18 TB
Overview

Characteristics





Infection


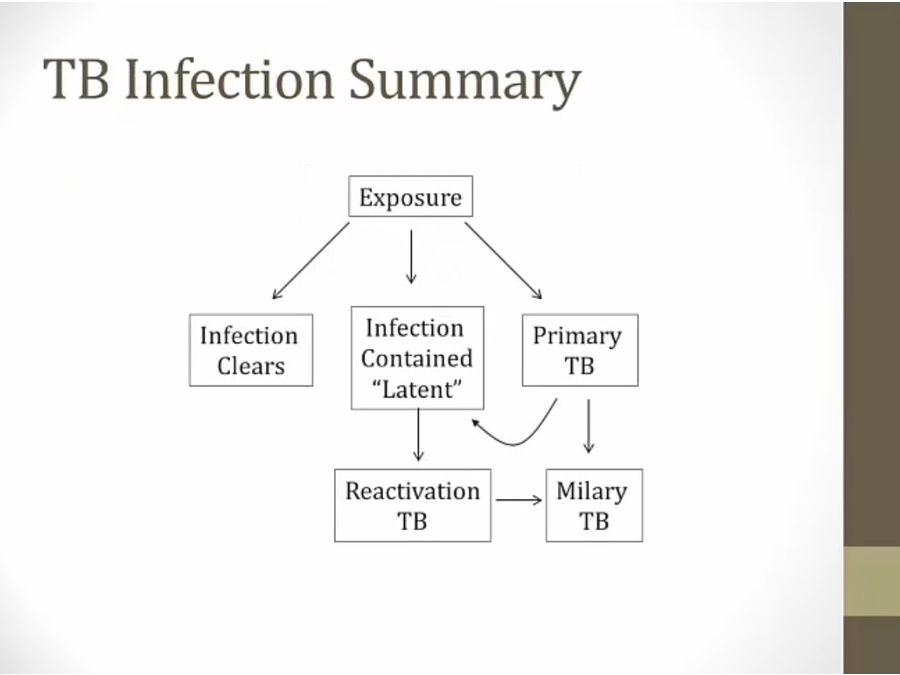
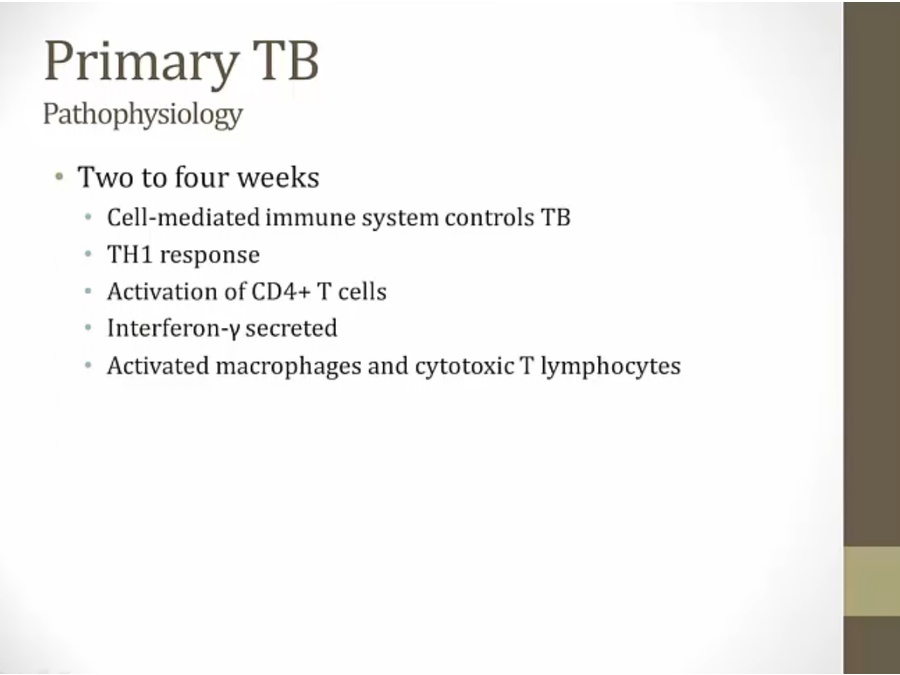
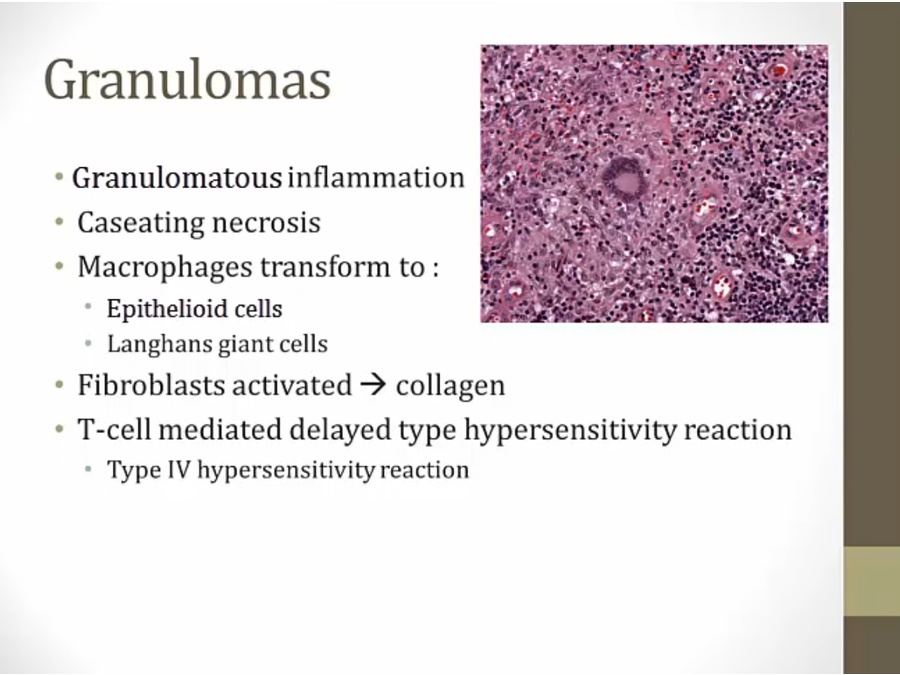
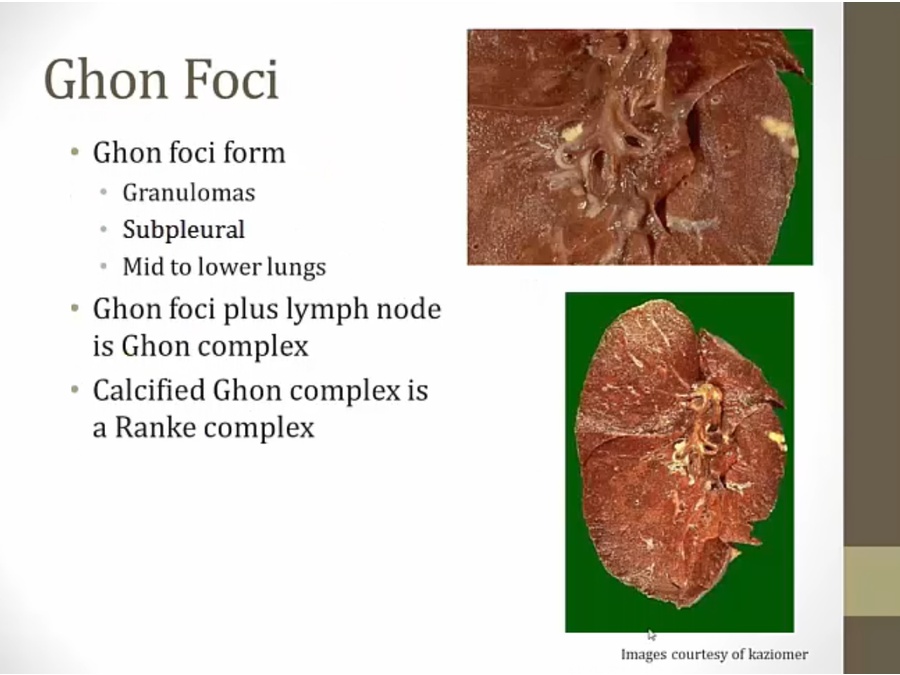
Primary




