01 Innate Immunity
_..
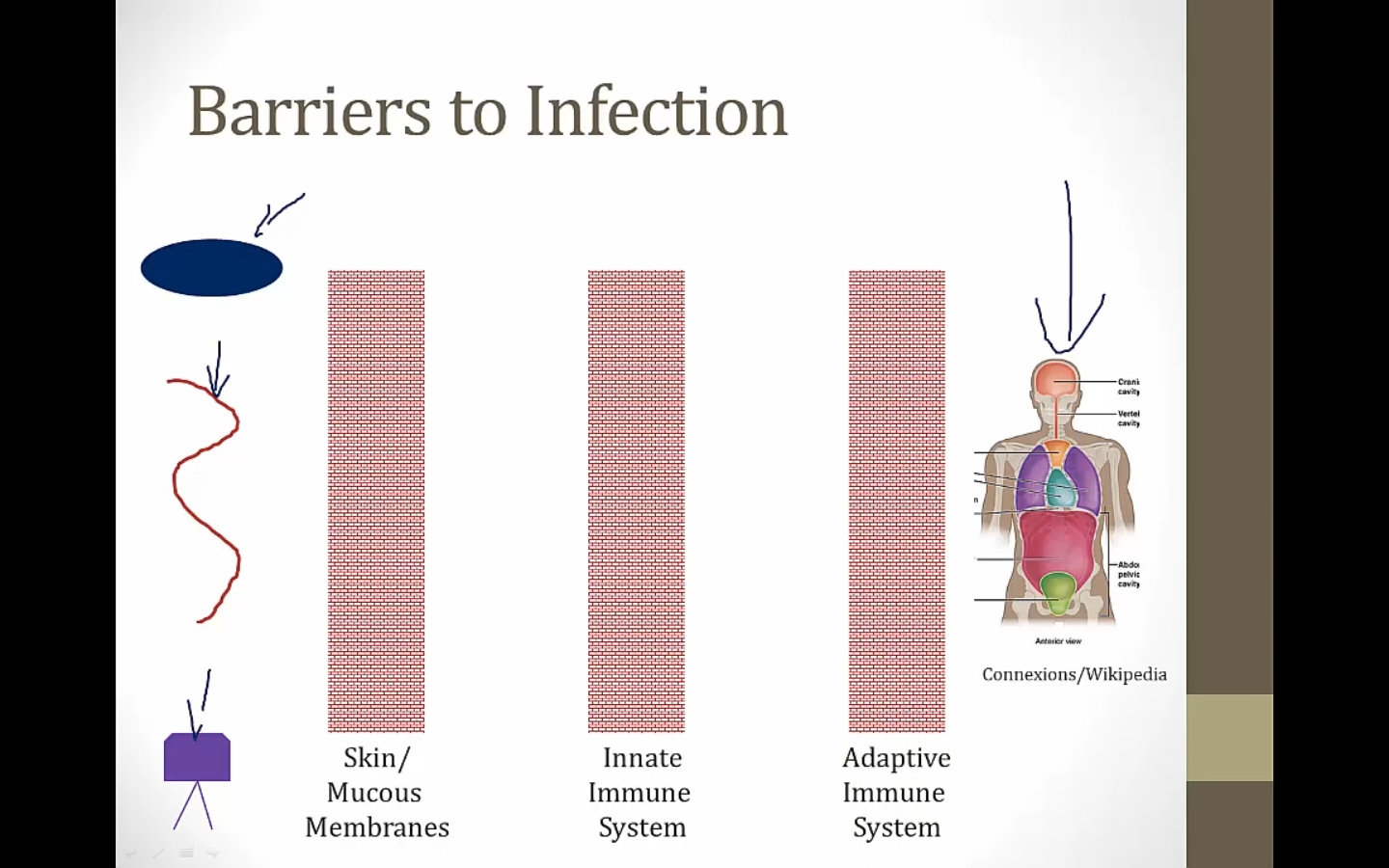
Innate vs adaptive
_..

_..

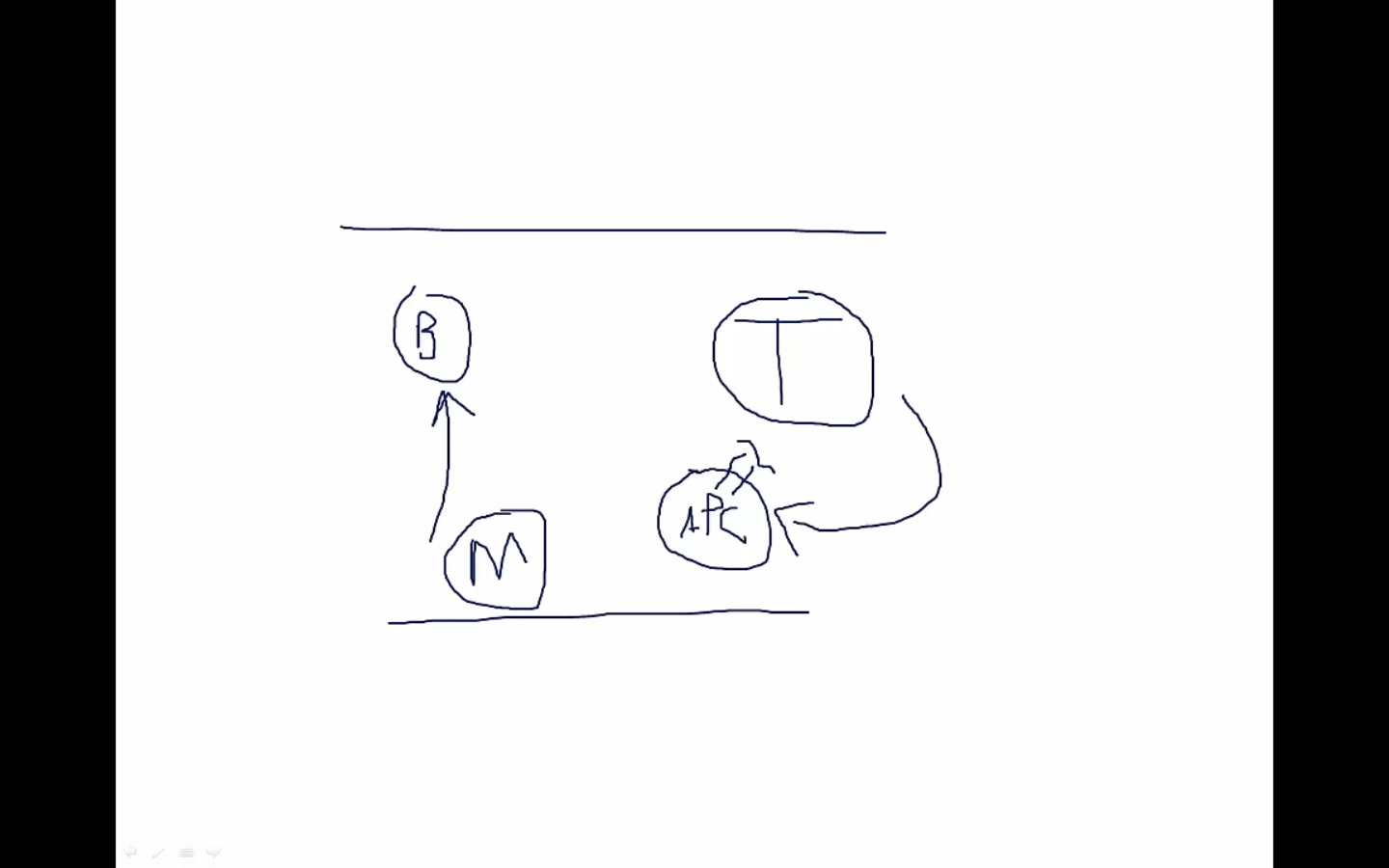
Innate immune response can react directly to invaders
T cells require antigen presentation from APC
If T cells can react to any thing, then autoimmune problems
Cytokines
_..

