14 EKG Basics
EKG components
_..

SA to LA and RA myocytes
HIS bundles, left and right BBB, purkinje embedded in myocytes
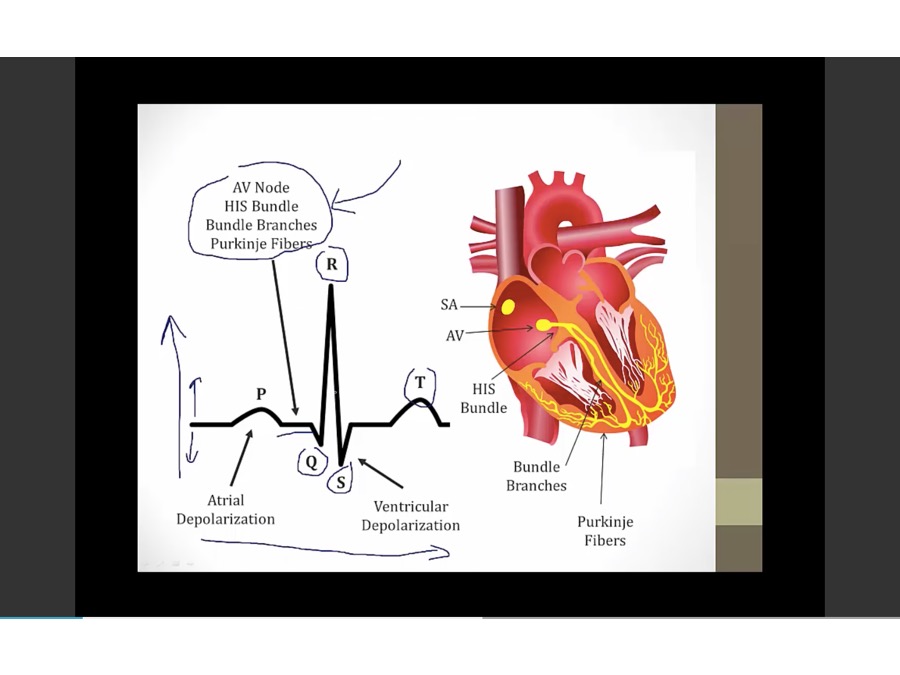
time x axis, electrical activity in y axis
P: atrial depolarization
flat after P: time for electrical activity to go to ventricles
QRS: ventricle depolarize
T: repolarization of ventricle. Atrial repolarization happens during QRS
Pacemaker and Hr
_..


speed by which electricity moves through heart
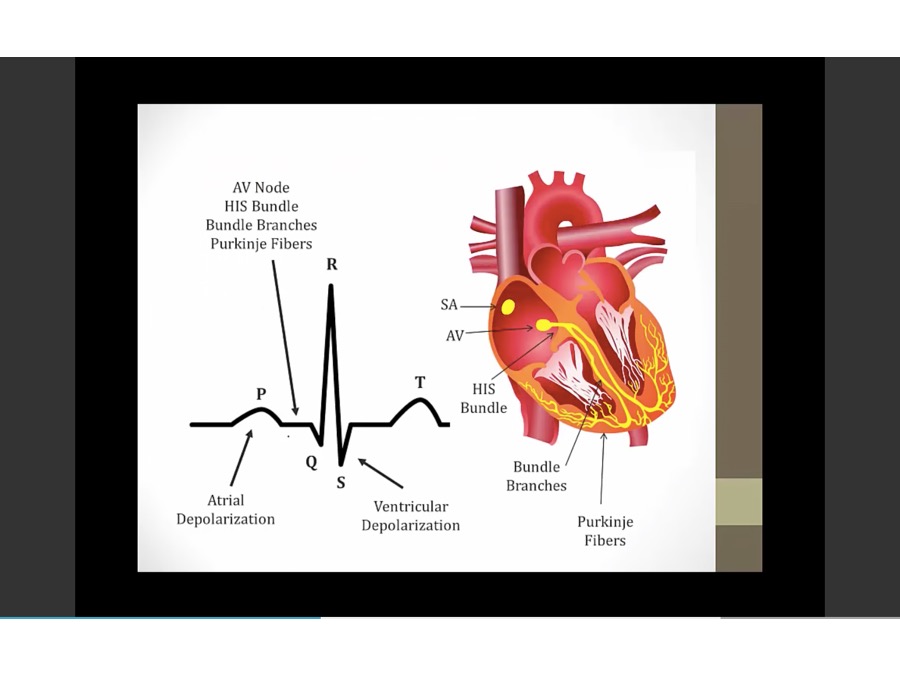
most of time between P and QRS is by AV nodal conduction
_..

