01 Autonomics
Sympathomimetics

NE acts as NT (e.g. BP); E acts as hormone (e.g. stress induced)
fight or flight Sympathetic mime: sympathomimetic

QISS: alpha-1, alpha-2, beta-1, beta-2 receptors are coupled to Gq, Gi, Gs, Gs respectively

Alpha scouts: alpha receptor agonists
Single lit alpha candle: alpha-1 agonist
3 "dags": alpha-1 receptor coupled to Gq -> IP3-DAG cascade

"Dag" with bone: IP3-DAG cascade-> increased intracellular calcium (smooth muscle cell in vasculature/sphincters)
Alpha-1 scout pulling red leashes: alpha-1 activation increases peripheral arterial resistance (vasoconstriction at small arteries, arterioles, precapillary sphincters)
Alpha-1 scout elevating MAP: alpha-1 activation increases mean arterial pressure (MAP)
Alpha-1 scout pulling blue leashes: alpha-1 activation increases venous return (venoconstriction) (good for increase CO)
Alpha-1 scout binoculars: alpha-1 activation at pupillary dilator muscle causes mydriasis (pupillary dilation)
Alpha-1 scout pulling pants string: alpha-1 activation causes urethral sphincter and prostatic smooth muscle contraction
Full bladder canteen: alpha-1 activation causes urinary retention



Two lit alpha candles: alpha-2 agonist
"No sympathy": alpha-2 agonists are sympatholytics (act centrally to decrease sympathetic tone)
Packed up alpha-2 camp tent: alpha-2 receptor coupled to Gi -> decreased cAMP
Alpha-2 scout packing up presynaptic wire: presynaptic alpha-2 receptors cause inhibition of neurotransmitter release

Welcome INSIDE mat: insulin
Rolled up welcome INSIDE mat: alpha-2 activation at pancreatic islet cells decreases insulin release
Alpha-2 scout dousing roasting pig: alpha-2 activation inhibits lipolysis and release of fatty acids
Alpha-2 scout emptying water from eyeball hat: activation of alpha-2 at ciliary body decreases aqueous humor production (glaucoma meds)
Brim of eyeball hat: brimonidine is an alpha-2 agonist used to treat chronic open angle glaucoma (decreases aqueous humor production)



βand cAMP: beta receptor agonists increase cyclic AMP (cAMP)

Beta-1 horn: beta-1 agonist
"I heart βand cAMP": beta-1 receptors are found on cardiac myocytes (including SA and AV nodes)
"I heart βand cAMP": beta-1 activation causes increased cyclic AMP -> increased intracellular calcium
Elevated heart clock: beta-1 activation increases heart rate (SA node)
Buff contracted bicep: beta-1 activation increases cardiac contractility
Heart hydrant: beta-1 activation results in increased cardiac output
Open rain umbrella: beta-1 activation increases renin release (JGA cells), increase BP/volume


Beta-2 tuba: beta-2 activity
"ROL" call sheet: beta-2 agonists used for bronchodilation have -"rol" suffix (albuterol, formoterol, salmeterol)
Beta-2 camper taking big breath: beta-2 activation leads to bronchoDILATION (increased cyclic AMP -> activates PKA)
Beta-2 camper with dilated sleeves: beta-2 activation causes coronary and skeletal muscle vasoDILATION -> decreases systemic vascular resistance (SVR)
Beta-2 camper roasting pig: beta-2 activation stimulates lipolysis and release of free fatty acids
Beta-2 camper producing marshmallows from liver-shaped bag: beta-2 receptor activation at the liver promotes gluconeogenesis
Beta-2 camper carrying s'mores INSIDE tent: beta-2 activation at pancreatic islet cells stimulates insulin release-> moves glucose into cells
Banana peels: beta-2 activation can cause hypokalemia (due to increased insulin activity)
Beta-2 camper filling eyeball balloon: beta-2 activation at ciliary body increases aqueous humor production (β antagonist for glaucoma)
Sleeping beta-2 camp counselor: beta-2 agonists relax uterine smooth muscle


