01 Bone Disorders
Osteoporosis
_Is a quantitative disorder of bone, meaning there is a reduction in bone mass despite the bone being sufficiently mineralized..
too much osteoclast, not enough osteoblast


_Primarily affects trabecular bone, resulting in decreased bone mass and density with fewer trabecular interconnections. Osteoclast and blast acts on bone surfaces. Trabecular bones have the most amount of surface areas..
Type I (postmenopausal) occurs in women 50-70 years old and presents primarily with fractures of the distal radius (Colles’ fracture) and vertebral bodies.
Type II (senile) occurs in patients over 70 years old and presents with fractures of the hip and pelvis. This type of osteoporosis does not show the same female predilection as type I osteoporosis..
_Risk factors include anything which contributes to an imbalance in bone production and bone resorption, resulting in diminishing bone mass.
Unmodifiable risk factors of osteoporosis include:
Caucasian ethnicity
Rheumatoid arthritis
Advancing age
Postmenopausal status
Previous fragility fracture
Genetics, including parental history of osteoporotic hip fracture
Modifiable risk factors of osteoporosis include:
History of heavy/protracted glucocorticoid use
Low body weight
Current cigarette smoking
Excessive alcohol consumption
Poor diet/exercise..
There are no clinical manifestations of osteoporosis until the patient suffers a fracture. Achy pain, in the absence of a fracture, is unlikely to be osteoporosis.
The incidence of fracture types related to osteoporosis is as follows (in order of decreasing frequency):
Vertebral body
Hip (femoral neck)
Distal radius
Vertebral body compression:
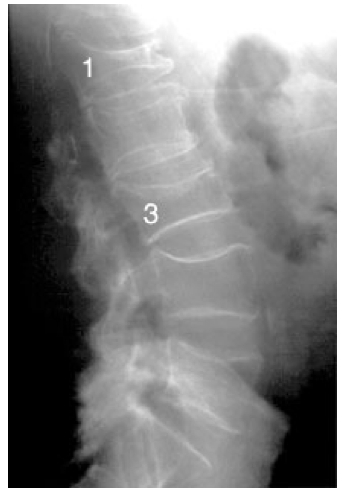
Accumulation of vertebral body fractures can cause progressive kyphosis of the thoracic spine (Dowager’s hump), respiratory compromise, restrictive lung disease, and an increased risk of pneumonia..
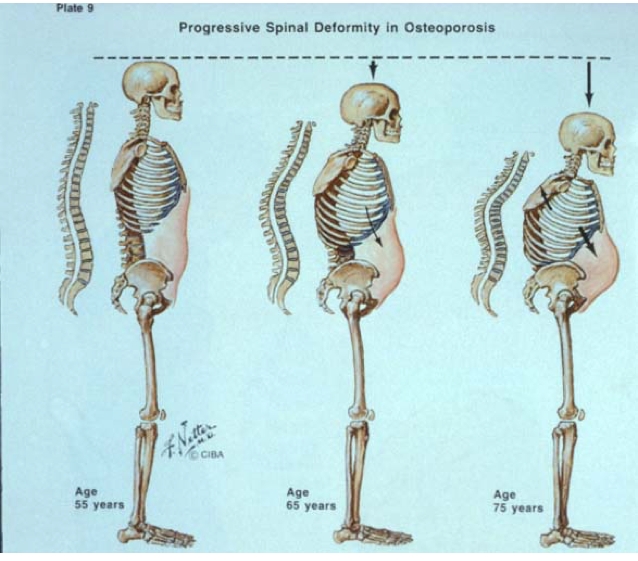

