07 Glycogen
muscles cannot release glucose from glycogen

1-4 linear linkage
1-6 branching
branching makes it more soluble and better storage


UDP: uridine

lysosomes can collect glycogen and break it down to glucose


glycogen phosphorylase shrink purple link down to 3 or so
debranching enzyme moves purple to red, releasing one molecule of glucose (green)
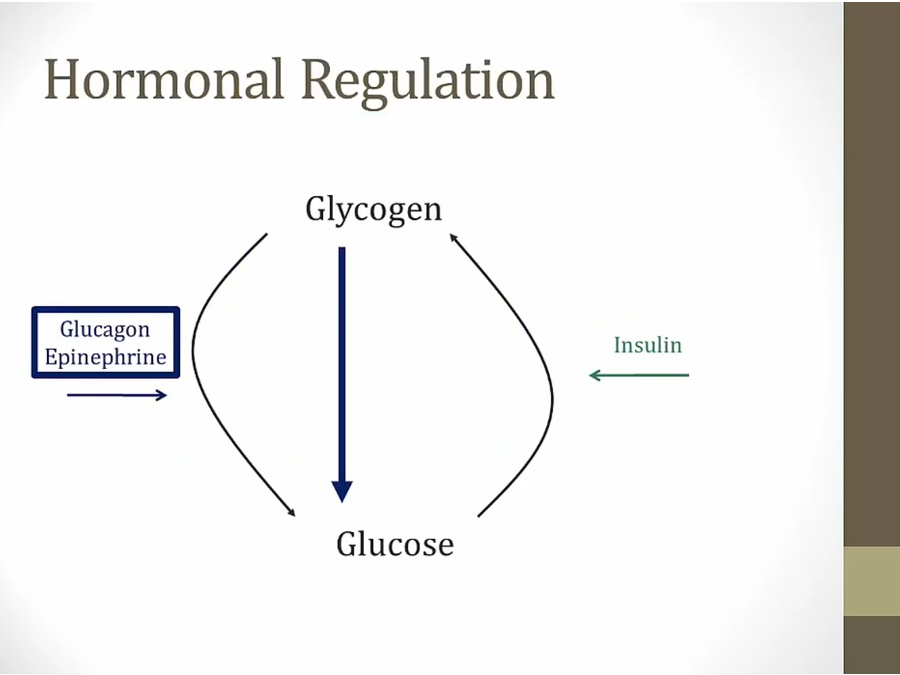

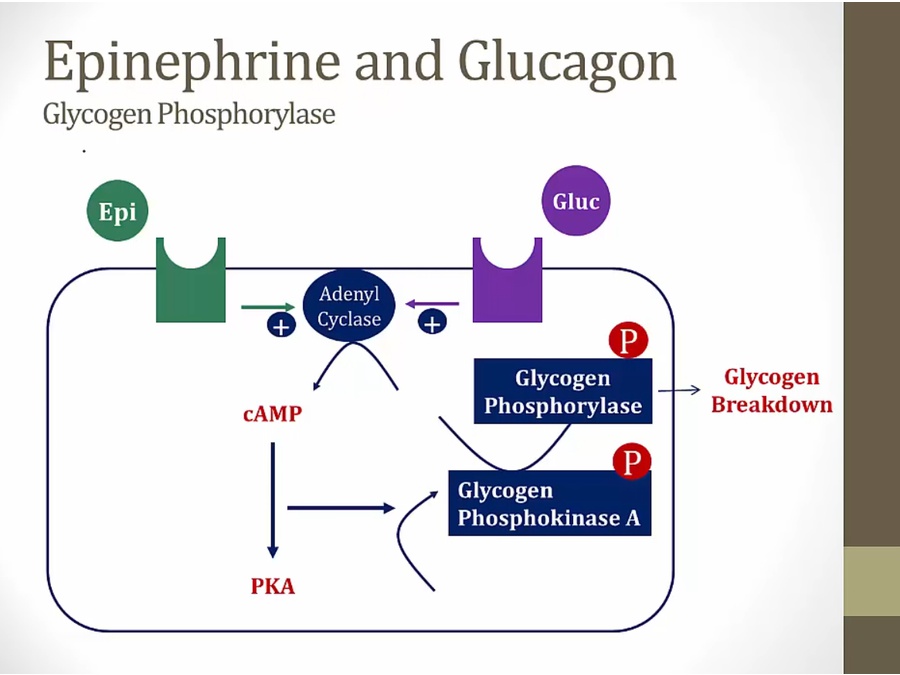
glucagon/E phosphorylates both enzymes both have opposite effects
glycogen phosphorylase activity increases
glycogen synthase activity decreases