interleukins: travel between leukocytes
CD
_..

Innate
_..

Neutrophils on call to assist macrophages when needed
_..

_..


Virus have double stranded RNA and some single stranded RNA that transiently gets copied to double
DNA in human is methylated; bacteria has unmethylated DNA
Macrophages
_..
macrophages guards, ready to consume any foreigners
_..
Phagocytosis
_..
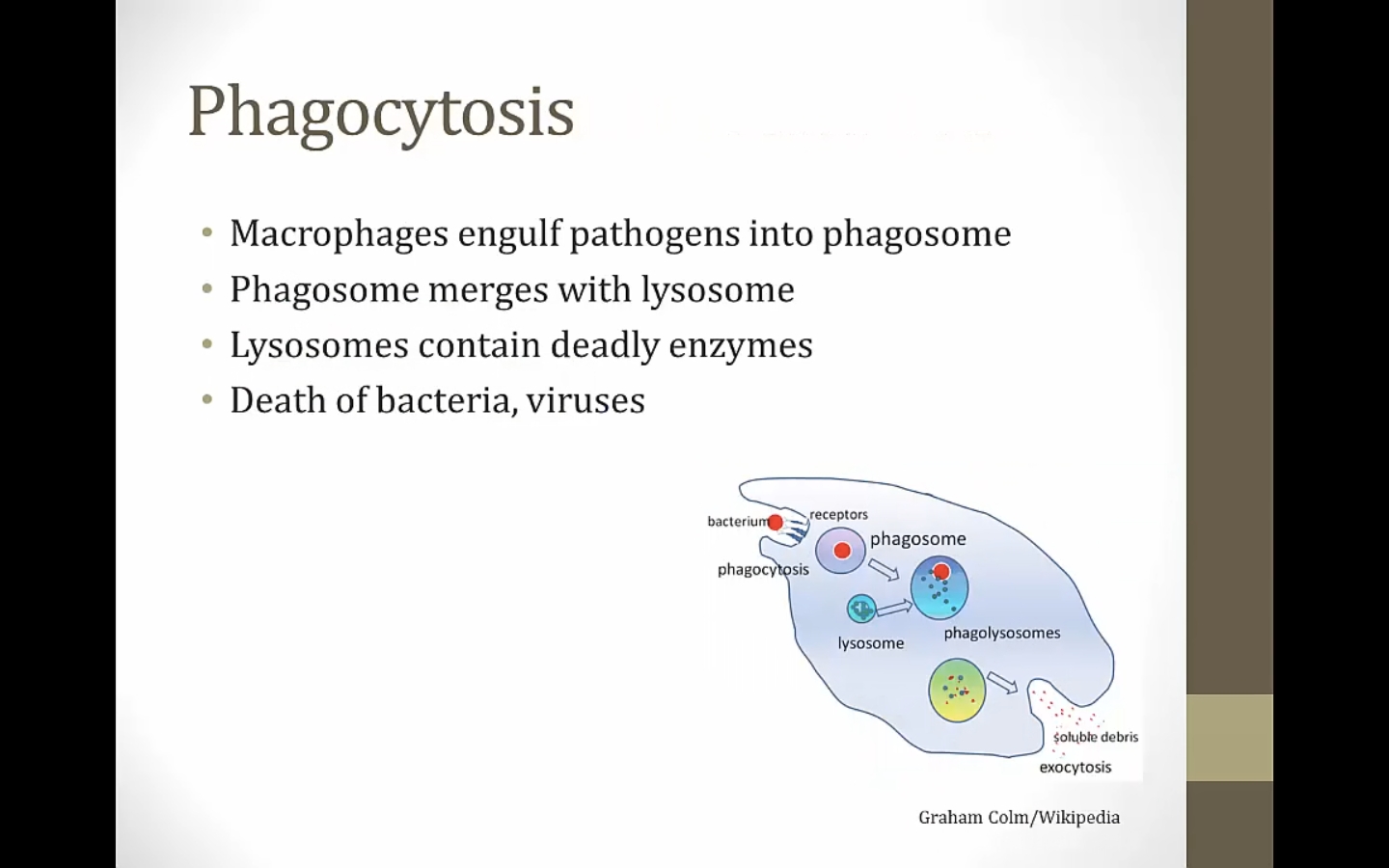
_..
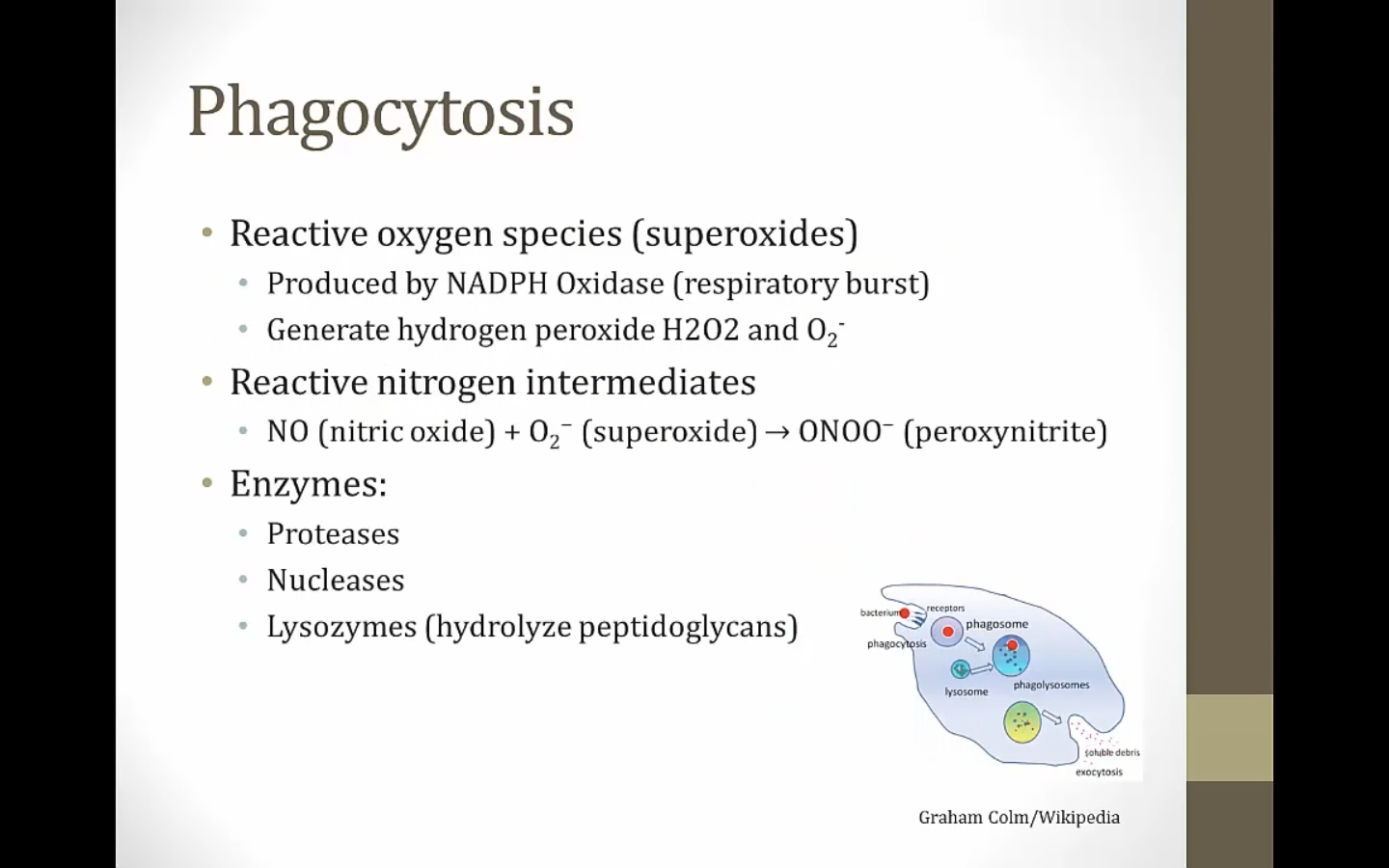
proteases break down proteins, nucleases nucleotides, lysozymes cell wall

tissue destruction from macrophages/neutrophils
_..

TB modifies surface of phagosome
_..

_..

Cytokines
_..

macrophages 1st line of defense: IL-1
_..

macrophages 1st line of defense: 1st IL
IL1 raises set point temperature
TNF-a kills tumors by causing coagulation in tumors, but can also cause DIC
_..

Neutrophils
_..

backup cells to macrophages
_..

