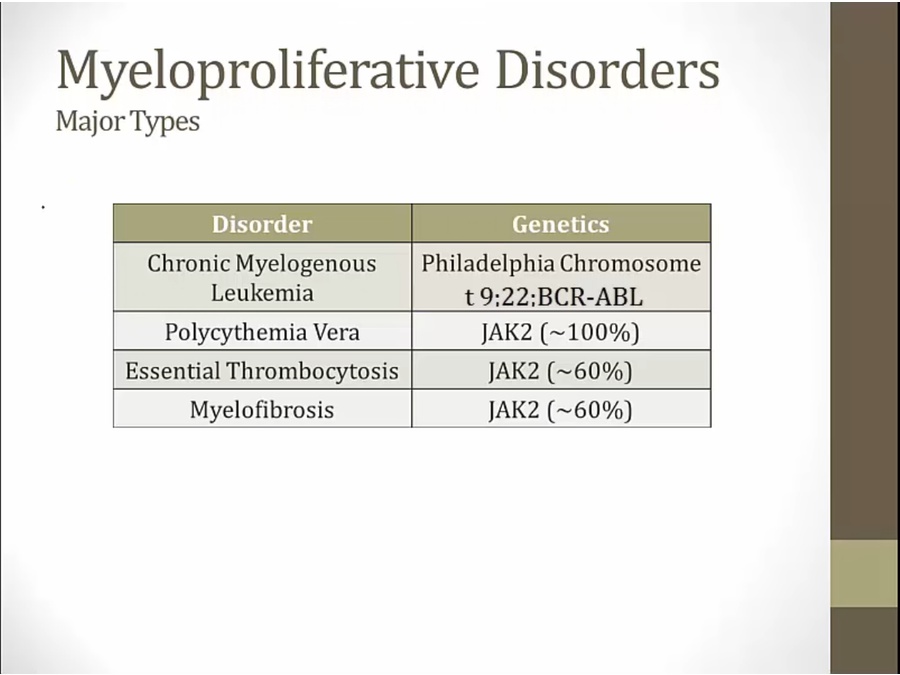
22 Myeloproliferative
Overview

proliferation of cells of myeloid lineage

myelofibrosis: overproduction of bone marrow fibrous tissues, low peripheral cell counts
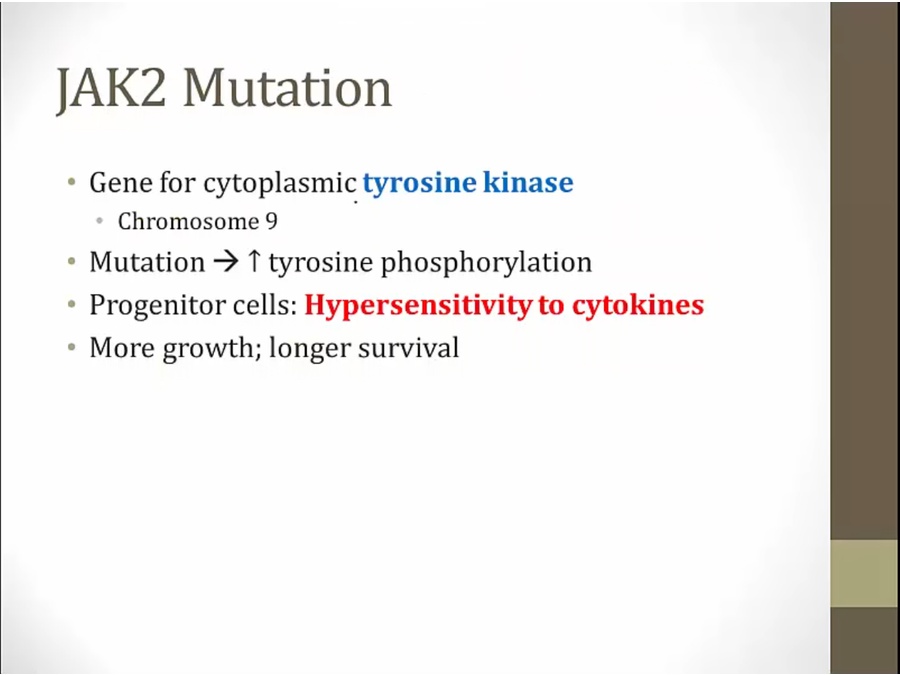
Mutations
Polycythemia Vera
Pathogenesis