insulin results in dephosphorylation of both and opposite effects



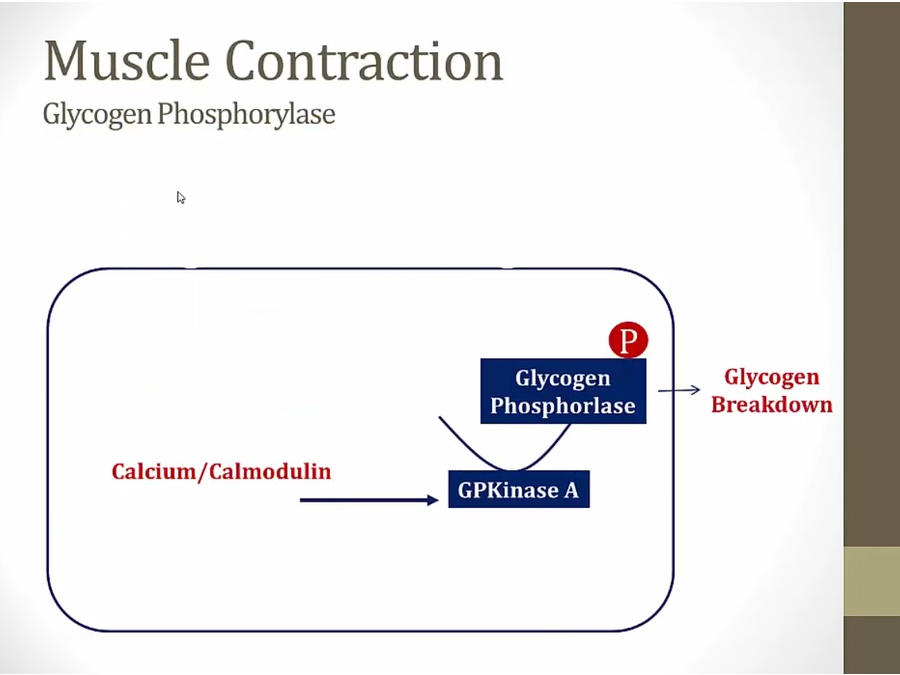
activate glycogen phosphorylase in absence of hormones
immediate activation instead of hormonal


Glycogen Storage Diseases

liver defective enzyme: hypoglycemia
enzyme defective in muscle: weakness
Von Gierke

can't release glucose between meals
can't get glucose out of liver = hepatomegaly

muscles will be ok
no symptoms of muscle weakness

consume corn starch between meals
Pompe


liver is ok, continue make glucose
no hypoglycemia symptoms

entrapment of glycogen inside muscle cells
enlarged tongue classic finding
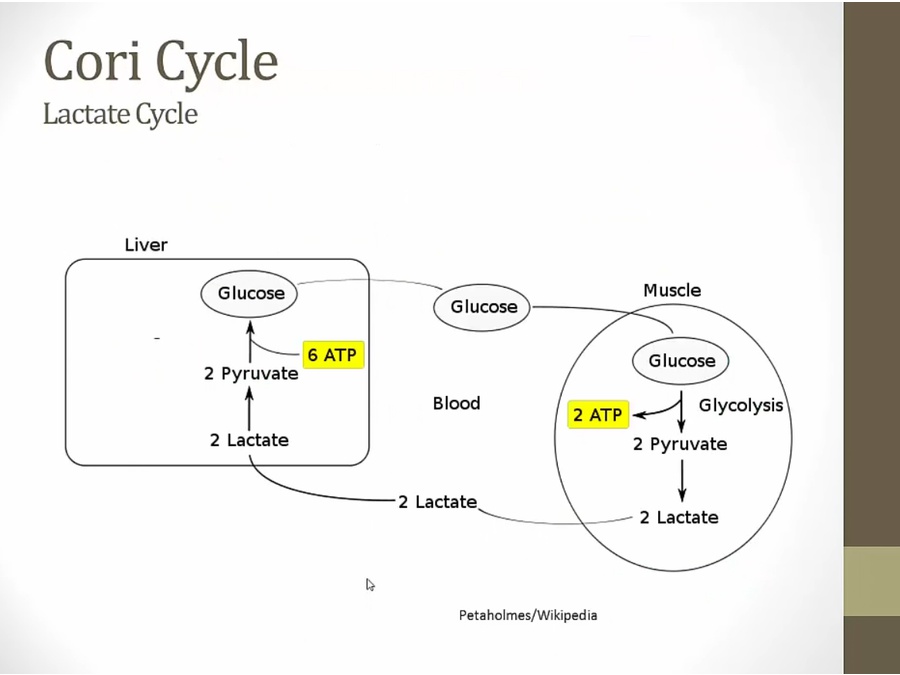
Cori


gluconeogenesis intact from other sources: hypoglycemia not as severe
no glucose in muscles either: weakness

usually no seizures
muscle symptoms distinguish from Von Gierke
McArdle

no liver problems, no hypoglycemis
muscle difficulties
can get muscle damage with exercise
Last updated