small box: 40 ms
big box: 200 ms
300 / # of big boxes
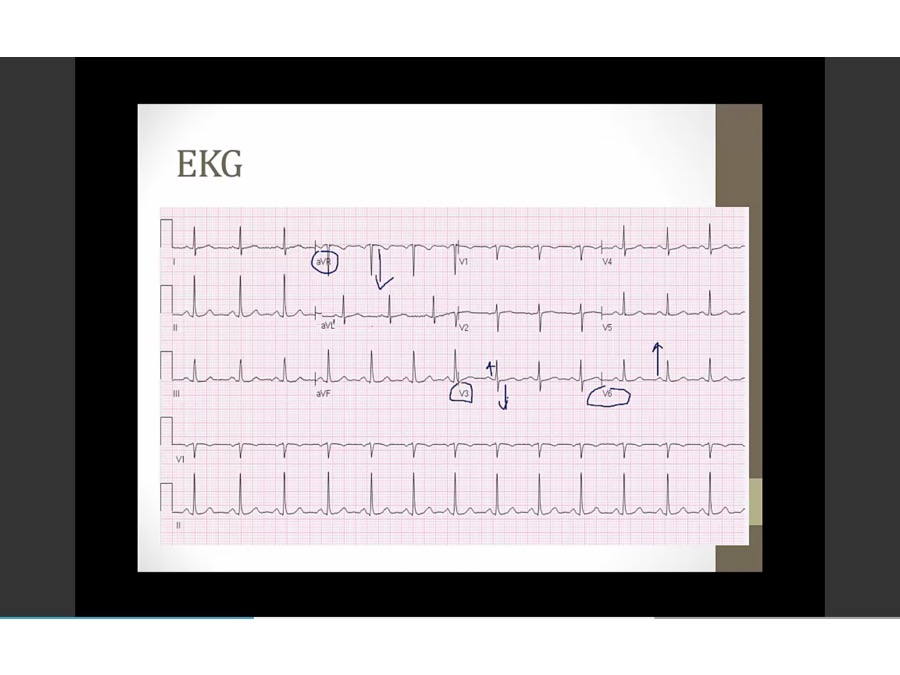
EKG lead
_..

some electrical activity to left, right
sum of all activity: arrow
each of 12 EKG leads look at summation from different POV = different QRS shape