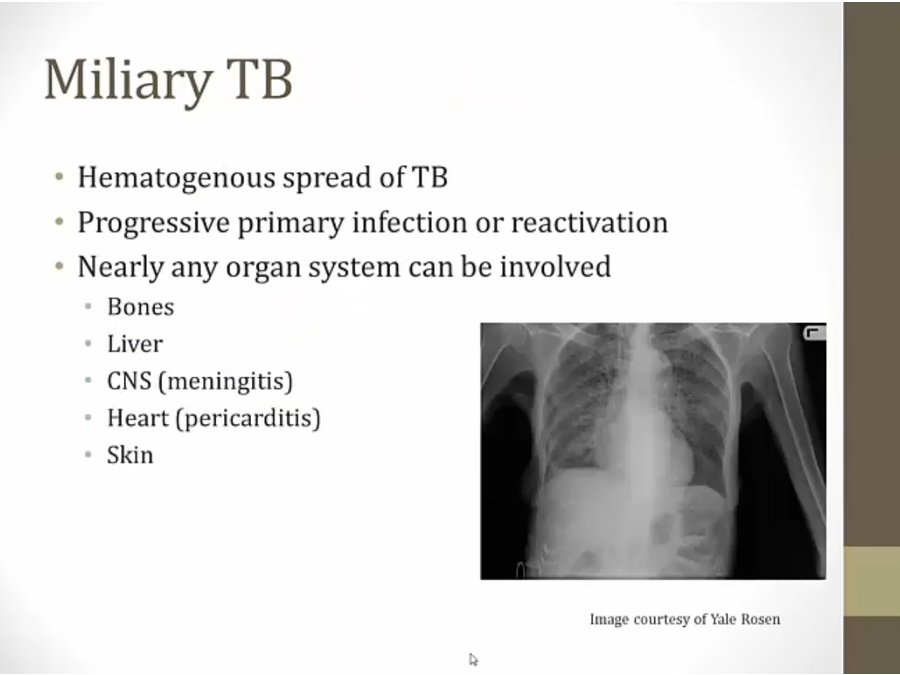
Miliary TB

Reactivated TB


Aspergilloma
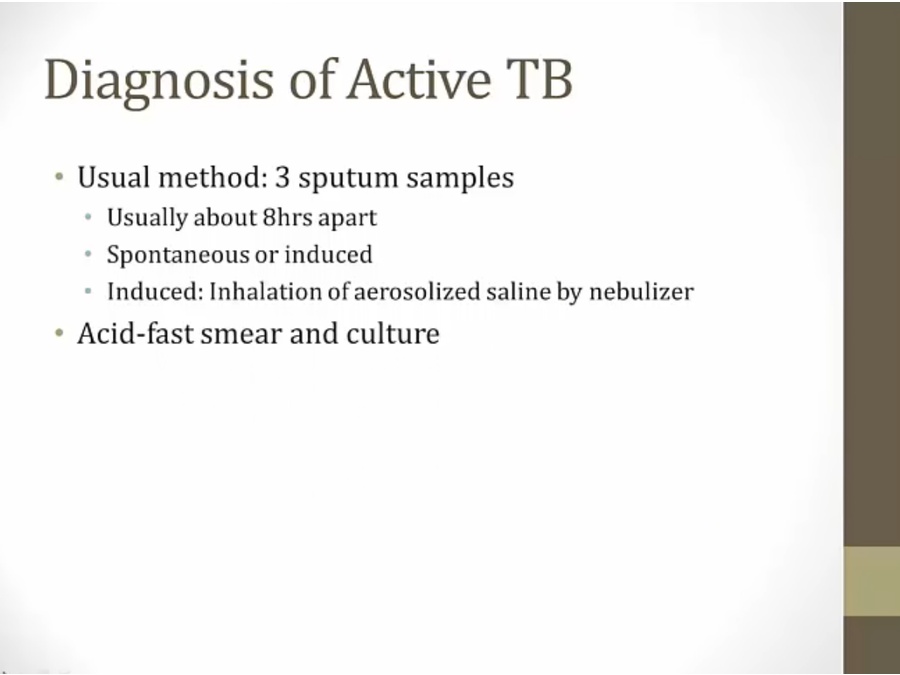