increased resistance to flow, stasis, thrombosis

histamine and PGE release after shower
Budd Chiari: blood clot in hepatic vein
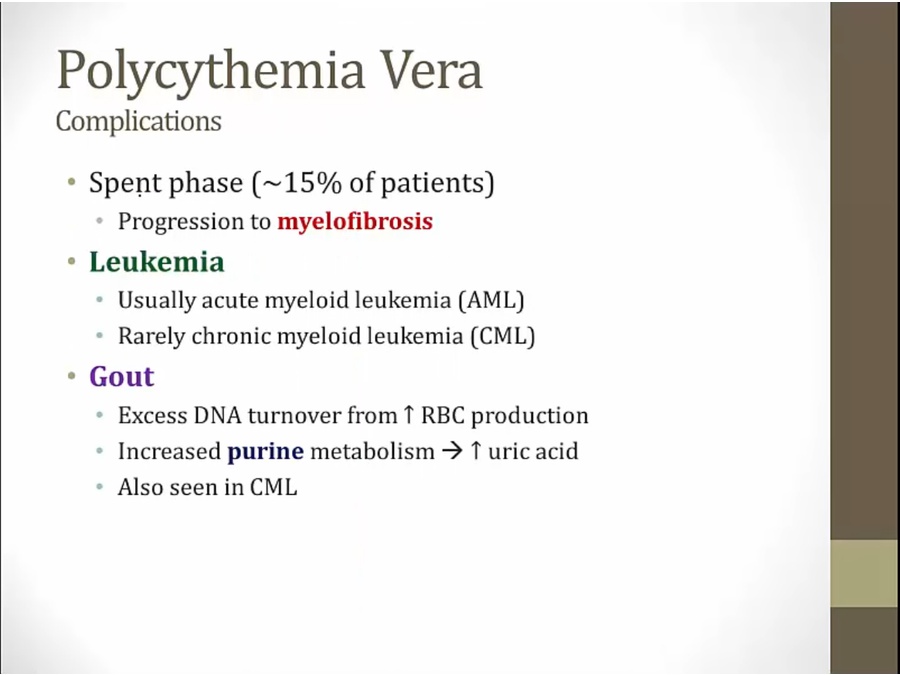
excessive proliferation: bone marrow burned out
progress to myeloid leukemia
Diagnosis
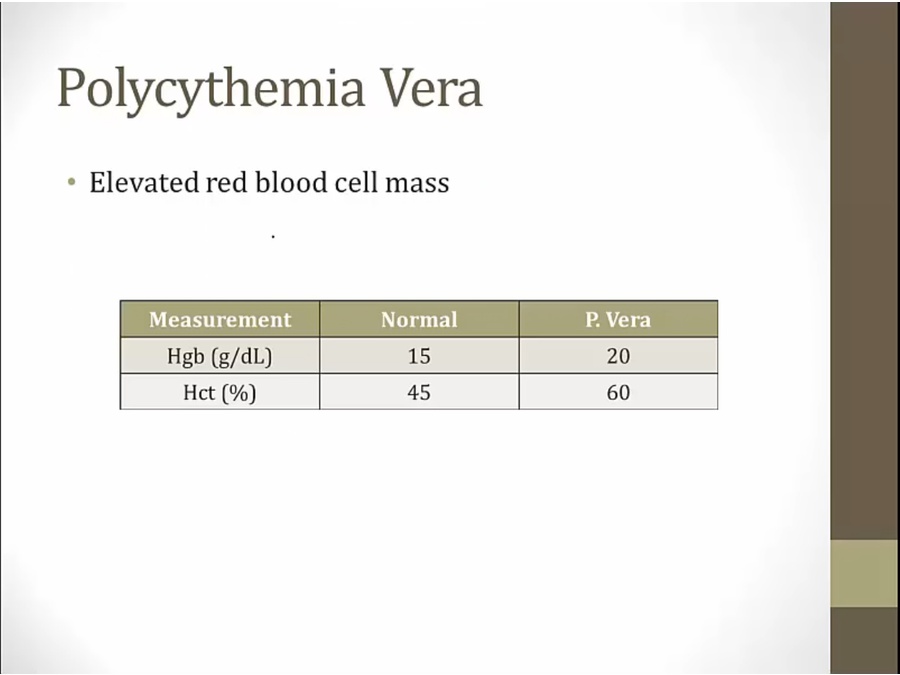

