypoglycemic because taking insulin
BB cause hypoglycemia and masks symptoms, except sweating (Ach receptors)
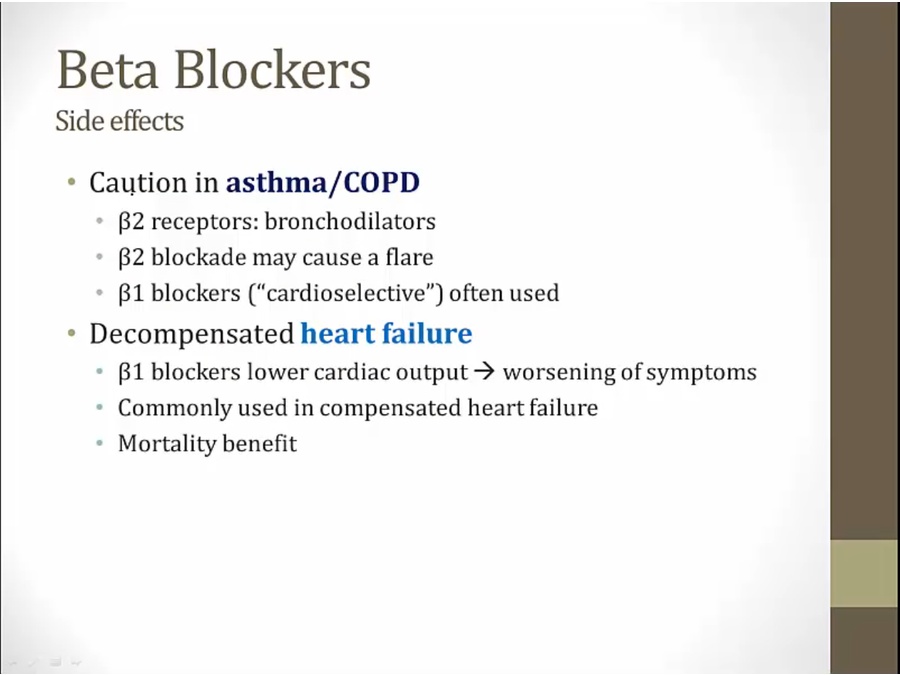
decompensated
acute HF: pt with pulmonary edema/sick from HF can get very sick with BB's lowering of CO
_..

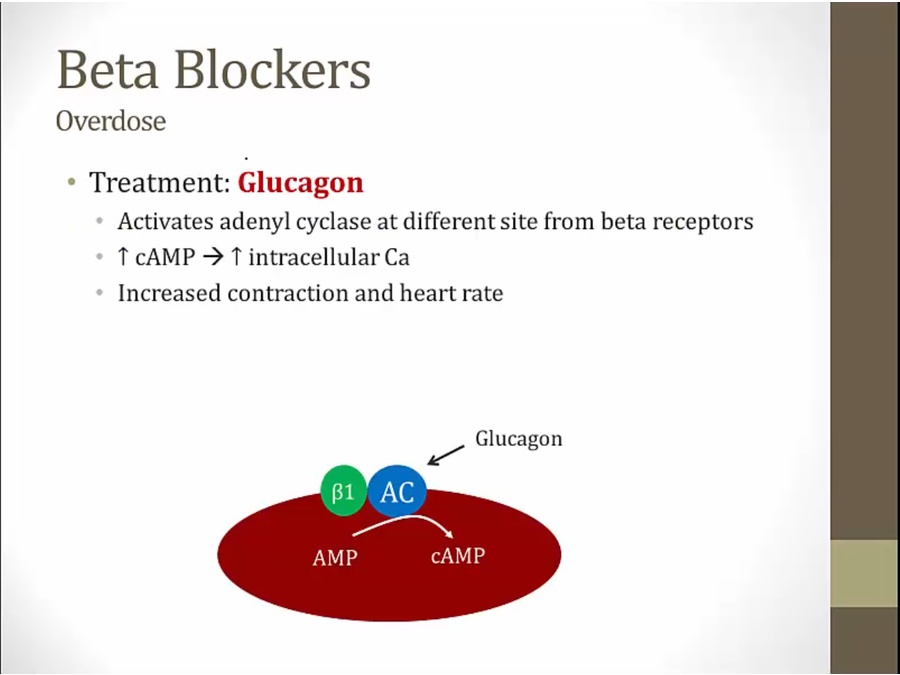
stimulates myocardiocytes at different site
stimulate heart and bypass beta receptors
Alpha Drugs
_..