Drugs

Flannel friends: phenylephrine (alpha-1 agonist)
Flannel friend holding single alpha candle: phenylephrine is an alpha-1 agonist

Flannel friend's nasal spray: phenylephrine treats nasal congestion (alpha-1 mediated local vasoconstriction reducing edema)
Flannel friend's binoculars: phenylephrine causes mydriasis (activates alpha-1 at pupillary dilator muscle)


map: Phenylephrine increases MAP (alpha-1 increase in SVR)
1st line: Phenylephrine increases systolic pressure (alpha-1 arteriolar constriction)
2nd line: Phenylephrine increases diastolic pressure (alpha-1 venous constriction)
Flannel friend's low dangling heart watch: phenylephrine causes reflex bradycardia (response to alpha-1 increase in MAP)
Pts with reduced autonomic function (diabetic neuropathy) can't have baroreceptor reflex = very high pressure in response

North compass: NORepinephrine (alpha>beta1 agonist) - a1, a2
North scout blowing beta-1 bugle: norepinephrine has some beta-1 activity (primarily an ALPHA AGONIST)

Norepinephrine increases MAP (alpha-1 increase in SVR)
Norepinephrine increases systolic pressure (alpha-1 arteriolar constriction)
Norepinephrine increases diastolic pressure (alpha-1 venous constriction)
North scout's low dangling heart watch: norepinephrine causes reflex bradycardia (response to alpha-1 increase in MAP)
North scout's buff contracted bicep: norepinephrine increases cardiac contractility (activates beta-1), although bradycarida
Norepinephrine increases pulse pressure (b2 activity)
Norepinephrine increases PULSE PRESSURE, difference between systolic and diastolic (beta-1 increase in contractility)

Septic tank: septic shock (phenylephrine and norepinephrine increase SVR and venous return to treat distributive/hypovolemic shock)

"Just DO BUgling": DOBUtamine (beta-1>beta-2 agonist)
Beta-1 bugle: dobutamine is primarily a beta-1 agonist
"Just DO BUgling" friend's beta-2 tuba: dobutamine has some beta-2 activity (primarily a BETA-1 AGONIST)

"Just DO BUgling" winding up heart flashlight: dobutamine increases heart rate, contractility, and cardiac output (beta-1 effects)
"Just DO BUgling" friend's dilated sleeves: dobutamine causes vasodilation -> decreases SVR (effects mild due to minimal beta-2 activity)
Dobutamine increases PULSE PRESSURE, difference between systolic and diastolic (beta-1 increase in contractility)
Dobutamine increases systolic pressure (beta-1 increase in CO)
Dobutamine can decrease diastolic pressure (beta-2 arteriolar dilation)

Batteries fallen out of heart flashlight: dobutamine can be used in cardiogenic shock
Dead heart batteries: cardiogenic shock (dobutamine increases contractility and CO to treat cardiogenic shock)
Dobutamine used for stress test (make heart work more without exercise )

"Iso-pro-tunnel" between beta-1 and beta-2 camps: isoproterenol (beta-1=beta-2 agonist)

Tunnel camper's elevated heart watch and contracted bicep: isoproterenol increases heart rate and contractility (beta-1 effects)
Tunnel camper's dilated sleeves: isoproterenol causes vasodilation -> decreases SVR (beta-2 effects)
Tunnel camper's dangling DIAmond earrings: isoproterenol decreases DIAstolic pressure (beta-2 vasodilation and decreased SVR)
Isoproterenol increases PULSE PRESSURE, difference between systolic and diastolic (beta-1 increase in contractility)
Isoproterenol decreases MAP (beta-2 decrease in SVR)
Isoproterenol decreases diastolic pressure (beta-2 arteriolar dilation)
dangling DIAmond earrings: decreased DIAstolic pressure (beta-2 vasodilation and decreased SVR)

"Do not disTURB": TERButaline prevents premature labor (beta-2 relaxes the uterus)
"I DREAM of band camp": ritoDRINE prevents premature labor (beta-2 relaxes the uterus)

