05 Platelet Disorders
Inherited
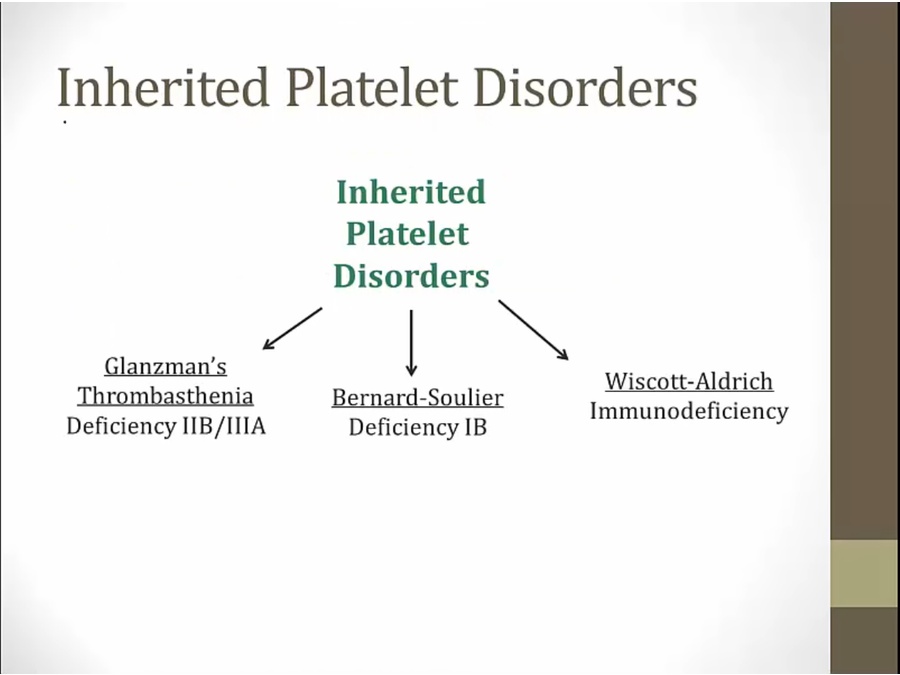
Glanzman's
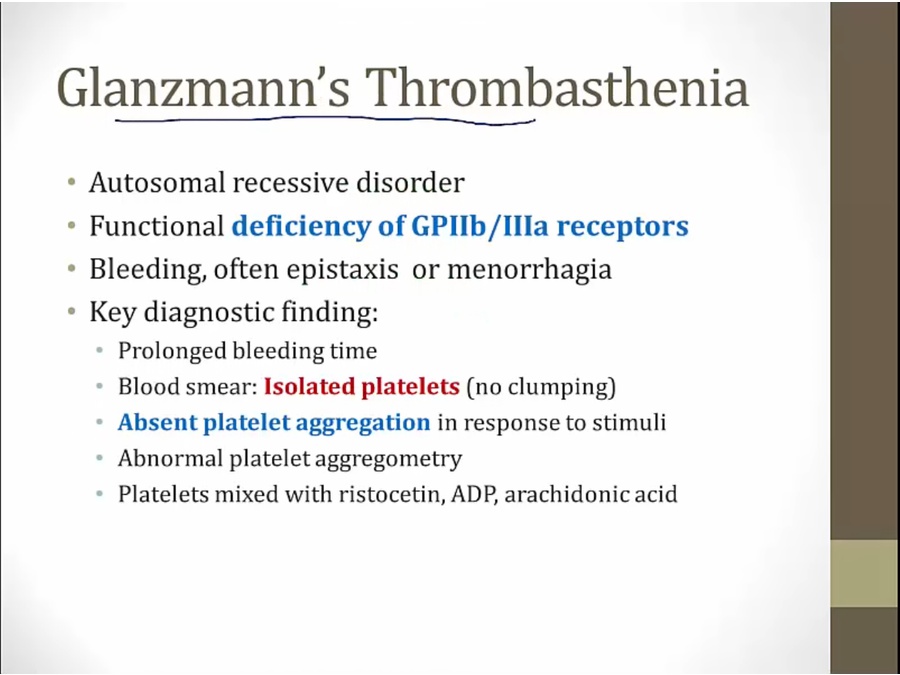
superficial bleeding
nl aggregation with ristocetin test
Bernard