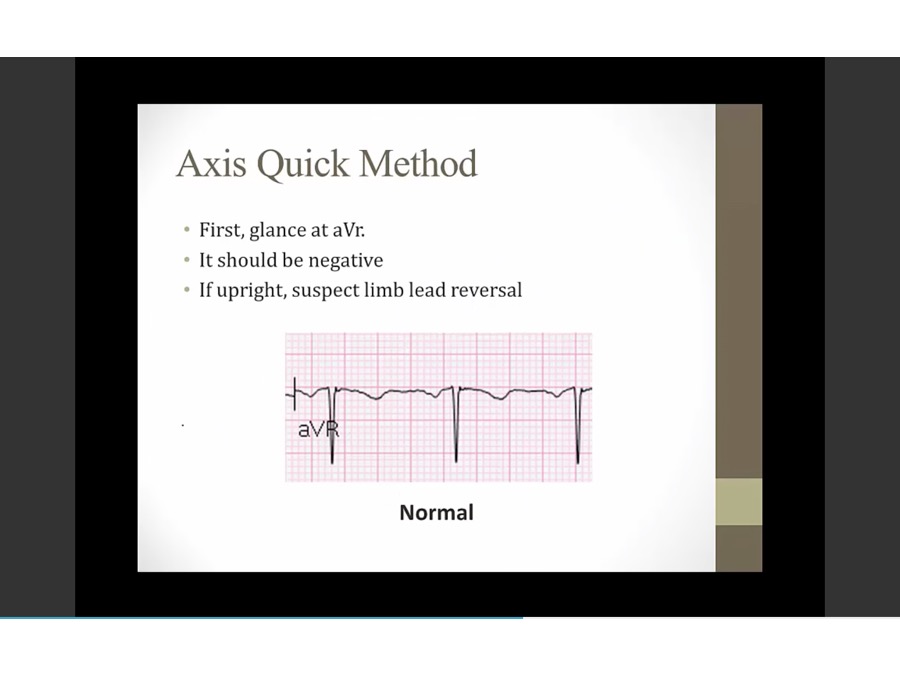
AVR: summation away, negative QRS
1, AVL: summation towards, positive

