16 Acute Leukemia

hallmark: increased WBC count in peripheral blood
lymphoma: increased WBC in lymph nodes
Classification

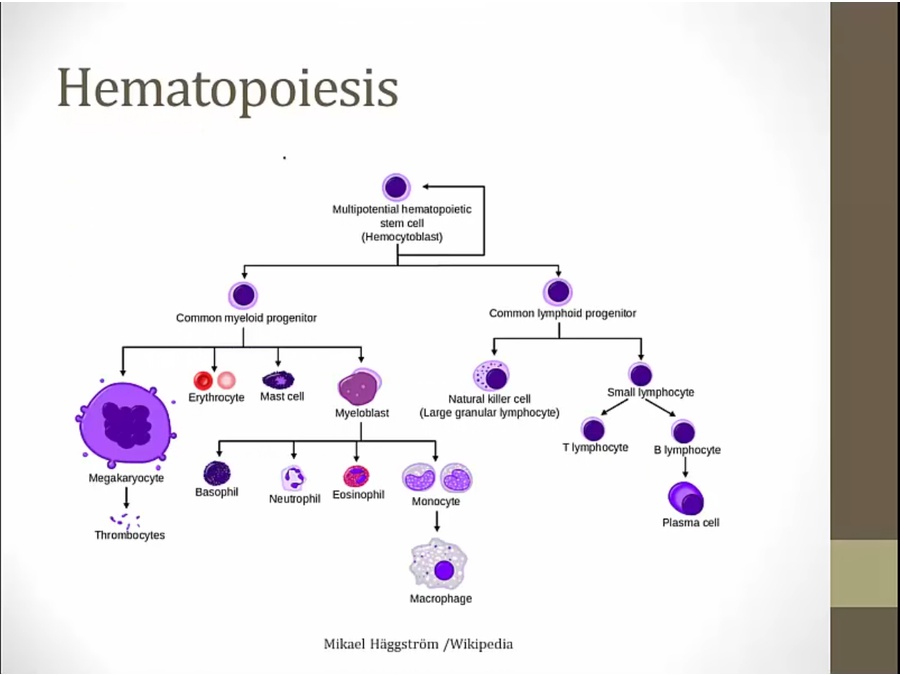
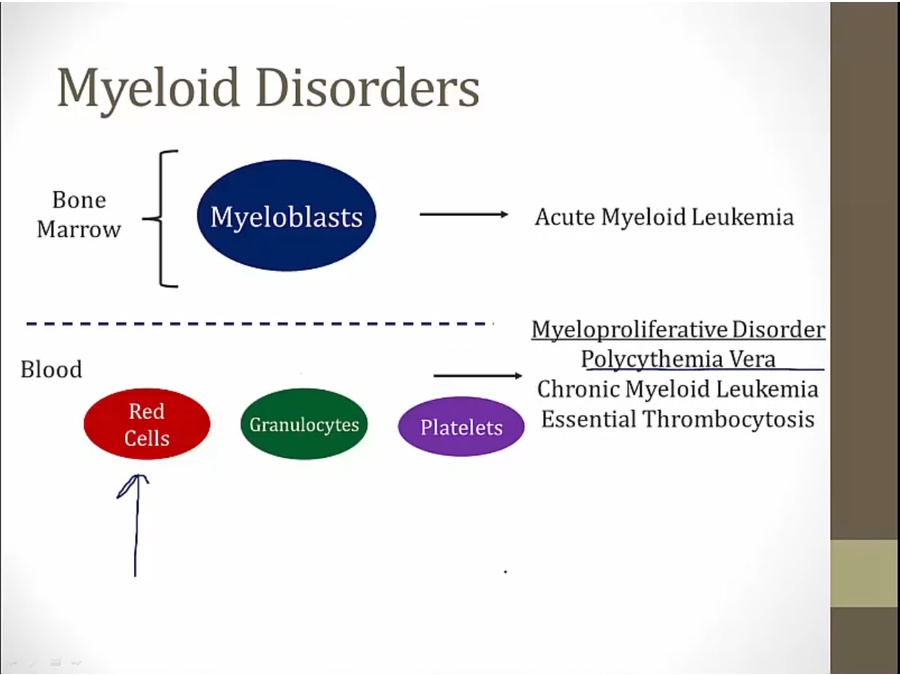
malignancy from myeloblasts: AML
progenitor cells become malignant and overproduces: myeloproliferative
red cell: polycythemia
granulocytes: CML, leukemia since WBC
platelets: thrombocytosis

