23 Porphyrias
Porphyrins Metabolism


anything increases activity of P450 can exacerbate condition


anemia can result with severe inhibition of enzymes

Porphyria

two common ones are hepatic porphyria: heme synthesis affected in liver
PCT

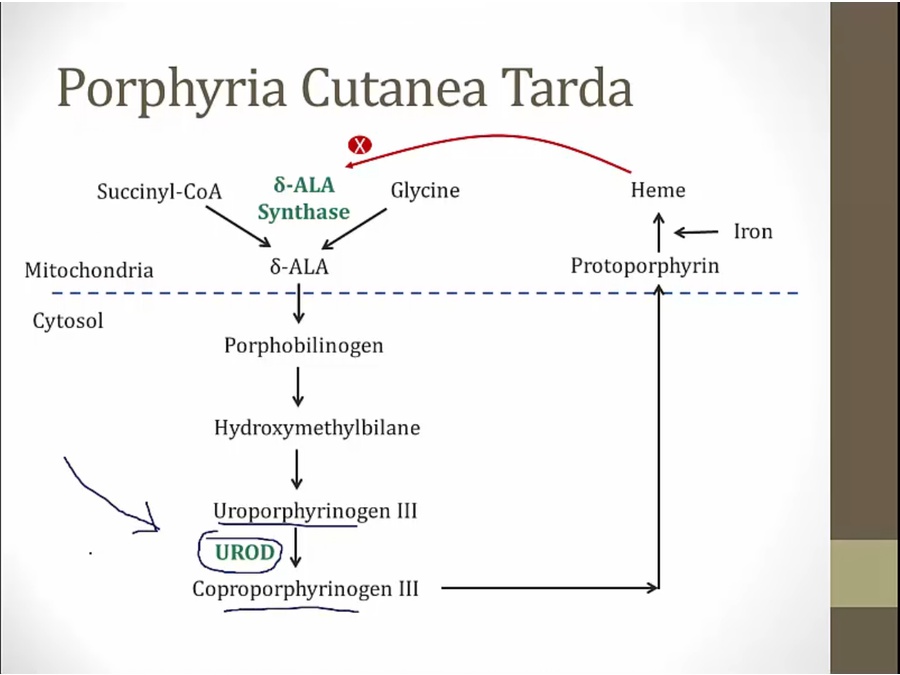

some carboxyl groups have 3 carbons, others 2

A for acetic, P for propionic

Uroporphyrinogen III must be oxidized, lose H2, to be converted to uroporphyrin III

skin major symptoms (cutanea)

heptatitis from uroporphyrins accumulation in liver
in kidney: tea colored urine
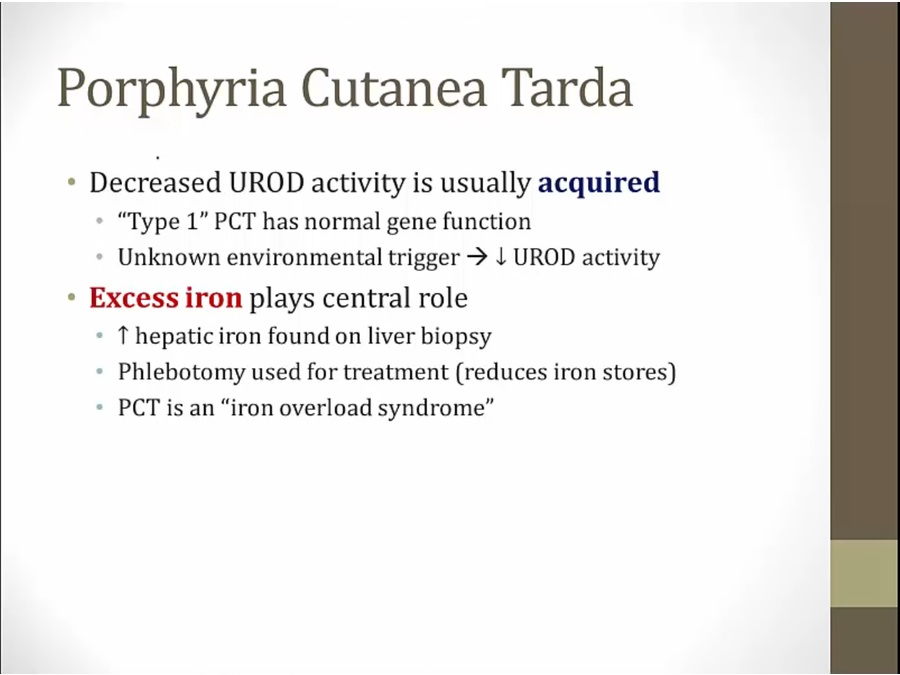
iron overload like hemochromatosis