QRS Axis
_..
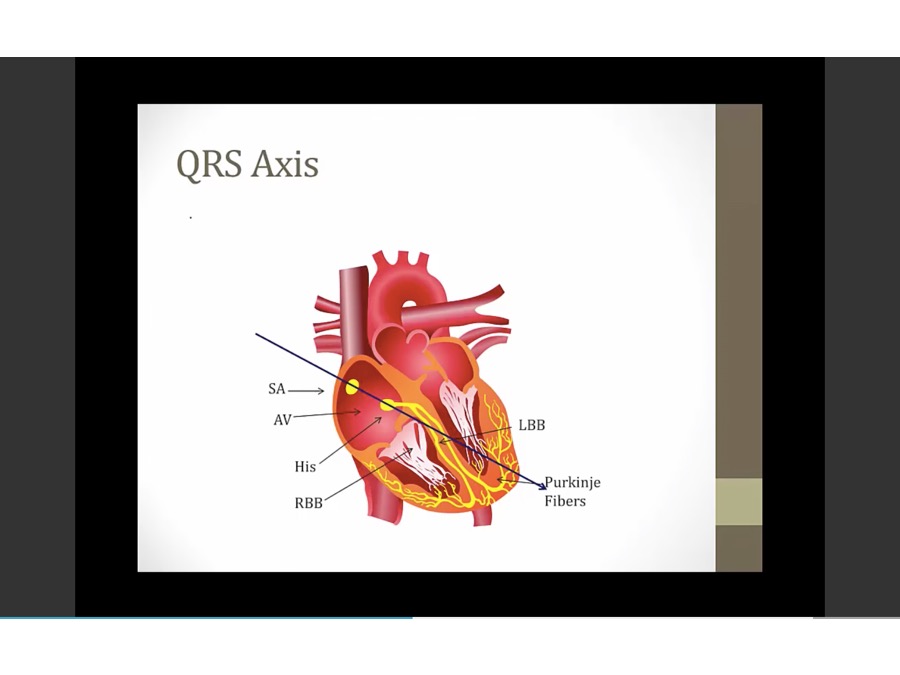


-30 and -90
V tach, activity not from SA node but from ventricle itself
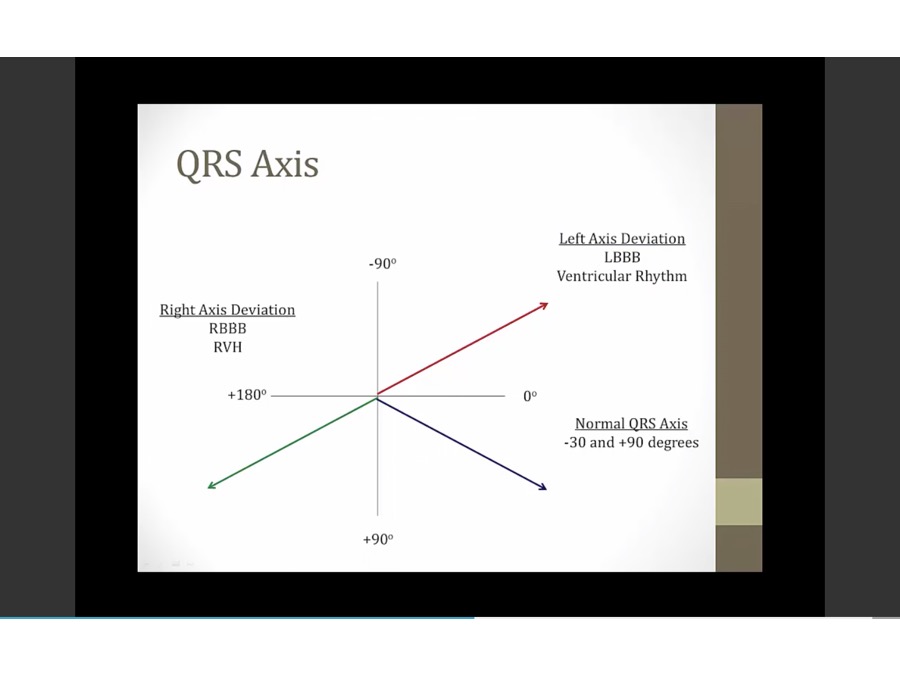
90 and 180

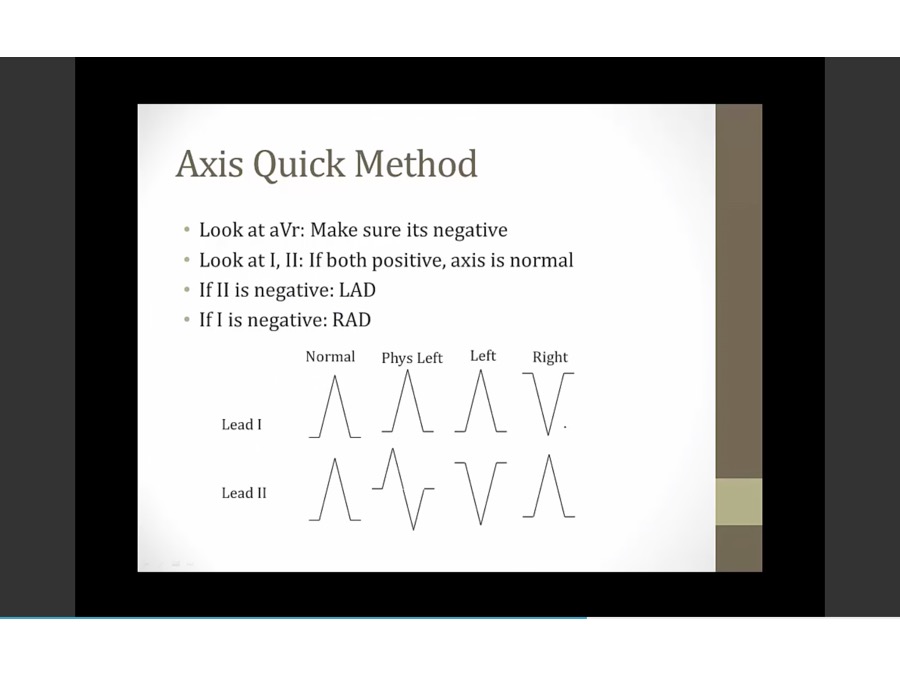
positive lead 1: toward 0
negative lead 1: towards 180
positive lead 2: going down
negative lead 2: going up
added lead 1 and 2 vectors to have summation vector


exception: part up part down, physiologic, slightly to left, nl

Intervals
_..