diagnosis must exclude other causes

hydroxyurea: converts RNA nucleotide to DNA nucleotide
Essential Thrombocytosis

elevated platelet count

must exclude polycythemia and CML
iron deficiency anemia: protective mechanism against blood loss

increased platelets but not functioning normally
overactivity of platelets

Myelofibrosis

primary: fibrous tissues overtaking bone marrow
secondary: spent phase in polycythemia
Primary
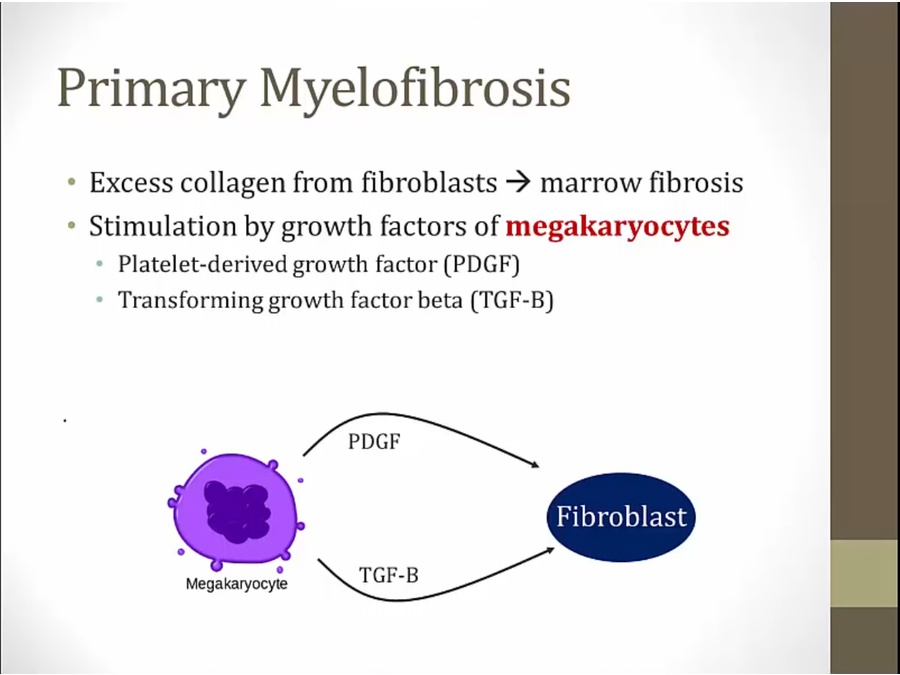
collagen overtakes bone marrow, pancytopenia
cytokines from macrophages