SL X: carbohydrate

Neutrophils always have SL X, normally nothing to bind to
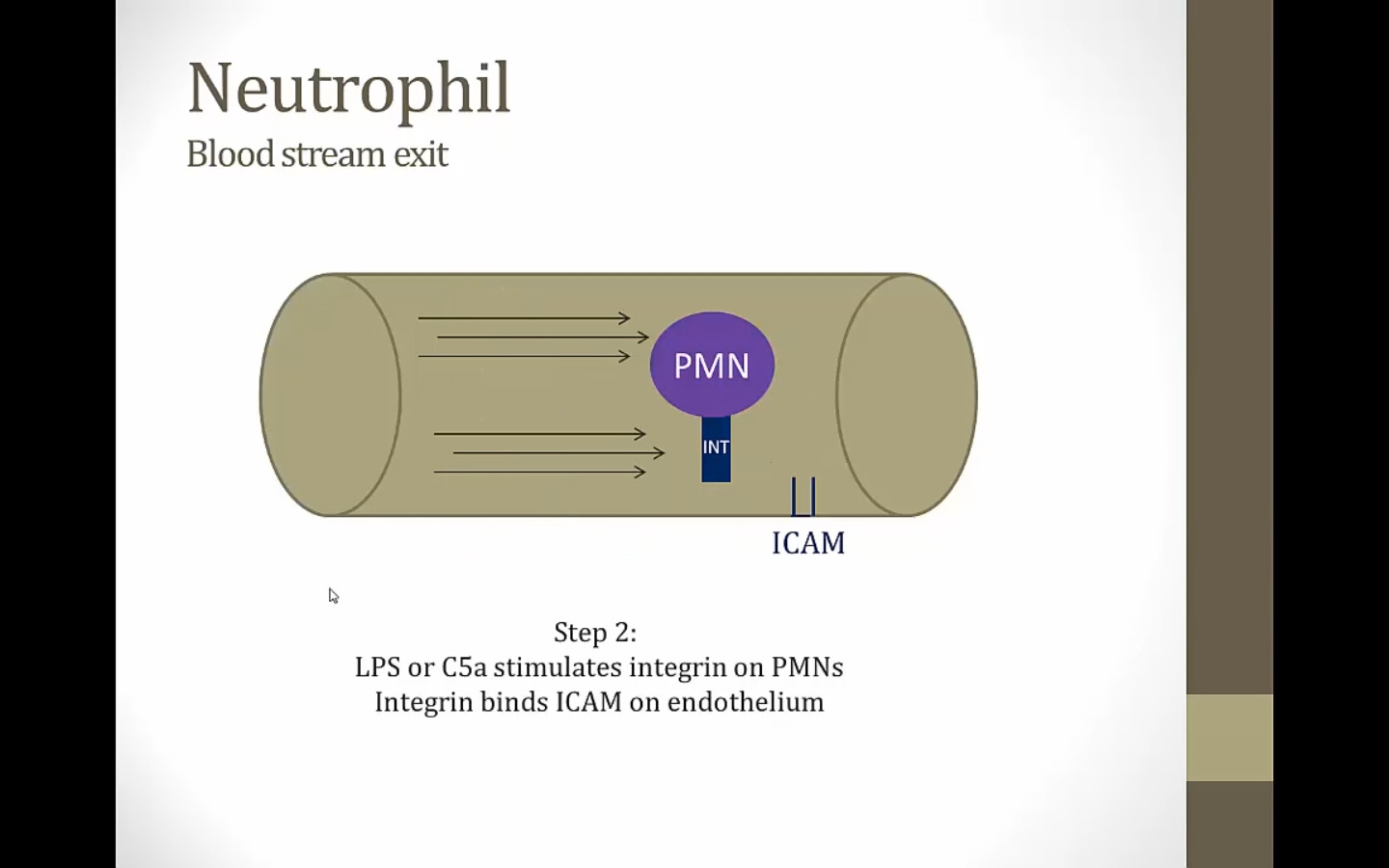
ICAM always on endothelial cells, normally can't bind anything
_..

alk phos: low in some leukemias (CML)
collagenase: breaks down collagen; lysozyme: breaks down cell wall; lactoferrin: found in breast milk and binds iron, lyse bacteria and kill cell in neutrophils

_..

LTB4
Complement
_..
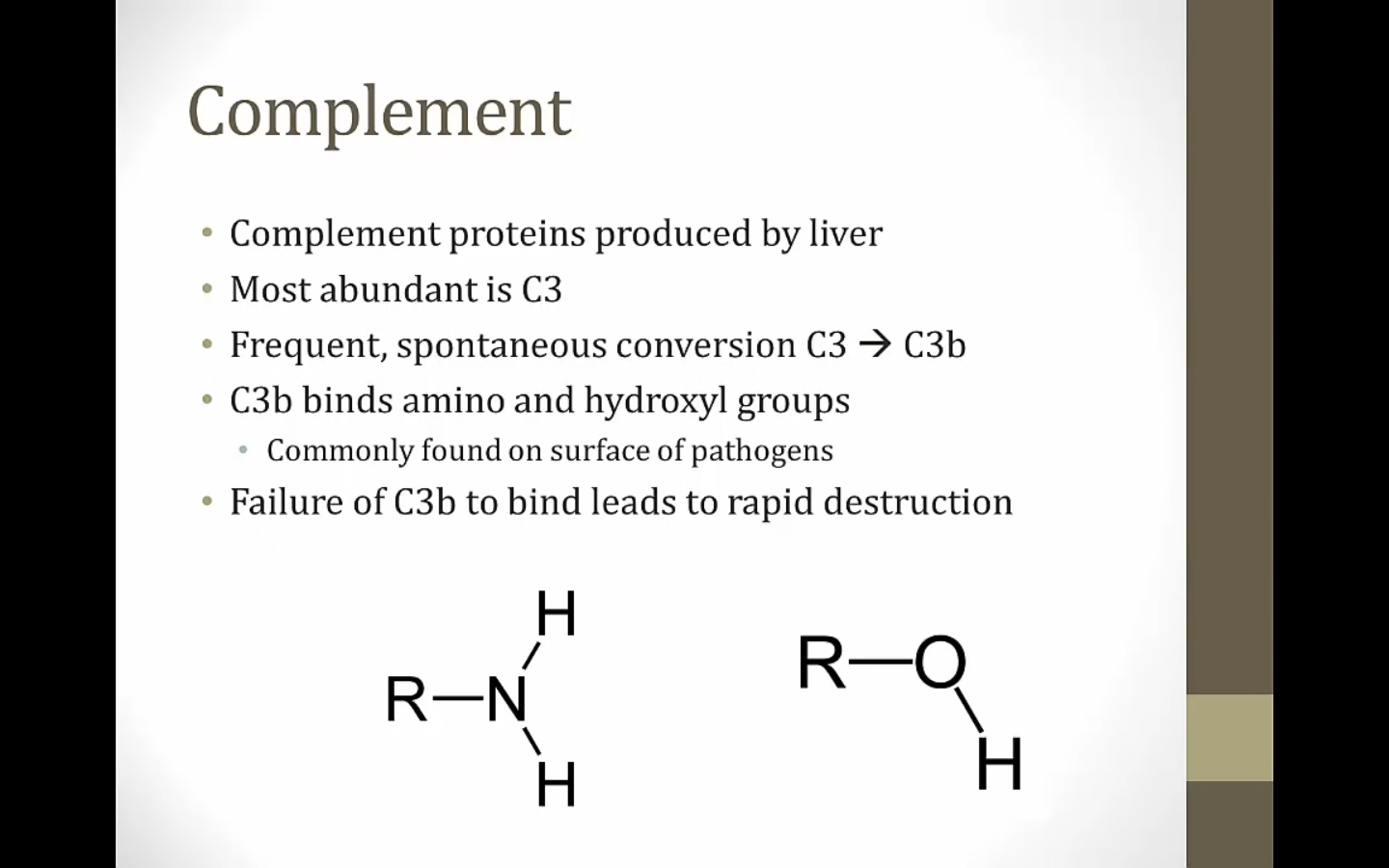
alternative pathway: spontaneous conversion

NK cells
_..

