02 NICU
Bronchopulmonary Dysplasia
Patho: longterm consequence of RDS:
Decreased surfactant, derecruitment of alveoli, lungs underdeveloped, O2 can't get to lung, lung scars
Demographics: premature infant with increase O2 demand who gets:
Increase FiO2 (risk for other things) > 28 days
Lung protective strategy to keep pressure down to avoid damage
Diagnosis: Xray, ground glass opacities
Treatment: surfactant postnatal. Corticosteroids to mom antenatal
complication: Diffused parenchymal lung disease from scarring.,
Retinopathy of Prematurity
patho: neoangiogenesis, worsened by increased FiO2
Demographics: premature infant, increased FiO2
Diagnosis: eye exams for all premature babies, see blood vessels
Treatment: laser ablavation
complication: eye blindness, early glaucoma even after treatment
Intraventricular Hemorrhage
path: highly vascular ventricles (involutes around wk 34), change in BP (septic shock, fluids)
demographics: premature before wk 34, screened with cranial doppler and imaged later on
symptoms: bulging fontanelles, ICP
diagnosis: cranial doppler
treatment: decreased ICP via surgery. VP shunts, drainage
complication: retardation, seizures.,

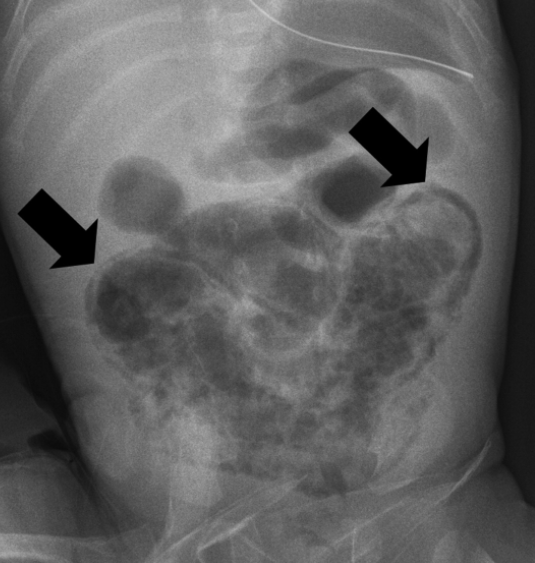
Necrotizing enterocolitis
path: dead gut
demographics: premature, in NICU for other problems
symptoms: ICU baby start having bloody bowel movement
diagnosis: xray shows air in wall (pneumatosis)
treatment: NPO, TPN, IV antibiotics against bowel anaerobes, surgery
complication: surgery and shortgut syndrome
Last updated