EPIC kiss between alpha and beta camps: EPInephrine (beta>alpha agonist)
Low side of EPIC raft: at LOW doses, epinephrine's BETA AGONIST effects predominate
EPIC DIAmond falling off LOW side of raft: at LOW doses, epinephrine decreases DIAstolic pressure (beta-2 vasodilation and decreased SVR)
EPIC elevated heart watch and buff contracted bicep: epinephrine increased heart rate and cardiac contractility (beta-1 effects)
High side of epic raft: at HIGH doses, epinephrine's ALPHA AGONIST effects predominate
Epinephrine increases MAP (alpha-1 increase in SVR)
Epinephrine increases systolic pressure (alpha-1 arteriolar constriction)
Epinephrine can decrease diastolic pressure (beta-2 arteriolar dilation)
Epinephrine increases PULSE PRESSURE, difference between systolic and diastolic (beta-1 increase in contractility)

Beta-2 tuba girl's EPIC inhaler: epinephrine causes bronchodilation (beta-2 effects)
"Anna + Phil": anaphylactic shock (epinephrine increases SVR and bronchodilates to treat anaphylactic shock) a1 for vasoconstriction, b1 for blood flow to tissues, b2 for bronchodilation
Indirect Sympathomimetics
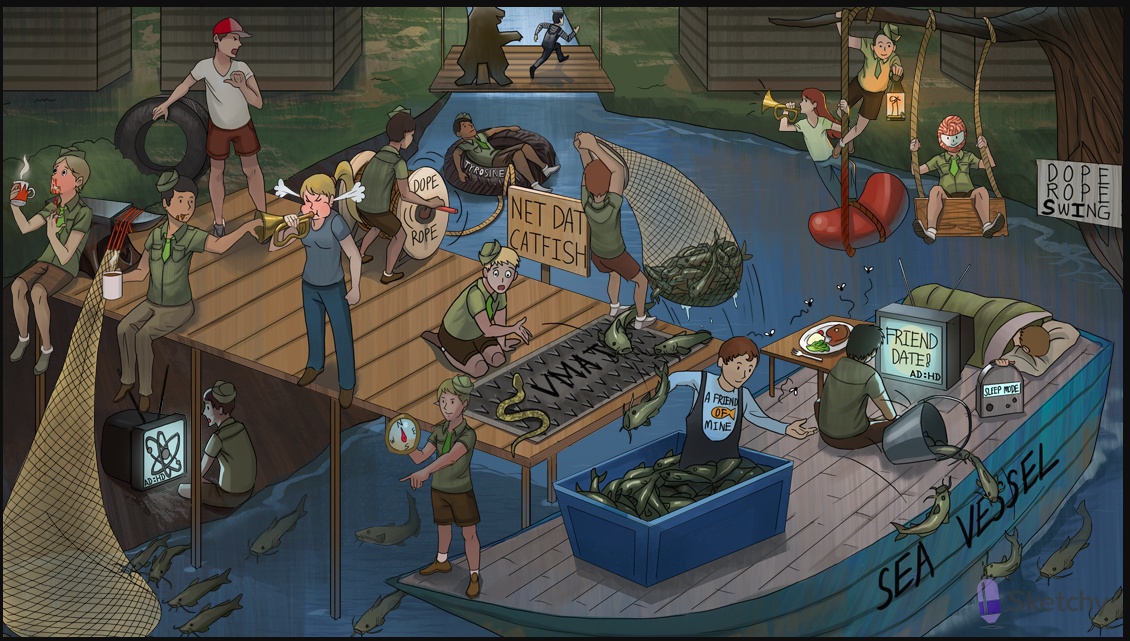