CLL: more mature lymphocytes
ALL

nonspecific symptoms, just don't feel well and feel sick
bone pain: marrow expanding, filling up with blasts
organs enlarge: blasts leak out of marrow and fill up organs
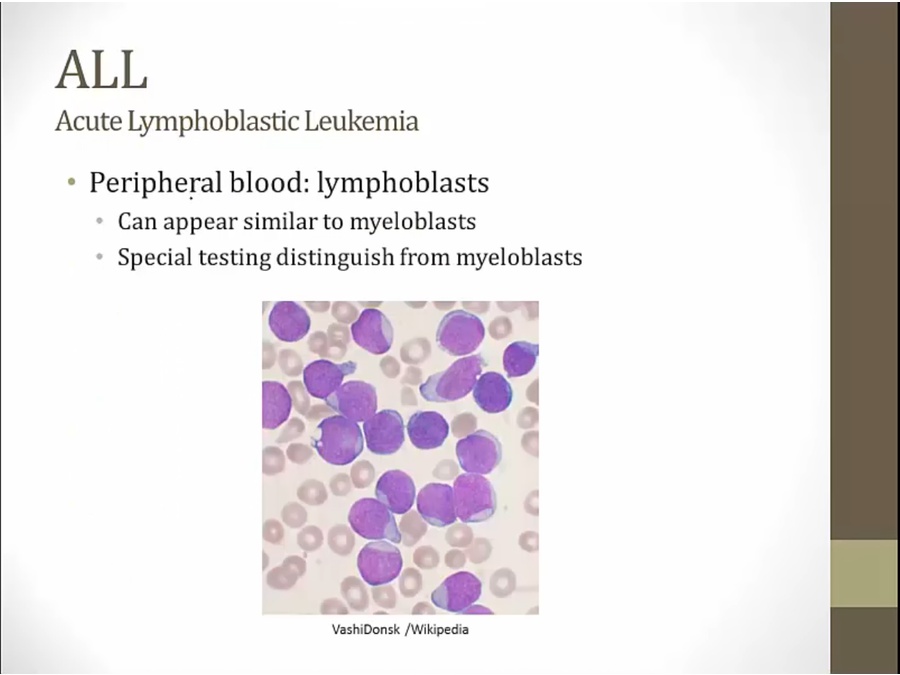
large cells with large nucleus

understand development to understand special tests. Know markers
CD10, 19, 20, 21: B cell
TdT: developing cell
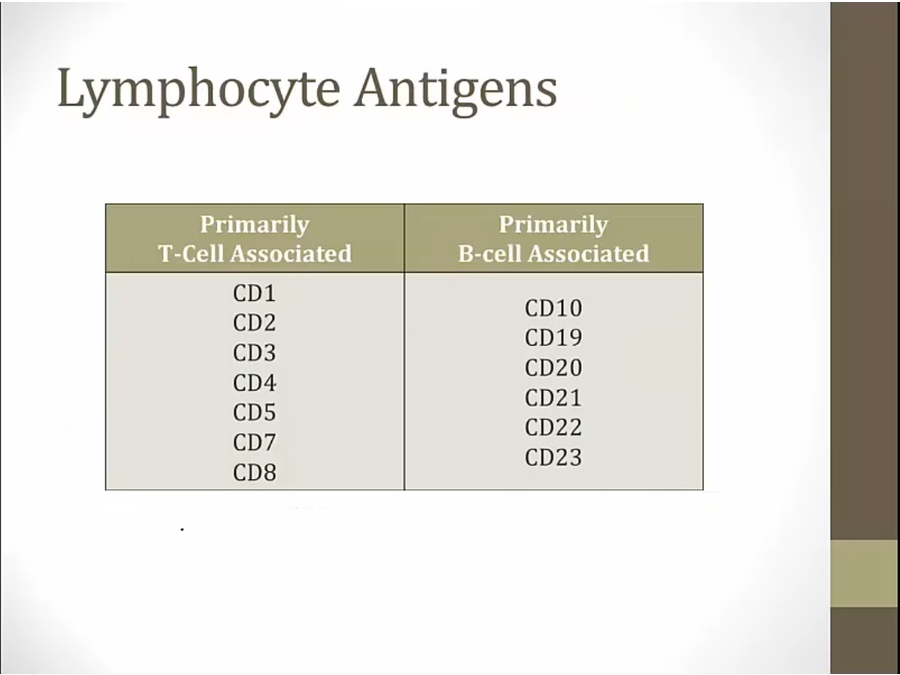
T lower number
B ALL

usually pre B
CD 10: CALLA, found on blasts in ALL

sanctuary sites: special treatment

ALL uncommon in adults, and worse outcome
12:21, common in children, thus good prognosis