PR: shorter than 1 big box
_..
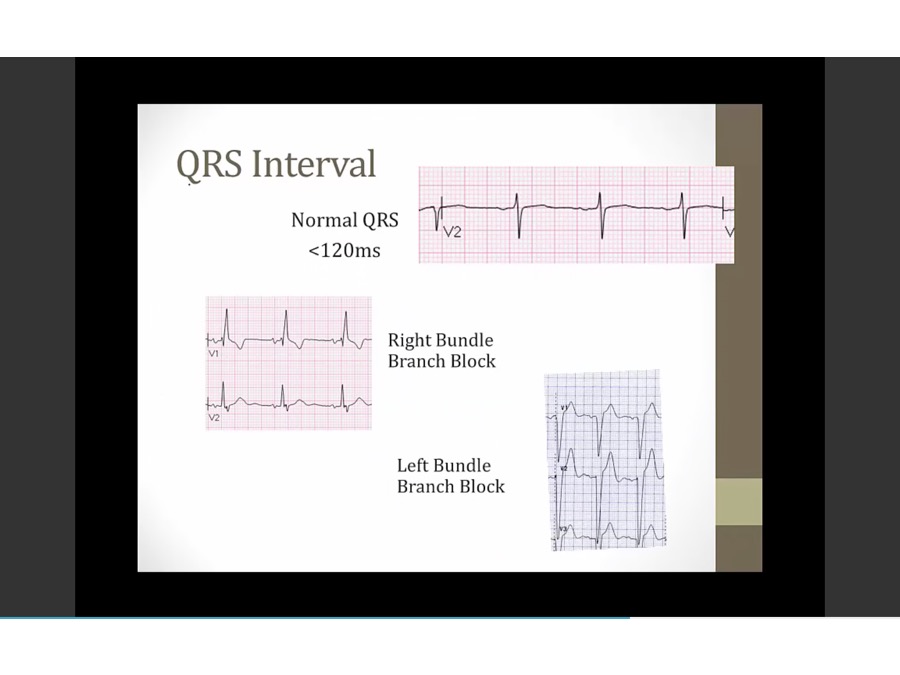
less than 3 small boxes

Inactivated peanut butter jar: TCAs block the cardiac fast Na+ channels, decreased contractility, QRS, QT propagation
Wide QRS crack: TCAs can widen the QRS complex on ECG
Twisted torsades streamer: TCAs can induce torsades

Lightly held peanut butter jar: class IA antiarrhythmics have an intermediate binding affinity for the Na+ channel (intermediate use-dependence, moderate slowing of the phase 0 upstroke)
Pushing away the curtain: class IA antiarrhythmics also block K+ channels, prolonging phase 2 and 3 of the cardiac action potential -> prolonged refractory period
Twisted torsades streamer: class IA antiarrhythmics can cause Q-T interval prolongation (precipitates torsades) (K channel prolongation)
Wide QRS shaped crack: class I antiarrhythmics widen the QRS complex on the ECG (decreased AP conduction velocity) (faster cells bind more and slow down more) (QRS widen as HR increases)
_..

