06 Renal Endocrine
_..

Renin
_..
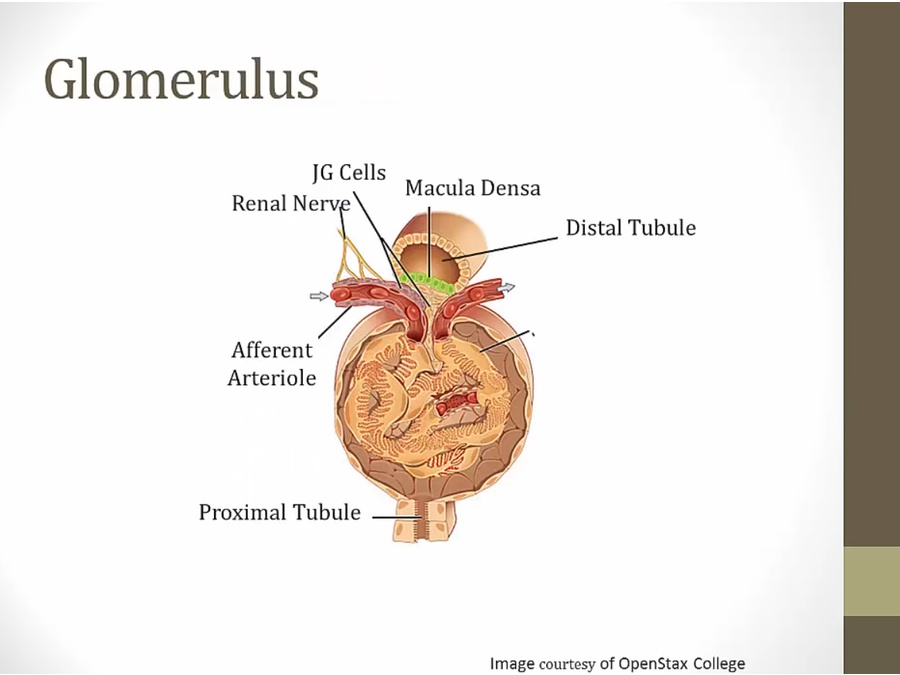
JG (juxto glomerulus): modified smooth muscle cells of afferent arteriole. Sits between afferent/efferent, distal tubule and glomerulus
macula densa: DCT

macula densa: sense NaCl levels
_..

_..
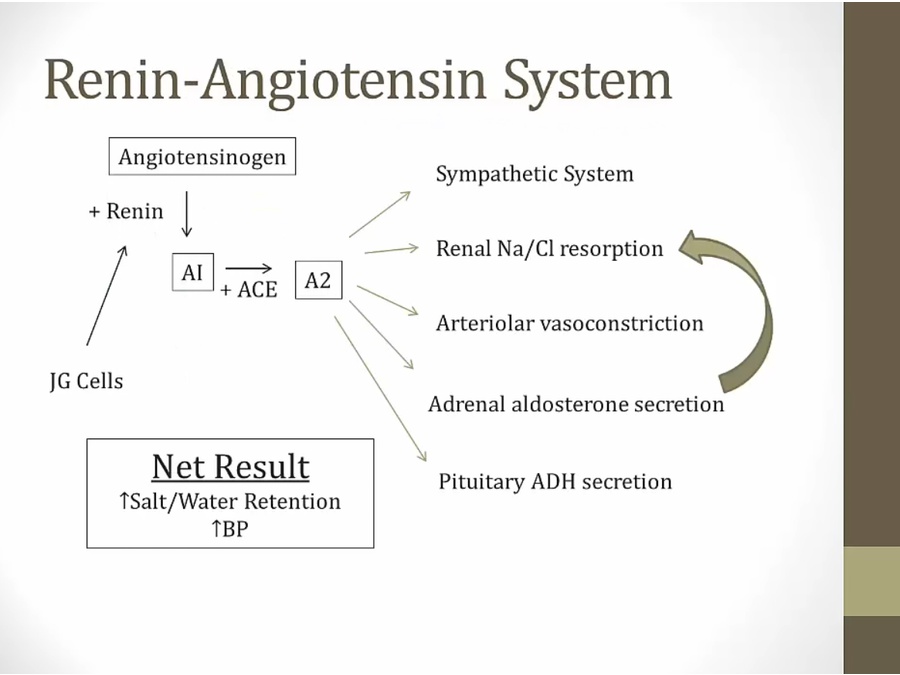
Ang: made by liver, in blood
renin finds Ang, convert to AI
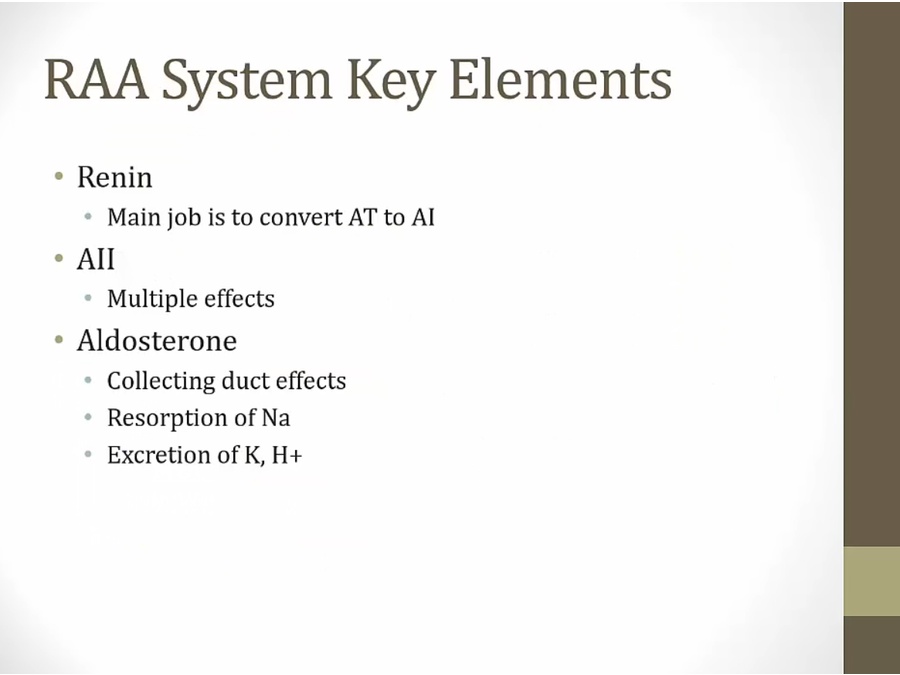
Ang II
_..