_..

_..

ADCC
_..
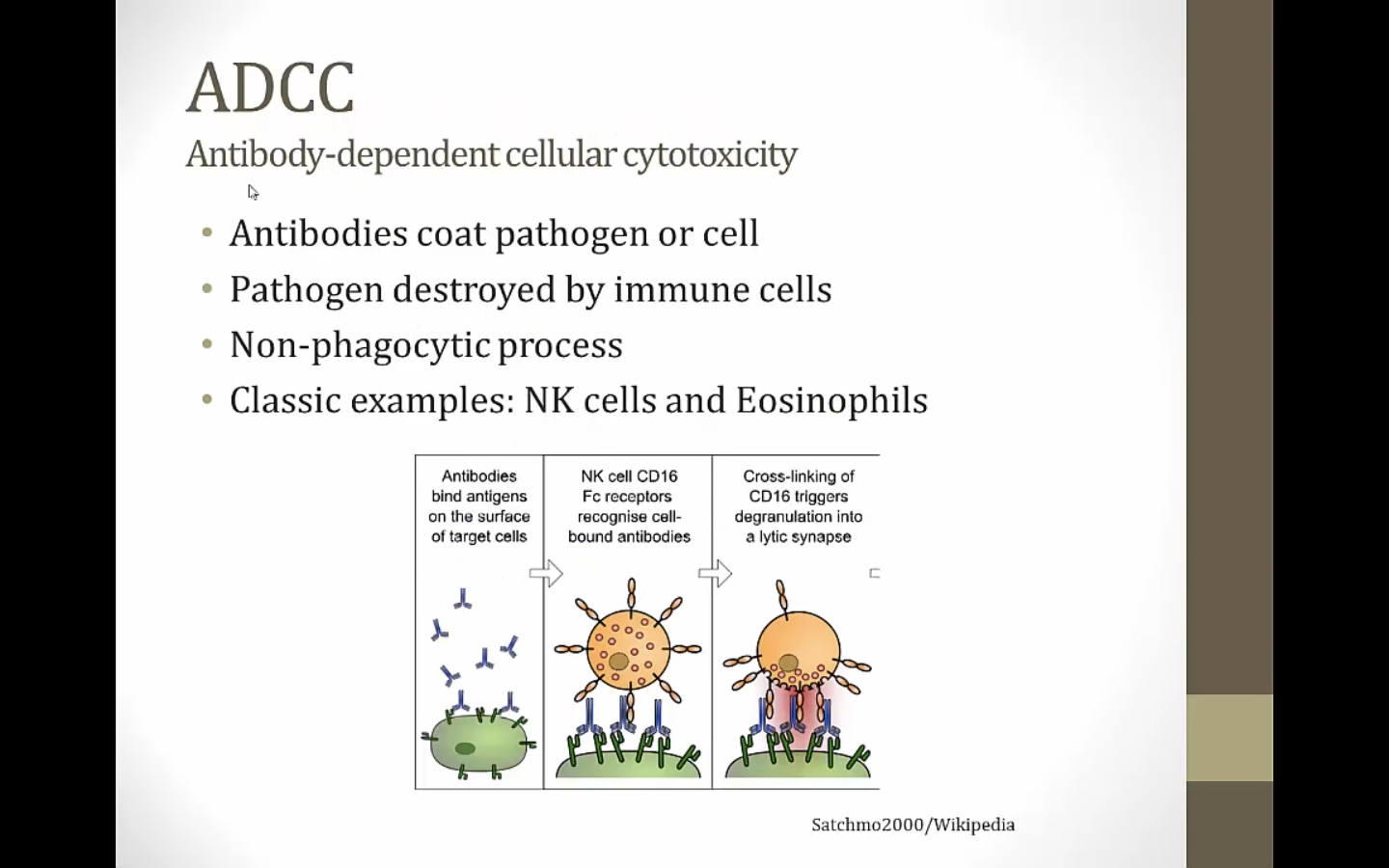
antibodies elements of adaptive immune system

_..