determine high porphyrin, then fractionate to determine high uroporphyrin


vampire hypothesis
consume heme/blood, inhibit heme synthesis
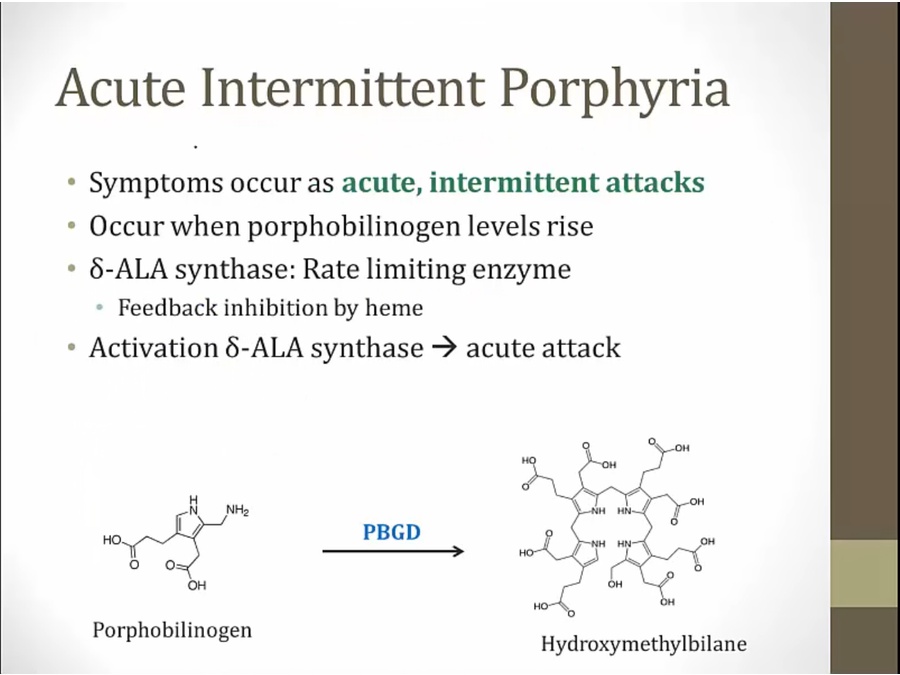
Acute Intermittent


late in pathway: skin symptoms
early in pathway: neurologic symptoms
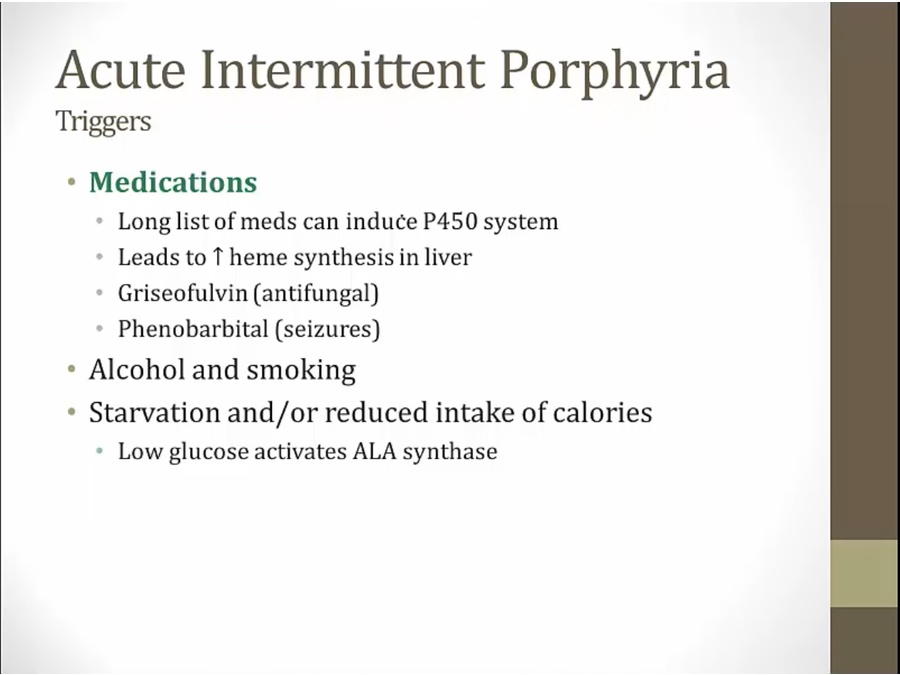
low glucose, increased ALA synthase, rising heme

