11 Diabetes
Overview
Diabetes: meaning polydipsis/polyuria..

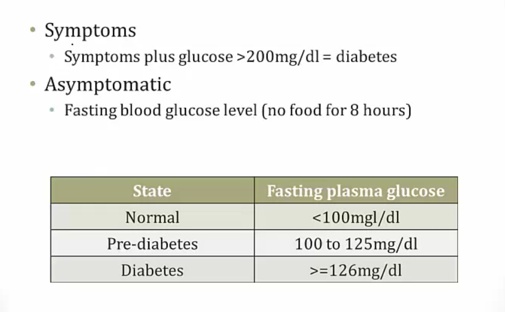
Diabetes Symptoms
_..

Complications:
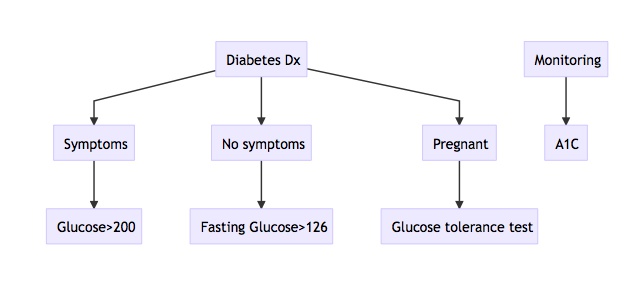
Diabetes Diagnosis
_Diagnosis:..
Asymptomatic as in no polyuria/polydipsia..
Glucose Tolerance Test
Just measuring glucose level is not helpful because elevated in pregnancy
Measuring glucose load response more helpful..

Hemoglobin A1C
_..
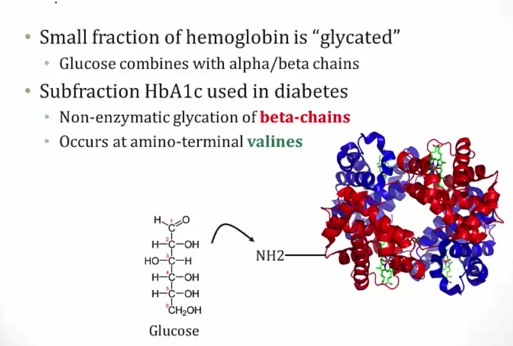
3 months because RBC lives for 3 months..

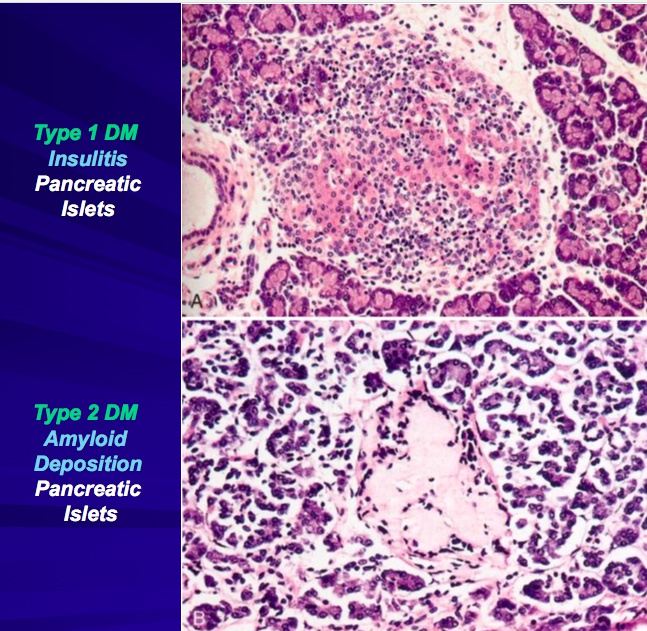
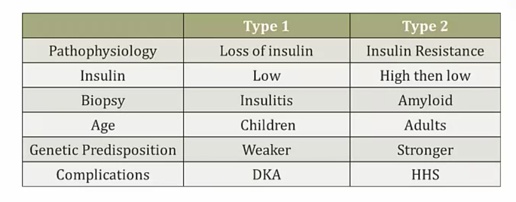
Type 1 Diabetes
aka insulitis