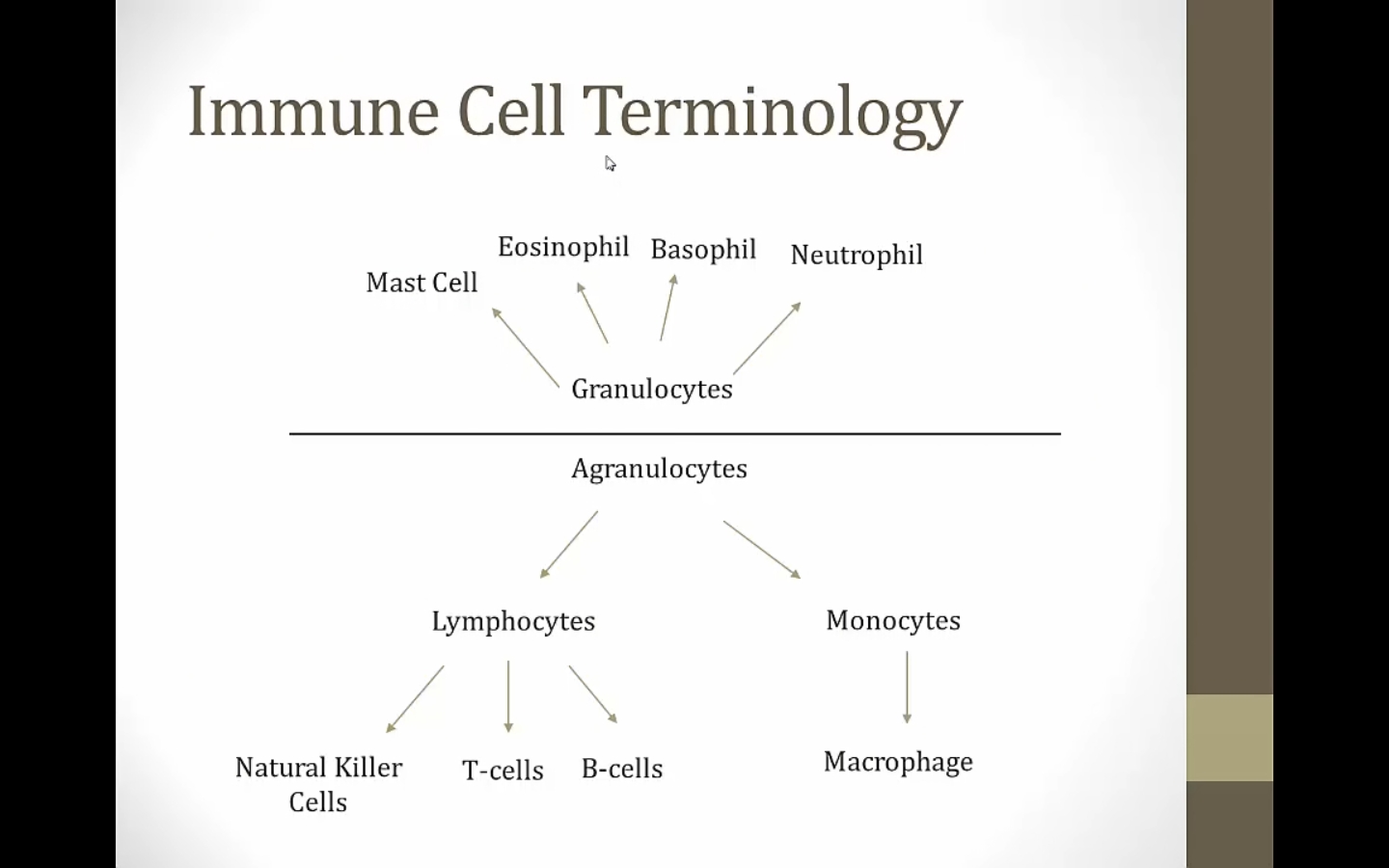
NK part of innate; T/B part of adaptive
Eosinophils
_..