tamsulosin very good for BPH


warm autoimmune hemolytic anemia
CCB
_..
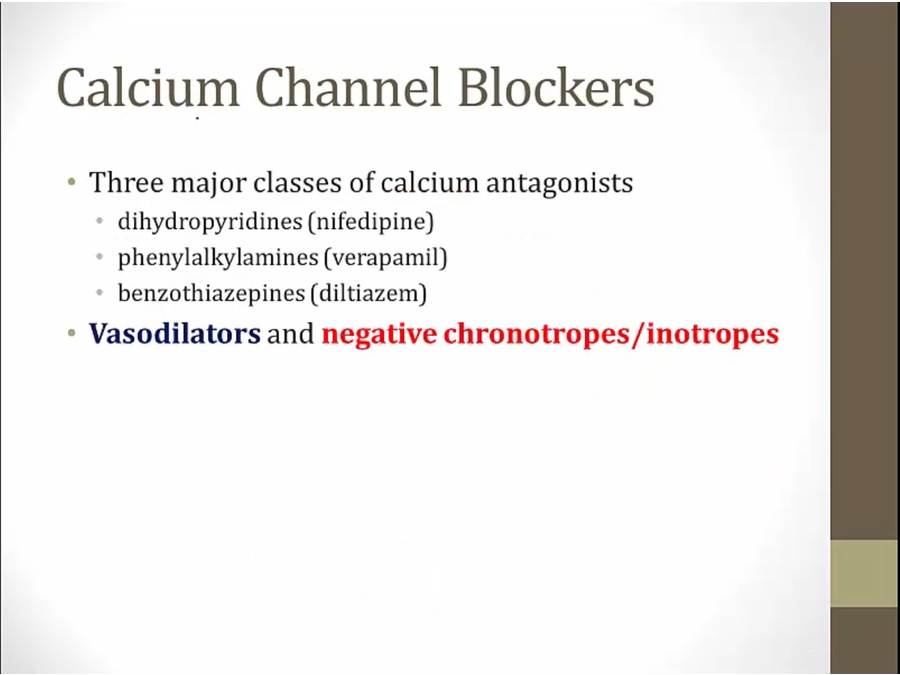

