Genetic Syndromes
aka Patau
path:
In most cases all or a majority of the extra 13 chromosome is present. Translocation can be a cause, thus imparting 10% risk of recurrence and the need for parental testing.
defect in the fusion of the prechordal mesoderm, an integral embryological structure affecting growth of the midface, eyes, and forebrain.
Risks
Advanced maternal age is commonly noted
Symptoms
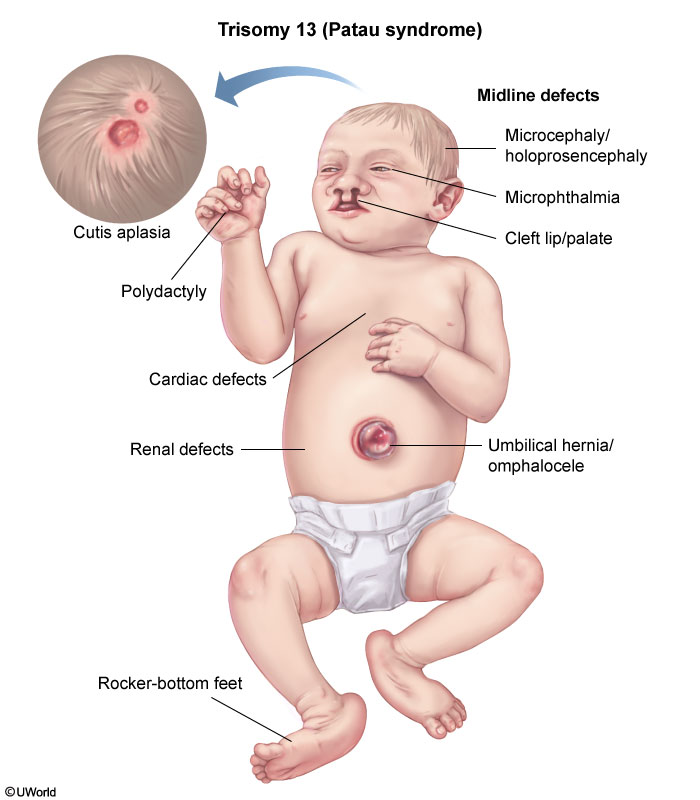
Precordal mesoderm fusion result in catastrophic midline defects, including holoprosencephaly, microcephaly, microphthalmia (small eyes), cleft lip/palate, and omphalocele. Abnormal brain development results in intellectual disability and seizures. Additional abnormalities include polydactyly and cutis aplasia (focal skin defect of the scalp).
complex heart lesion including atrial septal defect (ASD), ventricular septal defect (VSD), and dextrocardia.
rocker bottom feet.,
Angelman
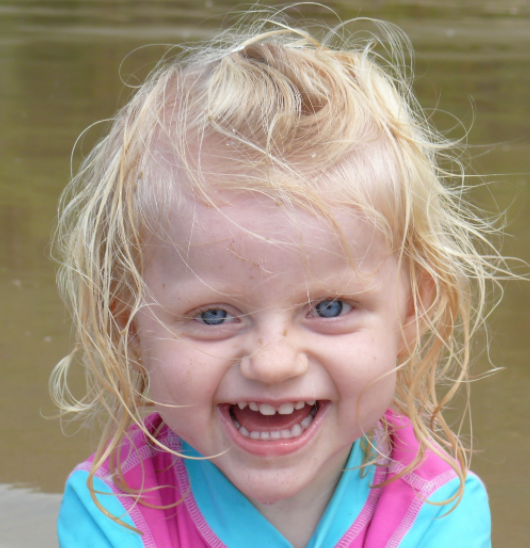
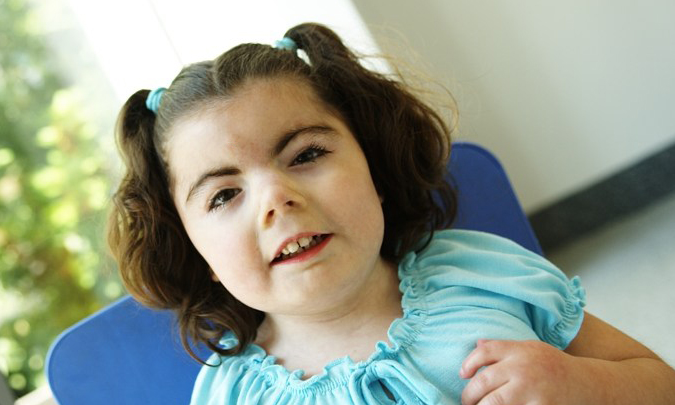
Aka “happy puppet syndrome” In most case
path: it is caused by an interstitial deletion of chromosome 15q1-q13; the deleted material always comes from the maternal side (the same deleted segment from the paternal side results in Prader-Willi).
symptoms
unusual gait and the unprovoked outbursts of laughter.
large mouth with tongue protrusion, hypopigmentation with blond hair and pale blue eyes.,

Cri Du Chat
path: Deletion of the short arm of chromosome 5 is the etiology.
symptoms:
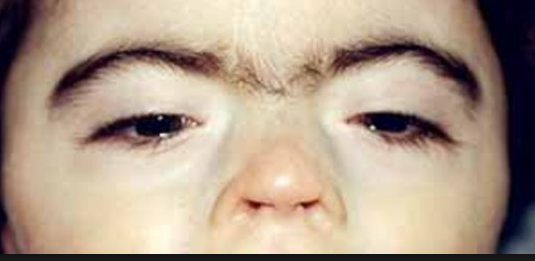
microcephalic, has a rounded face, hypertelorism, and epicanthal folds
The distinctive, catlike cry is likely caused by abnormal laryngeal development; it tends to resolve with time. Profound mental retardation, self-injury behavior, hypersensitivity to sound, and repetitive behaviors are commonly seen. About 85% of cases are paternal in origin.,
Cornelia de Lange
symptoms: Features include bushy eyebrows, hirsutism, limb defects, VSD, and mental retardation.,
Last updated