_..
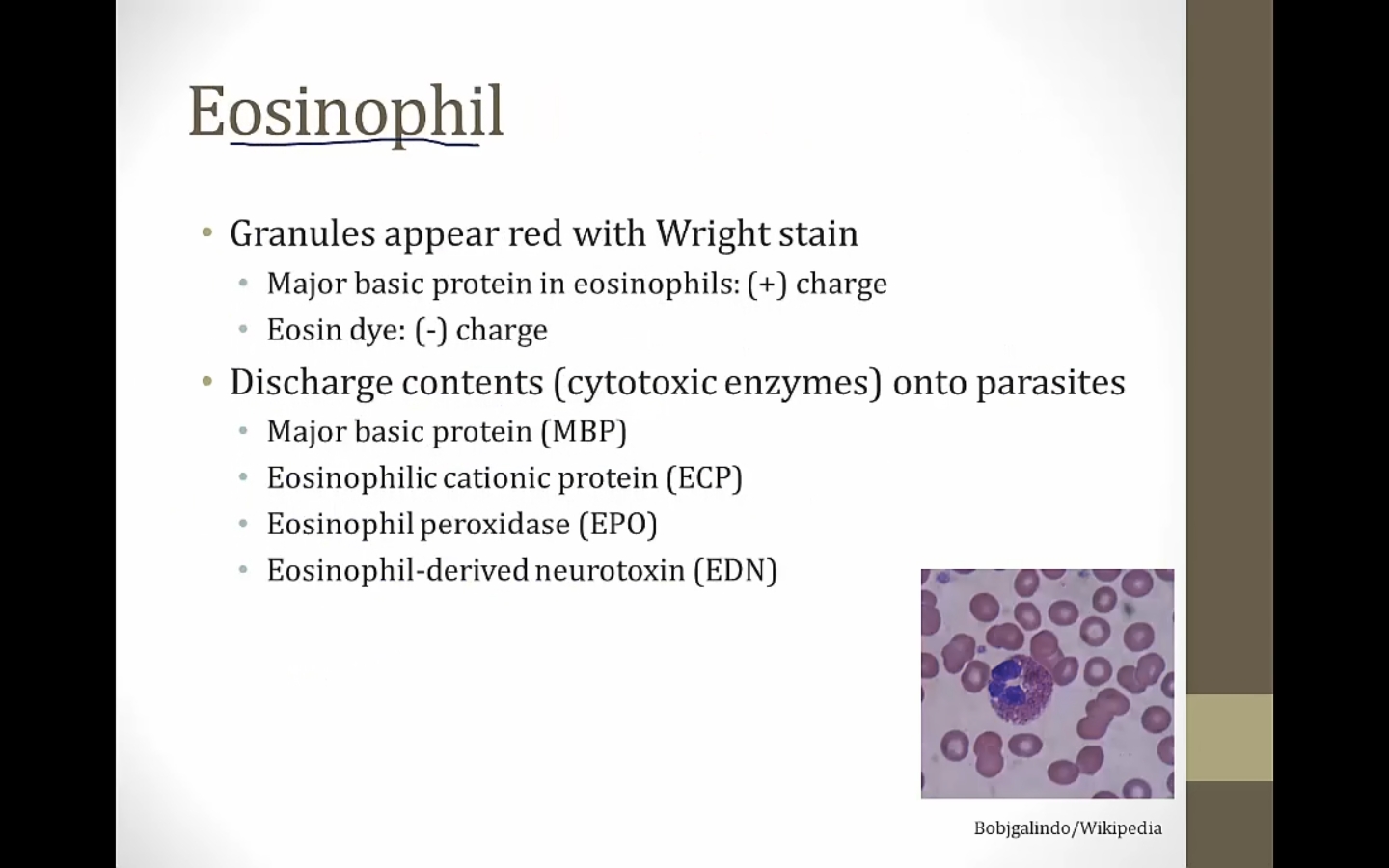
positive charge picks up Eosin dye
_..
Basophils
