07 CO 2
Transportation
_..


CO2 stored as HCO3 to be transported to lungs
Bohr Effect
_..
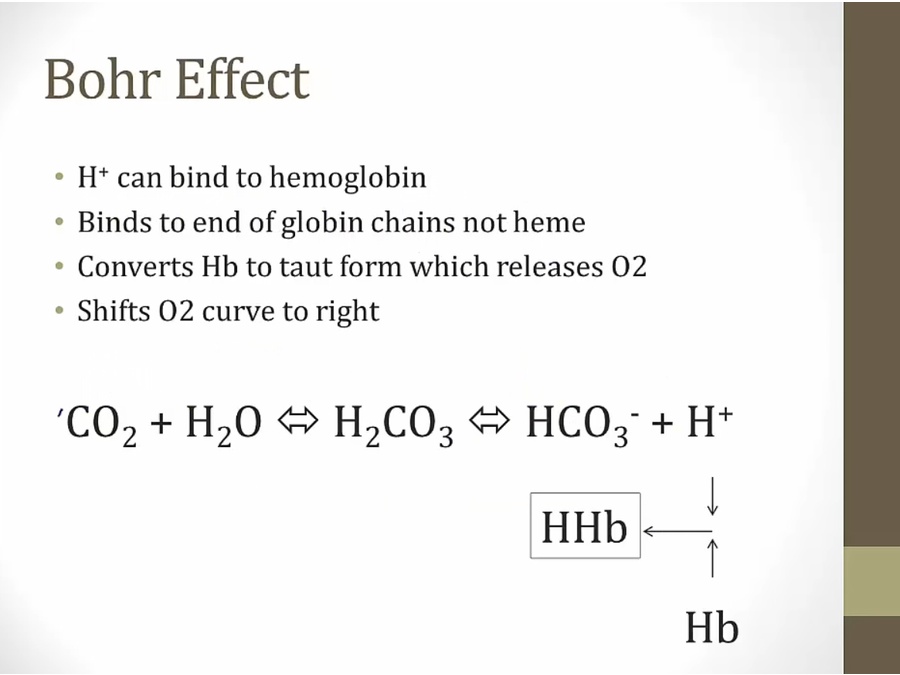
conversion produces H+ ion that binds to globin chain to form HHb

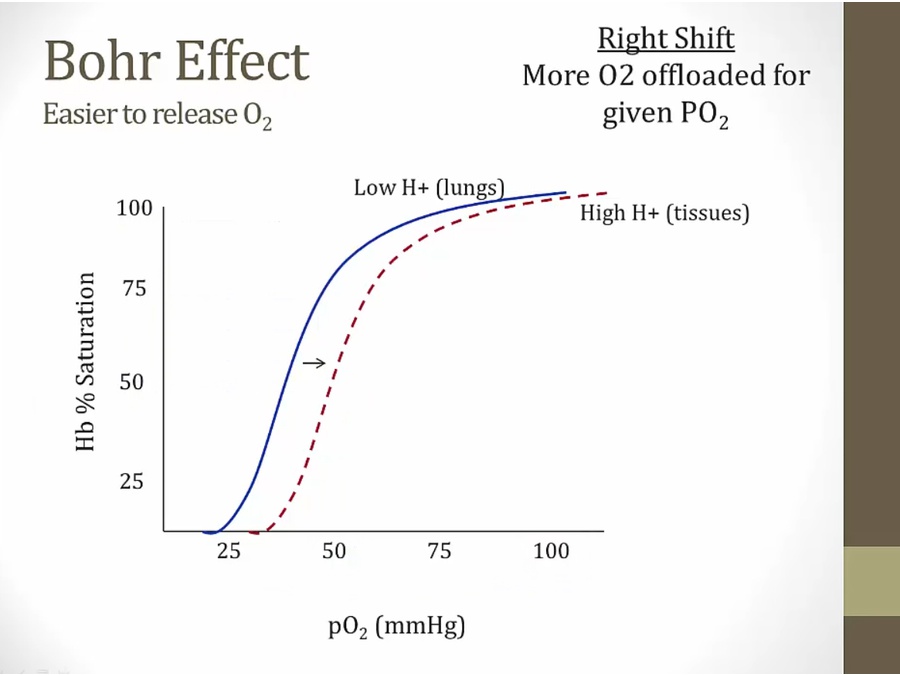
instead of dropping from 100 to 75% at tissue PO2 50 mmHg, drop to 50%, better unloading
Bohr effect helps unload O2 via H ion binding to Hb
Cl Shift
_..

high bicarb inside cell diffuse out, in exchange for Cl
Haldane
_..




x: level of CO2
y: amount CO2 bound to Hb
purple line: normally, more PCO2 in blood = more bound to Hb
in reality, blue line: even more bound to Hb at low O2 level
_..

Bohr for O2
High Altitude
_..

small box: someone living at high altitude



mild polycythemia
Exercise
_..



arterial side maintain normal rate: not hypoxic or hypercapnea

Cerebral blood flow
_..

cerebral vasodilator
left, O2: at normal range, O2 does not change cerebral blood flow much
right, CO2: at normal range, powerful effect on blood flow

Breathing
_..

CO2 in blood stream major stimulus, not O2
PNS chemoreceptor: only kick in under severe hypoxia, normally CNS working
_..

hypoxemia stimulate respiratory rate, can get low with O2 = high CO2, confusion

in hospital on ventilation, O2 can make O2 saturation high and mask hypoventilation
put on ventilator

hypo ventilating, CNS symptoms
Last updated