trisomy 21
translocation less frequent in down syndrome
T ALL
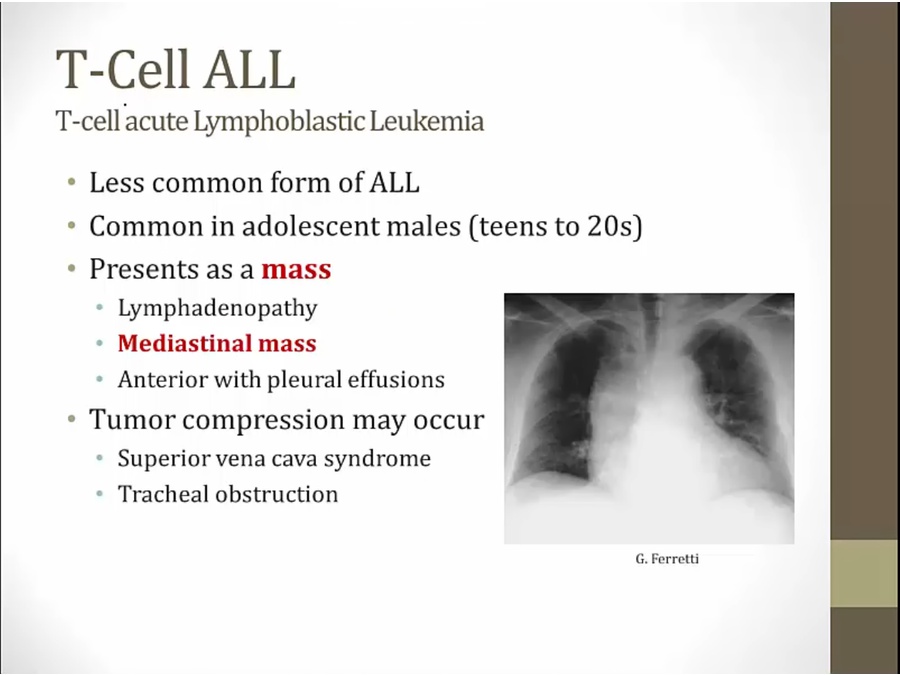
older kids
thymus: where T develop
thymus usually involved and enlarged: widened mediastinal mass
tracheal obstruction: difficulty breathing

AML
gums: classic presentation of thrombocytopenia
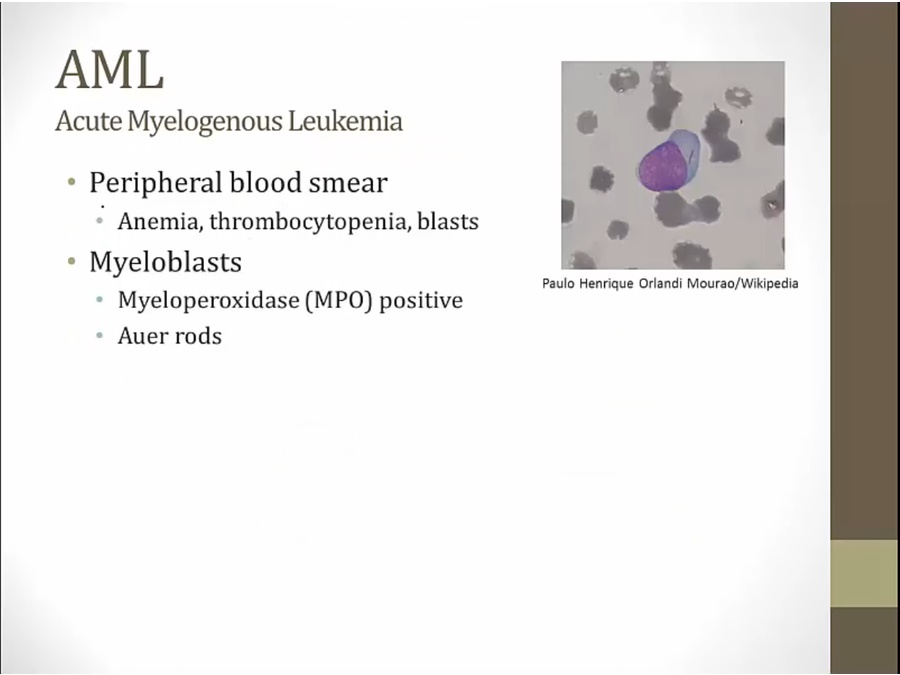
see few RBC, platelets
blasts are myeloblasts: no lymphoblast surface antigens
MPO stain positive

if MPO from auer rods spill into blood, cause DIC
APML




high frequency of DIC
pts often thrombocytopenic from leukemia. If DIC occurs, can get very sick
suspect APML if blasts in periphery and DIC on presentation
MDS

minor versions of AML
no high number of blasts, not leukemia
symptoms of pancytopenia
blasts less than 20% in bone marrow
sideroblasts often seen in bone marrow biopsy

cancer treated with chemo
Last updated