Indirect view of sympathetic mime: Indirect sympathomimetics
Catfish: catecholamines (epinephrine, norepinephrine, dopamine)
Dock: adrenergic nerve terminal (site of action of indirect sympathomimetics)
Retrieving tire: tyrosine (the amino acid precursor to catecholamines) is transported to nerve terminal
L-shaped rope handle: tyrosine is converted to L-DOPA
Dope rope: L-dopa is converted to dopamine
Sea vessel: vesicle containing neurotransmitters in the presynaptic neuron
"V" mat: vesicular monoamine transporter (VMAT)
Catfish transported to sea vessel: catecholamines are transported by VMAT into presynaptic vesicle
North-facing compass on sea vessel: dopamine is converted to norepinephrine in the vesicle
Hauled in catfish NET: norepinephrine transporter (NET) transports norepinephrine (and dopamine) back into the presynaptic neuron
NET DAT catfish: dopamine transporter (DAT) transports dopamine back to the presynaptic neuron

"My tire!": metyrosine (a tyrosine analog) prevents conversion of tyrosine to L-DOPA

Hot cocoa: cocaine
Hot cocoa scout ignoring catfish net: cocaine inhibits the norepinephrine transporter (NET and dopamine transporter (DAT)

Stimulated hot cocoa scout: cocaine can cause agitation, pupillary dilation, hypertension and tachycardia
Bloody nose: cocaine can cause nasal mucosal atrophy or septal perforation to due vasoconstriction
Constricted red crown: cocaine can cause coronary vasospasm and myocardial ischemia
Constricted net on anvil: cocaine induced coronary vasospasm can cause angina

High pressure blocked bugle: beta-blockers can cause severe hypertension in cocaine intoxication (unopposed alpha-1 stimulation)

Atom next to empty net: atomoxetine (NET inhibitor)
Distracting HD TV: atomoxetine treats attention deficit and hyperactivity disorder (ADHD)

Serpent blocking "V" mat: reserpine inhibits VMAT, depleting neurotransmitter stores

A FRIEND of MINE releasing catfish: amphetamines displace catecholamines (norepinephrine, dopamine) into synapse; good for attention to tasks
Distracted by HDTV while catfish are released: amphetamines can be used to treat ADHD
Friend Date on HDTV: methylphenidate (an amphetamine derivative) treats ADHD
Untouched dinner: stimulants (e.g. amphetamines, methylphenidate, modafinil) suppress appetite

Sleeping scout hitting "sleep mode": modafinil is a stimulant used to treat narcolepsy
Untouched dinner: stimulants (e.g. amphetamines, methylphenidate, modafinil) suppress appetite

Untouched dinner: stimulants (e.g. amphetamines, methylphenidate, modafinil) suppress appetite

Single rope swing: D1 receptor
Double rope swing: D2 receptor
Dope rope SwIng: D1 and D2 are coupled to Gs and Gi, respectively

Low kidney tied to single rope: low doses of dopamine act on D1 receptors to increases renal blood flow
Beta bugler in the middle: medium doses of dopamine activate beta-1 receptors (cardiac activation)
Alpha scout up high: high doses of dopamine activate alpha-1 receptors (pressor effects)
Brain helmet on double rope swing: D2 receptors are found in the CNS
Alpha drugs
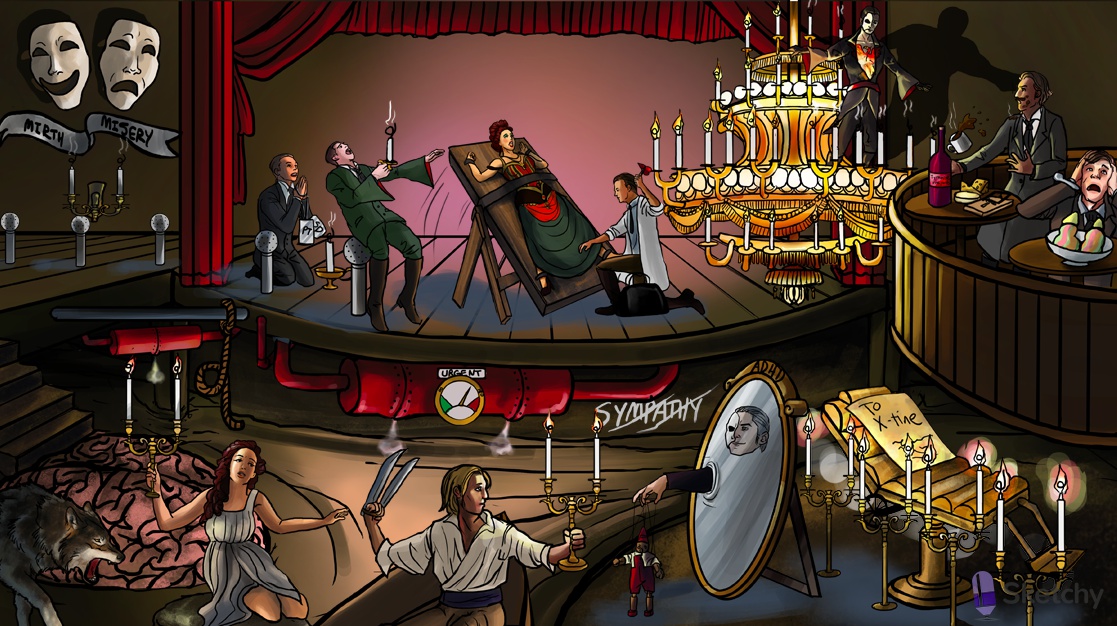