_..
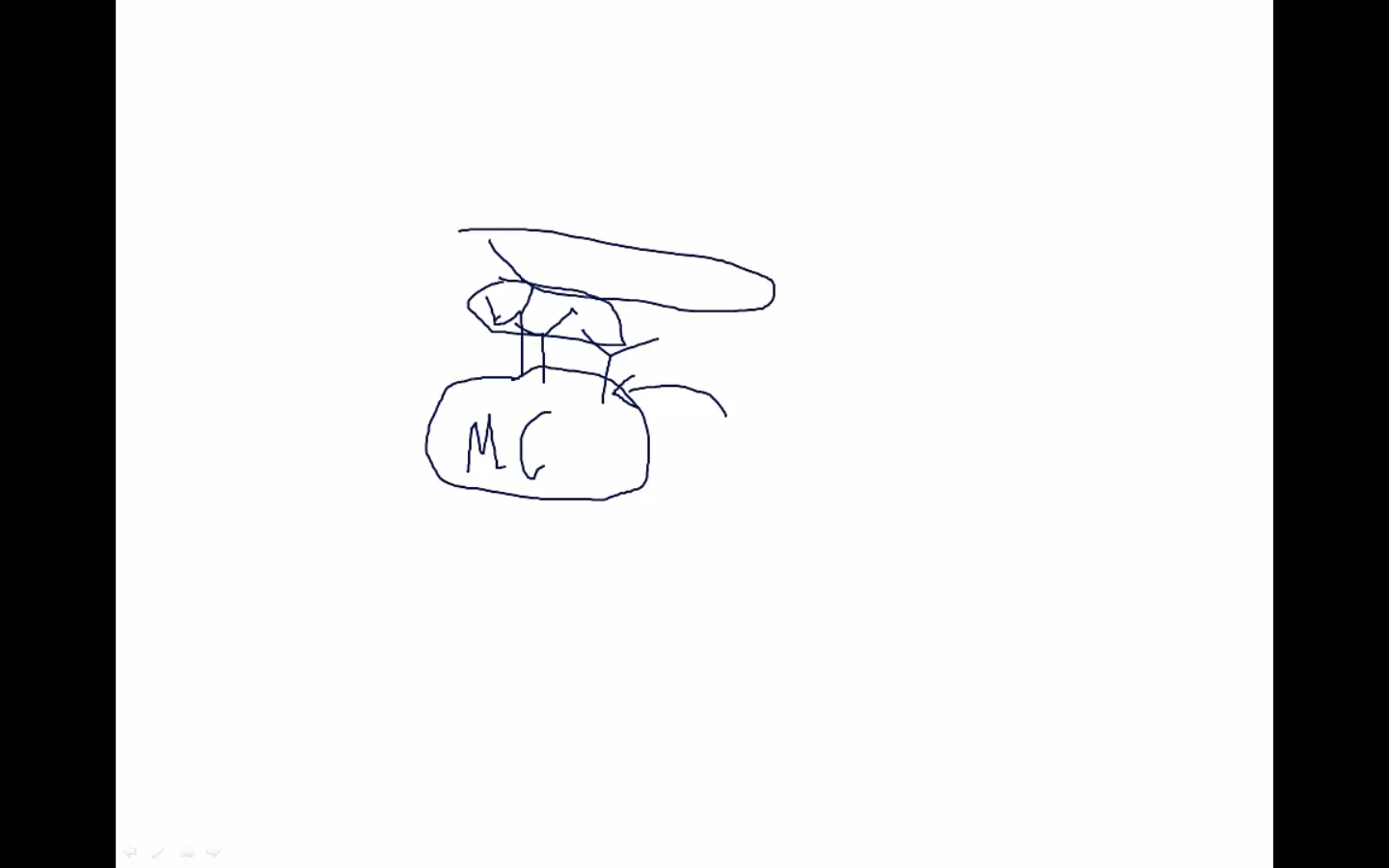
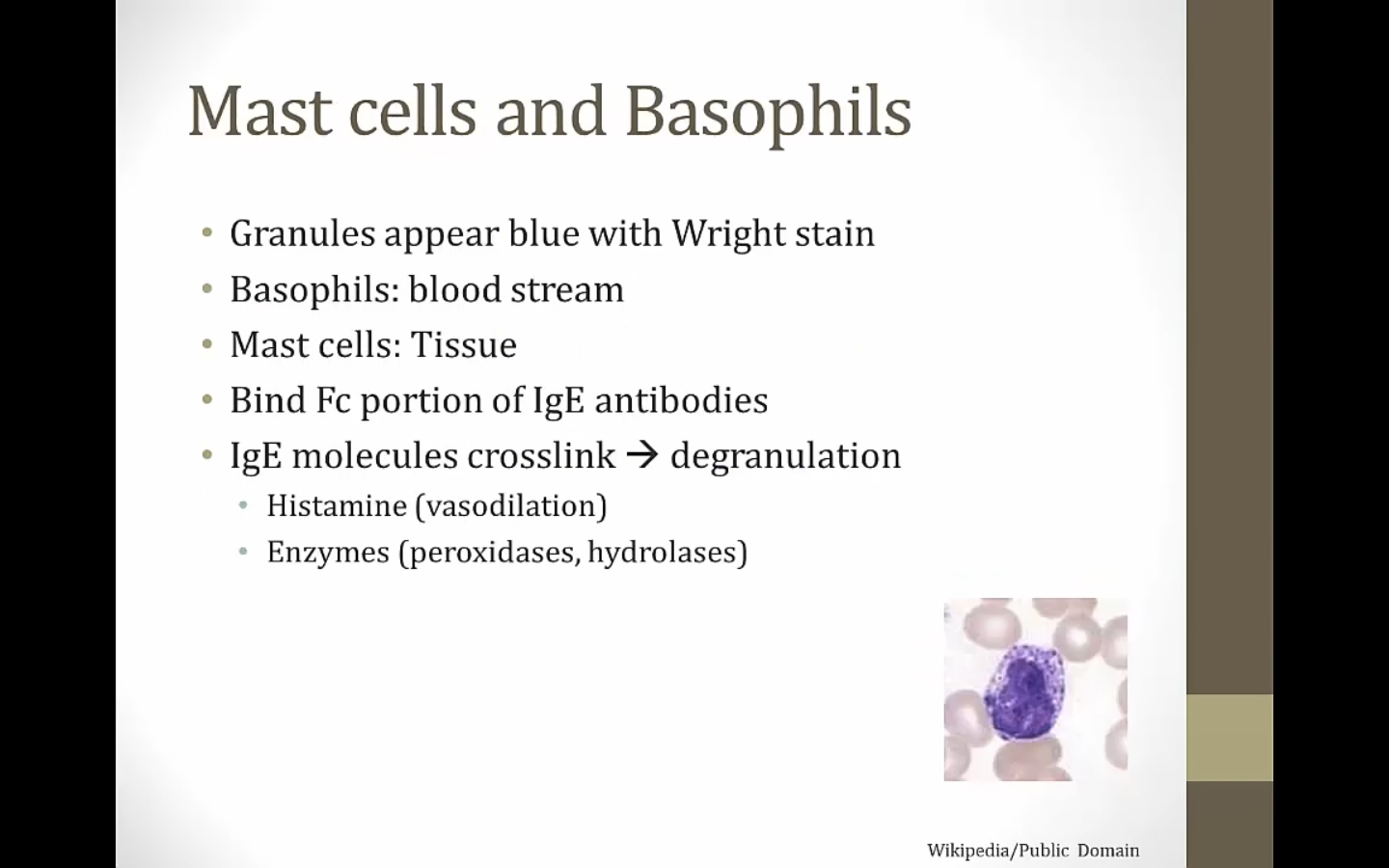