Islet cell antibodies are found in the vast majority of T1DM patients, as well as asymptomatic family members. Islet antigens that are the targets of autoimmune attack may include insulin and the β-cell enzyme glutamic acid decarboxylase (GAD).
.,
_Association with HLA-DR3 and DR4.,
_.,
lifelong insulin

weight loss, low muscle mass, always wanting to eat
..
Diabetic Ketoacidosis
 .,
.,
Type 2 still has insulin, thus less common
 .,
.,
Trauma/infection increases epinephrine
Fruity breath from acetone
Dehydration -> hypotension
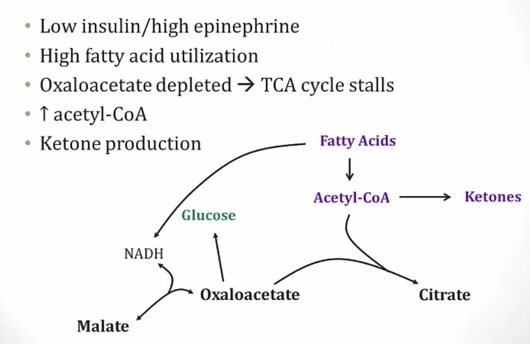
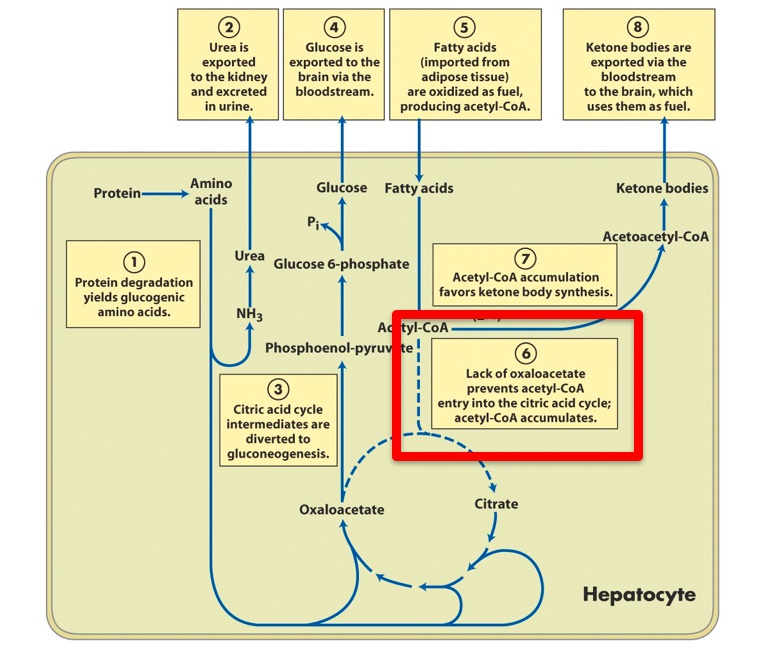
Ketones made from lipolysis
Oxaloacetate depletion from high NADH pushing towards malate
can get mild hyponatremia from loss of Na in urine
_..
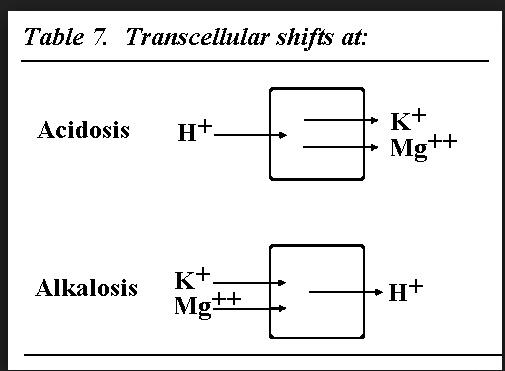
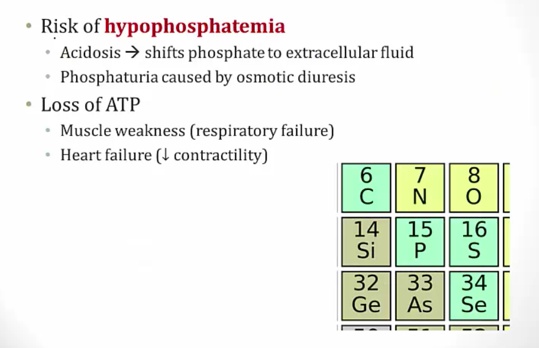
.,
Patients with DKA and respiratory failure, always ckeck phosphate
_Symptoms:


.,
_..
Hyperglycemia long term > brain makes taurine molecules to match osmolarity (doesn't happen in type 2)
Give fluid too fast > blood osmolarity drop
Water goes to brain, brain edema
Use IV mannitol to treat
_Associated with mucormycosis:.,
classic case: DKA patient in recovery with new onset fever/headache/eye pain
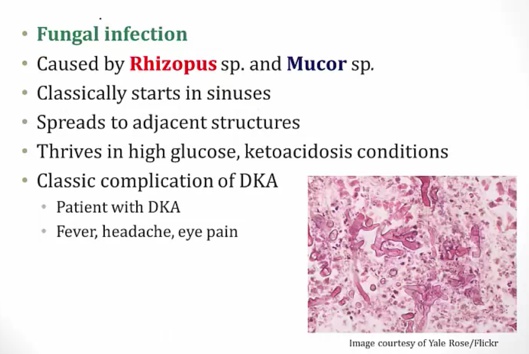
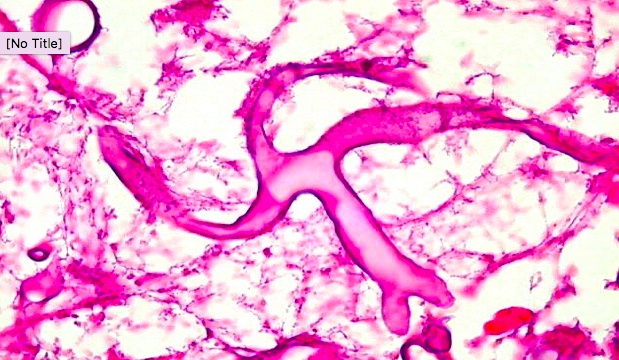
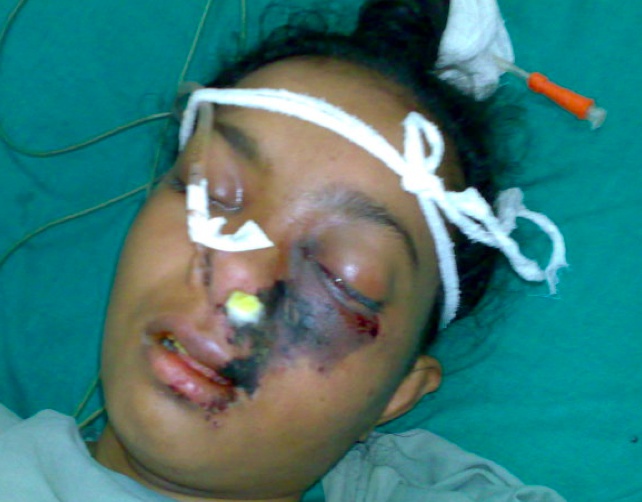
_Treatment:

K lost in urine. Add K after a few hours of insulin

.,
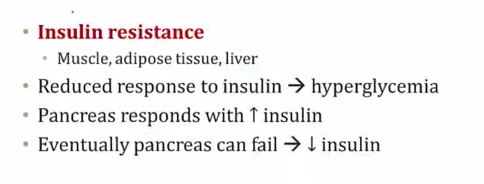
Type 2 Diabetes
.,

.,

more free FA bad because used for fuel instead of glucose
Left: apple shape. Right: pear shape..
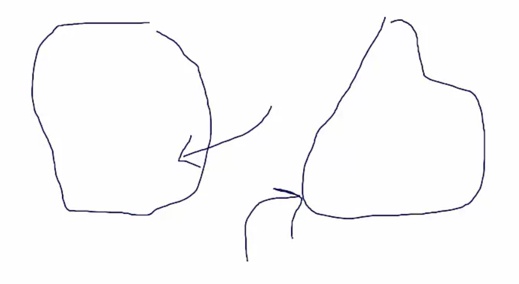
_..