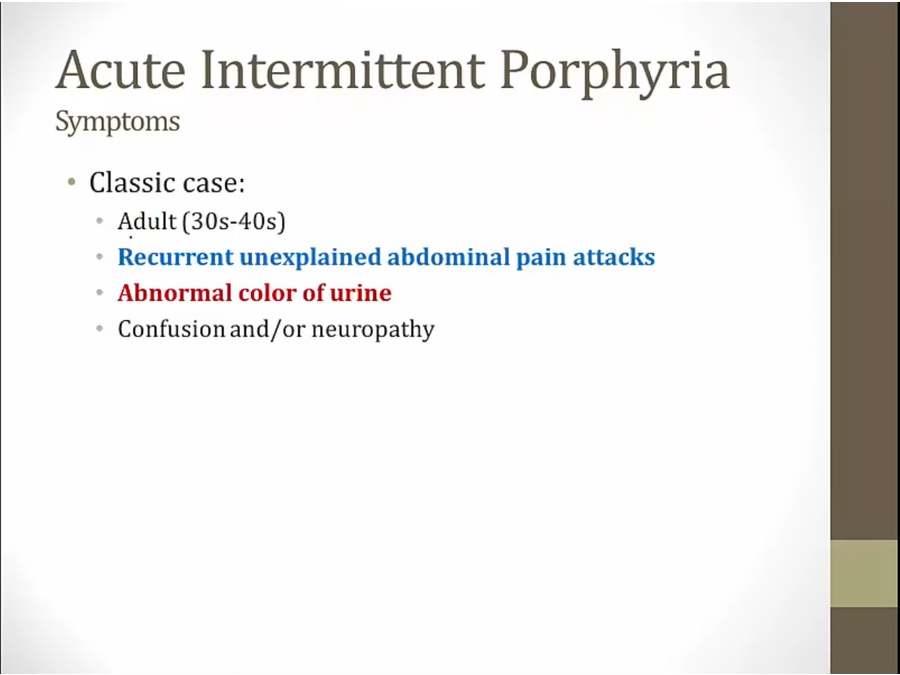
confusion, delirium, dementia
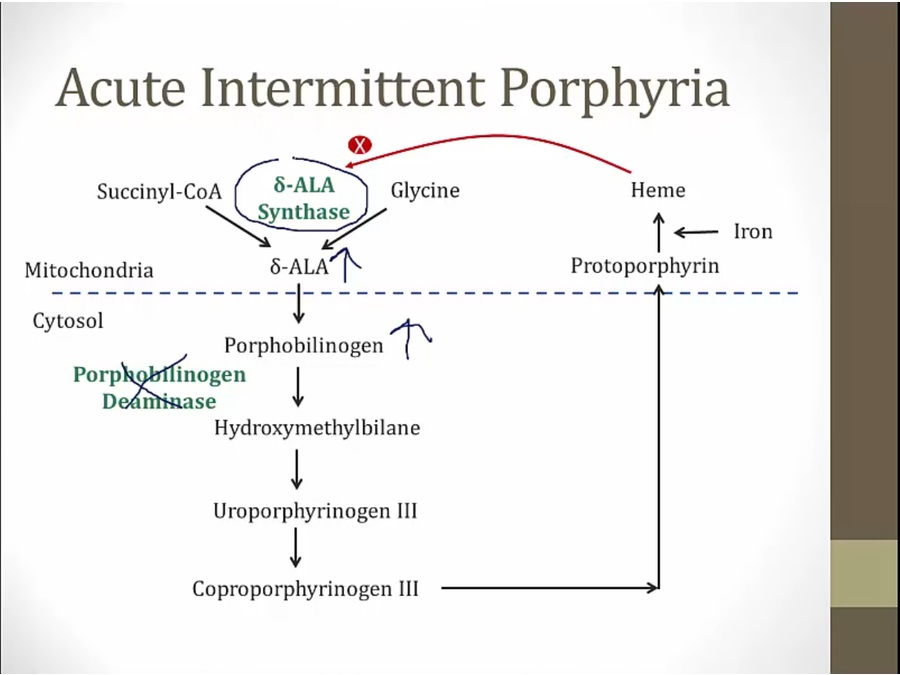
inhibited porphobilinogen deaminase and increased D ala synthase leads to increased D ala and porphobilinogen
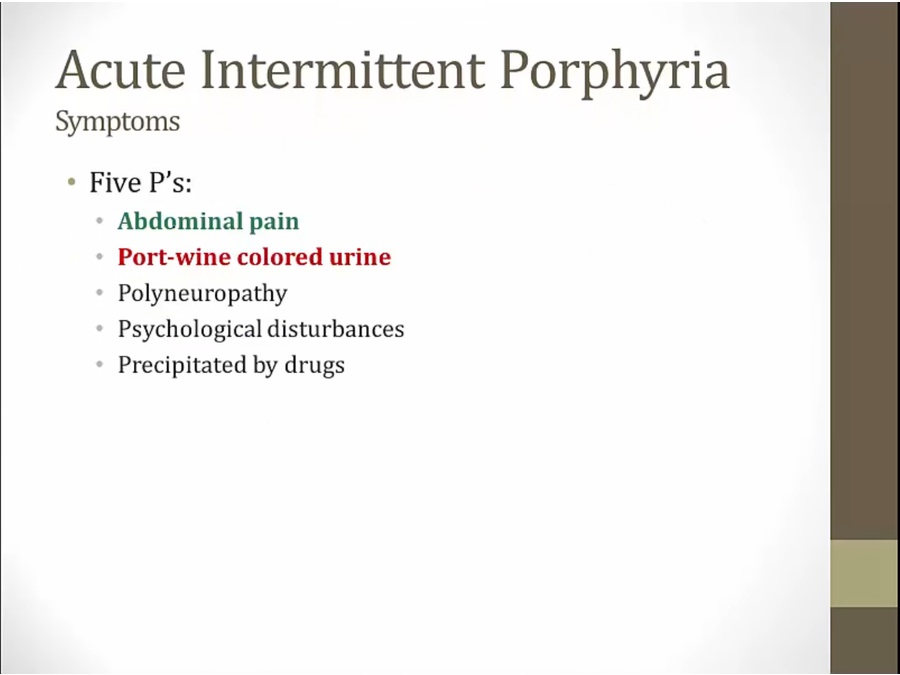
urine darkens over time