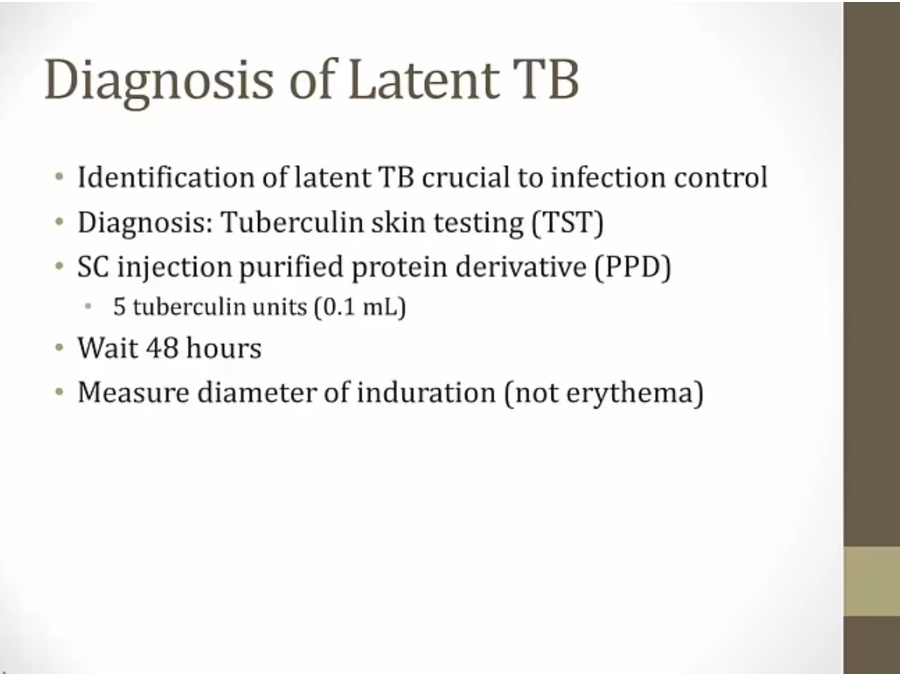
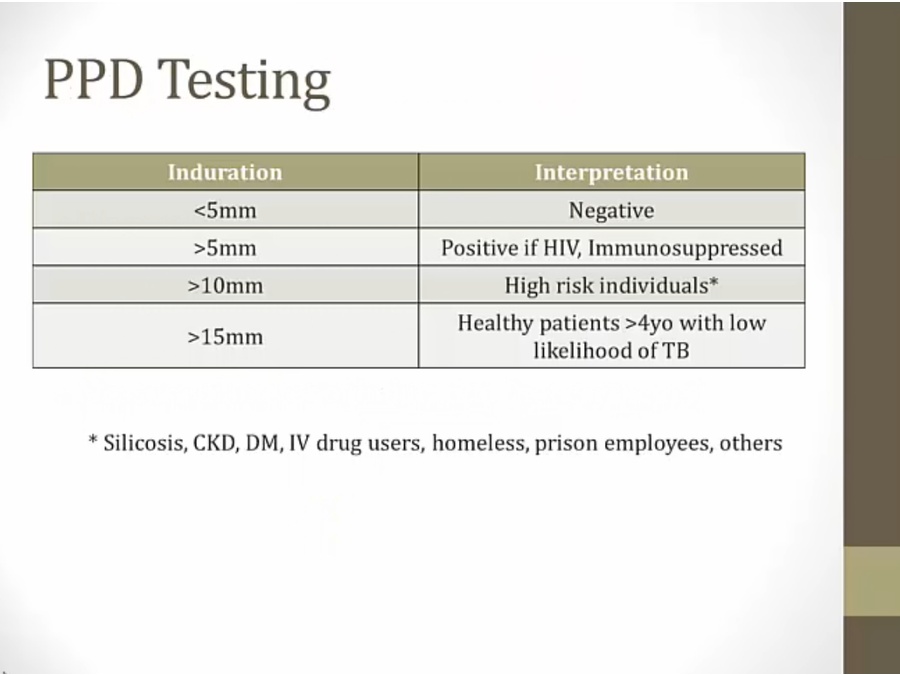
Diagnosis