Insulin Resistance
_..
Type 2 associated with obesity
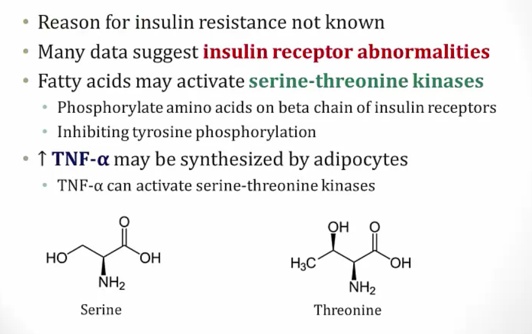
Adipocytes make TNF-a and FA
TNF-a and FA activates serine-threonine kinase
serine-threonine kinase phosphorylates beta chain, inhibits tyrosine phosphorylation
result is decreased number of available insulin receptors
Amyloid
_Histology

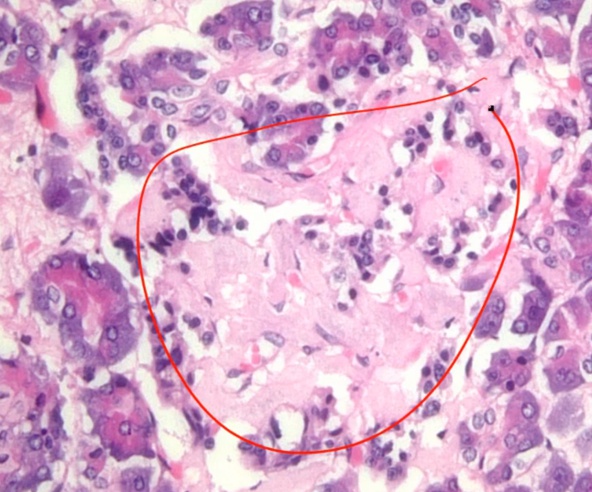
.,

accumultates in type 2 diabetes islets
Acanthosis Nigerians
_..

Insulin tells keratinocytes to grow
Hyperglycemic Hyperosmolar Syndrome, HHS

.,
Similar to DKA of type

high serum osm from glucose

.,
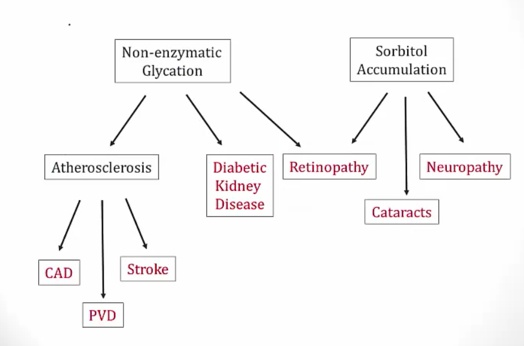
Diabetic Complications
_..


Nonenzymatic Glycation
_..

AGE cause problems
_..

Macroangiopathy:..
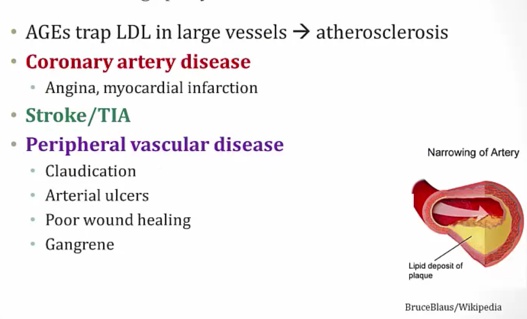
Microangiopathy:..

put on dialysis
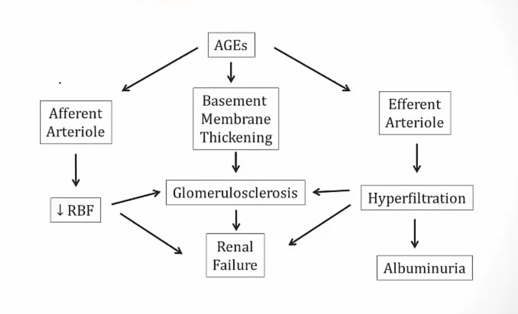

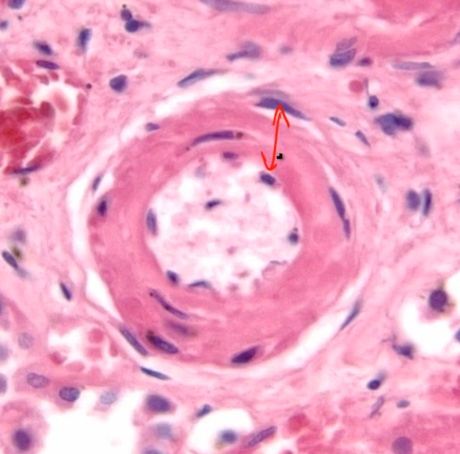
Caused by AGE and hyperfiltration..