increase Na/H2O
increase bicarb absorption in PCT
harder to get blood through whole system, thus lower RPF, FF goes up
_..

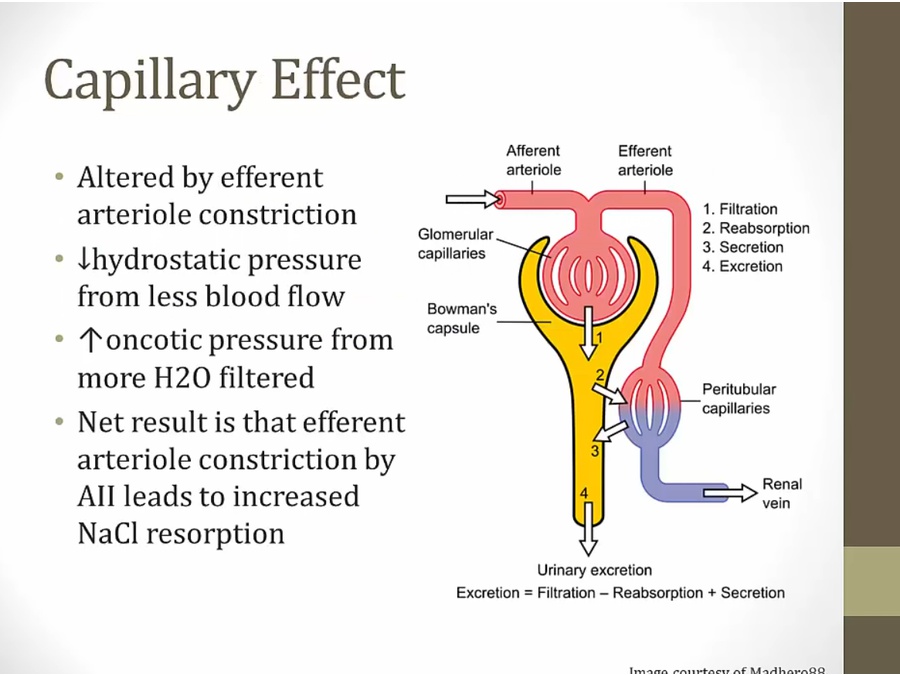
Hydrostatic effect:
less fluid go to peritubular because of constriction
low hydrostatic pressure in peritubular capillaries
result: water drawn out
Oncotic effect:
protein stay in efferent, increase oncotic pressure
high oncotic pressure
fluid out
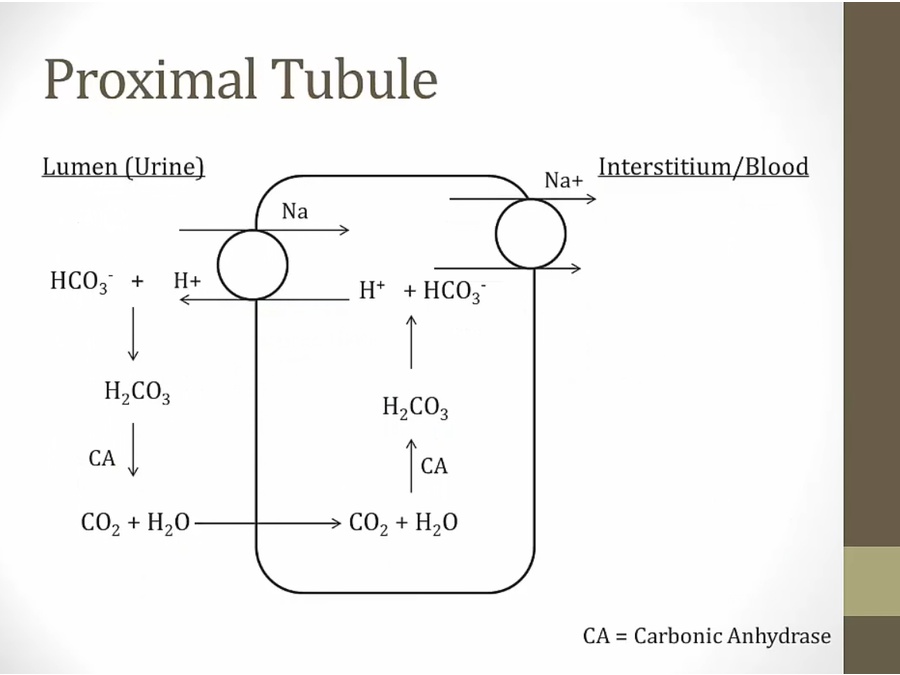
AII activate Na/H antiporter
Na absorption, H2O absorption
Contraction alkalosis: more H+ out to lumen, combine with bicarb to form water, absorption
Aldosterone
_..

