01 Pulmonary Anatomy
Lobes
_..


RLL pneumonia
_..

left: sharp angle
vomit and then pneumonia: usually right sided
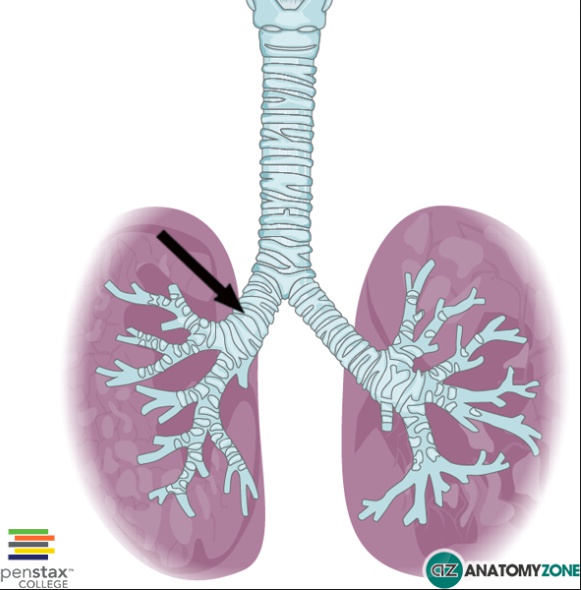

supine: superior portion of right inferior lobe or posterior portion of right upper lobe
_..

right PA: anterior to right bronchus
left PA: superior to left bronchus
_..

caval foramen: IVC
esophageal hiatus: esophagus
aortic hiatus

_..

dyspnea: can't contract diaphragm to breath
other side move down, push affected side up
Respiration
_..

quiet: diaphragm sole muscle

accessory muscles: in hospital, see pts contract neck/abd when breathing = respiratory distress
Respiratory tract
_..

URI: does not involve lower respiratory tract (sinusitis, pharyngitis, etc.)

_..

barrier to infection
Alveoli
_..

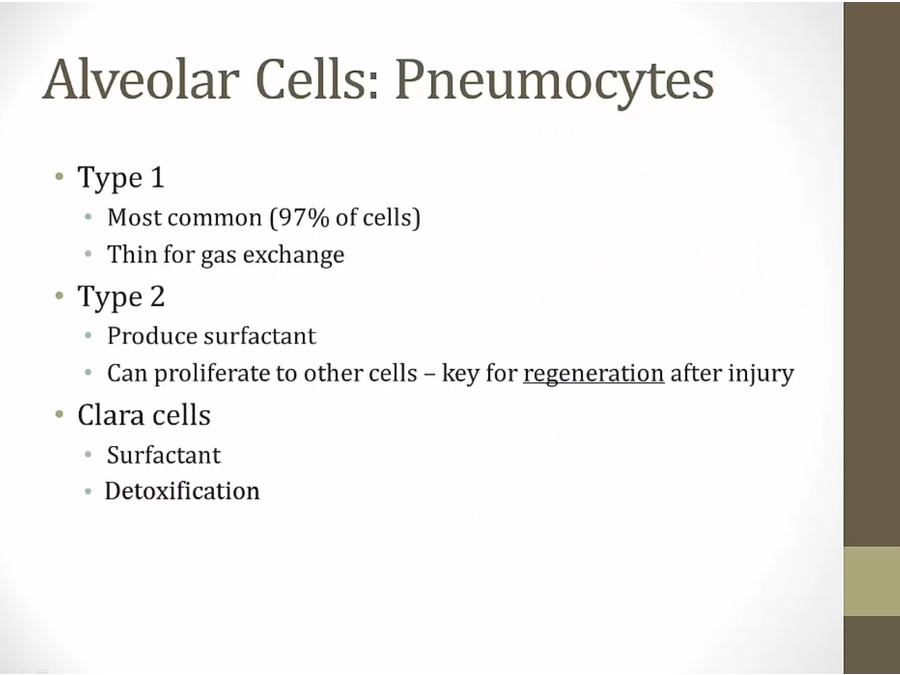
clara: not in alveoli, in terminal bronchioles
Surfactant
_..

surfactant: alveoli stay open when exhale

Laplace law
if pressure in sphere below distending pressure, alveoli collapse
low sphere: small radius, distending pressure high, takes more pressure to keep small sphere open, also more likely to collapse
when inhale, alveoli gets large; when exhale, gets smaller
result: when alveoli need the air to keep open, air leaves, distending pressure gets high
surfactant shrinks surface tension as radius falls during exhalation
when exhale, surfactant molecules gets closer, concentration higher, reduce surface tension
falling radius and surface tension offsets one another

NRDS
_..

NRDS if not mature
_..

hyaline: glass like, what alveoli looks like
give O2: all goes to healthy alveoli, sick ones collapsed (shunting)

high glucose from mother stimulate baby's pancreas to make insulin

all related to O2
bronchopulmonary dysplasia: hyperplasia and fibrosis of airways (exposing premature lung to high O2 concentration, O2 toxicity)
Last updated