_Patients over the age of 65 may have insurance coverage for DEXA scans for osteoporosis screening..
Fragility fractures occur with minimal impact from falls from a standing height or less, such as a Colles' fracture of the distal radius or a vertebral body fracture. NOTE: It may sometimes be important to distinguish a true fragility fracture from a pathological fracture. The latter is associated with osteolytic malignancy and presents as pain preceding a fracture that occurs with minimal trauma (e.g. picking up a grocery bag) and is not associated with a fall from a standing height or less.
Risk for future fragility fracture is much greater in patients with a history of existing fragility fracture..
_ While not indicated strictly for the evaluation of osteoporosis, labs reveal normal serum calcium, phosphate, alkaline phosphatase and parathyroid hormone (PTH)..
_ The diagnosis of osteoporosis can be made clinically in a patient presenting with a fragility fracture and otherwise clinically consistent picture (postmenopausal female, over 70 years old, no evidence of malignancy, etc.), or based on a dual X-ray absorptiometry (DXA) scan measurement of bone mineral density showing a T-score more than 2.5 standard deviations below the mean..
_Measurement of femoral neck bone mineral density is used to estimate risk of hip fracture and any major osteoporosis-related fracture (wrist, hip or vertebral body) in untreated patients with the fracture risk assessment tool (FRAX). This uses clinical data, risk factors, and the patient’s bone mineral density as measured at the femoral neck to calculate the risk for a fragility fracture within the next ten years..
_Since estrogen has a protective effect on bone, hormone replacement therapy is a treatment option for women with type I (postmenopausal) osteoporosis. (Note that estrogen is not a first-line therapy due to an increased risk of stroke and thromboembolism)..
1st line: Bisphosphonate
Hormone replacement for type 1
SERMs
Denosumab
Teriparatide
Weight bearing exercise
Ca, Vit D supplementation
stop smoking
Regular weight-bearing exercise helps to maximizing peak bone mass, which is key in the prevention of osteoporosis.
Calcium and vitamin D supplementation is recommended for all ages.
Smoking accelerates bone loss; cessation is encouraged for the prevention of osteoporosis..
Paget
_Aka osteitis deformans.,
_Is characterized by massive bone turnover caused by increased and unbalanced osteoclastic and osteoblastic activity. The increased activity leads to the formation of abnormal bone architecture.
Believed to be caused by both genetic and environmental factors. Inheritance appears to be autosomal dominant with variable penetrance. There is some evidence linking Paget disease of bone to a slowly progressive viral infection from a member of the paramyxovirus family, such as the measles or respiratory syncytial virus, although this theory is controversial.
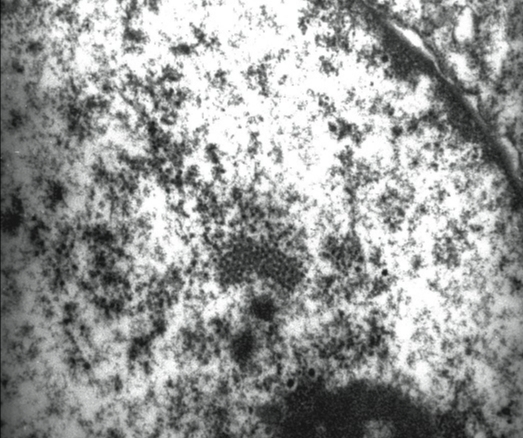
Paget's disease, on electron microscopy the nuclei of the osteoclasts contain particles that resemble paramyxovirus in their shape and orientation..
_The pathogenesis of Paget disease of bone involves 4 phases:
Lytic phase
Mixed phase
Sclerotic phase
Quiescent phase..
Lytic phase
_Is characterized by increased osteoclast activity and normal osteoblast activity. This results in massive bone turnover that leads to poorly organized woven bone.
The initiating lesion in Paget disease of bone is caused by an excessive increase in osteoclast activity. This activity lead to shaggy lytic bone lesions.,

Paget's disease, an osteoclast in pagetic bone contains many more nuclei than a usual osteoclast. A few of the nuclei contain eosinophilic intranuclear inclusion-like particles

Paget's disease, section of bone shows prominent and irregular basophilic cement lines and numerous lining osteoclasts and osteoblasts
Mixed phase
_Osteoclastic activity decreases while the activity of osteoblasts greatly increases and predominates during this phase.
The initial lytic insult in osteitis deformans is followed by a robust osteoblastic response, which results in increased alkaline phosphatase levels in the serum.
Excessive activity of osteoblasts leads to increased production of disorganized woven bone, also known as “mosaic bone,” which is weak, thick, and highly vascular with ragged lytic areas of radiolucency throughout the bone matrix.,
Sclerotic phase
_Osteoclastic activity declines to negligible levels, while the activity of osteoblasts remains elevated.
Woven bone is replaced by focal pockets of abnormal, highly cellular lamellar bone with irregular “cement lines.”
The decreased levels of osteoclastic activity leads to absent/minimal bone turnover, and results in the production of sclerotic bone that is characterized by:
Enlarged/widened bones
Absent Haversian systems
Marrow spaces replaced by vascular fibrous tissue.,

Quiescent phase
_Characterized by minimal osteoclast and osteoblast activity.,
Symptoms
_ Skull involvement that presents as:
Headaches
Increased hat size
Hearing loss if it involves the bone surrounding the inner ear and/or narrows the auditory foramen
Loss of vision and other cranial nerve lesions may also occur (however it is uncommon)
Commonly, there is involvement of weight bearing bones that manifests in bone pain, long bone “chalk-stick fractures,” and large joint osteoarthritis..


_..X-ray imaging reveals thickened bone cortex with shaggy radiolucent lytic lesions interspersed throughout the bone matrix. Bone with these features are described as having a cotton wool appearance.
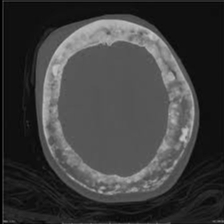

“Chalk-stick fractures” are fractures, typically of long bones, in which the fracture is transverse to the long axis of the bone, like a broken stick of chalk. Commonly seen in Paget’s disease of bone and osteopetrosis.

_Patients with Paget disease of bone are at increased risk of developing osteogenic sarcoma (osteosarcoma).
Pagetoid bone is highly vascular with extensive arteriovenous shunting that may significantly increase blood flow, leading to increased cardiac output. This results in compensatory left ventricular hypertrophy and eventually, in severe cases of Paget disease of bone, high-output heart failure..
_Serum chemistry levels reflect the increased bone turnover present in Paget disease and show:
Normal calcium levels
Normal phosphate levels
Normal parathyroid hormone levels
Increased alkaline phosphatase levels..
_The treatments for Paget’s disease of bone include:
Bisphosphonates (eg, alendronate, pamidronate, etidronate) are first-line agents
Calcitonin is the drug of choice if there is extensive disease in weight-bearing bones..
Last updated