large platelets on smear
abnormal ristocetin assay

Wiskott- Aldrich

Acquired
ITP
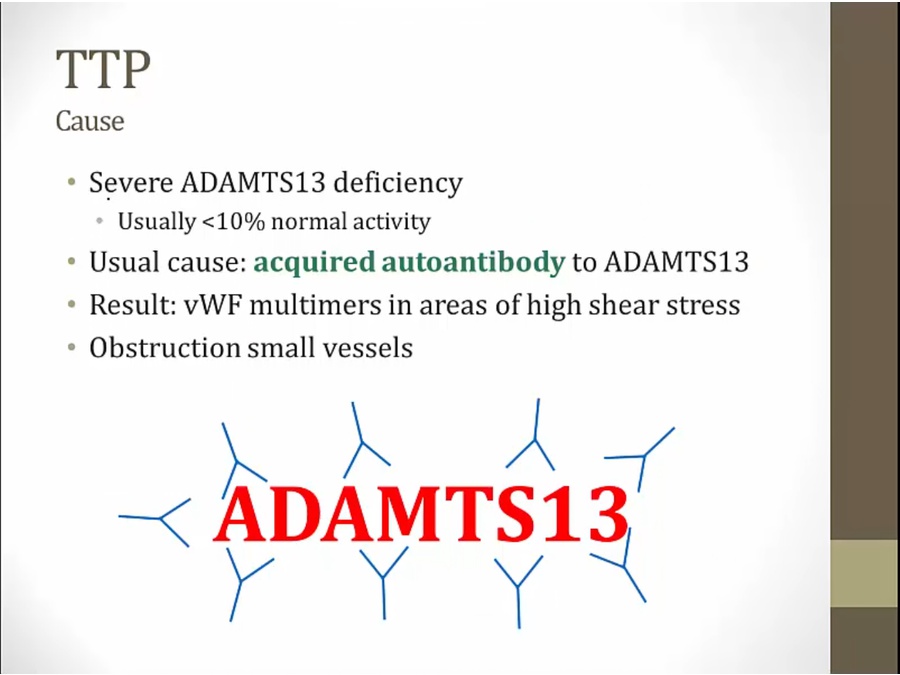
TTP
HUS
DIC
Uremia
thrombocytopenia
vWF
Hayde's
ITP
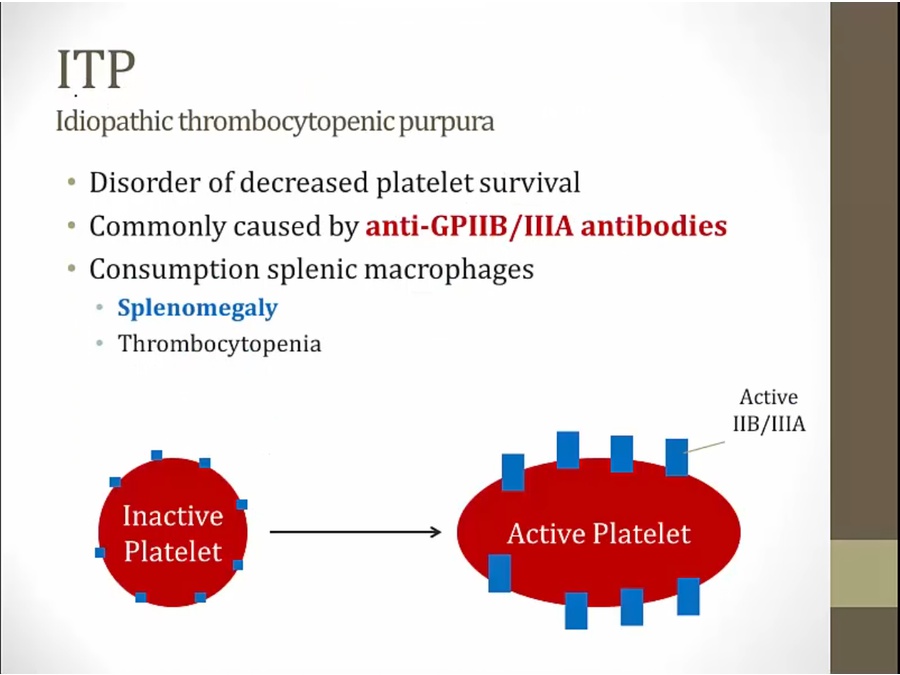
don't live as long as they should = low number
macrophages clear antibody bound platelets