Claw weapon: clonidine (alpha-2 agonist)
2 lit alpha candles: alpha-2 receptor agonist

Brain-shaped platform: alpha-2 agonists given systemically affect the CNS (inhibition of sympathetic tone -> reduced blood pressure)

Crossed out "sympathy": alpha-2 agonists (e.g. clonidine) are sympatholytics
High pressure pipes: clonidine treats hypertension (reduced sympathetic tone)
Urgent pressure: clonidine is useful in the treatment of hypertensive urgency
Distracting mirror: clonidine can be used to treat ADHD
Tourette's marionette: alpha-2 agonists (e.g. clonidine) are useful in the management Tourette's syndrome

Alpha shaped rope: a-methyldopa (alpha-2 agonist)
2 lit alpha candles: alpha-2 receptor agonist

Brain-shaped platform: alpha-2 agonists given systemically affect the CNS (inhibition of sympathetic tone -> reduced blood pressure)
High pressure pipes: a-methyldopa treats hypertension (reduced sympathetic tone)

Pregnant: a-methyldopa is primarily used to treat gestational hypertension
Lupus wolf: a-methyldopa can cause a lupus-like syndrome

To X-tine: tizanidine (alpha-2 agonist)
2 lit alpha candles: alpha-2 receptor agonist
Relaxing chair: tizanidine (alpha-2 agonist) is a muscle relaxant

Phantom: phentolamine (reversible alpha-1 and alpha-2 receptor antagonist)
Extinguished single and double alpha candles: alpha-1 and alpha-2 antagonist
Dilated sleeves: phentolamine causes vasodilation (alpha-1 antagonist effect)
Hot cocoa: alpha antagonists (e.g. phentolamine) can be used to treat cocaine toxicity (avoid beta blockers due to unopposed alpha vasoconstriction)
Mousetrap protecting wine and cheese: MAO inhibitors can prevent the metabolism of tyramine -> hypertensive crisis (treat with alpha blockers e.g. phentolamine)

Irreversible phoenix tattoo: phenoxybenzamine (irreversible alpha-1 and alpha-2 receptor antagonist)
Hot cocoa: alpha antagonists (e.g. phentolamine) can be used to treat cocaine toxicity (avoid beta blockers due to unopposed alpha vasoconstriction)

Wine and aged cheese contain the sympathomimetic tyramine (metabolized by monoamine oxidase-A (MAO-A))
Mousetrap protecting wine and cheese: MAO inhibitors can prevent the metabolism of tyramine -> hypertensive crisis (treat with alpha blockers e.g. phentolamine)