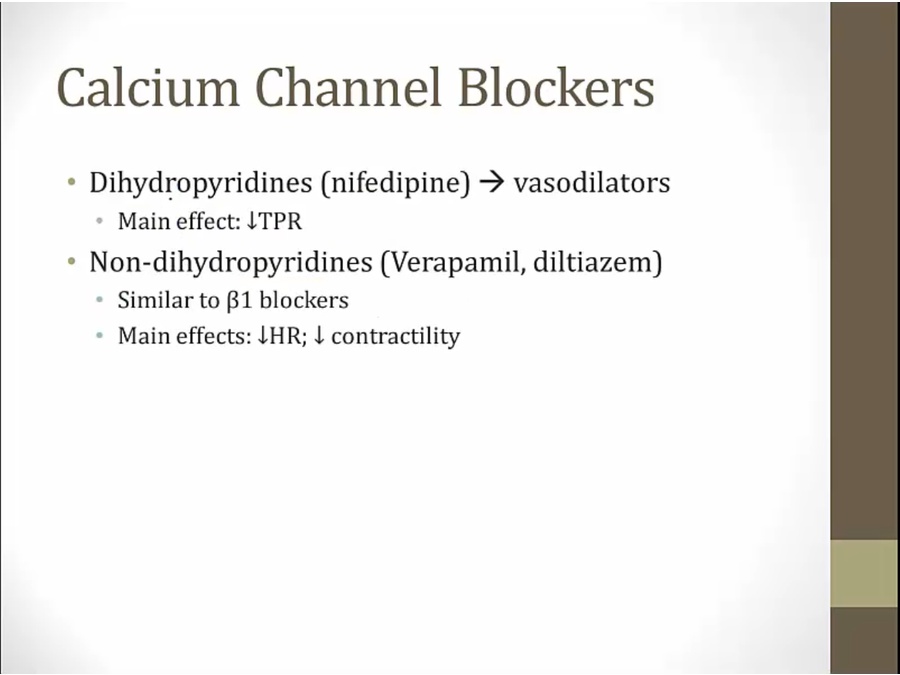
Dihydropyridines
_..
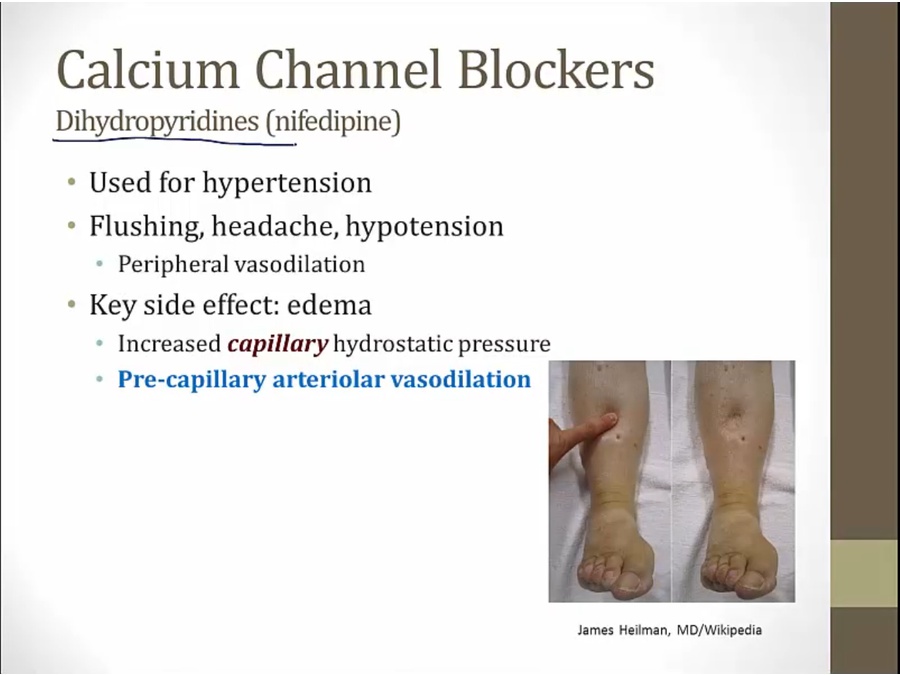
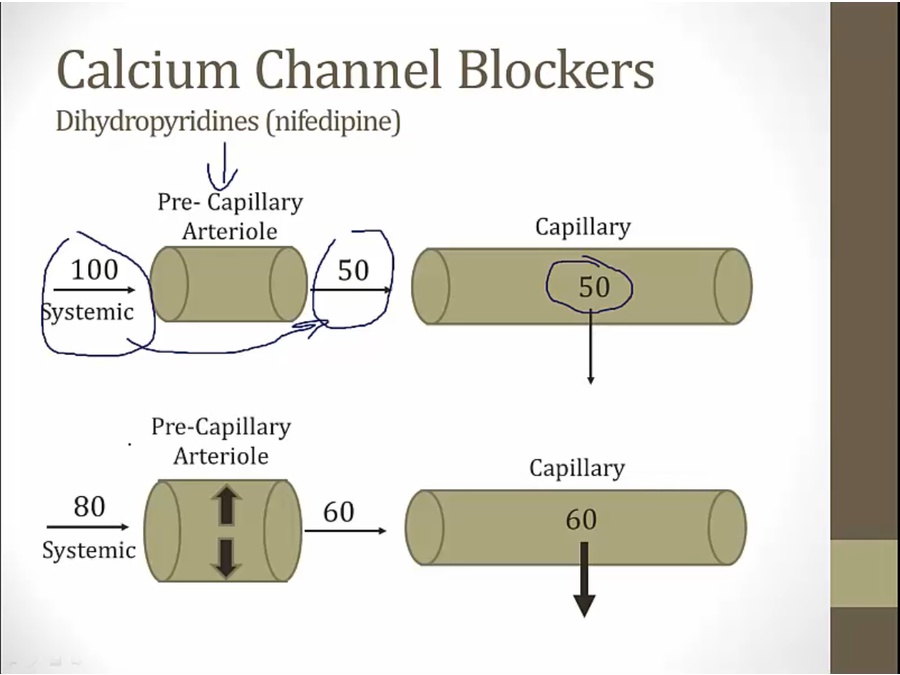
pt not taking CCB: arteriole constrict, leading