platelet thrombi: platelet low, coagulation factors not consumed
TTP

much more dangerous
low platelets, thrombosis
thrombus form in small vessels, consumes platelets, thrombocytopenia


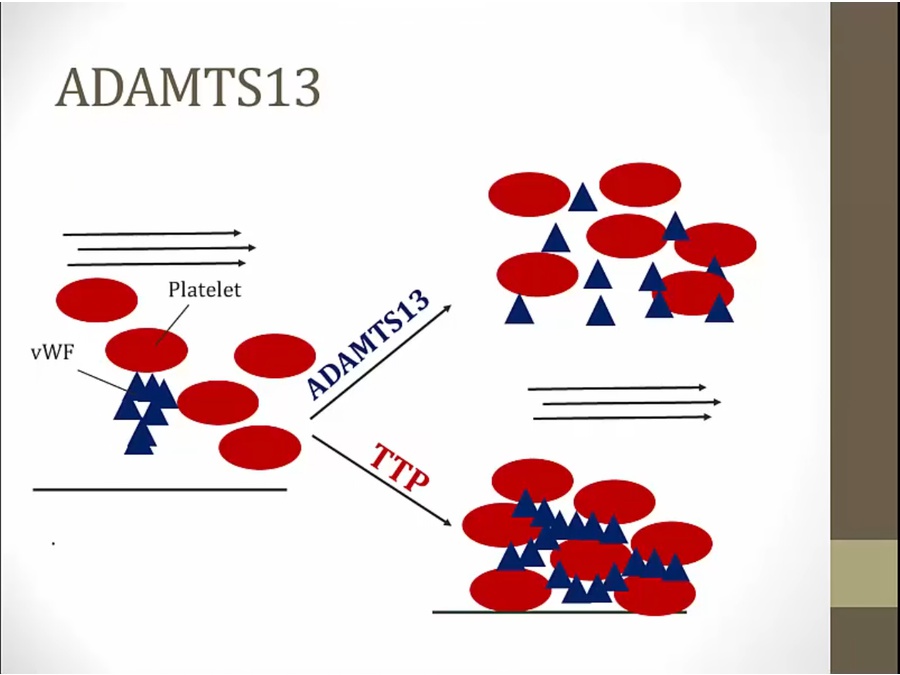
TTP: build up of platelets and RBC, obstruction
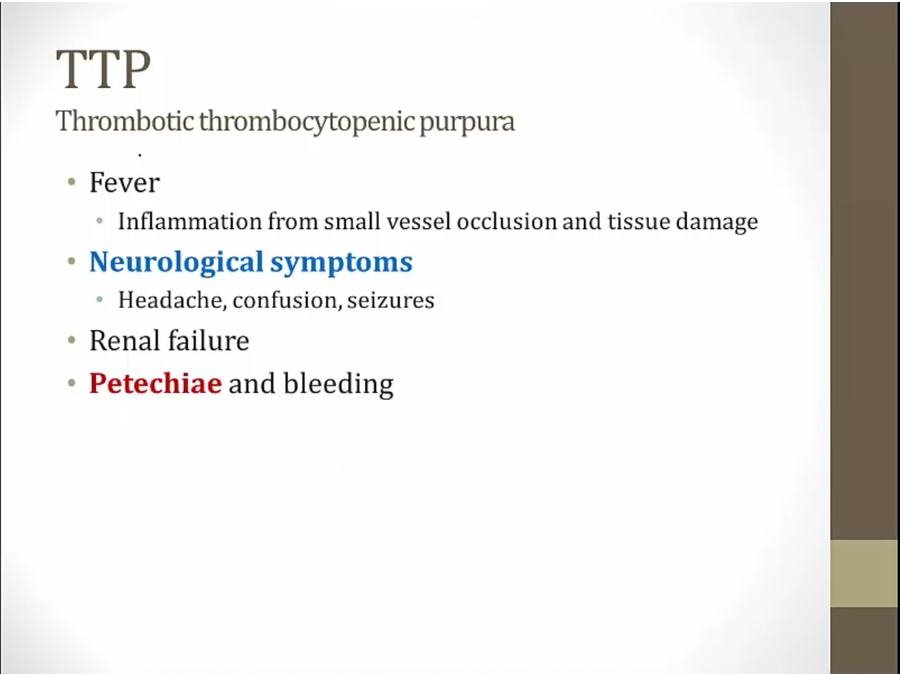
small vessel occlusion in CNS