_..

_..

Sclerosis of entire kidney:
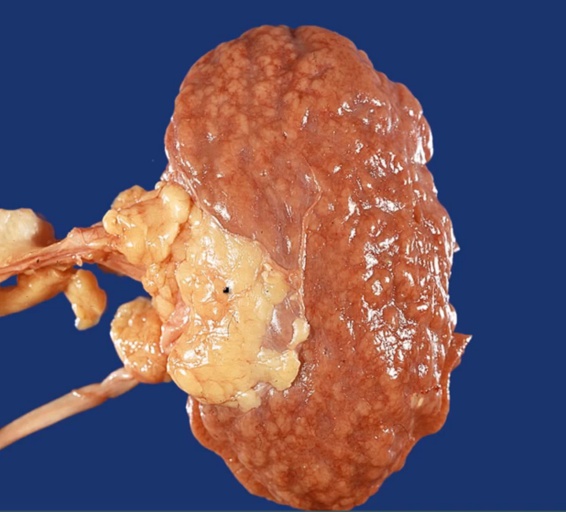
pyelonephritis and scarring with infection. Atrophic and smaller:
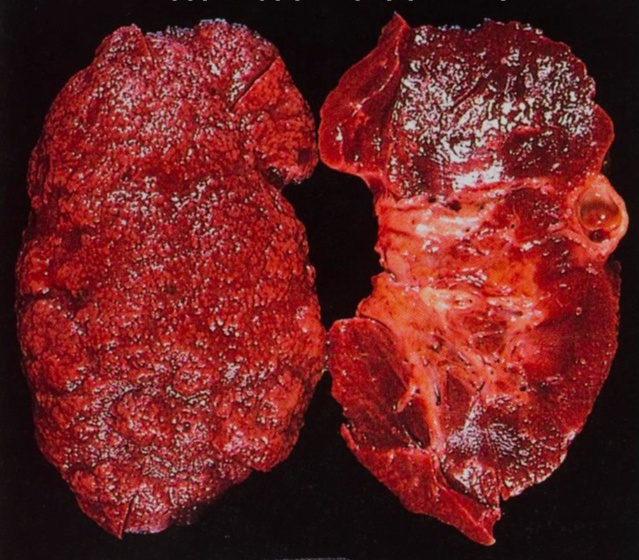
papillary necrosis, triangular necrosis:
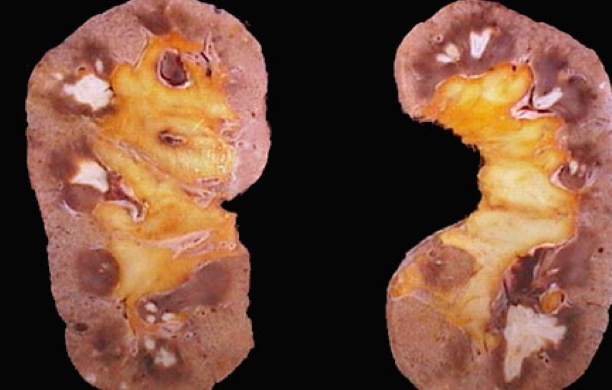
Diffuse:
Nodular:
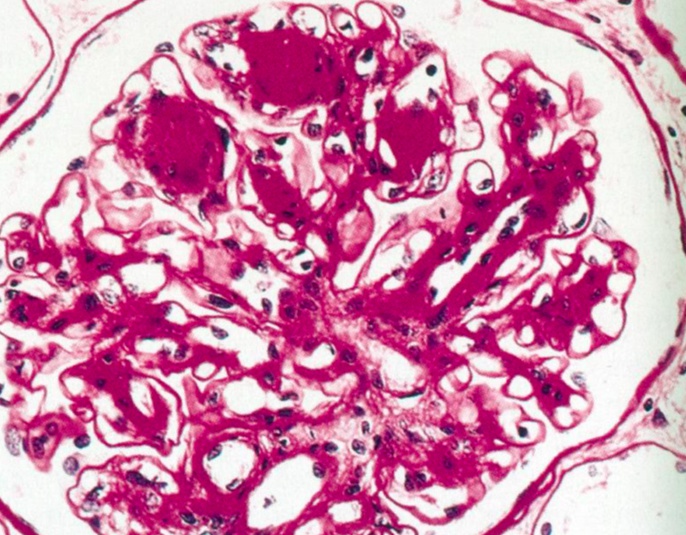
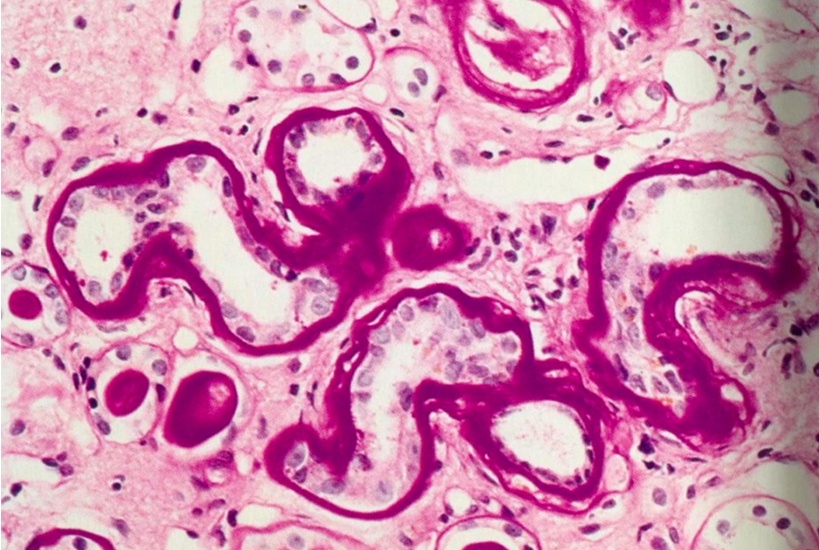
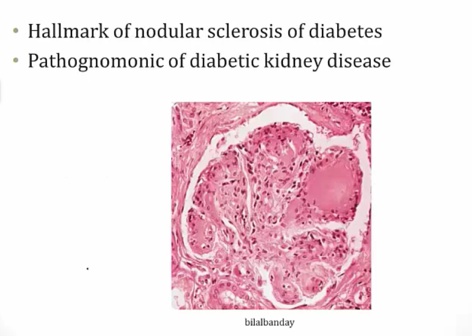
Kimmelstiel-Wilson Nodules
_..
Sorbitol
_..