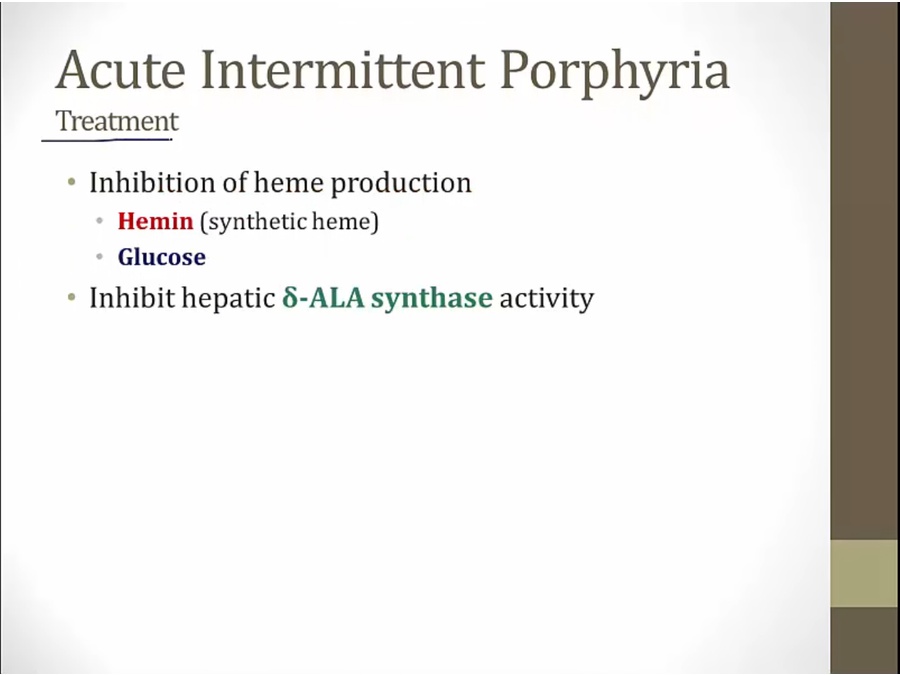
avoid triggers
Last updated