thrombi primarily made of platelets, do not consume clotting factor

platelet thrombi: platelet low, coagulation factors not consumed

HUS

distinguish from TTP: no fever or CNS symptoms (TTP only with kidney)

platelet thrombi: platelet low, coagulation factors not consumed
DIC

both platelets and fibrin, increased PT, PTT

TF activate coagulation cascade
sepsis: high levels of cytokines and endotoxins


every blood test abnormal


platelet thrombi: platelet low, coagulation factors not consumed
Uremia

caused by toxins, not platelets
Thrombocytopenia


Von Willebrand



heavy periods common early presentation

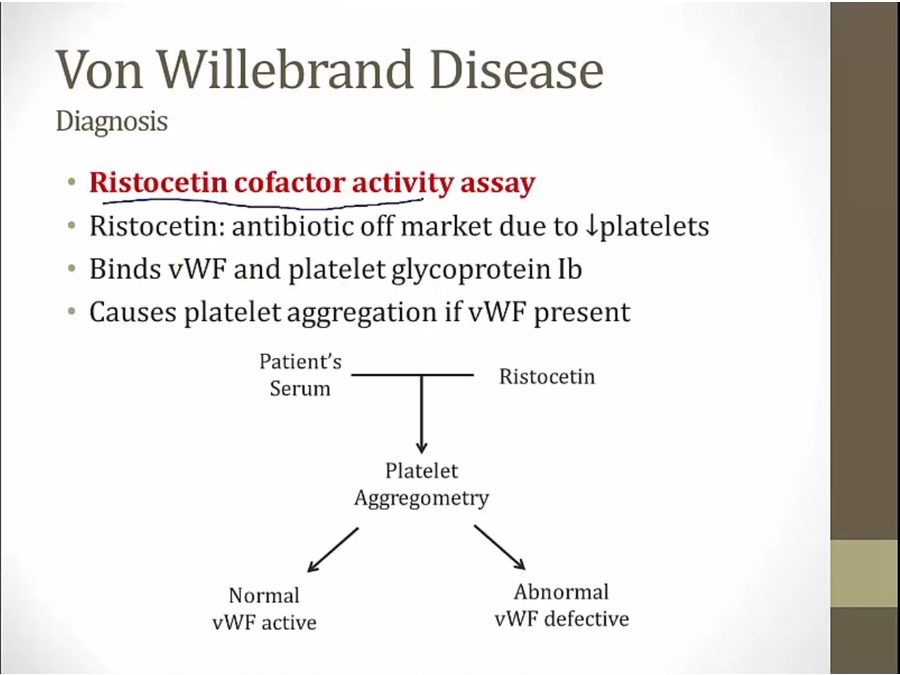
ristocetin test normal in glanzman
ristocetin test also abnormal in Bernard

Hayde's

aortic stenosis: increased risks of angiodysplasia
overactivity of ADAMST13, breaking down multimers, causing VWF to be less efficient
Last updated