less than half QRS - QRS
left: T begin immediately without flat portion
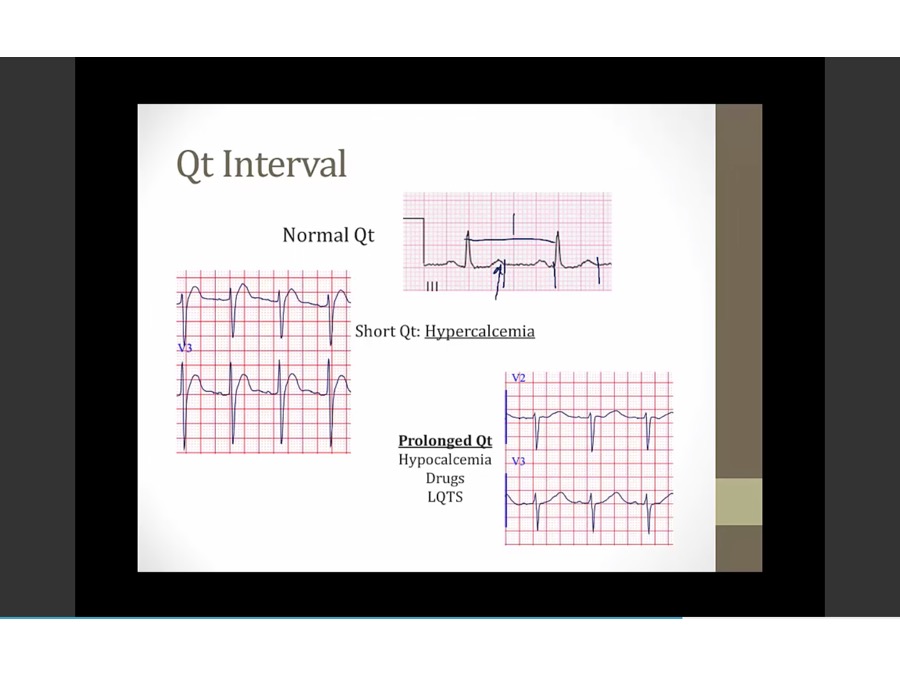
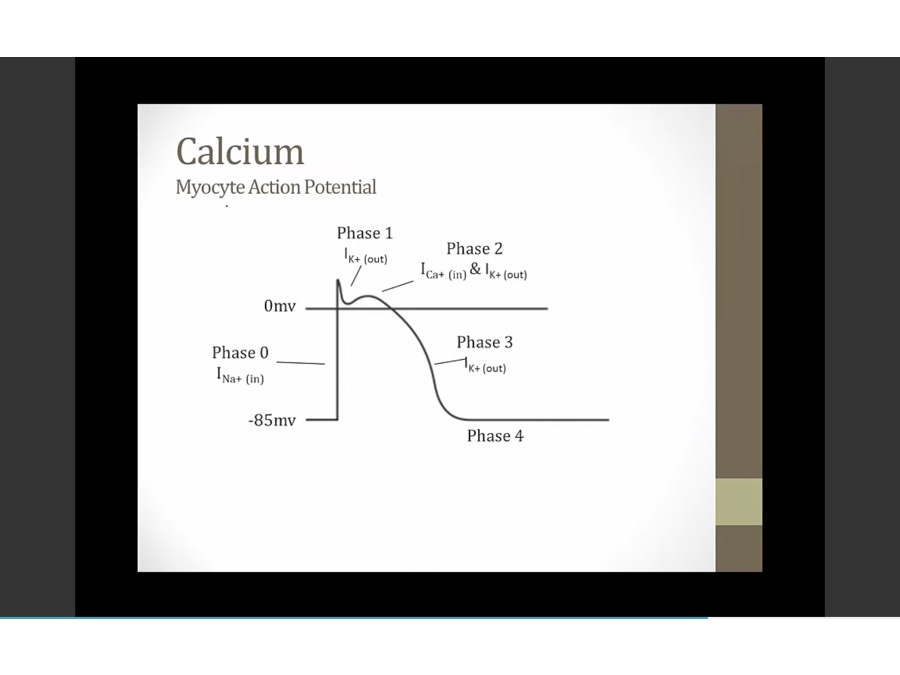
hypocalcemia: less driving force to move Ca in, longer for Ca to go in, longer for QT interval to occur (myocyte in ventricles to depolarize, repolarize )


Torsades strip: risk of prolonged Q-T interval


Twisted streamer: FGAs can cause torsades de pointes

Lightly held peanut butter jar: class IA antiarrhythmics have an intermediate binding affinity for the Na+ channel (intermediate use-dependence, moderate slowing of the phase 0 upstroke)
Pushing away the curtain: class IA antiarrhythmics also block K+ channels, prolonging phase 2 and 3 of the cardiac action potential -> prolonged refractory period
Twisted torsades streamer: class IA antiarrhythmics can cause Q-T interval prolongation (precipitates torsades) (K channel prolongation)
Wide QRS shaped crack: class I antiarrhythmics widen the QRS complex on the ECG (decreased AP conduction velocity) (faster cells bind more and slow down more) (QRS widen as HR increases)