Treatment

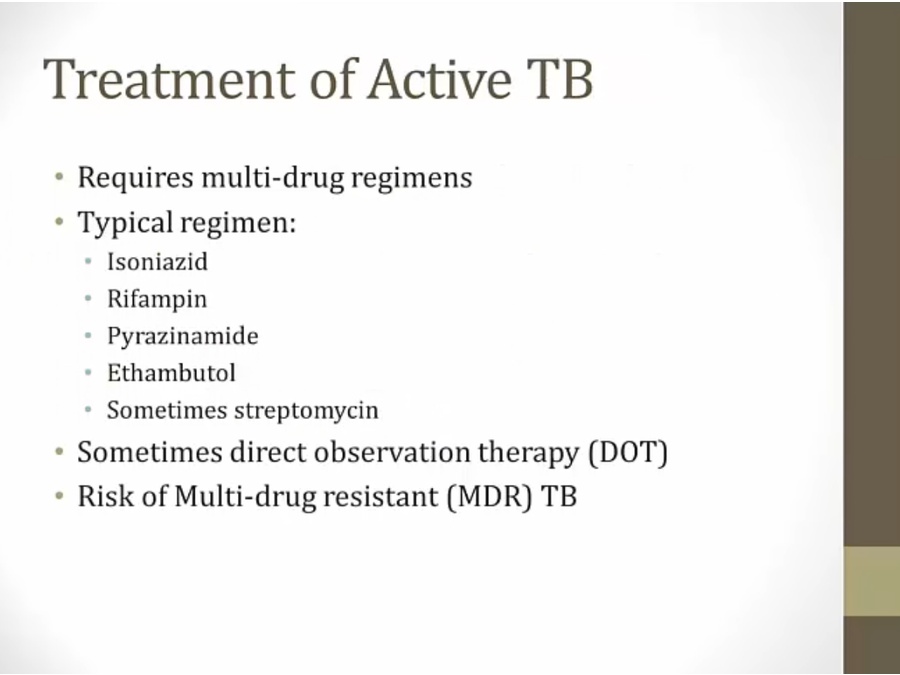
INH


Rifampin


Pyrazinamide

Ethambutol

Streptomycin

Last updated