Frozen colorful dessert: pheochromocytoma (catecholamine secreting tumor of the adrenal medulla)
Brain freeze: catecholamine excess in pheochromocytoma causes headaches, hypertension, palpitations, sweating (use alpha blockers (e.g. phentolamine) preoperatively to control blood pressure)

Tiltable: alpha receptor antagonists can cause orthostatic hypotension (alpha-1 antagonist effect)
Heart shaped reflex hammer: alpha blocker induced hypotension causes reflex tachycardia
Dilated sleeves: alpha-1 antagonists "-osins" cause vasodilation

Opera singer: "-osin" suffix of alpha-1 selective antagonists (e.g. prazosin, terazosin, doxazosin, tamsulosin)
Extinguished single alpha candle: alpha-1 receptor antagonist
Banister compressing prostate: alpha-1 antagonists (e.g. terazosin) treat symptoms of BPH (relax smooth muscle in the urethra and prostate)
Praying opera singer: prazosin (alpha-1 antagonist)
PTSD dog tags: prazosin can be used to treat PTSD

2 extinguished alpha candles: alpha-2 receptor antagonist
Mirth and Misery: mirtazapine (atypical antidepressant with antagonist effects at alpha-2 and other a receptors)
Happy face: mirtazapine enhances serotonin release and treats depression
Beta drugs
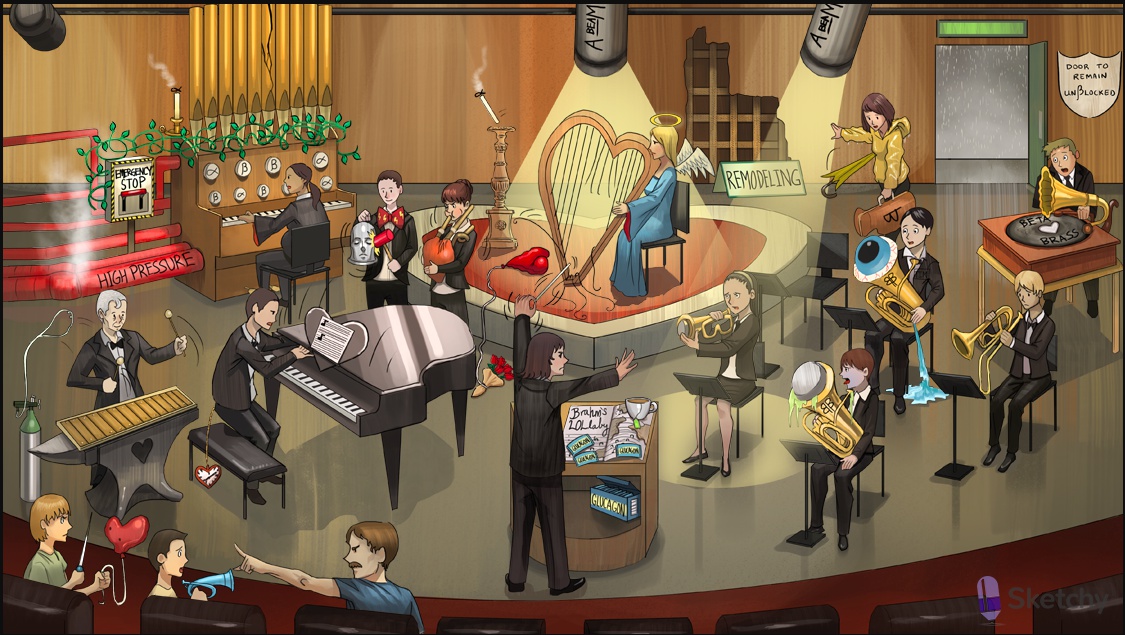

Muted beta-1 bugle and beta-2 tuba: beta adrenergic receptor antagonists (beta blockers)
Brahm's LOLlaby : "-lol" suffix of beta blockers (e.g. propranolol, metoprolol, atenolol)

Weak arm: beta blockers decrease cardiac contractility (by antagonizing beta-1 receptors in the myocardium) (ionotropy)
Music notes: beta blockers suppress activity at the SA and AV nodes (by antagonizing beta-1 receptors) (chronotropy)
Low dangling heart watch: inhibition of SA node activity can cause bradycardia