to lower hydrostatic pressure in capillaries
CCB: dilate arteriole, higher hydrostatic pressure
_..
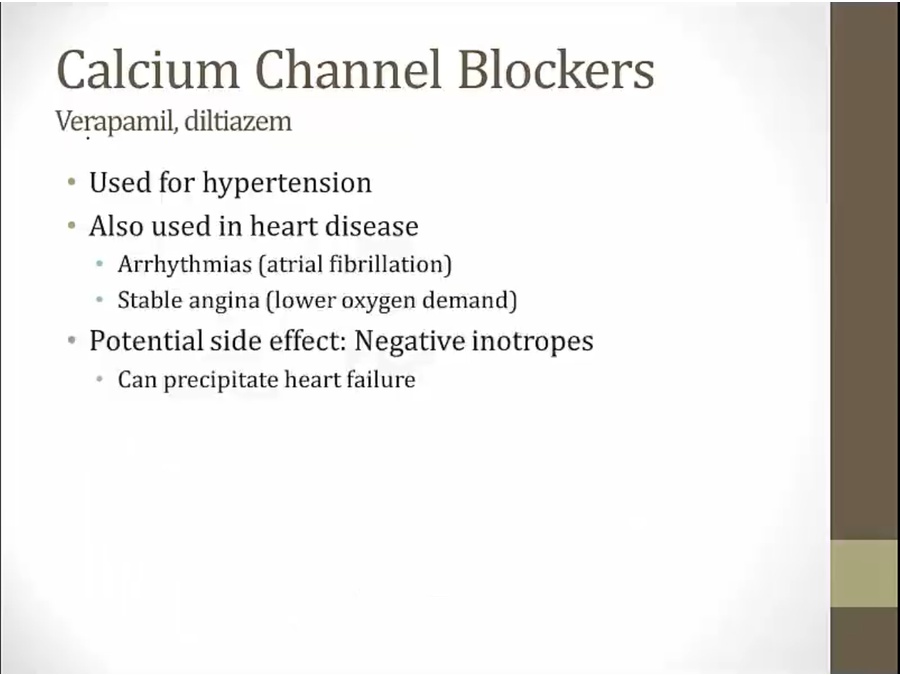
like b1, slow HR, decrease contractility