adrenal makes too much aldosterone
_..


ANP
_..

released by heart
opposite of renin
relax smooth muscle via cGMP to dilate afferent
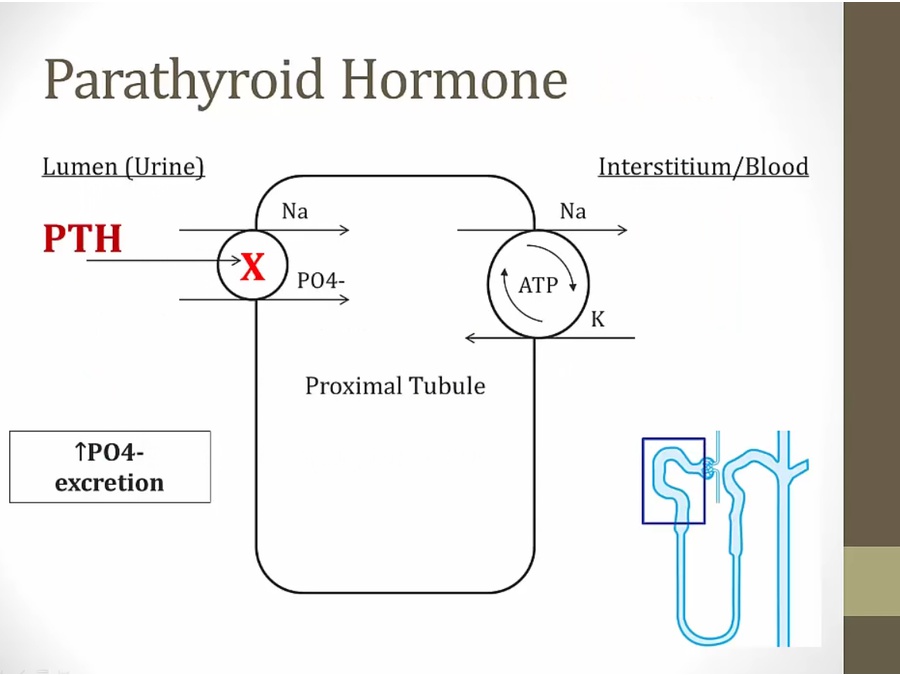
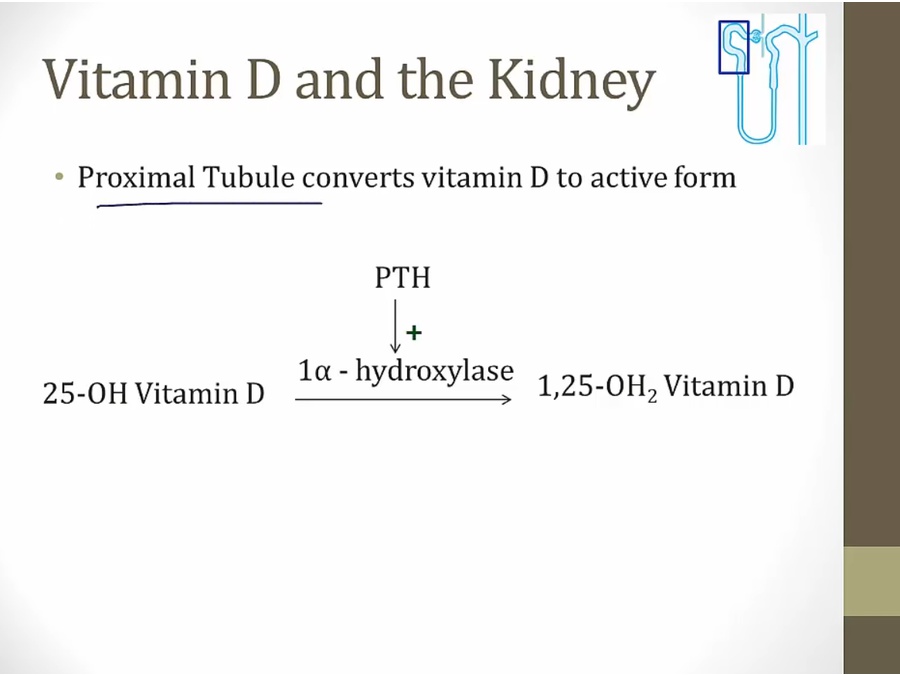
PTH
_..