bone marrow fails, other organs take over jobs

increased metabolism from extramedullary hematopoiesis and severe anemia
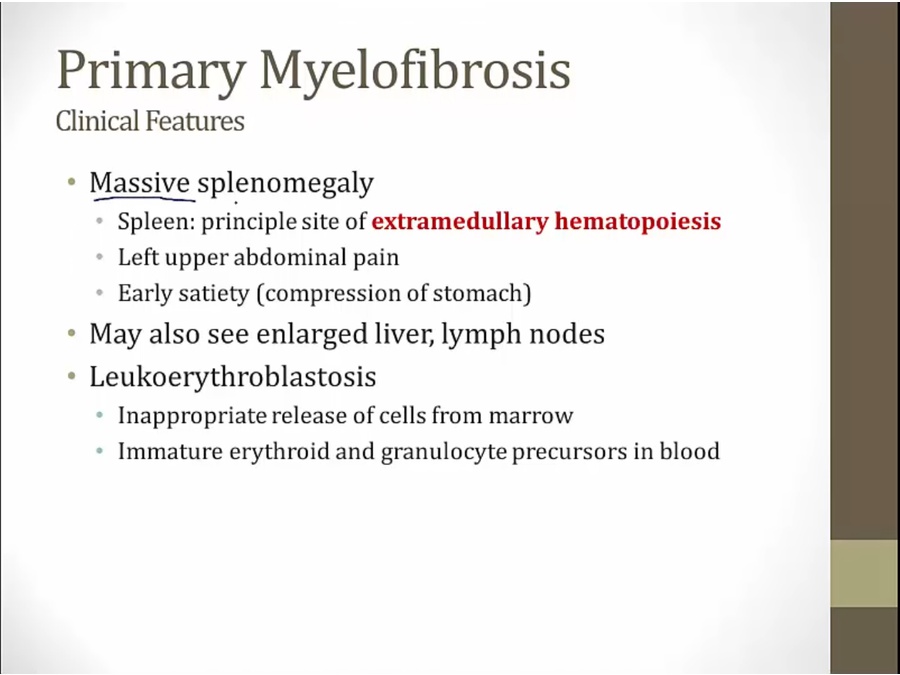
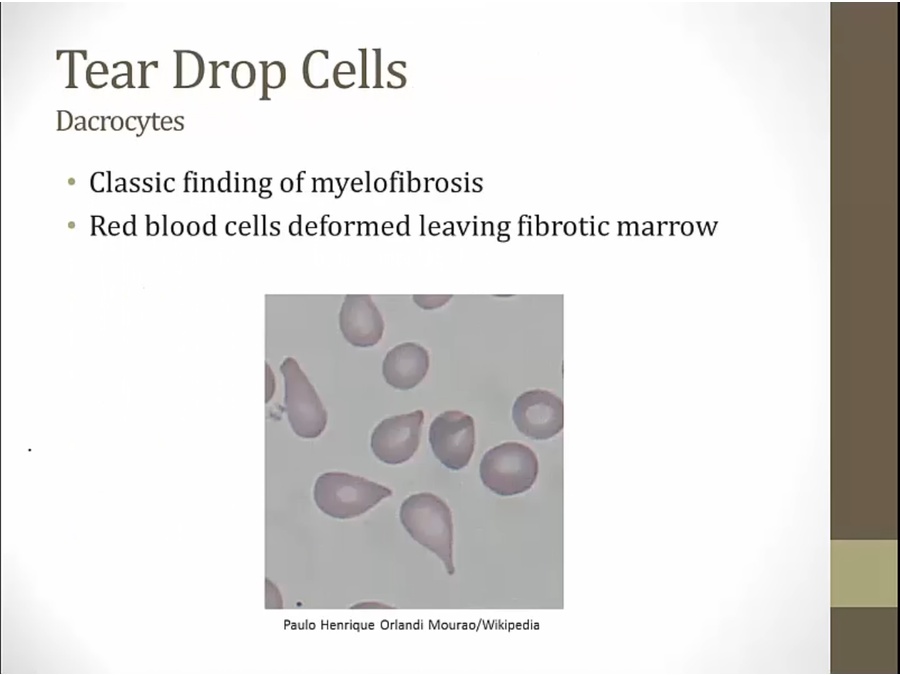
immature precursor cells pushed out of bone marrow
Langerhan Histiocytosis