A-BEAM spotlight on beta-1 bugler: beta-1 selective antagonists (e.g. Atenolol, Betaxolol, Esmolol, Acebutolol, Metoprolol) A through M
Nebivolol

A-BEAM spotlight on heart: the beta-1 selective antagonists primarily suppress adrenergic stimulation of the heart (cardioselective)
Broken heart strings under A-BEAM spotlight: cardioselective beta blockers are useful in the acute treatment of MI and other acute coronary syndromes (ACS)
Failing heart balloon in the A-BEAM spotlight: cardioselective beta blockers are useful in the management of chronic heart failure

Extinguished alpha candle on CARVED candleholder: carvedilol is a nonselective beta blocker and alpha-1 blocker
CARVED candleholder next to failing heart: carvedilol (in addition to cardioselective beta blockers) is useful in the management of chronic heart failure.

Angina anvil: beta blockers are useful in the management of chronic stable angina. Slow Hr, increase diastolic time, decrease contractility
Discarded oxygen line: beta blockers treat angina by reducing myocardial oxygen demand (decreased heart rate and contractility)
Angel: beta blockers (e.g. carvedilol and cardioselective agents) reduce mortality in chronic heart failure and post-MI
Remodeling: beta blockers reduce cardiac remodeling by protecting the heart from excess circulating catecholamines
Big obstructed heart bag: beta blockers are useful in the management of hypertrophic obstructive cardiomyopathy. Slow down heart, allow more filling
Rhythm inducing record: beta blockers have antiarrhythmic properties

High pressure pipes: beta blockers are useful in the treatment of hypertension (especially in patients with heart failure or post-MI). Decrease CO
Closed rain umbrella with blocked beta-1 bugle: beta blockers inhibit production of renin (antagonize beta-1 receptors at the JGA)

Alpha and beta organ stops with extinguished alpha candle: labetalol ("alpha-beta-lol") is a nonselective beta blocker and alpha-1 blocker
Dilated sleeves: labetalol antagonizes alpha-1 receptors causing vasodilation
Pregnant organist: labetalol treats hypertension in pregnancy
Emergency stop: labetalol is useful in hypertensive emergency (due to combined alpha and beta blocking effects)
Dissected organ pipe with ivy: IV beta blockers (e.g. labetalol, propranolol, esmolol) are useful in the acute management of aortic dissection

Ivy: IV beta blockers (e.g. labetalol, esmolol) treat hypertensive emergency
Dissected organ pipe with ivy: IV beta blockers (e.g. labetalol, propranolol, esmolol) are useful in the acute management of aortic dissection

Pounding head bell: beta blockers can be used for migraine prophylaxis
Big stormy bowtie: beta blockers are useful for the symptomatic treatment of thyroid storm (blocks increased sympathetic activity) (treat with propanolol, propylthiouracil, prednisolone)
Shaking baton: beta blockers treat essential tremor
Draining the muted beta-2 tuba: topical nonselective beta blockers (e.g. timolol) treat glaucoma (antagonize beta-2 receptors on the ciliary epithelium -> decreased aqueous humor production)


Droopy trombone: beta blockers can cause impotence in men
Remain un-blocked: beta blockers can cause or exacerbate heart block (due to excessive suppression of AV node conduction)
Wheezing beta-2 tuba player: nonselective beta blockers can exacerbate asthma and COPD (antagonize beta-2 mediated bronchodilation). Block b1 and b2 causing vasoconstriction

Agonizing plastic bugle: acebutolol (a selective beta-1 antagonist with partial agonist activity)
Agonizing pin: pindolol (a nonselective beta blocker with partial agonist activity)
Popping failing heart: beta blockers with partial agonist activity (e.g. pindolol, acebutolol) should be avoided in patients with heart failure or a history of MI

Glucagon packets: glucagon treats beta blocker toxicity (stimulates heart via glucagon receptors)
Last updated