Polyol pathway
_Alternative glucose pathway:..
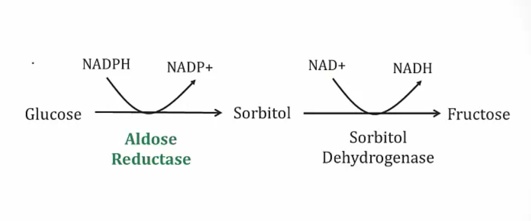
Little activity at normal glucose level but increased activity at chronic hyperglycemia
End result is increased sorbitol because second step is slow
_..

_..

_..
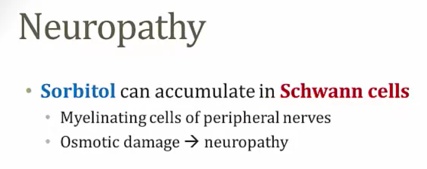
_.,
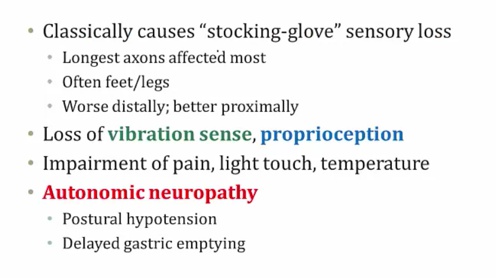
sensory loss more than motor
distal more than proximal
B12: equally proximal and distal
diarhea
Diabetic Foot Disease
_..