langerhan: type of histiocyte

malignant cells precursor myeloid cells, not really langerhan, just look like it

tennis racket

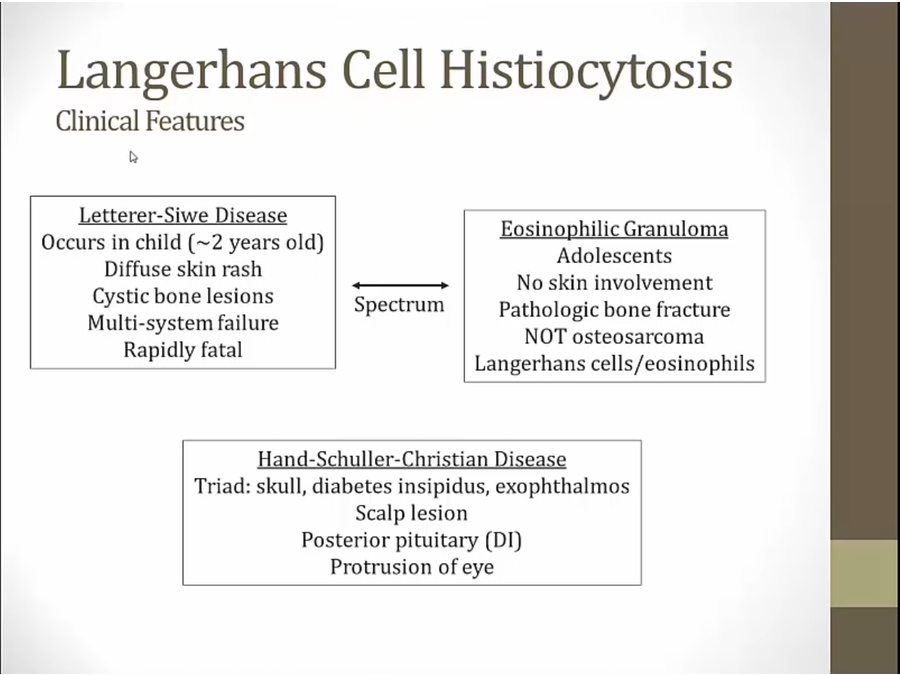
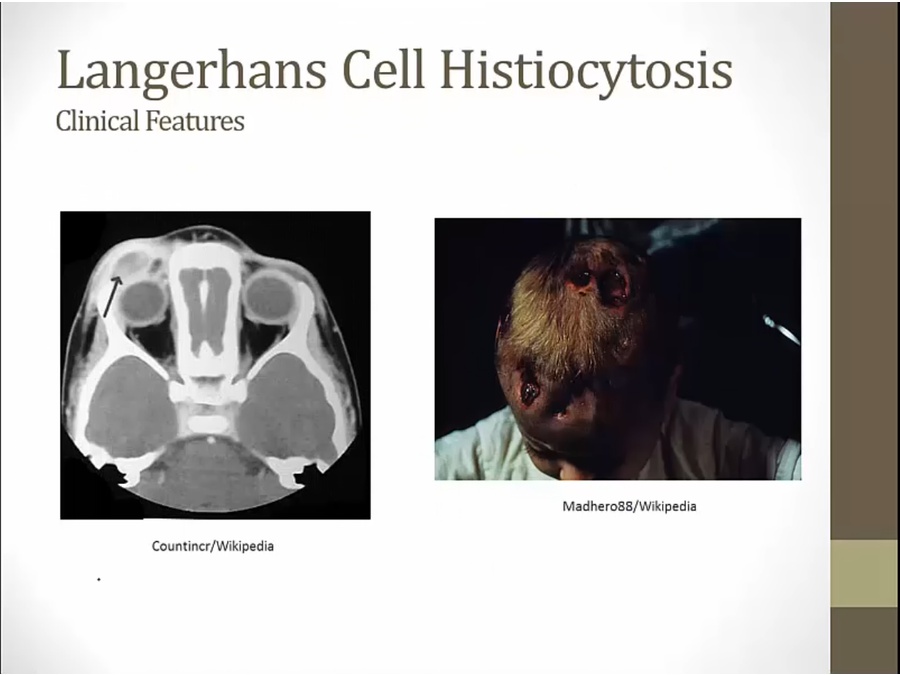
most severe: letterer-siwe
least severe: eosinophilic granuloma, presenting with bone fracture and langerhan cells/eosinophils
Last updated