AII
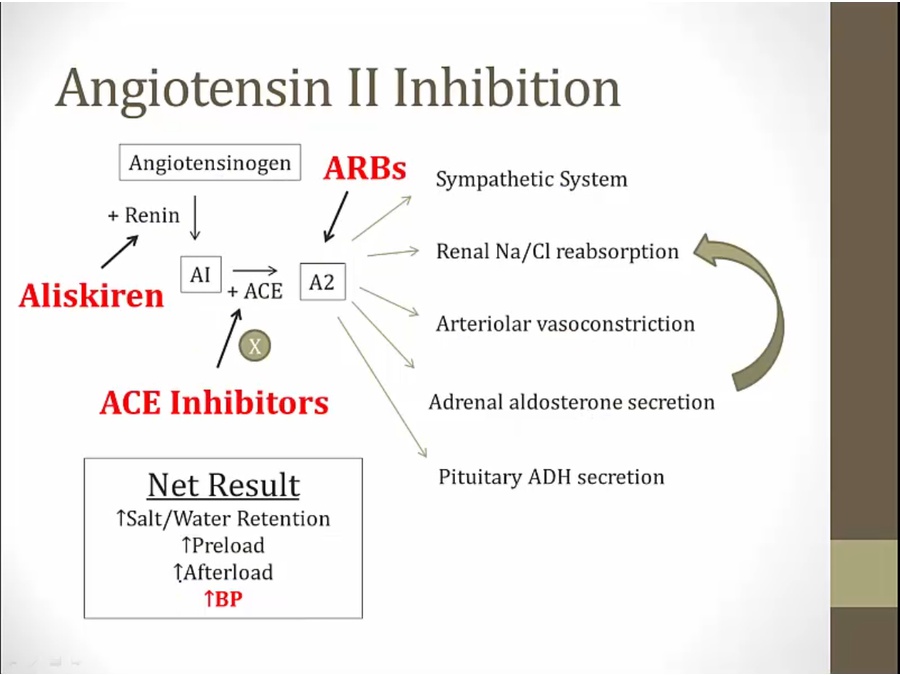


inhibits renin, decrease AI production

HCTZ: used often for antihypertensives by inhibit Na absorption
Hydralazine


Hypertensive Emergency
_..

rapid acting drugs that can be titrated carefully
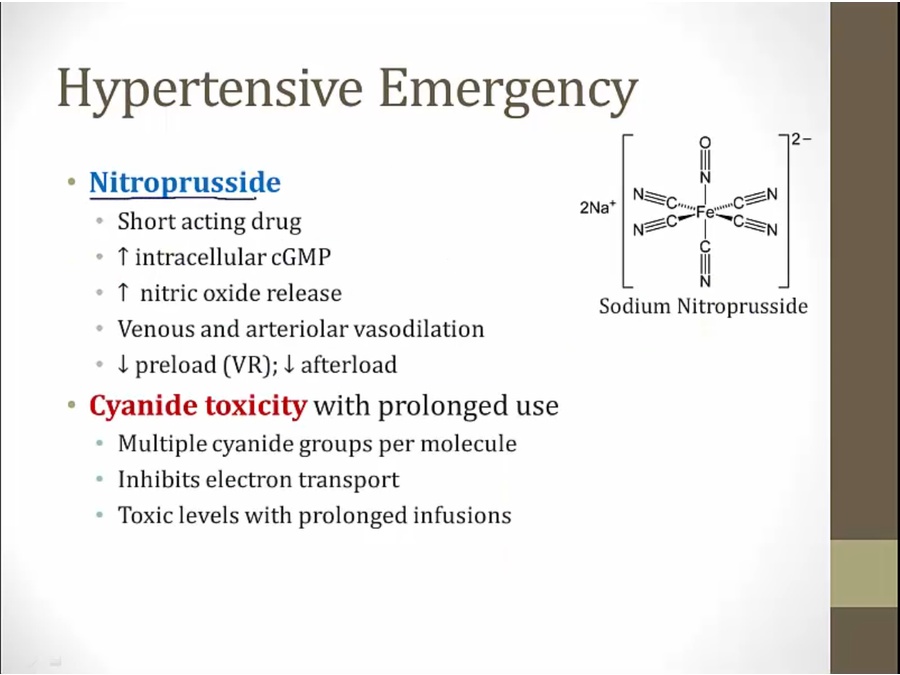

increased renal perfusion

Antihypertensive SE
_..


diuretic pts: dependent on AII to maintain BP
ACE I block AII
occurs with first dose of ACE I given to diuretic pt

Choosing Antihypertensives
_..


RAAS blockade leads to malformation
ACE I: decrease AII, renal failure
aldosterone decrease: more K
Last updated