low Ca most important
alcoholics very low Mg
_..

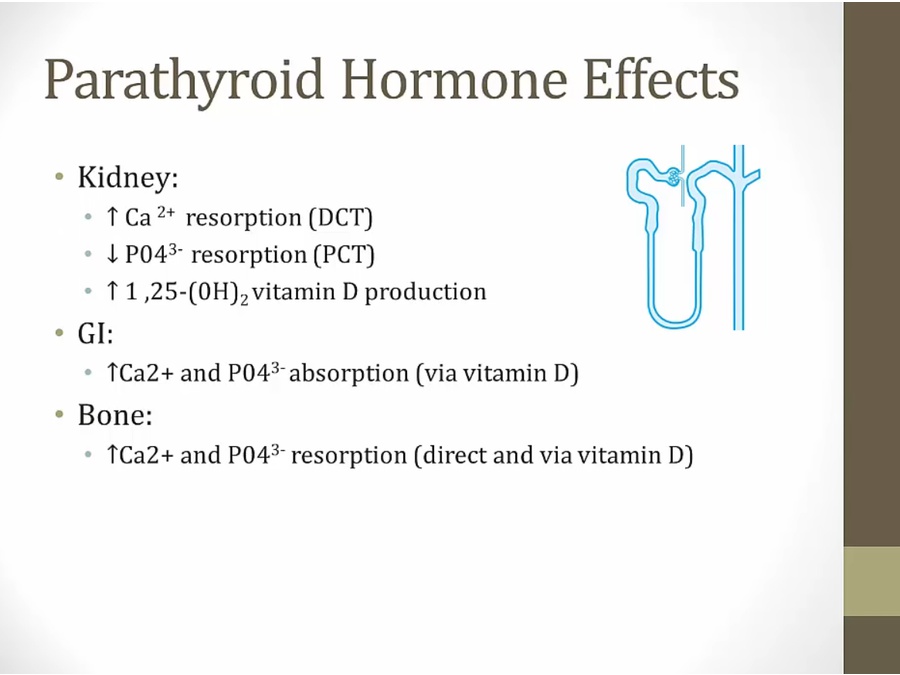
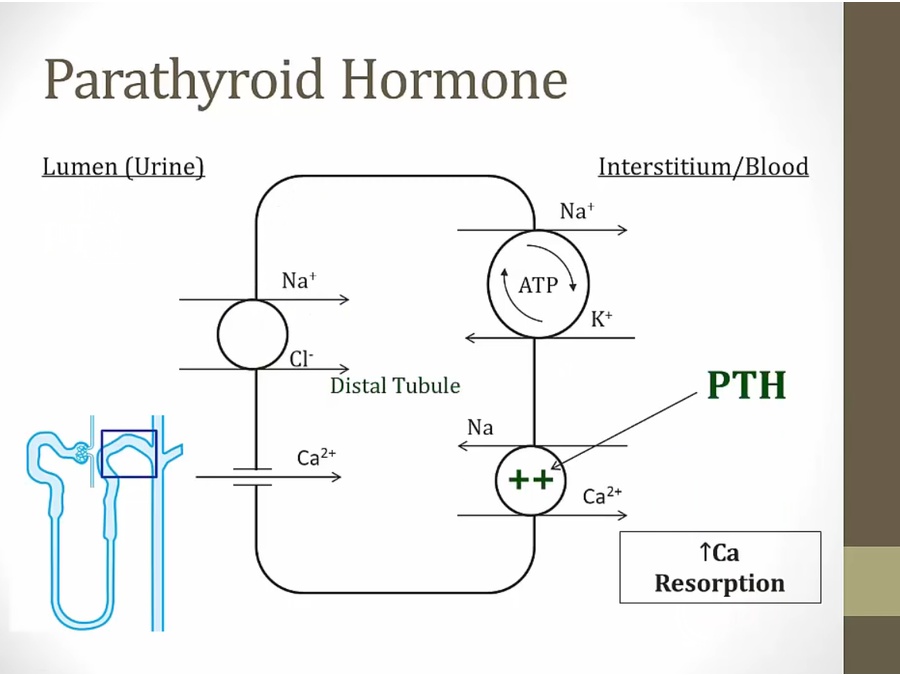
increase Ca absorption in DCT
Vid D
_..