helminths binds multiple IgE, triggering cross link and degranulation
Dendritic Cells
_..
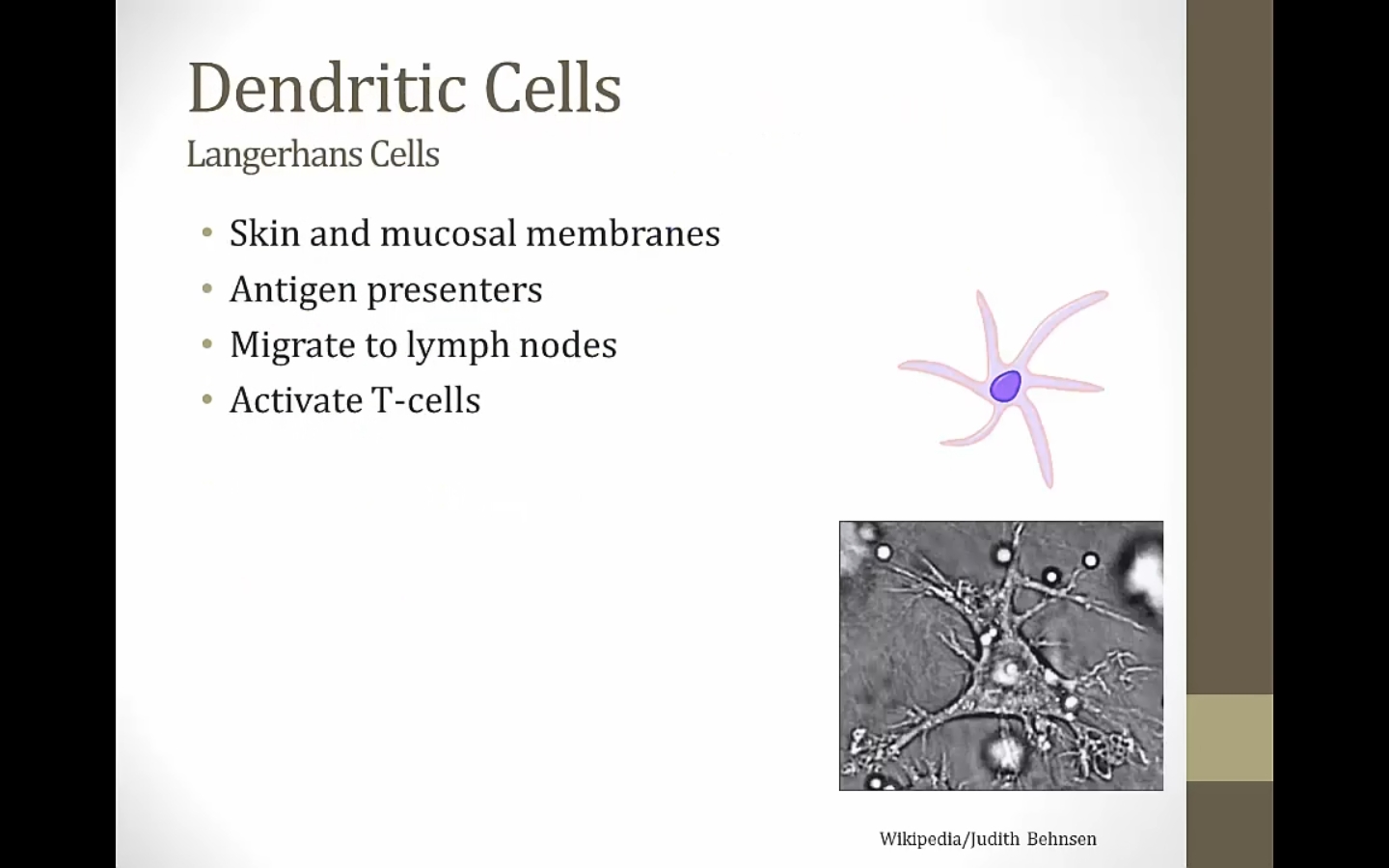
star shaped
professional antigen presenters
battle raging in tissue; dendritic cells pick up antigen to present to T cells
_..
_..
Last updated