Pushing away the curtain: class III antiarrhythmics block K+ channels prolonging phase 2 and 3 of the cardiac action potential -> prolonged refractory period
Twisted streamer: sotalol, dofetilide, and ibutilide can induce torsades (although all type III antiarrhythmics can widen the QT interval)

Inactivated peanut butter jar: TCAs block the cardiac fast Na+ channels, decreased contractility, QRS, QT propagation
Wide QRS crack: TCAs can widen the QRS complex on ECG
Twisted torsades streamer: TCAs can induce torsades
_..


Torsades strip: risk of prolonged Q-T interval


Twisted streamer: FGAs can cause torsades de pointes

Lightly held peanut butter jar: class IA antiarrhythmics have an intermediate binding affinity for the Na+ channel (intermediate use-dependence, moderate slowing of the phase 0 upstroke)
Pushing away the curtain: class IA antiarrhythmics also block K+ channels, prolonging phase 2 and 3 of the cardiac action potential -> prolonged refractory period
Twisted torsades streamer: class IA antiarrhythmics can cause Q-T interval prolongation (precipitates torsades) (K channel prolongation)

Pushing away the curtain: class III antiarrhythmics block K+ channels prolonging phase 2 and 3 of the cardiac action potential -> prolonged refractory period
Twisted streamer: sotalol, dofetilide, and ibutilide can induce torsades (although all type III antiarrhythmics can widen the QT interval)

Inactivated peanut butter jar: TCAs block the cardiac fast Na+ channels, decreased contractility, QRS, QT propagation
Wide QRS crack: TCAs can widen the QRS complex on ECG
Twisted torsades streamer: TCAs can induce torsades
_..
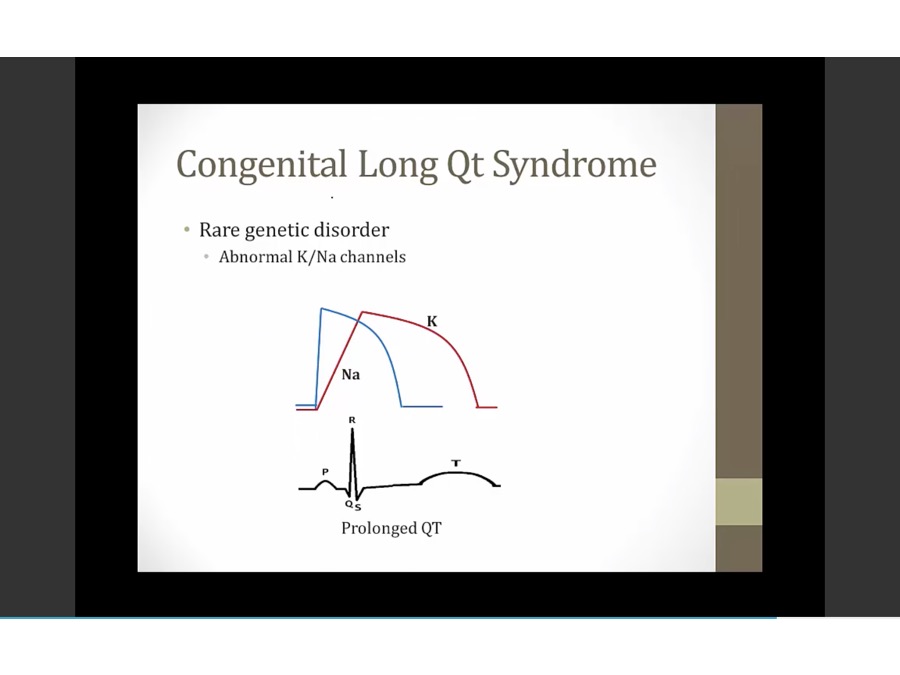
longer to depolarize/repolarize, longer QT

not really seizures, passing out from torsades
_..

hyperacute: precede ST elevation in ischemia

Last updated