PVD: peripheral vascular disease
_..

O2 chamber drives O2 into ulcer for healing
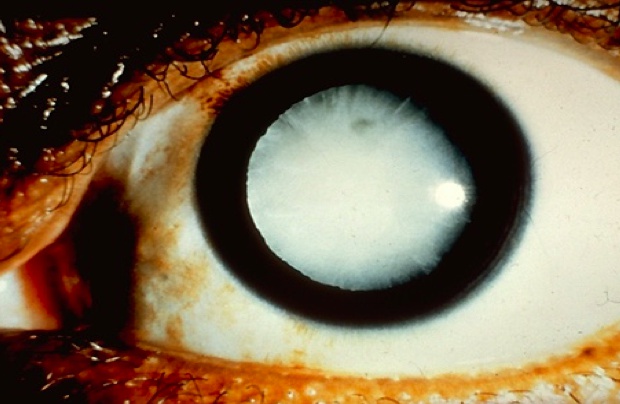
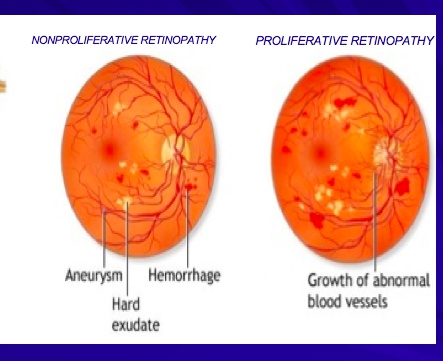
Diabetic Retinopathy
_..
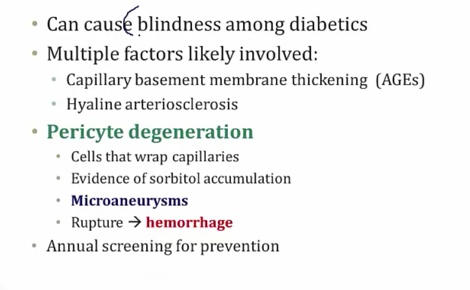
Both AGE and sorbitol involvement
_..
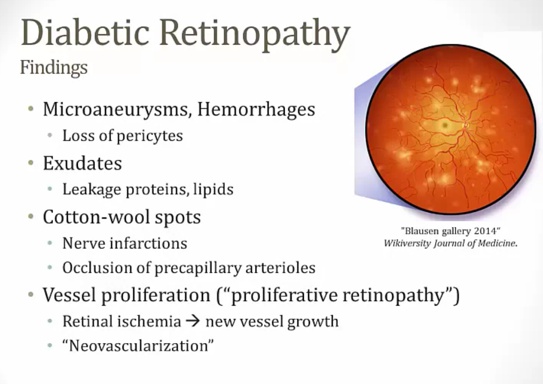
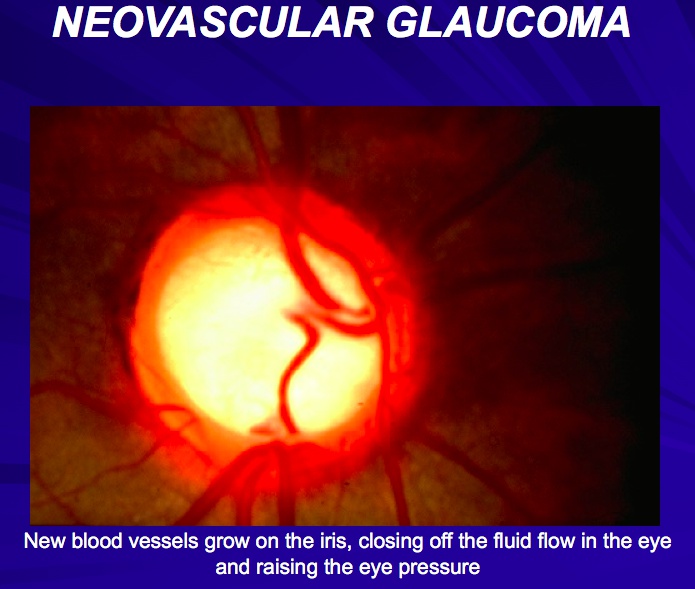
_..
Last updated