D2 less active, not important
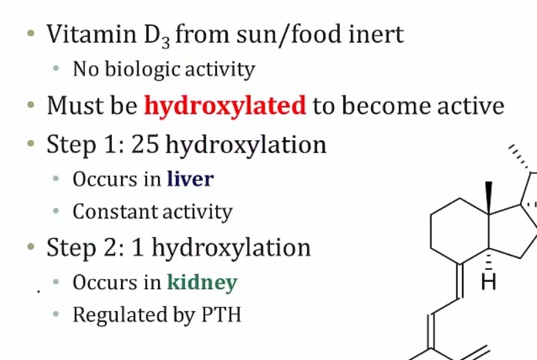

25- OH longest half life
_..

_..
_..
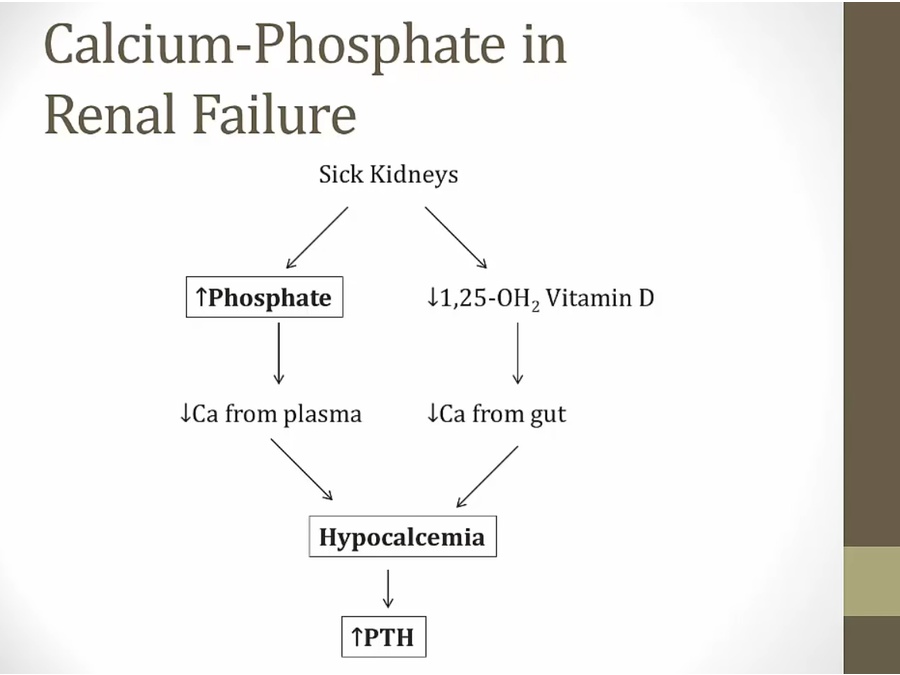
renal failure: increase phosphate from unable to excrete
secondary hyper PTH from renal failure
EPO
_..

peritubular interstitial cells
acts in bone marrow
_..

association with increased mortality
Last updated